- Changing mode
There are many reasons why the cheek becomes numb. Numbness is not always associated with any disease. More often, the phenomenon occurs for a short time, due to an uncomfortable position of the head, prolonged sitting in an uncomfortable position, during an attack of fear or panic. Less commonly, the cheek becomes numb due to damage to the nervous tissue or vascular pathology. If a symptom occurs frequently, you should consult a doctor to determine the cause and prescribe treatment.
Most often, cheek numbness does not require treatment, but there may be exceptions.
general information
The trigeminal nerve consists of sensory and motor fibers. It originates in the structures of the brain and is divided into three branches:
- ophthalmic: responsible for the eye, forehead and upper eyelid;
- maxillary: innervates the area from the lower eyelid to the upper lip;
- mandibular: involves the chin, lower jaw, lips and gums.
With neuralgia, one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve are affected, which determines the main symptoms of the pathology. People over 45 years of age are most susceptible to the disease, and women get sick more often than men.
Make an appointment
Inflammatory process on the root of the tooth
If you are wondering why the lower jaw is numb, then the first thing you need to pay attention to is the condition of the oral cavity. An unpleasant symptom can be caused by dental diseases such as periodontitis and a cyst on the root of the tooth. Then, in addition to discomfort, a slight tingling sensation may be observed in the jaw and chin area, as well as pain when pressing or chewing food on the causative tooth.
The photo shows a cyst
Causes
The causes of trigeminal neuralgia can be of different nature:
- compression of the entire trigeminal nerve or its branches against the background of: enlargement of the arteries or veins of the brain (aneurysms, atherosclerosis, strokes, increased intracranial pressure due to osteochondrosis, congenital developmental features);
- tumors of the brain or facial tissues in close proximity to nerve fibers;
- congenital anomalies of bone structure, narrowed openings through which nerve branches pass;
- injuries of the skull, facial area: bone fractures, post-traumatic scars of soft tissues;
- proliferation of scar tissue after injury, surgery, inflammation;
The risk of developing trigeminal neuralgia increases significantly:
- over the age of 50;
- against the background of mental disorders;
- with regular hypothermia;
- with insufficient intake of nutrients and vitamins into the body (anorexia, bulimia, malabsorption, etc.);
- with regular overwork, stress;
- for helminthic infestations and other helminthiases;
- for acute infections: malaria, syphilis, botulism, etc.;
- for chronic inflammation in the oral cavity (caries, gingivitis, abscesses, etc.);
- against the background of autoimmune lesions;
- with excessive exposure to allergies;
- for metabolic disorders.
What is arthrosis of the TMJ
Arthrosis of the TMJ is a disease that destroys the components that form the joint (Greek arthron joint, suffix oz - destruction). First, the articular cartilage is destroyed, then the following occurs in the articular elements:
- proliferation (tissue growth);
- calcification (calcium redistribution) and ossification of cartilage;
- hyperplastic (proliferation) and destructive (destruction) processes in the epiphyseal parts of bones (these are the rounded ends of the bones - the head and fossa);
- reactive-inflammatory (from the word “response”) changes in the synovial membrane;
- fibrosis (overgrowth of connective tissue) with hardening of the joint capsule, which affects nearby muscles, tendons and ligaments.
With the destruction of cartilage, its shock-absorbing functions are reduced, and impacts are transmitted directly to the bone. Patients involuntarily increase the destruction by reacting emotionally to events - they clench their teeth, not daring to say too much, with a “stony” face and tense muscles, compressed blood vessels and stress hormones, they face the blows of fate. The amount of nutrients decreases, the TMJ would be happy to recover - but there is no building material. Instead, the epiphyseal sections of the bone are flattened under pressure, and bone growths appear on them.
Then the joint enlarges, compressing the nerve endings located nearby. The pain radiates to the ear, back of the head, and teeth. When the jaw moves, a specific clicking sound appears (occlusion-articulation syndrome).
ICD codes M.19. 0 (1, 2, 8 – last digit changes)
Symptoms
The main characteristic symptom of trigeminal neuralgia is paroxysmal pain. It comes suddenly and in its intensity and speed of spread resembles an electric shock. Typically, intense pain forces the patient to freeze in place, waiting for relief. The attack can last from a few seconds to 2-3 minutes, after which there is a period of calm. The next wave of pain may come within hours, days, weeks or months.
Over time, the duration of each attack of neuralgia increases, and periods of calm are reduced until a continuous aching pain develops.
The provoking factor is irritation of trigger points:
- lips;
- wings of the nose;
- eyebrow area;
- middle part of the chin;
- cheeks;
- area of the external auditory canal;
- oral cavity;
- temporomandibular joint.
A person often provokes an attack when performing hygiene procedures (combing hair, caring for the oral cavity), chewing, laughing, talking, yawning, etc.
Depending on the location of the lesion, the pain takes over:
- the upper half of the head, temple, orbit or nose if the ophthalmic branch of the nerve is affected;
- cheeks, lips, upper jaw – if the maxillary branch is affected;
- chin, lower jaw, as well as the area in front of the ear - with neuralgia of the mandibular branch.
If the lesion affects all three branches or the nerve itself before it is divided, the pain spreads to the entire corresponding half of the face.
Painful sensations are accompanied by other sensory disturbances: numbness, tingling or crawling sensations. Hyperacusis (increased hearing sensitivity) may be observed on the affected side.
Since the trigeminal nerve contains not only sensory, but also motor pathways for the transmission of impulses, with neuralgia the corresponding symptoms are observed:
- twitching of facial muscles;
- spasms of the muscles of the eyelids, masticatory muscles;
The third group of manifestations of neuralgia are trophic disorders. They are associated with a sharp deterioration in blood circulation and lymph outflow. The skin becomes dry, begins to peel, and wrinkles appear. Local graying and even hair loss in the affected area is observed. Not only the scalp suffers, but also the eyebrows and eyelashes. Impaired blood supply to the gums leads to the development of periodontal disease. At the time of the attack, the patient notes lacrimation and drooling, swelling of the facial tissues.
Constant spasms of muscle fibers on the diseased side lead to facial asymmetry: narrowing of the palpebral fissure, drooping of the upper eyelid and eyebrow, upward movement of the corner of the mouth on the healthy side or drooping on the diseased side.
The patient himself gradually becomes nervous and irritable, and often limits himself to food, since chewing can cause another attack.
How dangerous is the disease?
TMJ arthrosis is silent and unnoticeable; people live with the disease for years without even knowing about the problem. But in vain.
Degrees of TMJ arthrosis
In the Russian Federation, the Kosinskaya classification of arthrosis has been adopted, which takes into account both symptoms and radiographic data. However, the TMJ is an exception to the rule: the joint “hangs”, held by muscles and ligaments, and does not experience weight loads comparable to other joints.
When at stage 1 according to Kosinskaya the joint space narrows, the pressure on the jaw simultaneously increases, which leads to problems with the teeth, but maintains the distance. The process is gradual, so this moment can be recorded on an MRI, but since there are no symptoms characteristic of the disease in the initial stage, it cannot be said unequivocally that this is stage 1 arthrosis. Only at stage 2, when symptoms appear (pain, facial asymmetry, etc.), and the patient finally consults a doctor, is a diagnosis made.
Stage 3 according to Kosinskaya: absence of joint space, sclerosis, necrosis, inability to open the mouth, chew and speak.
Damage to the TMJ by arthrosis
Possible complications
Arthrosis is not only a problem of the joint. Compensatory, in an effort to maintain chewing function, the body redistributes the load, which leads to tooth loss and rapid wear.
The previous diseases will be reflected in TMJ synovitis, and then the inflammatory process will affect the ear and nose (with decreased hearing, nasal congestion on one side), a headache will appear, which can radiate to the neck, back of the head and not stop.
The face will lose symmetry and become pasty (the skin appears loose, finely swollen, and grayish in color). Feeding is possible only through a tube; already at the second stage the ability to fully open the mouth is lost
Any localization and form of arthrosis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
Exacerbations
Osteoarthritis is not arthritis; a chronic disease does not have periods of exacerbation. But this does not mean that the pain will be equally aching. The inflammatory process (cold, infection, virus) spreads to the joint with the development of synovitis. Swelling and pain appear, which can appear at any radial point (from the teeth to the back of the head). The source of inflammation expands, the oral cavity, ears, and breathing through the nose are at risk.
You need to understand that the brain is located nearby. And you shouldn’t wait for necrotic tissue to give rise to oncology.
Diagnostics
A neurologist diagnoses trigeminal neuralgia. During the first visit, he carefully interviews the patient to find out:
- complaints: nature of pain, its intensity and localization, conditions and frequency of attacks, their duration;
- medical history: when pain attacks first appeared, how they changed over time, etc.;
- life history: the presence of chronic diseases, previous injuries and operations is clarified, special attention is paid to dental diseases and interventions.
A basic examination includes assessing the condition of the skin and muscles, identifying asymmetry and other characteristic signs, checking the quality of reflexes and skin sensitivity.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following is carried out:
- MRI of the brain and spinal cord with or without contrast: allows you to identify tumors, consequences of injuries, vascular disorders; sometimes the study is replaced by computed tomography (CT), but it is not as informative;
- electroneurography: study of the speed of nerve impulse transmission through fibers; allows you to identify the fact of nerve damage, assess the level of the defect and its features;
- electroneuromyography: not only the speed of impulse passage along the nerve bundle is studied, but also the reaction of muscle fibers to it; allows you to assess nerve damage, as well as determine the sensitivity threshold of trigger zones;
- electroencephalography (EEG): assessment of the bioelectrical activity of the brain.
Laboratory diagnostics includes only general studies to exclude other causes of painful attacks, as well as to assess the condition of the body as a whole (usually a general blood and urine test is prescribed, as well as a standard set of biochemical blood tests). If the infectious nature of the disease is suspected, tests are carried out to identify specific pathogens or antibodies to them.
Additionally, consultations with specialized specialists are prescribed: ENT specialist (if there are signs of nasopharynx pathology), a neurosurgeon (if there are signs of a tumor or injury), and a dentist.
Causes of jaw clenching during trismus
- inflammation of the masticatory muscles;
- inflammation of the gums;
- caries;
- abscess;
- inflammation of the periosteum of the lower jaw;
- jaw injuries (cracks, fractures, dislocations);
- dousing with cold water;
- animal or insect bites.
Trismus can also be a consequence of the following diseases:
- osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- periostitis;
- neurosis;
- epilepsy;
- meningitis;
- hysteria;
- arthrosis of the jaw joint;
- cancerous tumors;
- convulsions;
- rabies;
- tetany;
- paralysis;
- tetanus;
- pulpitis in the acute stage, etc.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
Treatment is aimed at:
- to eliminate the cause of damage;
- to alleviate the patient's condition;
- to stimulate the restoration of nerve structures;
- to reduce the excitability of trigger zones.
Properly selected treatment can reduce the frequency, intensity and duration of pain waves, and ideally achieve stable remission.
Drug treatment
Trigeminal neuralgia requires complex treatment using drugs from several groups:
- anticonvulsants (carbamazepine and analogues): reduce the excitability of nerve fibers;
- muscle relaxants (baclofen, mydocalm): reduce muscle spasms, improve blood circulation, reduce pain;
- B vitamins (neuromultivit, milgamma): stimulate the restoration of nerve fibers, have an antidepressant effect;
- antihistamines (diphenhydramine): enhance the effect of anticonvulsants;
- sedatives and antidepressants (glycine, aminazine): stabilize the patient’s emotional state.
For severe pain, narcotic analgesics may be prescribed. Previously, drug blockades (injecting the problem area with anesthetics) were actively used, but today this method of treatment is almost never used. It contributes to additional damage to nerve fibers.
Treatment of the root cause of the disease is mandatory: elimination of dental problems, taking medications to improve cerebral circulation, etc.
Physiotherapy and other non-drug methods
Non-drug methods complement drug therapy well and help stabilize patients’ condition. Depending on the condition and concomitant diseases, the following may be prescribed:
- ultraviolet irradiation: inhibits the passage of impulses along nerve fibers, providing an analgesic effect;
- laser therapy: reduces pain;
- UHF therapy: improves microcirculation and prevents muscle atrophy;
- electrophoresis with analgesics or antispasmodics to relieve pain and relax muscles;
- diadynamic currents: reduce the conductivity of nerve fibers, significantly increase the intervals between attacks;
- massage of the face, head, cervical-collar area: improves blood circulation and lymph outflow, improving tissue nutrition; must be carried out with caution so as not to touch trigger zones and provoke an attack; the course is carried out only during the period of remission;
- acupuncture: helps relieve pain.
Surgery
The help of surgeons is indispensable when it is necessary to eliminate nerve compression. If indicated, the following is carried out:
- removal of tumors;
- displacement or removal of dilated vessels pressing on the nerve (microvascular decompression);
- expansion of the bone canals in which the branches of the nerve pass.
A number of operations are aimed at reducing nerve fiber conductivity:
- exposure to a gamma knife or cyber knife;
- balloon compression of the trigeminal node: compression of the node using an air-filled balloon installed in close proximity to it, followed by death of the nerve fibers; surgery often leads to partial loss of sensation and decreased muscle movement;
- resection of the trigeminal node: rarely performed due to the complexity and large number of complications.
Make an appointment
Characteristics of sinus lifting and bone grafting
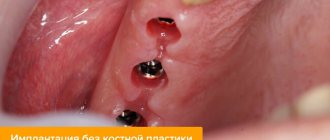
Bone grafting in dentistry is designed to increase the volume of bone tissue to create suitable conditions for placing a dental implant. An increase in the volume of hard tissues can be carried out both through the use of one’s own bone material and with the use of synthetic substitutes. Bone grafting is performed on both the lower jaw and the upper jaw.
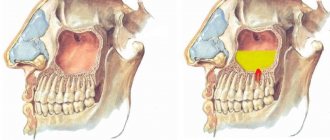
Sinus lifting is an operation performed exclusively on the upper jaw and, in essence, is a type of bone grafting. Its task is to raise the bottom of the maxillary sinus in order to increase the volume of bone mass. Additional bone material can be either your own or artificial. There are two ways to perform a sinus lift: open and closed. They differ in the complexity of execution and the ability to add different amounts of bone tissue.
Dental implant placement should not be confused with bone grafting or sinus lifting. These are two different operations, although they can be performed simultaneously. If there is initially a small amount of bone tissue, it may not be possible to place a dental implant immediately. Then, first, bone tissue is built up, and only a few months later, an artificial tooth is implanted.
Complications
Without treatment, trigeminal neuralgia gradually progresses. Over time, a pathological pain focus forms in one of the parts of the brain. As a result, the pain covers the entire face, is provoked by any minor irritant and even the memory of an attack, and subsequently becomes permanent. Vegetative-trophic disorders progress:
- irreversible atrophy of the facial muscles is formed;
- teeth become loose and begin to fall out due to advanced periodontal disease;
- baldness is increasing.
Due to constant pain, the patient's sleep is disturbed and severe depression develops. In severe cases, patients may commit suicide.
Problems in the upper jaw
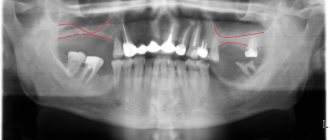
Numbness after sinus lifting and bone grafting in the area of the upper teeth and gums is less common than in the lower jaw. This is due to the fact that the innervation of these structures is carried out by three groups of branches of the maxillary nerve, intertwined with each other and forming the dental nerve plexus. Such a structure is quite difficult to damage or completely disable.
The loss of sensitivity in the area of the upper lip and upper half of the cheek cannot in any way be associated with dental interventions due to the fact that completely different branches of the maxillary nerve go to them.
Damage to the alveolar branches or dental plexus
This complication can only develop in conjunction with penetration into the maxillary sinus during surgery, which should not occur if the operation is performed correctly.
Local, mild numbness develops. One or two teeth may be involved with incomplete loss of sensitivity.
Improper placement of the implant or complications in the postoperative period
Dislocation of the skeleton of a prosthetic tooth can occur due to injury, inflammatory processes, or neglect of the dentist’s recommendations. Diagnosis of this condition is not particularly difficult due to the obvious pathological state of the implant.
There may be loss of sensitivity due to chronic odontogenic sinusitis. The condition develops over a long period of time, occurs with severe symptoms of sinusitis, and numbness develops in extremely severe and advanced cases.
Prevention
Prevention of trigeminal neuralgia is a set of simple measures that significantly reduce the risk of developing pathology. Doctors recommend:
- undergo regular preventive examinations;
- at the first signs of the disease, seek help (the sooner treatment is started, the greater its effect will be);
- eat right, get the required amount of vitamins, minerals, unsaturated fatty acids;
- regularly engage in light sports and gymnastics;
- get enough sleep and rest;
- minimize stress and physical overload;
- avoid hypothermia and harden yourself;
- to refuse from bad habits.
Treatment options
If the nerve trunk, plexus or branches of the nerve are damaged or compressed, there are two ways to solve the problem.
The first is to leave everything as is, without performing surgery. Such a solution to the problem is acceptable in case of incomplete loss of sensitivity or a small area of focus, with the exception of cases with displacement of the denture. Compression of the nerve due to regenerative processes will stop progressing after a certain point, “frozen” in one place. Odontogenic sinusitis can be treated with medication using antibiotics.
The second method is to perform surgery. The operation is indicated for injuries during sinus lifting and bone grafting, displacement of dentures or bone mass, extensive or complete loss of sensation. During the operation, the cause of the numbness is eliminated and, if necessary, the damaged nerve is sutured. Restoration of sensitivity takes a long time, sometimes never returning to its original state.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
If you or your relative are bothered by severe pain in one or another part of the face, the neurologists of the Health Energy clinic will come to the rescue. We will conduct a full diagnosis to identify the causes of the pathology and prescribe comprehensive treatment. At your service:
- modern drug regimens to reduce the frequency and intensity of attacks;
- physiotherapeutic procedures: magnetotherapy, laser therapy, electrophoresis, phonophoresis, etc.;
- delicate therapeutic massage;
- acupuncture;
- help from a psychologist if necessary.
Left or right cheek goes numb: reasons not related to illness
Numbness of the face is not always associated with any pathology. Especially if episodes of sensory impairment are short-term and rare.
Parts of the face may become numb due to incorrect head position, prolonged sitting in an uncomfortable position, general hypothermia, or during periods of severe emotional shock. In these cases, there is no need to worry; numbness does not pose a danger to the human body.
Common causes of numbness that are not associated with illness:
- Incorrect work and rest schedule. Parts of the face may become numb if the head is in one position for a long time. For example, when working at a computer, reading, if breaks are not taken during work.
- Uncomfortable pillow. Uncomfortable head position during sleep can lead to compression of nerves and blood vessels. In the morning this will manifest itself in the form of numbness in different parts of the face.
- Panic attacks. The cheeks may become numb during panic attacks, during periods of severe shock. Numbness goes away along with other symptoms of nervous tension.
Advantages of the Health Energy Clinic
The Health Energy Clinic is a multidisciplinary medical center where every patient has access to:
- screening diagnostic programs aimed at early detection of diseases and pathologies;
- targeted diagnostics using modern equipment and laboratory tests;
- consultations with experienced specialists, including foreign ones;
- modern and effective comprehensive treatment;
- necessary certificates and extracts;
- documents and appointments for spa treatment.
Trigeminal neuralgia is a serious pathology that can seriously disrupt a person’s normal lifestyle. Don't let pain and fear take over your thoughts, get treatment at Health Energy.