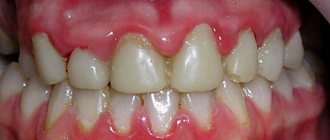
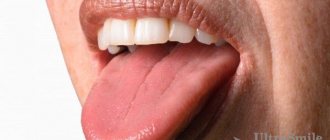
Malocclusion
Incorrect bite formation leads to permanent injury to the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue. As a result, the muscle organ swells and increases in size. Due to constant biting, teeth marks are left on the sides of the tongue.
The disease can be cured only after correcting the malocclusion. To do this, the doctor selects a design to straighten the dentition. For minor violations, patients are prescribed to wear orthodontic plates, trainers, and silicone trays. In case of more serious pathology, the defect is corrected using braces. The course of treatment can take from 3 months to 2 years.
Cracks in the tongue: causes, symptoms and treatment
A change in the shape and color of the tongue, the appearance of signs of its damage is the basis for seeking medical help. What makes life especially difficult for a person is the formation of long-term non-healing cracks, which indicates the presence of a serious problem. To effectively treat cracks in the tongue, it is necessary to identify the causes of the disease.
Sometimes the presence of cracks and grooves in the tongue is not accompanied by unnatural or painful sensations and can only be detected during examination by a dentist, ENT specialist or therapist. But this doesn't always happen. Patients often complain of the following related problems:
- pain;
- burning sensation;
- feeling that the tongue is loose;
- there is blood and ichor;
- elevated temperature;
- swelling and itching appeared;
- it becomes painful to chew;
- there is a problem with speech;
- increased salivation appeared;
- change in natural color;
- taste disturbance;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor.
If cracks appear on the tongue, and the phenomenon is accompanied by one of the listed symptoms, then they speak of a progressive disease. This inflammatory process is referred to as glossitis; the prognosis for recovery from it is usually favorable. The appearance of erosions, furrows and ulcers indicates damage to the deep parts of the tongue. In this case, you should definitely contact a specialist.
Sometimes the tongue cracks and becomes covered with ulcers due to general damage to the ENT organs. Thus, tonsillitis or fungal pharyngitis can cause swelling and the appearance of white grooves. This condition is not isolated as an independent disease. Treatment in such cases begins with eliminating the underlying problem.
Types of glossitis
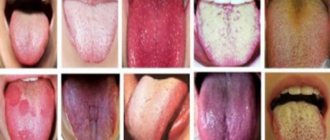
In total, there are more than ten types of glossitis, three of which are accompanied by the appearance of cracks in the tongue. They have quite pronounced visible differences. To independently diagnose the type, you can compare the current state of the tongue with photos of classic manifestations of the disease.
Folded glossitis takes its name from the main external manifestation - the presence of folds. Sometimes, with this type of disease, a cracked tongue is present from birth. If it does not hurt, is not loose and there are no other unpleasant sensations, then the condition is considered normal. However, with deep cracks in the tongue, treatment is still necessary.
The problem of a folded tongue is often only of an aesthetic nature, although people with this feature are recommended to have constant monitoring by a dentist.
Desquamative glossitis is characterized by focal damage to the surface with almost imperceptible shallow cracks.
The papillae desquamate and a whitish heterogeneous layer forms. The affected areas quickly recover, acquiring a natural color, and those adjacent to them become inflamed. The geometry of white areas (plaque) on the surface often changes.
In advanced cases, due to the large number of cracks, a person feels the tongue is loose.
Diamond-shaped glossitis is characterized by the presence of a rhombic or oval-shaped area of red-blue color. It is located in the middle of the tongue, in the region of the posterior third. The tongue cracks in the center, so that the entire affected area seems to be divided into two parts. This type can be chronic, and during exacerbations, pain and burning begin.
The position of the cracks is not random. Localization is divided into three types, each of which is caused by specific problems. You can independently identify the type of localization by assessing the position of the cracks in the tongue: in the center, on the sides or at the tip.
The presence of cracks only at the tip of the tongue indicates the following causes of the problem:
- Thermal damage. Hot food first comes into contact with the tip of the tongue and causes major damage to it. Often the problem is contact with a hot metal spoon.
- Chemical damage. Occurs from contact with spicy, sour foods or corrosive substances.
- Physical impact. The tip can crack due to an incorrect bite or a cut on the sharp protruding parts of the incisors and canines.
cracks on the sides of the tongue
The formation of cracks in the tongue in the middle has a different reason, since it is almost impossible to injure this area without affecting the periphery. This means that inflammation is an indicator of pathology or disease of internal organs.
In addition, the formation of cracks in the center is possible when the middle area dries out, local circulation is impaired, or the immune system is weakened.
There may be only one crack; upon examination, it appears as if the tongue has split into two parts.
The presence of cracks on the sides of the tongue can be caused by various reasons.
If the inflammatory process is present on the side on one side, then this means physical damage from the sharp edges of small and large molars or dentures.
If the tongue is cracked on both sides, it means that there are serious malfunctions in the functioning of the body , where glossitis acts only as an indicator of pathology.
Causes of cracks
Folded glossitis can be detected immediately after the birth of the child. The cause is most often a hereditary predisposition, rather than a sign of any disease. Therefore, if a child has a cracked tongue, this is not yet a reason to start urgent treatment. Only if the grooves bleed or other problems are present should you seek medical help.
The causes of cracks in the tongue can be very different, but they all require diagnosis and elimination. The first type of prerequisites is of a dental nature; the problem arises due to the following phenomena:
- cuts to the organ by sharp edges of teeth or an incorrectly selected prosthesis;
- if diseases of the oral cavity or ENT organs are not treated for a long time;
- irritation from eating excessively hot, spicy, salty or sour foods;
- allergic reaction to medications or toothpaste taken.
The second type of reason, which explains why cracks appear on the tongue, can be described as indicator. It indicates the presence of a disease of the organs or circulatory system.
Another reason for the appearance of cracks in the tongue in adults may be a banal vitamin deficiency, leading to a decrease in immunity. It is usually observed in the following cases:
- the onset of the period from February to April, when there is no supply of vitamins from fresh vegetables and fruits for a long time;
- period of growing up with changes in hormonal levels;
- breastfeeding period.
Medical assistance
If the tongue is cracked and hurts, is swollen on the sides, or there are other signs of the progressive development of the disease, then treatment must be started immediately . A protracted process can progress to a more complex stage, up to necrosis or oncology.
Constant inflammation causes intoxication of the body and is fraught with the entry of pus into the gastrointestinal tract.
Only a doctor can give a qualified answer to the question of why the tongue cracks.
Due to the variety of possible causes of cracks in the tongue, the problem arises of which doctor to contact in order to establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. First of all, you need to get examined by a dentist.
This is necessary to identify prerequisites associated with problems in the oral cavity, or to exclude such a scenario.
If, as a result of a dental examination, the cause of cracks in the tongue was not identified, this means that the problem may be caused by diseases of the internal organs. Usually the patient knows or guesses from how he feels about its existence. Depending on the type of possible pathology, you need to contact a specialized specialist.
If there are no obvious signs of illness, you need to consult a therapist or pediatrician. You can first take a general blood test and do an ultrasound of the internal organs.
Therapeutic treatment
First of all, to get rid of glossitis, it is necessary to diagnose and determine the nature of its occurrence, since it is impossible to cure cracks in the tongue without eliminating the provoking factor.
The treatment method should be developed by a specialist in the underlying disease. Additionally, symptomatic treatment of the entire oral cavity is used, depending on the type of lesion.
To do this, use the following methods:
- drug therapy aimed at improving local blood circulation in the tissues of the oral cavity;
- prescribing physiotherapeutic procedures such as electrophoresis;
- use of antiviral ointments;
- the use of drugs that stimulate epithelial restoration;
- taking antibiotics for fungal complications;
- administration of local anesthetics for severe pain.
Use of traditional medicine
At home, you can use well-known methods to help heal wounds in the mouth, eliminate pain, relieve swelling and other symptoms. However, before treating cracked tongue with folk remedies, you need to ensure their compatibility with the prescribed medications.
The most effective are the following recipes:
- Herbal infusion of chamomile, celandine, sage and calendula. For adults, you can add St. John's wort. Take after meals in the form of baths or lotions. Promotes wound healing and relieves swelling.
- Compresses from fermented milk products. Soften scars and scabs. The procedure should be done in the morning for 15 minutes.
- Sea buckthorn or olive oil. In the morning you need to drop a few drops on the mucous membrane and in the middle of the tongue, then do not drink or eat for 15 minutes. Softens dry formations on the tongue and mucous membranes.
- Honey. Has wound-healing and antimicrobial effects. A piece of the product can be placed in the middle of the tongue and dissolved. Gives a good effect if cracks bleed.
- Propolis tincture (for adults only). The strongest disinfectant: has antimicrobial, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. Since alcohol tincture cannot be used in its pure form if there are open wounds, you need to dilute 1 teaspoon in 100 grams of warm tea. Drink after meals.
Folded tongue
This is a congenital anomaly in which the tongue is excised by longitudinal and transverse folds, wavy, uneven at the edges. As a rule, the disease is accompanied by an increase in the size of the organ and its thickening; teeth marks can be seen on the sides. Usually the pathology is asymptomatic and does not cause discomfort; pain and inflammation can appear after infectious diseases, with the development of stomatitis or glossitis.
The folded tongue requires good hygienic care, since bacterial plaque easily accumulates in the cracks and creates a convenient environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Such a disease is incurable; therapeutic procedures are necessary only when stomatitis and glossalgia develop.
Other dental problems
When teeth imprints constantly appear on the tongue and cheeks, while a person manages to bite and injure the mucous membrane, this can indicate not only malocclusions, but also other dental pathologies:
- incorrectly installed crowns, fillings and dentures,
- presence of chipped and damaged teeth,
- abnormal structure of the temporomandibular joint,
- bruxism,
- lack of teeth,
- anomalies in the growth and eruption of third molars: for example, “eights” can grow into the cheek, cause crowding of the row and provoke bite pathologies.
Liver diseases
In people suffering from serious liver diseases (viral hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver), the tongue has a characteristic appearance - the mucous membranes are red, hyperemic, the surface is smooth, glossy, the papillae are smoothed. Often such symptoms are accompanied by swelling of the organ and an increase in its size, as a result of which the edges are constantly bitten by the teeth, forming wavy sides.
Among the additional external symptoms, patients note the appearance of spider veins, xanthomatous plaques, and erythema (redness) of the palms on the surface of the skin. Patients complain of pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting, indigestion and stool disorders.
The disease must be treated by a general practitioner, infectious disease specialist, surgeon or oncologist.
Vitamin deficiency
If there is a lack of vitamins B and D in the human body, the surface of the tongue dries out, cracks, becomes inflamed, becomes coated, and bad breath appears.
When an allergic reaction to vitamins occurs, the muscular organ swells, and dents from the teeth are clearly visible on its lateral surfaces. With a lack of vitamin B₃, the organ cracks, painful sensations appear, and a burning sensation occurs while eating. If an infection occurs, an acute inflammatory process develops, purulent ulcers form, and the person’s well-being worsens. To treat the disease, it is necessary to compensate for the lack of vitamins in the body.
Other diseases of the tongue. Scalloped tongue (K14.8)
Scalloped (toothed tongue) - a change in the shape of the tongue, in which its edges acquire a round-toothed or scalloped outline. Often combined with macroglossia Macroglossia is a pathological enlargement of the tongue; observed as a developmental anomaly or in the presence of a chronic pathological process in the tongue or swelling of the tongue.
Notes
from this subcategory :
– “Other diseases of the lips and oral mucosa” – K13 – “Geographic” tongue” – K14.1 – “Atrophy of the papillae of the tongue” – K14.4 – “Hypertrophy of the papillae of the tongue” – K14.3
– “Congenital macroglossia” – Q38.2
– “Other congenital anomalies of the tongue” – Q38.3
This subcategory includes: scalloped tongue. The following clinical conditions also belong to this code K14.8 and are described under the same code, but in different cards for ease of diagnosis:
All the clinical conditions described above, as a rule, are complications of some pathology. Thus, the code of this subheading should be used as a complication of any underlying disease or as a code for a concomitant pathology. The code can be used as a code for the underlying disease only in case of a preliminary diagnosis.
Description:
As a rule, it has a chronic course. Acutely occurs with swelling of the tongue due to various reasons. When the cause of the swelling is eliminated, it also quickly disappears.
Mobile application “MedElement”
Download the application for ANDROID / for iOS
Mobile application “MedElement”
Download the application for ANDROID / for iOS
The reason for the change in the shape of the tongue is high pressure on the tissue of the tongue, for example during bruxism. Bruxism is involuntary, uncontrolled by consciousness, clenching and grinding of teeth at night (sometimes during the day). It is observed more often in childhood and young age, the habit of sucking the tongue to the teeth, and increased size of the tongue.
In this case, the contours of the teeth are imprinted on the edge of the tongue in the form of oval impressions, which are sometimes bordered by a white, raised scalloped ridge. A serrated tongue may be associated with a distinct white line on the buccal mucosa.
A scalloped tongue can be observed in the following diseases and conditions: – damage to the temporomandibular joint (instability of the lower jaw); – systemic diseases (acromegaly, amyloidosis and others); – hereditary diseases (Down’s disease and others); – hypothyroidism; – parafunctional disorders (bruxism and others); – swelling of the tongue due to other reasons; – may be associated with sleep apnea syndrome due to tongue hypertrophy;
– can be observed in healthy individuals.
Note A scalloped tongue is often described as a specific marker of gastrointestinal disease, for example, sphincter of Oddi dysfunction or some kind of colitis. There is no clear evidence supporting this approach to the etiology of this condition.
For example, in a large cohort study, tongue lesions (not only scalloped tongue) were found: - in diabetes mellitus - in 29.03%; – with hypertension – in 28.63%; – for heart and vascular diseases – in 25.15%; – for hematological diseases – in 17.54%; – for liver diseases – in 23.86%; – for other gastrointestinal diseases – in 22.38%; – in 20.69% of cases, changes in the tongue were associated with tumors. No specific correlations were identified between the type of systemic pathology and the nature of the tongue lesion. The scalloped tongue was the rarest find.
Sign of prevalence: Rare
A scalloped tongue is rare. In a large population study (Hungary, 1995-1999), among 5034 patients with systemic diseases, scalloped tongue was detected in approximately 1.5% of cases (5th place out of 6 different tongue pathologies identified).
According to some studies, the incidence of scalloped tongue in children is almost two times lower than in adults.
This fact confirms the assumption that the prevalence of oral lesions increases with age, which may be associated with prosthetics and other dental care.
discomfort at the edges of the tongue; discomfort on the tip of the tongue; burning along the edges of the tongue; teeth marks on the edges of the tongue; teeth marks on the tip of the tongue; macroglossia The main complaints with a scalloped tongue are discomfort and a slight burning sensation along the edges of the tongue (sometimes).
On examination, the tongue is usually enlarged; On the side surfaces there are imprints corresponding to the teeth. Scalloping of both edges is usually observed, but it may be present only on one side or limited to the part of the tongue that is directly pressed against the teeth.
A scalloped tongue may be associated with the following symptoms:
– anemia, unexplained weight loss, fatigue (indicate possible hypersplenism; Hypersplenism is a combination of an enlarged spleen with an increase in the number of cellular elements in the bone marrow and a decrease in formed elements in the peripheral blood.); - weight gain, lethargy, chills and other symptoms (may indicate hypothyroidismHypothyroidism is a thyroid insufficiency syndrome characterized by neuropsychiatric disorders, swelling of the face, limbs and torso, bradycardia); – pain, discomfort when eating spicy and hot foods, bad breath and other symptoms that may indicate an oral infection; – sleep apnea syndrome Apnea – temporary cessation of breathing, which may indicate macroglossia Macroglossia – pathological enlargement of the tongue; observed as a developmental anomaly or in the presence of a chronic pathological process in the language.
There is no need to diagnose a scalloped tongue other than visual inspection. High-resolution digital photography is useful for assessing process dynamics.
The patient should be referred to a general practitioner. When combining a scalloped tongue with macroglossia, see the subsection “Hyperptrophy of the tongue.”
There are no specific laboratory tests to confirm or refute the diagnosis. Any identified deviations indicate an etiologically significant or concomitant pathology.
In all cases, various tests for infections are useful (syphilis, tuberculosis, actinomycosis Actinomycosis is a chronic infectious disease of humans and animals caused by actinomycetes and characterized by granulomatous damage to tissues and organs with the development of dense infiltrates, the formation of abscesses, fistulas and scars) and, if indicated, genetic tests for congenital diseases.
A scalloped tongue is differentiated from glossitis and tongue atrophy. Complications of a scalloped tongue include: – decubital (bedsore, traumatic) ulcers of the tongue;
– infection of damaged edges with the development of glossitis.
Treatment for scalloped tongue is aimed at eliminating the underlying etiological cause. As symptomatic therapy, the installation of acrylic screens (splints, mouthguards) and consultations with a psychologist (for parafunctional disorders) are of great importance. If there is a pronounced reaction to food, a diet excluding hot, spicy, hard foods is indicated.
Patients usually need consultations with a general practitioner/pediatrician. Consultations with other specialists (neurologist, endocrinologist, otolaryngologist, speech therapist, gastroenterologist) may also be necessary.
A scalloped tongue in itself is not a life-threatening condition. The prognosis is determined by the underlying disease.
Primary prevention has not been developed.
Secondary prevention comes down to preventing infection and consists of careful oral hygiene.
- “Effects of surgical reduction of the tongue” Ueyama Y, Mano T, Nishiyama A, Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, No. 37(6), 1999
- “Epidemiologic survey of tongue lesions and analysis of the etiologic factors involved” Voros-Balog T, Dombi C, Vincze N, Banoczy J.
, Fogorvosi Szemle journal, No. 92(5), 1999 - “Glossoptosis (posterior displacement of the tongue) during sleep: a frequent cause of sleep apnea in pediatric patients referred for dynamic sleep fluoroscopy” Donnelly LF, Strife JL, Myer CM, Am J Roentgenol., No. 175(6), 2000
- “Glossoptosis-apnea syndrome in infancy” Cozzi F, Pierro A.
, Pediatrics, No. 75(5), 1985 - “Hypoglossal nerve palsy” Ivan WC Tsui, David PN Chan, Hong Kong Med J, vol. 15, No. 3, 2009
- “Mandibular distraction osteogenesis for pediatric airway management” Miloro M., J Oral Maxillofac Surg., No. 68(7), 2010
- “Myasthenia gravis – a rare presentation with tongue atrophy and fasciculation” J. Burch, C. Warren-Gash, V. Ingham, M.
Patel, D. Bennett, KR Chaudhuri, Age and Aging journal, No. 35, 2006 - “Oral mucosal lesions in a representative cross-sectional study of aging Germans” Reichart PA, Community Dent Oral Epidemiol., No. 28(5), 2000
- “Surgical correction of the enlarged tongue” Taher A., The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery, vol.
3, №1, 2008 - “Pierre Robin sequence - an early diagnostic sign of Stickler syndrome (clinical case)” Muzychina A.A., Maleeva I.A., “Medical and social problems of the family”, v. 17, no. 3-4, 2012
If you are not a medical professional:
- By self-medicating, you can cause irreparable harm to your health.
- The information posted on the MedElement website and in the mobile applications “MedElement”, “Lekar Pro”, “Dariger Pro”, “Diseases: a therapist’s guide” cannot and should not replace a face-to-face consultation with a doctor. Be sure to contact a medical facility if you have any illnesses or symptoms that concern you.
- The choice of medications and their dosage must be discussed with a specialist. Only a doctor can prescribe the right medicine and its dosage, taking into account the disease and condition of the patient’s body.
- The MedElement website and mobile applications “MedElement (MedElement)”, “Lekar Pro”, “Dariger Pro”, “Diseases: a therapist’s reference book” are exclusively information and reference resources. The information posted on this site should not be used to unauthorizedly change doctor's orders.
- The editors of MedElement are not responsible for any personal injury or property damage resulting from the use of this site.
Source: https://diseases.medelement.com/disease/%D0%B4%D1%80%D1%83%D0%B3%D0%B8%D0%B5-%D0%B1%D0%BE%D0% BB%D0%B5%D0%B7%D0%BD%D0%B8-%D1%8F%D0%B7%D1%8B%D0%BA%D0%B0-%D1%84%D0%B5%D1% 81%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%87%D0%B0%D1%82%D1%8B%D0%B9-%D1%8F%D0%B7%D1%8B%D0%BA -k14-8/13637
Hypothyroidism
This disease is caused by a malfunction of the thyroid gland. The pathology is manifested by swelling of the tongue with characteristic marks of teeth on its surface. Patients are inactive and find it difficult to talk due to dry mouth. There is a sensation of a foreign object in the mouth, the tongue becomes tangled.
External symptoms of the disease include a yellow tint to the skin, swelling of the face, increased hair loss, deterioration of memory and intellectual abilities, disruption of the digestive tract, and disorders of the genitourinary system. Hypothyroidism is treated by an endocrinologist.
Why does the problem occur in pregnant women?
Teeth imprints on the tongue during pregnancy may be associated with the pathologies that we listed earlier, but most often they appear for the following reasons:
- dehydration of the body against the background of severe toxicosis,
- iron deficiency anemia: the muscle organ becomes red, swollen and numb,
- candidal stomatitis: then the unpleasant symptom is accompanied by the appearance of a dense cheesy coating,
- lack of B vitamins and folic acid,
- physiological swelling of organs due to the accumulation of fluid in the body in late pregnancy.
“I constantly noticed this problem during pregnancy. Especially after I get nervous. It was very noticeable in the later stages, in the summer, in the very heat. I was also constantly thirsty, I always felt that my mouth was very dry, and my tongue was swollen as a result. And I drank water and drank... True, the doctor scolded me all the time, saying that my whole body and all my internal organs were swelling. As soon as I gave birth, everything returned to normal...”
Anastasia K., review from woman.ru
Gastrointestinal diseases
The oral cavity and digestive organs are in direct communication. Diseases of the stomach and intestines cause acidity in the mouth, creating a convenient environment for the proliferation of bacteria. A persistent white or yellow bacterial coating appears on the surface of the tongue and mucous membranes, spots or erosions may form, the organ becomes inflamed and increases in size.
A symptom of the development of gastrointestinal diseases is the root of the tongue coated with plaque.
Peptic ulcers of the stomach, duodenum, duodenitis, dysbacteriosis, gastritis with high acidity, and colitis can cause such symptoms. Additionally, patients are bothered by abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, stool disorders, and flatulence.
To treat the pathology and eliminate plaque on the root of the tongue, you need to consult a gastroenterologist. During therapy, plaque and swelling disappear. If erosions have formed on the mucous membranes, it is necessary to do regular antiseptic mouth rinses with Chlorhexidine, Miramistin or Chlorophyllipt.
Rough tongue: reasons (what is it), with a white coating, uneven edges, taste zones
A healthy tongue should be moist, smooth, and pink in color.
The formation of a thin layer of whitish plaque is allowed. Visually, this organ may appear velvety due to the clearly visible papillae.
However, in some cases it may change its color and texture, which in most cases signals the development of diseases. If your tongue has become rough, you should think about your health.
Pathologies of the digestive tract
Reflexes that can influence the motor and secretory functions of the stomach and intestines are produced by tongue receptors. The opposite effect also occurs.
That is, internal organs influence the appearance of pathological reflexes on the surface of the tongue. For example, its rough root and white coating will tell the doctor that the patient suffers from gastritis with low acidity.
Pain and burning sensations in the esophagus, heartburn can complement the clinical picture.
A rough tongue covered with a gray coating may indicate the development of an intestinal ulcer. An additional factor indicating this pathology is heartburn and a burning sensation in the mouth.
Colitis, in addition to roughness, is characterized by an increase in the size of the tongue; teeth marks may even remain along its edges. With duodenitis and biliary dyskinesia, the thickness of the plaque increases significantly. A slight roughness of the tongue rarely causes discomfort. But a dense coating can negatively affect the sense of taste, reducing the sensitivity of the papillae.
Diagnosis and treatment
Any changes in the tongue indicate the development of the disease, a lack or excess of various compounds in the human body. In medicine there is the concept of linguodiagnostics. It refers to obtaining information about the state of the body by studying the linguistic surface.
If the mucous membrane in the mouth becomes unpleasant to the touch, rough, and other signs appear, you should visit a therapist, who, in turn, will refer the patient to a dentist, infectious disease specialist, or gastroenterologist. The best period for diagnosis is morning. Diagnosis is carried out on an empty stomach.
First, the doctor projects the location of the internal organs in the tongue, after which he notes the violations.
The specialist also takes into account the color of the tongue, its shape, the presence of plaque and its shade, the mobility of this organ, as well as various formations, as a result of which it becomes clear why roughness and other symptoms began to be felt in the mouth.
Light plaque can be removed by brushing your tongue and teeth. To do this, it is recommended to purchase a special scraper or brush. For better cleansing, after these actions you should rinse your mouth with a disinfectant.
In this case, the doctor will prescribe a comprehensive treatment for the underlying disease. With successful treatment, symptoms should disappear.
In addition, it is necessary to limit the consumption of fermented milk products and sweets, as well as give up bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse).
Causes
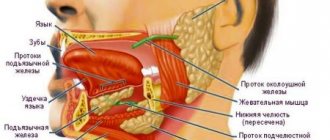
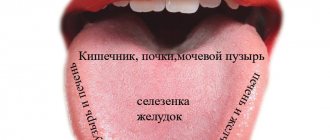
Experts divide the surface of the tongue into five parts depending on which organ they are responsible for:
- lateral surface on the left and right (the right is responsible for the excretory system, the left for the functioning of the liver);
- middle region (behind the spleen and stomach);
- tip (for the heart and lungs);
- posterior wall (for the functionality of the kidneys and digestive system).
In the photo there are zones responsible for taste:
When diagnosing pathologies of the oral cavity, the doctor relies on these data.
There are many reasons that cause a rough tongue:
- infection in the intestines;
- severe dehydration of the body: this causes dry mouth;
- liver pathologies;
- disruption of the functioning of the stomach and gallbladder, duodenum: in this case, the roughness is accompanied by the formation of bitterness in the oral cavity, and with the development of gastritis and duodenitis, flaky areas on the tongue may occur.
- thyroid diseases;
- excess or deficiency of nutritional compounds in the body;
- prolonged use of antibiotic drugs in excessive amounts;
- chronic tonsillitis;
- proliferation of fungal microorganisms in the human body;
- glossitis;
- development of diabetes mellitus, disruptions in the functionality of the endocrine system: in this case, cracks appear on the surface of the rough organ;
- diseases of the spleen, heart and kidneys: in this case, the pathology is accompanied by swelling.
- blood diseases: the formation of ulcers of varying severity and volume is possible.
Also, roughness and irritation on the tongue and throat can be associated with a thermal or chemical burn.
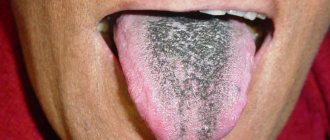
White plaque
Also, the appearance of white plaque can be caused by alcohol abuse, smoking, long-term use of medications, and dehydration.
By the location of the white plaque on the rough organ of the oral cavity, you can find out the reason for its appearance:
- the central part signals gastric diseases;
- at the end - about heart disease;
- at the root - about intestinal pathologies;
- at the edges - about diseases of the spleen or liver;
- on the back of this organ - about impaired functioning of the pancreas;
- in the sky - about the development of candidiasis;
- in the area of the tonsils - about a sore throat.
Also, the villi on the surface of the tongue may become white due to excessive consumption of fermented milk products, sweets, and antibiotic medications.
Dryness
The feeling of a dry mouth can be explained by insufficient salivation.
Dryness may indicate dehydration, especially if this symptom is accompanied by elevated body temperature, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Dryness in the mouth can occur due to frequent smoking or alcohol abuse, as well as as a side effect of the use of medications. In addition, this symptom may occur due to the development of certain diseases:
- diabetes mellitus;
- Parkinson's or Alzheimer's diseases;
- stroke;
- anemia;
- hypotension;
- Sjögren's syndrome;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- HIV infections.
A dry tongue with a white coating may indicate:
- disrupted process of keratinization of filiform papillae cells;
- glossitis or stomatitis;
- drug abuse;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcerative lesions, gastritis, pancreatitis, oncology of the digestive organs);
- oral thrush;
- intoxication of the body;
- heart, lung and kidney diseases;
- weakened immunity;
- disruption of the endocrine system.
If these phenomena occur, you should seek advice from a doctor.
Jagged edges
Rough edges of the tongue are not considered a dangerous condition. This phenomenon is a consequence of the development of diseases in the body. The reasons for the formation of the dentate organ include:
- Macroglossia (swelling). As a result of this pathology, the organ becomes enlarged, resulting in dental imprints.
- Dehydration.
- Hypothyroidism. In the presence of this disease, swelling of not only the tongue, but also the face may appear.
- Disturbances in the functionality of the thyroid gland.
- Diseases of the circulatory system.
- Bad habits (clenching your jaw or pressing an organ against your teeth for a long time, which can cause a feeling of anxiety).
- Lack of vitamins and mineral compounds.
- Temporomandibular joint syndrome.
- Diseases of the bladder or liver in chronic form.
- The body's response to the use of toothpaste, as well as to the consumption of low-quality sweet products containing inexpensive dyes.
- Poisoning with salts of heavy metals.
Also, irregularities in the tongue can signal problems with the digestive system or diseases of the paranasal sinuses.
Tuberosity
Factors that provoke the formation of a bumpy tongue can be:
- enlarged taste buds (papillae) on an organ in the oral cavity;
- heartburn, gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- malfunction of the pancreas;
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- diabetes;
- injury to the tongue during surgical treatment or harsh cleaning of the organ;
- warts due to papilloma virus;
- stomatitis.
- impaired metabolism.
- thrush in the oral cavity, ordinary or candidal glossitis.
- leukoplakia.
In addition, tubercles can occur when the immune system is weakened, emotional stress, hormonal imbalance, or celiac disease.
Why does the symptom appear?
The overall picture of the oral cavity almost always directly affects the condition of the tongue. If there is caries, pulpitis, stomatitis, periodontitis or candidiasis in the mouth, all this affects its condition.
Pathologies of a muscular organ can be independent or complement the clinical picture of other diseases in humans. Independent diseases are rare.
These include various mechanical damage - injuries, burns, rubbing against braces, crowns or dentures.
If a rough tongue appears, this should be alarming. Often this can be a sign of an underlying disease. Often the appearance of roughness is accompanied by the appearance of plaque, inflammation of the papillae, a dry tongue appears, its surface is rough, geometric patterns appear on it, swelling, hyperemia of the mucous membrane, and an increase in the volume of the organ.
Sometimes dry mouth is a symptom accompanying the development of diabetes. In this case, the surface of the tongue is dry and slightly rough. Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the cause of this phenomenon. The most common causes of the appearance of rough mucous membrane of a muscular organ include:
- diseases of the endocrine system, in particular disorders of the thyroid gland;
- dysfunction in the functioning of the digestive system, liver and gallbladder;
- intestinal tract infections;
- chronic tonsillitis;
- glossitis (during its development, the tongue has a rough, painful mucous membrane);
- anemia;
- angina;
- alcohol or food intoxication, infectious diseases;
- long-term use of antibacterial drugs in large dosages;
- development of fungal microorganisms in the oral cavity.
Often the causes of dryness and roughness lie in severe dehydration of the body. General intoxication can occur due to poisoning and the development of intestinal infections. Liver dysfunction is also accompanied by similar symptoms.
If the surface of the organ is covered with cracks, this may be a sign of diabetic disease or a malfunction of the endocrine system.
The causes of dryness and roughness may lie in a significant deficiency or excess of vitamins or minerals in the body - hypovitaminosis or hypervitaminosis.
Paleness of the surface of the organ, which is accompanied by roughness, can signal malfunctions in the functioning of the digestive tract and stagnation of food.
It is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner to determine the cause of such symptoms and begin adequate treatment in a timely manner.
Diseases of the gallbladder and duodenum, for example gastritis or gastroduodenitis, can also manifest such symptoms. Additionally, a bitter taste may be felt in the mouth.
Swelling and roughness of the mucous membrane can be a sign of diseases of the cardiovascular system, malfunctions of the urinary system, and spleen.
The first symptom of a disorder in hematopoiesis is the appearance of ulcers of different sizes on the surface of the organ, dryness of the mucous membrane.
And if additional pain appears in the epigastric region, a grayish coating, this indicates the development of gastritis, pancreatitis, gastroduodenitis, gastric or duodenal ulcers.
Irritation and roughness can occur after a thermal burn or mechanical injury (for example, constant rubbing against the sharp edges of a filling, prosthesis or crown). Therefore, you need to promptly contact your dentist and treat any problems that arise.
Source: https://prime-medical.ru/shershavyy-yazyk-prichiny-chto-eto-s-belym/
Nervous system diseases
With disorders of the nervous system, unpleasant painful sensations occur, tingling in the tongue, a disturbing feeling of dry mucous membranes, hyperesthesia, burning, disturbances of taste, diction, swelling and the appearance of bacterial plaque. This disease is called stomalgia, most often it affects women during menopause or after suffering shocks. Symptoms of the disease decrease with eating, especially when eating spicy foods. Unpleasant sensations are localized on the tip and sides of the swollen tongue, its edges are wavy, and dents from the teeth are visible.
The main causes of pathology are recently experienced tragic events in life: the death of relatives, cancer of loved ones, personal problems. Patients are easily excitable, constantly look at their tongue in the mirror, and are pathologically afraid of developing cancer.
Treatment of stomalgia is carried out comprehensively. It includes medication, psychotherapy, physiotherapy, acupuncture, and oral sanitation.
Uneven, wavy edges of the tongue may indicate the development of a serious illness. Therefore, if such a symptom appears, you should consult a dentist and therapist. Timely treatment will help avoid the development of severe complications.
How do they look
Small cracks in the tongue can be completely invisible to the naked eye; only an experienced doctor can examine them using special instruments. The larger ones are clearly visible to the naked eye; they resemble longitudinal or transverse grooves on the tongue. Deep cracks look like crevices; sometimes the tongue appears to be cracked or split into two parts. If you notice such a problem, consult a doctor, even if nothing is bothering you at the moment. If an infection gets into the crack, the course of the disease may be complicated by the inflammatory process.