Structure and functions
The tongue is a muscular organ without bones, covered with a mucous membrane.
Main functions:
- is directly involved in the pronunciation of sounds;
- determines the taste of what a person eats and drinks;
- is an integral element of the digestive system - it carries out the primary processing of food before it enters the esophagus.
The structure of the organ is quite simple, but very interesting. The tongue is divided into two parts: the back - the root and the front - the body or, as it is also called, the back, which has a velvety structure. The top is covered with papillae, which are responsible for taste buds.
Diagnostic signs
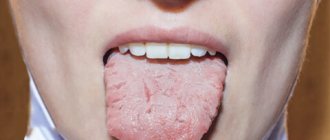
If vital processes are balanced, the body functions without failures, the human tongue has a healthy appearance. This is manifested in its smooth, velvety surface, uniform pink color and transparent coating of saliva. There should be no discomfort, burning, tingling or lack of sensitivity in any areas.
Photo: tongue of a healthy person
In the human body, pathologies are determined by the following characteristics:
- Color and its uniformity on the surface of the tongue.
- Smell, color and consistency of plaque.
- Relief.
- The shape of the organ and the lines in the middle.
- Movements.
- Sensation of taste.
Diagnosis of health using the tongue should be carried out as follows: stick it out as much as possible, look in the mirror and analyze all the indicated characteristics. The sensations of taste and touch, as well as the accumulation of plaque, should be monitored throughout the day. All features that were identified should be compared with text descriptions.
If the patient tells the doctor about changes in health status and language diagnostic results, he is prescribed an examination to clarify the diagnosis.
Correspondence of tongue zones to internal organs
Ancient Chinese doctors determined that each section of this muscular organ is associated with a specific element. Modern medicine has established how the areas of the human tongue are associated with diseases of the internal organs. The correspondence is shown in the table:
| Zone | Element | Organs |
| Tip of the tongue | Fire | Small intestine, heart muscle |
| Transverse stripe between tip and central area | Metal | Colon, immunity, respiratory system |
| Middle | Earth | Stomach, spleen, pancreas |
| Sides | Tree | Gallbladder, liver |
| Rear end | Water | Organs in the lower abdomen, reproductive and urinary systems |
| Fold dividing the tongue into left and right parts | — | Spine |
For a more informative diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account both the general condition of the tongue and the condition of its individual sections. It is important to understand that the doctor draws conclusions not only from indirect external changes, but also from the results of laboratory and instrumental studies, and when making a diagnosis, one should rely more on conclusions confirmed by analyzes.
Diagnosis by color: what does the color of the tongue mean?
The color of this organ partly depends on the shade of its own tissues, and partly on the plaque accumulated on it. By studying the color of the tongue, you can determine what this sign indicates and go to a therapist to check your assumptions. Below is a comparison of the color of tongue coating and diseases that may be associated with it:
- A coated yellowish tongue is a symptom of improper functioning of the liver, gastrointestinal tract and a sign of people who smoke.
- Bright red plaque indicates the presence of hematological and cardiovascular pathologies.
- A reddish coating is a sign of inflammation of infectious or non-infectious origin.
- A dark red coating is a manifestation of intoxication.
- A red tip of the tongue is a symptom of pelvic organ diseases.
- Burgundy plaque – the presence of acute infections.
- Crimson – a manifestation of a severe infection with severe fever.
- A blue or purple tongue is a symptom of lung or heart disease.
- Blue plaque is a sign of kidney disease.
- Gray – the presence of chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
- Black plaque is a sign of infection with a chromogenic fungus or a state of acidosis.
- Pallor is a symptom of fungal infection, acute respiratory viral infection, anemia, tissue dehydration, and exhaustion of the body.
- A pale underside of a person’s tongue is a sign of liver disease and the associated gallbladder.
- A dirty gray coating is a consequence of the vital activity of parasites.
Presence of stains
In some diseases, the color of the tongue is uneven; distinct or unclear spots and stripes may be observed:
- The presence of red and white spots indicates the presence of scarlet fever.
- White spots on the edges or over the entire surface indicate the development of thrush.
Thrush on the tongueWhite scaly spots on the tongue indicate the presence of lichen planus.
- White spots on the lower part of the tongue are observed with vascular diseases of the brain or with oxygen starvation.
- The presence of one round white spot indicates a shift in the acid-base balance of gastric juice.
- A red spot on the tip of the tongue or along the edges is an injury caused by rough food or biting with teeth.
- Red dots on the top indicate mononucleosis or problems with hematopoiesis.
- Reddened areas with horny scales are a likely sign of a tumor.
- A red spot surrounded by yellowish blisters is a symptom of erythema.
- Reddened areas on a dry tongue are a sign of brain disease.
- Red blisters around the edges are a symptom of herpes.
- Yellow spots are a sign of inflammatory processes, diseases of the hematopoietic organs, oncology, necrosis, and a consequence of smoking.
- Purple areas indicate blood stagnation.
- Brown spots are a sign of a circulatory system disease or bleeding in the mouth.
- Blue spots are a sign of hemangioma, intoxication or blood diseases.
- Blackening of individual areas is a sign of chemical burns, a consequence of smoking, long-term use of antibiotics, stomatitis or gastrointestinal disorders.
Diagnostics by form
The definition of a human disease by language is also based on an analysis of its outline and shape of the midline:
| Tongue shape | Definition of disease by language |
| Thin | Metabolic failures |
| Thick | Dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and liver |
| Long | Heart problems |
| Convex | Pulmonary pathologies |
| Hydropic | Disturbed digestive processes |
| Midline curvature | Spine pathologies |
| One side of the tongue is adjacent to the cheek | Pathologies of cerebral circulation, strokes |
| The tongue has changed shape and relief | Hypo- or vitamin deficiency |
It is difficult for a person without medical education to determine from photographs or descriptions which organ shape is normal for him. Thus, a thick tongue can be mistaken for swelling. Therefore, you should not draw conclusions about your health status and treatment on your own ; it is better to consult a doctor and tell him about your assumptions.
Nature of the relief
Normal taste buds form a smooth, velvety surface. By the relief of the tongue you can determine the disease in an adult or child, how to do this:
Photo: symptom of “varnished tongue”Excessive roughness indicates dehydration, problems with the salivary glands, overdose of antibiotics, atropine drugs or fat-soluble vitamins.
- Increased roughness on a person’s dry tongue, sometimes with tooth marks, can indicate a gastrointestinal disease, such as appendicitis, intestinal infections, and ulcerative pathologies. If cracks and uneven edges are added to the dryness, this is a possible sign of diabetes.
"Cardinal's language"The “varnished tongue” symptom, in which the surface becomes excessively smooth due to atrophy of the taste buds, is observed with colitis, stomach cancer or problems with the absorption of vitamin B
- Diagnosis by the color of the tongue and its relief is clear in case of pellagra - hypovitaminosis of nicotinic acid and vitamin B. The tongue looks ribbed due to cracks and is covered with a brown coating that is difficult to remove. The scarlet "cardinal tongue" shown in the image to the right then forms. At a later stage, a “varnished tongue” appears.
Photo: “geographical language”Alternating normal and inflamed papillae form a “geographic tongue” - a peculiar pattern with grooves that is more common in children with allergies or mental disorders. The projection of spots onto internal organs will help diagnose which organ suffers from food allergies, vitamin deficiency, and atopic dermatitis.
Movement and sensitivity
Normally, a person moves his tongue without difficulty, without trembling or muscle pain . If there are diseases of the nervous system and neurasthenic syndromes, characteristic trembling appears, and with strokes, patients find it difficult to chew and talk. With hemorrhages in the brain, both the sensitivity of taste buds and the sense of touch on surfaces are partially or completely absent.
The causes of trembling can be not only neurological, but also endocrine. The progression of brain diseases in later stages leads to a decrease in muscle size.
If uncharacteristic sensations or burning occur, you should contact a neurologist. If only the surface of the organ hurts, it is covered with plaque, turns pale, you need to show it to the dentist, this may be a sign of inflammation of the mucous membrane - stomatitis.
The function of taste buds is also used in diagnosing diseases by the tongue; it can change with burns, smoking or hormonal imbalances and is often accompanied by the accumulation of plaque.
In pregnant women, a change in taste preferences and aversion to normal food may appear in the first trimester or persist for the entire 9 months. For some women, this feature is the first sign of successful conception.
What a healthy tongue should look like
A healthy tongue should be pink and have a fold along its surface. It should be soft upon palpation and should not hurt when moving in different directions. The taste buds on the organ should be clearly visible. A small amount of white plaque does not always indicate the presence of any pathology; as a rule, this is the norm. A significant accumulation of plaque on the tongue may indicate the development of the following diseases:
- caries;
- gingivitis and other periodontal diseases;
- candidiasis.
Also, the cause of white or yellow plaque can be gastrointestinal diseases, food allergies or lack of vitamins. Plaque thickening may signal a chronic disease.
Ulcers and wounds on the tongue
Ulcers on the surface of the tongue are not uncommon and can occur for a variety of reasons:
- tongue injury;
- burn;
- dental problems in the oral cavity;
- Crohn's disease and other gastrointestinal problems.
Usually the ulcers are small in size, but present in large numbers, so they cause a lot of inconvenience and discomfort to a person. It is impossible to ignore wounds and ulcers on the tongue, especially if they arise without a reason.
One of the types of disease in which the body gives such a symptom is syphilis, therefore, treatment should be immediate and professional. However, in the case of this disease, the ulcer will be present on the tongue in the singular.
Its surface is bright red, shiny and hard. In addition, it is completely painless. The formation of warts at the root of the tongue or on its sides is a sign of HIV, and flat ulcers on the tip of the tongue, the sides or along the midline indicate the onset of tuberculosis.
Differences by color
Many people know that by the color of the tongue one can understand that something is wrong with the body. It is not a myth that some diseases are reflected on the tongue by a characteristic shade of plaque.
Let's look at the most common ones:
- influenza accompanied by high body temperature - burgundy coating;
- heart problems, anemia, malnutrition – pale color;
- blood diseases and pathologies of the respiratory system - purple tint;
- gastrointestinal diseases, jaundice or smoking - gray or yellow color;
- problems with the liver or spleen, dysentery, advanced viral diseases, abscess - black plaque;
- kidney pathologies – bluish tint;
- circulatory disorders, heavy metal poisoning – blue color;
- fungal infection and general dehydration of the body - white plaque;
- dental diseases – whitish or dark brown color.
How to keep your tongue healthy
The tongue, like teeth, is visible to others, and if it looks unhealthy, you may feel self-conscious. If your dentist or therapist has already determined that the discoloration of your tongue is not due to disease, you can improve its appearance by gently brushing your tongue twice daily during your normal oral hygiene routine. Use a toothbrush with a special scraper or pad to clean your tongue and cheeks.
Also, get into the habit of sticking out your tongue and examining it after brushing your teeth, this will allow you to immediately notice changes in its color or detect other problems. However, you need to understand that a healthy tongue color does not guarantee good dental health. Remember to visit your dentist regularly to check the health of your teeth, gums, and overall mouth.
Anatomy of the human tongue
The mucous membrane, penetrated by blood vessels, contains taste buds, glands, and lymphatic formations. It is covered with four types of papillae:
- Thread-like - oblong in shape, performing tactile functions by holding food.
- Mushroom-shaped, located everywhere except the apex and middle of the body. Responsible for the perception of taste.
- The leaf-shaped ones are located on the side and serve as taste analyzers.
- Grooved - large formations near the root, taste receptors.
The number of papillae is an individual value. Those who have a small amount often experience hunger, having difficulty sensing the characteristics of food.
Products interact with receptors that recognize sweet, bitter, sour, salty tastes, transmitting corresponding impulses to the brain. Full sensations arise when the senses of smell, touch, and vision are connected. Previously, it was believed that one group of receptors reacts to a specific taste, but this is misleading.
Fun fact : Women are more sensitive to sweet foods. The peculiarity is explained by the large number of receptors in the fair half.
The main component of the organ is muscles that provide mobility in different directions.
- Skeletal, originating from the bones - temporal, hyoid, lower jaw.
- Own, capable of changing shape and providing movement.
Another component is the salivary glands located near the root of the tongue (posterior) and the tip (anterior).
Functions
The tongue is not only an organ of taste, but a participant in several types of human activity, performing important functions:
- movement of food into the esophagus;
- primary digestion of saliva enzymes;
- sound production;
- protection against infection;
- absorption of certain medications (sublingual administration).
Papillae of the tongue.
The organ is important in infancy: with its help, sucking occurs - the only way the baby receives nutrients.
Red tipped tongue
The tip of the tongue corresponds to the area of the heart. If you do not have any signs of illness, a red tip of your tongue may indicate emotional problems.
Loss of the ability to counteract and regulate thermogenic hormones is usually indicated by a bright red tongue. This is typical for men who, for some reason, take hormonal drugs, or women who are entering menopause.
How to get rid of plaque
A small white coating that appears on the tongue after a night's sleep can be easily removed during morning hygiene procedures. But if it cannot be removed, it completely covers the taste buds and constantly appears again, then this is already regarded as a sign of a disease of the internal organs. Treatment in this case is prescribed by a doctor after examination and an accurate diagnosis.
You need to brush not only your teeth, but also your tongue. It is better to use a special scraper. Photo: AndreyPopov / Depositphotos
For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, drug therapy may include antiulcer drugs, drugs that improve digestive processes, and normalize the composition of intestinal microflora. Dietary nutrition is recommended. Spicy and fatty foods are excluded from the diet. Limit sweets. Food is taken in small portions 5-6 times a day. Depending on the location of the inflammatory focus and the severity of clinical manifestations, the diet is adjusted by the doctor.
Infectious diseases are treated with antibiotics. To reduce the activity of the inflammatory process, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are included in the treatment regimen.
Sources
- Tsepov L. M., Tsepova E. L. Lesions of the mucous membrane of the mouth and tongue in persons with pathology of the gastrointestinal tract // Bulletin of the Smolensk Medical Academy. No. 1. 2011.
- Sakharuk N.A. Oral candidiasis // Bulletin of VSMU. Volume 6. No. 1. 2007
- Agaev I. A. Language is the mirror of the body // Biomedicine. 2/2010.
- Makedonova Yu. A., Poroisky S. V., Gavrikova L. M., Afanasyeva O. Yu. Manifestation of diseases of the oral mucosa in patients who have had Covid-19 // Bulletin of Volgograd State Medical University. Issue 1 (77). 2021