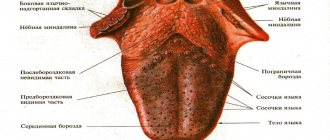
Causes of stomatitis
In children, as in adults, stomatitis can be caused by viruses, fungi, bacteria, allergies and injuries. About six months after birth, the child loses the immunity received from the mother, the protective power of the immune system changes, and the child’s body becomes more susceptible to infections. The oral mucosa in children is more delicate and easier to injure; children also more often “bite” their cheeks after dental treatment due to a temporary loss of sensitivity after anesthesia, which causes traumatic stomatitis.
Children are not always motivated to brush their teeth, so poor hygiene can also cause stomatitis.
With the following diseases, stomatitis is observed in children much more often: chronic tonsillitis, diabetes mellitus, heart defects, chronic hepatitis.
Factors influencing the occurrence of the disease
Candida bacteria live in the body of almost every person, but they do not always lead to the development of thrush. The following factors can provoke the disease in a child:
- previous colds, acute respiratory viral infections;
- internal chronic diseases;
- diabetes;
- appearance of the first teeth.
External factors also influence the development of fungus, such as:
- contacts of the baby with infected adults;
- artificial feeding;
- prematurity;
- toys, household items with fungus settled on them;
- poor hygiene by a nursing mother.
Classification of HRAS (chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis)
| CLASSIFICATION | A COMMENT | ||
| classification: | According to the degree of damage to the mucous membrane: | a comment: | 1) Superficial (catarrhal, fibrinous) 2) Deep (ulcerative, necrotic) |
| classification: | According to the clinical course: | a comment: | 1) acute 2) chronic |
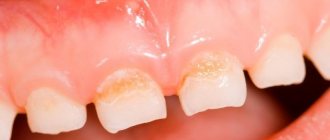
All types of stomatitis occur in children, but the most common are: herpetic, candidal and traumatic stomatitis.
Acute herpetic stomatitis
It occurs most often, and mainly affects children from 10 months to 3 years.3 The appearance of rashes is preceded by inflammation of the lymph nodes.
With a mild form
In acute herpetic stomatitis, the temperature rises to 37-37.5°C, the general condition is satisfactory, slight swelling and redness may occur on the gums, then up to six blisters appear, which burst with the formation of painful aphthae surrounded by a red rim.
Afta is a round-shaped erosion. Aphthae may merge together. The rash appears once, and after 1-2 days the erosion gradually heals.
Moderate form
Acute herpetic stomatitis is characterized by deterioration of the child’s well-being, weakness, and headache. The child is capricious, has no appetite, the lymph nodes are enlarged and painful, the temperature rises to 38-39°C, the symptoms resemble ARVI. The oral mucosa is swollen, reddened, rashes appear (bubbles, then erosions) of 10-15 pieces, and often there are rashes on the face. Salivation increases, and gingivitis appears (inflammation of the gums, accompanied by bleeding). The rash may appear several times, i.e. after the old ones heal, new ones appear. Healing of erosions takes up to 4-5 days. Bleeding gums and swollen lymph nodes persist for some time after the erosions have healed.
Severe form
It begins as an acute respiratory viral infection, there is pain in the muscles, joints, tachycardia and bradycardia (increased and slow heartbeat), and nosebleeds may even be observed. In this form, the temperature is high up to 40°C, gingivitis is pronounced, the mucous membrane is bright red, swollen, the child’s lips are dry, the mucous membrane of the eyes is swollen, reddened. The rashes constantly appear again, their number can reach 100. Rashes often appear around the mouth, on the eyelids, on the mucous membranes of the eyes, between the fingers, on the earlobes. Simple gingivitis turns into ulcerative (a more severe form of gum inflammation, with the formation of ulcers), salivation increases, and bad breath appears. Recovery is long and hospitalization is often required.
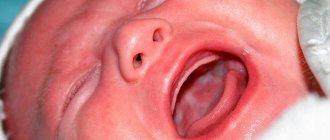
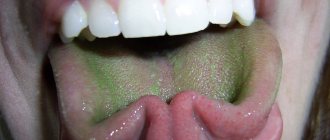
A newborn has a white coating on the tongue - what to do?
The method of treating white plaque on a baby's tongue
depends on the cause of its appearance
. If the whitish spots are the remains of breast milk or formula, you need to clean the baby’s tongue. Use boiled water to rinse the baby's mouth with it after feeding.
If the defect is caused by disorders of the nervous system, contact a pediatric neurologist to identify the cause of the neurosis and take care of the baby’s peace of mind. There is no need to clean the tongue; the defect will go away on its own.
The appearance of whitish spots on the tongue may mean that the baby has digestive problems. Pay attention to your child's nutrition. The primary task is to eliminate dysbiosis by selecting a different formula during artificial feeding or adjusting the mother’s diet during breastfeeding. These actions are enough to eliminate the symptoms.
A white coating on the tongue of a newborn child may appear due to infectious diseases of the oral mucosa: herpes, scarlet fever, chicken pox. The disease occurs with elevated body temperature.
It is impossible to do without drug treatment. To avoid complications and the disease becoming chronic, the doctor may refer the baby for inpatient treatment.
Treating thrush
Treatment of a mild stage of thrush involves wiping the tongue with a soda solution. With its help, you can easily clean whitish accumulations and prevent the growth of bacteria.
Pay more attention to personal hygiene rules:
- For “artificial” babies, be sure to pour boiling water over the nipple and bottle before feeding.
- Clean and boil rubber toys regularly.
- Replace outdated nipples with new ones in a timely manner, taking into account the manufacturer's recommendations.
- When breastfeeding, keep your nipples clean. Before latching your baby, do not forget to wash your breasts with warm water. During the treatment of the disease, additionally treat it with soda solution.
- During lactation, try to avoid taking antibiotics, normalize your diet, fill it with vitamin products.
- After feeding, remove milk residues.
Important point! Do not kiss a sick baby on the lips, do not lick the pacifier - you risk becoming infected yourself and adding harmful bacteria and viruses with your saliva. Even after recovery, refrain from such actions.
A dense, cheesy coating on the baby’s tongue, palate and gums, and the appearance of whitish pimples indicate a complex stage of thrush. Drug treatment is carried out in strict compliance with the doctor’s instructions, without violating the regimen. Immunomodulatory and antifungal drugs are prescribed.
How to clean the tongue of a newborn
The most important factor influencing the speed of recovery from thrush is oral hygiene. Parents can clean the surface of their baby's tongue at home. Procedure:
- Make a weak 2% soda solution: 1 tsp. Dissolve baking soda in a glass of boiled water.
- Before cleaning your newborn's tongue, wash your hands with plain soap. Wrap a little sterile bandage around the pad of your index finger.
- Soak a bandaged finger in a soda solution and massage the problem surface with it. You need to clean your tongue as carefully as possible, without pressing.
- Repeat the procedure after each feeding, 4-5 times a day.
In addition to soda solution, you can clean the child’s damaged mucous membranes with medicinal gruel. To prepare it, mix 1/2 tablet of Nystatin (125 thousand units) with 1 ml of liquid vitamin B12. Apply the resulting mixture to the gums, palate, and plaque-covered surface of the tongue. Repeat the treatment after each feeding.
To remove unpleasant plaque, traditional medicine advises using honey and lemon juice. Be careful, such components can cause an allergic reaction in the baby and complicate treatment.
Enteroviral vesicular stomatitis (arm - leg - mouth)
Caused by enteroviruses. It also occurs in adults, but in 95.7% of cases children are affected.6 It is characterized by seasonal occurrence (summer - autumn) and group incidence.4 It is observed mainly in children under 10 years of age. Vesicular stomatitis is contagious, so it is recommended to use separate utensils and hygiene products. Characteristics for this disease: temperature 37.5-38, weakness, headache, muscle pain, rash on the palms, soles, as well as blisters on the hard palate and pharynx, which then turn into erosions that are almost not painful.
Acute pseudomembranous candidal stomatitis (thrush)
Acute pseudomembranous candidal stomatitis (thrush) occurs:
- Light shape
- Medium-heavy forms
- Severe form
The main symptom of the disease is a white or yellow coating.
With a mild form
The plaque is located in islands, most often on the tongue and cheeks. Children are restless, sleep poorly, and suck the breast sluggishly. Older children may complain of a burning sensation. The plaque is easily removed; underneath there is a bright red mucous membrane. The disease lasts no longer than 7 days.5
Moderate form
The plaque is located on the cheeks, tongue, hard palate, and mucous membranes of the lips. Under the plaque, erosions form, which sometimes bleed. The plaque is more difficult to remove. Lymph nodes are sometimes enlarged and painful. The duration of the disease is 10-15 days, there are relapses.
Moderate form
The plaque is dirty gray, almost cannot be removed, and is located on the tongue, cheeks, soft palate, tonsils, pharynx, and mucous membranes of the lips. Cheilitis appears in the corners of the mouth - inflammation of the lips. The oral mucosa is dry and inflamed. The child’s health is impaired, the child refuses to eat, and the temperature rises. Lesions in the genital area, neck folds, and between the fingers are also common. The disease is long-term, with frequent relapses.
Symptoms of the disease
As a rule, the highest concentration of fungus is found on the surface of the inside of the cheeks, tongue, pharynx and tonsils, and palate. At an early stage of the development of the disease in children, redness of the mucous membranes is observed; they become swollen, the sensitivity of the mucous membrane increases, which is why children are often irritable, capricious, and their appetite and sleep are disturbed. The primary episode of the disease usually occurs in a more acute form; Patients may experience general symptoms: fever, headaches and dizziness, nausea or vomiting, deterioration in general health.
Some time after the onset of the disease, white grains begin to appear on the surface of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, which gradually increase in size and merge together, forming plaques, and then plaque covering large areas of the mucosa. During this stage, patients suffer from severe dryness and swelling in the mouth. The mucous membranes become painful. Burning, itching and other unpleasant sensations are most often associated with the development of an allergic reaction caused by the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and the release of toxins during their life processes. The pain intensifies when eating and swallowing food, when eating hot, sour, spicy foods and drinks. Infants often refuse to eat.
The plaque formed during candidiasis has a very characteristic appearance and resembles milk films or remains of cottage cheese. It consists of destroyed cells of the mucous membranes, food debris, bacterial mass, fibrin and keratin. Flakes, scales and plaque can also appear outside the mouth - on the edges of the lips. The spread of infection to the lips is called candidiasis. Because of this disease, the skin in the corners of the lips dries out and cracks; In some cases, the infection affects the entire surface of the lips, resulting in cracking and peeling.
In mild and moderate forms of the disease, plaque is easily scraped off, and underneath it, areas of erosion (ulceration) or maceration (softening) of the mucous membrane are found. A longer course of the disease and the lack of adequate treatment leads to deep damage to the mucous membranes, as a result of which blood appears on their surface, turning the plaque brown or brownish.
Bacterial stomatitis in children
Necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis is more common in weakened children and is caused by fusobacteria and spirochetes. May be a sign of periodontal disease (progressive destruction of periodontal tissue). It is characterized by the appearance of painful ulcers, weakness, gingivitis (inflammation of the gums), enlarged and painful lymph nodes, difficulty eating, speaking, and bad breath.
Often, erosions in traumatic stomatitis can become infected through dirty hands, toys and other objects, then bacterial stomatitis develops, so it is important to pay attention to antiseptic treatment.
Why does a baby have a white coating on the tongue?
Pediatricians identify the following factors that provoke the appearance of white plaque on the tongue of infants:
- weak, immature immunity;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract: constipation, dysbacteriosis, early complementary feeding, gastritis;
- treatment with antibiotics, allergies to them;
- low level of hemoglobin in the blood, vitamin deficiency;
- diabetes;
- hormonal changes, disruptions;
- infection through the mother's birth canal, through dirty toys, a pacifier;
- dry mouth.
Attention! Why a newborn has a white coating on the tongue and what measures to take to eliminate it are determined by a specialist after a detailed examination of the child. Self-medication is harmful to the baby’s health; do not give in to advice from TV or the Internet, even if it is from Dr. Komarovsky himself.
Traumatic stomatitis in children
A specific form of traumatic stomatitis in children is Bednar's aphthae . This is a traumatic erosion of the oral mucosa. In children, unlike adults, the mucosal epithelium consists not of four layers, but of two, so it is easily injured. The cause may be early teething, a rough nipple from the mother, or a long nipple on the bottle. Erosion is most often located in the middle of the palate or opposite the cutting edge of the teeth. The child begins to refuse food, cries, and sleeps poorly.
Traumatic stomatitis also occurs in children when wearing braces. Erosions have uneven edges, are painful, and are usually located on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and lips, less often on the tongue.
Causes of oral candidiasis
A healthy person is still a carrier of fungi of the genus Candida, since they are part of the microflora and calmly coexist with other microorganisms without causing harm. But any change in the balance in the body can lead to rapid proliferation of bacteria and the development of disease. A weakened state of immunity plays a key role in the etiology of oral candidiasis, but any of these reasons can be the starting point for the onset of the disease:
- pregnancy;
- immunodeficiency states;
- infectious processes;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics or improper use of medications;
- injuries and damage to the oral mucosa;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- contact with an already sick person.
Drug-induced stomatitis
Occurs when there is an allergy to a drug. Often, allergies can occur to antibacterial, antimicrobial drugs, vaccines, iodine. The mucous membrane is red, swollen, the lips and tongue also often swell, blisters appear, which burst, leaving erosion. The gums are inflamed and bleed when touched. General manifestations are possible, such as urticaria, nausea, vomiting. In severe cases, anaphylactic shock occurs (an emergency condition manifested by decreased blood pressure, shortness of breath, fainting, suffocation), Quincke's edema (an atypical reaction of the body, manifested by rapid and severe swelling)
Both conditions are extremely dangerous and require immediate action and calling an ambulance!
Prevention of stomatitis in children
In children's groups, infections spread especially quickly. Therefore, if a child is infected with the herpes virus, he needs to stay at home until he recovers. Children who have been in contact with sick people should use antiviral ointments for 5 days.
If a pregnant woman has herpes or candidiasis, she should treat it before giving birth. If you have the herpes virus during the period of illness, you should use separate utensils, do not kiss children, and wear a mask.
Kindergartens and other preschool institutions must be cleaned and objects, including toys, must be treated with disinfectants.
To avoid allergic reactions, you should seek help from an allergist to identify existing allergies.
It is worth preventing a decrease in immunity; hardening works especially well in childhood. It is worth limiting your intake of fast carbohydrates, because... they create a favorable environment for the development of candidiasis. An important point is the proper nutrition of the child; regular intake of vitamins, especially vitamin C, is essential.
Tantum® Propolis
For children over 14 years of age , you can use Tantum® Propolis lozenges; they contain a lot of vitamin C, which will strengthen the immune system, and propolis has an anti-inflammatory effect, preventing the occurrence of infections.7
Find out more
Prevention of Bednar's aft is preparing the breasts for feeding, using special creams to soften the skin, prevent cracks, and it is also worth choosing the right bottle. In case of injury due to braces, you need to use orthodontic wax; here it is important to prevent the wounds from becoming infected, so it is better to treat them with antiseptic solutions and sprays.
Tantum® Verde spray will relieve pain at the site of injury and its antiseptic effect will prevent infection.8,9
How to avoid thrush in a child:
- the most important thing is strict adherence to child and personal hygiene;
- you also need to make sure that you yourself do not suffer from thrush;
- timely hygiene of the child after defecation;
- do not lick baby pacifiers (as the risk of fungal infection increases), you should always have several sterile pacifiers in stock;
- do not bathe your baby in a shared bathroom (this can even lead to the development of other diseases);
- You should avoid keeping your child in a diaper or nappy for a long time (this will prevent the growth of fungi);
- regularly check the condition of the child’s genitals: there is no redness or discharge;
- For preventative purposes, it is necessary to regularly sterilize baby bottles and nipples.
If a pathology caused by fungi is suspected, in particular if there is damage to the skin, hair, or nail plates, skin and nail scales are taken for examination in our medical center (the procedure is painless and safe).
To clarify the diagnosis, other types of studies (blood, feces, urine) may be required. Treatment of any disease should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor. It is very important to control the treatment process, since fungi grow slowly in the human body and therefore the positive effect is not immediately visible. And the disappearance of the manifestations of the disease does not mean complete recovery, because the remaining elements of the fungus can give rise to a new growth of the disease.