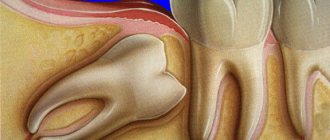
In our time, implantology has achieved truly incredible success. Experienced surgeons are able to implant, at a time, not only one tooth root, but an entire row of teeth. Of course, such operations require highly qualified dentists. However, sometimes negative consequences occur after operations, and even during the operations themselves. Less commonly, they occur several years after the seemingly successful implantation of implants into the jawbone. For each such case there are reasons. In this article we will tell you about them.
Why might complications occur?
There may be several reasons for complications after implantation of artificial dental roots. Some of them relate to the mistakes of dentists, and some of them relate to the fault of the patients themselves.
Medical errors include the following:
- incorrect choice of implant length;
- overheating of bone tissue at the site of implant installation;
- insufficient disinfection of the patient’s oral cavity;
- incorrect choice of prosthesis design;
- an error in assessing the physiology of the patient’s body in terms of susceptibility to a foreign body;
- use of low-quality titanium implants;
- use of outdated surgical equipment;
- careless installation of the prosthesis on the root.
The following reasons should be attributed to the fault of the patients themselves:
- careless oral hygiene after implantation;
- the patient's inability to give up bad habits;
- eating solid food during the implant healing stage;
- Irregular use of medications recommended by the surgeon.
Treatment
An x-ray allows the dentist to understand exactly what the problem is. Mostly, complications are caused by inflammatory processes. Anti-inflammatory therapy, antiseptic surface treatment, and hygienic care are carried out.
In case of peri-implantitis, inflamed tissue is removed, the pin is cleaned and treated with an antiseptic.
In some cases, complications after dental implantation require removal of the post. For example, if the implant breaks, it is rejected, or treatment of inflammatory processes is not successful.
The implant is removed by carefully twisting it out of the bone, trying to minimize trauma to surrounding tissue.
The issue of re-implantation is considered in each case separately. Most often, a two-stage protocol is impossible without bone grafting. But with the one-step method, you can do without it. In any case, you will have to wait until the inflamed tissues recover. However, it should not be delayed to avoid bone loss.
The decision to re-implant after removal of a dental implant must be made by the doctor. It takes into account all the factors necessary for the success of the operation. If rejection is caused by biological reasons, low immunity, smoking, then the positive result of re-implantation is in doubt and it is better to use alternative prosthetic methods.
Possible mistakes of surgeons
Negative consequences can occur even during careless operation. Let's name a few medical errors that, unfortunately, although rarely, happen.
Sometimes the doctor inadvertently overheats the head of the titanium root. This occurs due to overheating of the bur and hollow in the jaw bone. The reason for this is untimely irrigation of both.
If the doctor begins to tighten the implant screws while the cement is hardening, this ultimately leads to incorrect root installation, since the cement in this case cracks.
If the doctor does not place the head of the implant tightly in the hollow of the jaw bone, there is a risk of inflammation occurring, as bacteria enter the gap. In addition, loose placement of the head can lead to an imbalance of mechanical load on the entire prosthetic structure. This can cause peri-implantitis.
Features of implantation in the upper jaw
The operation of implanting titanium roots into the upper jaw is always accompanied by considerable difficulties. This is due to the difficulty of access to the implant installation site and the close location of other organs. Often such operations are accompanied by complications. To make matters worse, the density of the maxillary tissue is lower than that of the mandibular bone. Because of this, it is necessary to drill a deep hole in the bone and install long implants. This can also cause postoperative complications.
During installation of the implant, the nasopalatine bundle, which is located in the center of the upper jaw behind the front teeth, may be injured. Such an injury causes prolonged bleeding, and this leads to the fact that the implant does not take root at all.
There is also a risk of damage to the sinuses and even nasal cavities. In both cases, sad complications are inevitable.
In case of damage to the neurovascular bundles located in the canine area, numbness of the upper lip occurs.
Dentistry knows cases where during implantation the integrity of the sinus floor was violated. This phenomenon leads to the occurrence of sinusitis.
There is also a risk of damage to the palatal artery, causing heavy bleeding.
All of the above may not happen if implantation is performed by experienced surgeons.
Professional installation of dental implants
You can insert high-quality dental implants. Price
for the implantation procedure depends on the chosen technique and material. The staff includes high-profile specialists with extensive professional experience.
To restore the dentition, high-quality titanium implants from trusted manufacturers are used, showing a high survival rate with minimal risks of complications.
Our center regularly holds promotions and special offers. There are discounts for citizens of preferential categories. An additional 3% discount on any dental procedures is provided to all patients who leave their reviews on the site (summed up with other discounts available to the client).
Write, share your experience and receive a pleasant bonus that will allow you to save a lot of money on medical procedures at the center of modern dentistry “Aesthetics”!
Implantation in the lower jaw
Installing artificial roots in the lower jaw is much easier. However, there are certain problems here too, since there are areas on the lower jaw that should never be disturbed.
If during the operation the surgeon disturbs the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve, then the patient’s oral cavity will completely lose sensitivity.
If the wall of the mandibular canal is damaged, numbness of the lower lip and part of the chin occurs.
Injury to the external branch of the facial artery generally leads to severe bleeding, and here one cannot do without the help of a surgeon.
In what cases can implants cause harm?
Dental implantation is a surgical operation during which the dentist intervenes in the body and disrupts the integrity of the mucous and bone tissue in order to install an artificial root in the jaw. Despite this implementation, in 97–99% of cases everything goes well, without complications. Negative consequences from implantation are possible, as a rule, in cases where:
- The doctor is not properly qualified and not experienced enough. This operation requires the specialist to possess special skills at a high level.
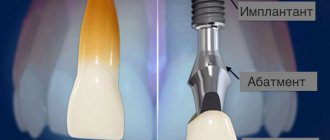
- A cheap implant system is being installed. The success of the operation also largely depends on the quality of manufacturing of the artificial root, abutment, and former.
- The preparatory stage was absent or proceeded with violations. Before surgery, you need to undergo laboratory tests, undergo X-ray diagnostics, and establish the absence of contraindications.
- Doctor's recommendations are not followed.
During the period of recovery and osseointegration, it is necessary to strictly follow all the specialist’s instructions and follow his instructions on lifestyle and nutrition.
If irregularities are allowed or certain factors operate, problems may arise after implantation.
Early complications
In the first days after implantation, the patient may experience pain, sometimes very severe. Often, the dentist even prescribes painkillers to patients, which should never be abused. If the pain does not disappear after a week, this indicates that there is inflammation or nerve damage.
About two hours after implantation, swelling occurs in the patient’s mouth, and this is quite normal. It may not go away for a week. At this time, it is allowed to apply ice to the swollen areas. If after a week the swelling has not subsided, then most likely there is tissue inflammation.
The patient's gums may bleed slightly for two to three days after surgery. Blood oozes at the site of the implanted root. If the bleeding is significant, the cause may be poor blood clotting or high blood pressure. If the bleeding continues, then most likely the surgeon damaged a blood vessel. This, in turn, can cause a hematoma to appear at the implant site. Because of this, postoperative sutures may come apart and the wound may begin to rot.
During the first week after implantation, the patient experiences an elevated body temperature. This is quite normal if the temperature does not exceed 37.5 degrees. If it is higher or does not subside after a week, this means that an inflammatory focus has formed in the oral cavity. This phenomenon is usually accompanied by swelling.
There are cases where in the very first days after surgery, patients’ sutures came apart. This happens due to their careless application, due to mechanical damage from solid food, or due to the onset of inflammation.
If within five hours after the operation there is numbness of the tissues near the oral cavity, then you should not be afraid of this, because the anesthesia has not yet completely worn off. If the numbness continues to persist, then the nerve may have been damaged during implantation.
Increasing swelling
After installation of the implant, the corresponding part of the face often swells, but after three to five days everything returns to normal. Long-lasting swelling indicates a complication. The cause of the pathological reaction can be:
- developing infection;
- allergic reaction to a titanium implant;
- improper preparation for surgery;
- disruption of the circulatory and lymphatic systems.
You should not try to relieve swelling on your own if it continues to grow. It is better to seek help from a dentist.
Late complications
Such complications can arise a year after the successful implantation of artificial roots and the installation of prostheses on them.
Peri-implantitis. Sometimes patients develop peri-implantitis after a year. In simple terms, this is inflammation of the bone tissue near the implant. Most often, the cause of its appearance is careless oral hygiene. Less commonly, the reason is a violation of the implant installation technology. In particular, there are known cases of damage to the gingival cuff and even the presence of cement in it.
It is possible to cure peri-implantitis with medication only at an early stage of its development. In this case, in any case, it is necessary to remove the prosthesis from the root and laser or ultrasonic cleaning of the implant itself. If tartar has formed in the oral cavity, then they must also be removed. Only after this are medications prescribed.
At a later stage of development of peri-implantitis, treatment is much more difficult. It is a complex of surgical and medical procedures. These include:
- ultrasonic sanitation of the oral cavity and gum pockets;
- opening the purulent focus and cleansing the tissue underneath;
- thorough disinfection of the implant;
- removal of dead tissue;
- prescribing a course of drug treatment.
The advanced stage of peri-implantitis cannot be treated. At this stage, the implant becomes mobile. In this case, it has to be removed from the jawbone. A new implant can be installed only after peri-implantitis is completely cured. Unfortunately, this is by no means a simple matter. Only 6 months after the cure of peri-implantitis is osteoplasty allowed, without which re-implantation of the titanium root in the same place is impossible.
Sinusitis. This complication manifests itself in the form of inflammation of the oral mucosa near the maxillary sinus. The treatment process does not require removal of the implant. Usually the problem is solved with drug treatment.
Mechanical damage. Complications due to mechanical damage arise solely through the fault of the patient when, in violation of the doctor’s recommendations, he became interested in eating too much solid food. In addition, mechanical damage to the structure can occur from malocclusion or bruxism. There are known cases where prostheses and even implants broke in such cases. It doesn't matter if the prosthesis breaks. It can be easily replaced. If the implant breaks, then its removal from the jawbone is required.
Long-term consequences after dental implantation
If early complications depend more on the doctor’s mistakes, then later ones are the patient’s responsibility. The vast majority of problems after dental implantation occur as a result of insufficient oral hygiene:
- Mucositis and hyperplasia.
Inflammation of the gingival cuff as a result of plaque formation on the head of the implant. The gums turn red, swell, and ulcers form on it. Plaque must be removed and care taken more thoroughly. - Late peri-implantitis.
Reason: poor hygiene and constant traumatic exposure. If your bone density is low, additional tissue will need to be grafted. - Sinusitis.
Inflammation of the maxillary sinuses can be caused by peri-implantitis. If the pin is mobile and there are signs of inflammation, the implant is removed and sinusitis is treated. If these signs are not present, then sinusitis is treated without removing the implant.
Non-survival of the implant
The phenomenon of implant rejection by bone tissue is extremely rare. There is only one way out of the situation - removal of the implants.
Implant rejection does not occur instantly, but in a certain sequence. Each stage of this phenomenon is accompanied by its own symptoms.
At the first stage of rejection, tissue inflammation occurs near the implant. This is followed by an enlargement of the pocket and thinning of the bone in the area of the implant.
In the second stage, the height of the jawbone around the implant noticeably decreases. At the same time, gum detachment occurs until the abutment is exposed. The implant becomes mobile.
The third and final stage is characterized by destruction of the alveolar process and rejection of the implant itself.
The beginning of the implant rejection process can be determined by the following signs:
- swelling of the gums in the area of the implant and next to it;
- general malaise;
- the appearance of pus in the oral cavity;
- the appearance of bleeding from the gums;
- enlargement of the gum pocket;
- implant mobility;
- increase in body temperature.
Problems during the second surgical stage
The second stage of dental implantation involves:
- opening the implant (to do this, the doctor cuts the gum above it);
- removing the plug;
- installation of a gum former.
Due to disorders of bone regeneration, the intraosseous element is twisted, and when implanting teeth in the upper jaw, it is pushed into the maxillary sinus. This complication is prevented at the stage of formation of bone tissue around the implant - during the period of osseointegration, CT is periodically performed to monitor the formation of bone structures.
There are opposite situations when the top of the implant is overgrown with bone tissue. This process is not considered a complication and does not have a special impact on the implantation process. The doctor cuts the periosteum and removes excess with a saw to properly install the healing abutment.
Safe complications
Even after an impeccably performed implantation, natural complications always occur, which are the body’s natural reaction to mechanical intervention. We list the complications that you do not need to be afraid of:
- body temperature up to 37.5 degrees;
- swelling of the face;
- feeling of heaviness in the maxillary sinus;
- minor hematomas;
- quite tolerable pain.
All these troubles can only be endured for a week. If they do not disappear further, then, most likely, something went wrong during the implant healing process.
Complete absence of upper teeth
Implantation of the upper jaw in the absence of teeth can be carried out in several ways.
- Basal implantation is the main and most common method of restoring dentition. 8–12 artificial roots are used, which are installed evenly along the dentition. The advantages of this method include the fact that the doctor selects deep sections of bone tissue that are not affected by atrophy, as well as “bypassing” the sinuses. Afterwards, the prosthesis is fixed to the implants - even relatively loose bone does not act as a hindrance, since a large number of supports are used. Zygomatic implants can also be used here. A fixed prosthesis is installed within 3–4 days.
- All-on-6 technology. Numerous reviews of dental implantation in the upper jaw using this technique allow one to judge its effectiveness. It can be used even with moderate bone atrophy. Installation of a fixed prosthesis is carried out on 6 implants. 4 of them are fixed in the lateral sections on both sides, 2 - in the frontal section. Zygomatic implants can also be used here.
- All-on-4 technology. The name speaks for itself - this is implantation on 4 artificial roots. The technique is used less frequently, since in this case the requirements for bone tissue parameters are much higher, and only minor atrophy is allowed. 2 implants are installed in the frontal zone, 2 - in the lateral zone. The use of zygomatic implants is allowed. The prosthesis is installed within 3–4 days.
- Zygomatic implantation. This is not an independent method; it is used as part of the protocols described above. Zygomatic implants are up to 6 cm long. They are necessary in order to involve the zygomatic bone in the process and reliably fix a fixed prosthesis.
How can complications be prevented?
Practice shows that by strictly following all doctor’s recommendations, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications. To do this you need:
- regularly take the medications prescribed by the doctor;
- carefully perform oral hygiene;
- quit smoking;
- undergo annual x-ray diagnostics of the oral cavity;
- stop eating solid food;
- strictly adhere to the postoperative diet.