Today, dentistry is focused on comprehensive patient care, which begins with diagnosing the oral mucosa and checking the integrity of the teeth. It is important to understand that the oral cavity is not separate from the body, but is capable of influencing key processes in the human body.
That is why during a modern dental appointment the doctor pays attention to the study of all systems of the human body. An indicator of pathological processes in organ systems is, first of all, the oral mucosa. If her condition deviates from the norm, then you first need to understand what caused it, and then take appropriate measures. For this reason, Taisiya Tereshchenko, a dentist of the highest category, spoke specifically for apteka24.ua about how to monitor the health of the oral mucosa and why Metrogyl Denta is needed.
Metrogyl gel is a reliable product in dentistry
Metrogyl Denta is a dental medicinal product produced by pharmaceutical companies in the form of a gel. Thanks to the combined composition, including:
- antibiotic;
- antiseptic,
- the medicine has a wide spectrum of antimicrobial action and is recommended by experts for use by both adults and children over 6 years of age.
The main active ingredients of the drug are metronidazole and chlorhexidine.
Metronidazole, known for its antimicrobial properties, is successfully used in medicine for:
- peptic ulcers;
- chronic colitis;
- inflammation of the urinary system;
- genital infections,
- as well as for the purpose of preventing complications that often arise after surgery.
Chlorhexidine is an effective antiseptic used in medical practice:
- during preoperative treatment of hands;
- when cleaning medical premises;
- for disinfection of instruments.
Thanks to its gel consistency, Metrogyl is successfully used in dentistry, but in addition, the product can help solve some cosmetic problems and stop the inflammatory processes of the external genitalia.
Metrogil:
instructions for use
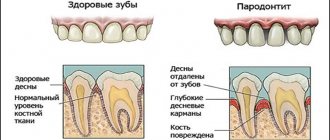
In dental practice, the drug is used to treat:
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis;
- bacterial stomatitis;
- lip inflammation;
- inflammatory processes of the hoods over wisdom teeth;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane;
- alviolite of the socket of an extracted tooth,
- It is also used as an additional agent in the treatment of periodontitis and periodontal abscess.
However, despite the effectiveness of Metrogyl, the instructions of which recommend its use for these diseases, an experienced doctor may prescribe other drugs, depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body and the complexity of the case.
Metrogyl denta goes on sale in laminated plastic tubes of 20 grams and is sold without a prescription.
Metrogyl, reviews of which from experts allow us to recommend to patients a relatively inexpensive and effective antiseptic drug, is often used as an everyday means of oral hygiene, which helps prevent many inflammatory processes.
Instructions for use of METROGYL DENTA® (METROGYL DENTA®)
A drug with antimicrobial action for topical use in dentistry.
In periodontitis, anaerobic bacteria are considered the predominant causative factor. Therefore, it is desirable to use pharmaceutical treatment specifically effective against periopathogenic anaerobic microflora instead of using broad-spectrum antibiotics with the associated risk of developing bacterial resistance and gastrointestinal complications. Metronidazole is a chemotherapeutic agent with activity against anaerobes such as Bacteroides species and spirochetes, which are widely believed to be the main pathogens associated with periodontitis.
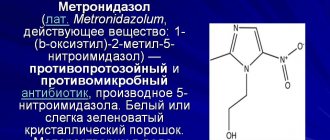
Metronidazole
Metronidazole is a 5-nitroimidazole derivative with activity against anaerobic protozoa and anaerobic bacteria.
Mechanism of action.
After metronidazole enters the body, it is reduced by intracellular electron transfer proteins. As a result of this change, a concentration gradient is maintained in the metronidazole molecule, which promotes intracellular transport of the drug. It is assumed that free radicals are formed, which in turn react with cellular components, and this leads to the death of the microorganism. Anaerobic bacteria associated with periodontal disease, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Wolinella recta, are highly sensitive to metronidazole. The lowest concentration of metronidazole required to inhibit 50% of strains (MIC50) is below 1 μg/ml for the corresponding anaerobes. Topical metronidazole may produce higher subgingival concentrations than those achieved with systemic administration. Therefore, a lower dose of the drug will be required.
Microbiological analysis included determination of total anaerobically culturable bacteria and the relative proportions of anaerobes, aerobes, black pigmented anaerobic gram-negative rods, Actinobacillus actinimycetemcomitans, streptococci and spirochetes.
Both treatments resulted in a significant reduction in pocket depth. The decrease in GDC was statistically significant during treatment and during subsequent visits to the doctor (p < 0.00001). Metronidazole gel tended to be a better treatment than stone removal throughout the period. The reduction in bleeding on probing was statistically significant during treatment and during follow-up (p<0.02).
Chlorhexidine gluconate
Chlorhexidine is a disbiguanide antiseptic and disinfectant with bactericidal or bacteriostatic action against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Mechanism of action.
At physiological pH, chlorhexidine salts dissociate, releasing a positively charged component. The bactericidal effect of chlorhexidine results from the binding of these cationic molecules to the negatively charged walls of bacterial cells and extramicrobial complexes. In low concentrations, chlorhexidine causes an imbalance in the osmotic balance of bacterial cells and the leakage of potassium and phosphorus, which gives a bacteriostatic effect. At high concentrations of chlorhexidine, the cytoplasmic contents of the bacterial cell are precipitated, which leads to its death.
Several hypotheses have been put forward regarding the mechanisms of action of chlorhexidine in relation to plaque inhibition.
1. Binds to bacteria that form oral plaque and affects their absorption by teeth.
2. Binding to glycoproteins in saliva and reducing pellicle formation and plaque colonization.
Chlorhexidine is poorly absorbed through intact skin or from the gastrointestinal tract. Does not accumulate in the body and is only minimally metabolized. If swallowed, chlorhexidine is primarily excreted in the feces. There are reports that extensive use of chlorhexidine for over 20 years has provided no evidence of absorption through intact skin.
The role of Metrogyl Denta® gel
The effectiveness of the drug is due to the presence of two antibacterial components in its composition:
- Metronidazole has an antibacterial effect, is active against anaerobic bacteria
that cause periodontal diseases: Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, Fusobacterium fusiformis, Wolinella recta, Eikenella corrodens, Borrelia vincenti, Bacteroides melaninogenicus, Selenomonas spp. - chlorhexidine is an antiseptic and antimicrobial agent, active against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria
(Treponema spp., Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Trichomonas spp., Chlamydia spp., Ureaplasma spp., Bacteroides fragilis). Some strains of Pseudomonas spp., Proteus spp. are weakly sensitive to the drug, and acid-resistant forms of bacteria and bacterial spores are also resistant. Does not interfere with the functional activity of lactobacilli.
When applied topically, the active substances of Metrogyl Denta® gel are practically not absorbed.
Metrogyl Denta® gel includes a suspension of metronidazole benzoate with propylene glycol. When applied, the gel flows and fills the dental pocket. Upon contact with the aqueous portion of either gingival cavity fluid or saliva, which contains esterases, it hydrolyzes the microbiologically inactive metronidazole benzoate into free metronidazole and benzoic acid. Metronidazole has an aerobicidal effect on bacteria located in the periodontal area. Metronidazole also has anti-inflammatory activity, which targets inflammation associated with periodontal disease.
Chlorhexidine is an antiseptic and disinfectant and has a bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect on a wide range of bacteria.
Metrogyl Denta® is active against aerobic and anaerobic flora present in the oral cavity and, in particular, in the gum pockets.
Systemic metronidazole at doses of 750-1000 mg/day for 2 weeks is known to reduce the growth of anaerobic flora, including spirochetes, and reduce the clinical and histopathological signs of periodontitis. Metronidazole, when used in addition to thorough scaling and root planing, significantly reduces the need for surgery compared with mechanical scaling alone. Topical metronidazole in gel form reaches high concentrations locally around the gum tissue and is therefore very effective. The simultaneous use of topical metronidazole helps to avoid side effects with long-term use of metronidazole in the mouth.
Taking into account the fact that oral infections are mixed in nature and are usually caused by aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, and the disease is chronic, long-term use of oral antibacterial agents can lead to side effects and the risk of developing bacterial multidrug resistance. In such cases, topical treatment containing a combination of antibacterial agents acting on aerobic and anaerobic bacteria simultaneously (metronidazole benzoate 1% and chlorhexidine gluconate 0.25%) is of paramount importance.
Again considering the involvement of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria in periodontal disease, the combination of metronidazole benzoate and chlorhexidine gluconate would have an important therapeutic advantage over chlorhexidine gluconate alone.
Application benefits
Despite the rather low concentration of active substances and the lack of analgesic effect, Metrogyl Denta gel has a number of advantages over more modern drugs used in medicine, for example:
- the drug is perfectly fixed on the mucous membranes;
- has a fairly high efficiency,
- In addition, its affordable cost allows you to regularly use this product for preventive purposes.
The active components of the drug allow you to influence pathogenic microorganisms, but are not able to block mediators of inflammatory processes in tissues, therefore, in the treatment of many diseases, experts recommend combined procedures to achieve a more effective result.
Metrogyl Denta for stomatitis
Stomatitis is a fairly common pathology of the mucous membrane, occurring in both adult patients and children, however, Metrogyl is effective only for bacterial forms of the disease and when diagnosing them, the drug allows for healing.
To heal ulcers, in these cases, applications are recommended, but the drug is absolutely ineffective for stomatitis caused by viruses.
When treating gums, the drug is applied to the affected areas of the mucous membranes, for example, using cotton swabs. The course of treatment for stomatitis lasts for 7-10 days, procedures are carried out 2-3 times a day.
Alviolite therapy involves placing a small amount of gel into the inflamed hole.
When teething through wisdom teeth, it is recommended to use the drug as a toothpaste, applying the product to the inflamed gums. In this case, using a toothbrush with gel, both teeth and gums are treated, but you should refrain from eating and drinking for half an hour so that a protective film is formed that will protect the oral cavity from pathogenic microorganisms.
Features of use
The use of Metrogil Dent gel, especially in the initial stages of treatment, can cause bleeding gums, increased swelling and burning. Such symptoms may appear within a few days, but if they continue, you should stop using the drug.
Despite the fact that no obvious contraindications or side effects have been identified for the drug, Metrogyl is not recommended for use for the treatment of:
- children under 6 years of age;
- women in the first trimester of pregnancy,
- In addition, it is not advisable to use the drug while breastfeeding and, if it is necessary to use it, you will have to stop breastfeeding.
Many experts recommend avoiding drinking alcohol during treatment with Metrogyl gel, since it contains an antibiotic that can be absorbed into the blood, even when applying applications.
In addition, the use of the drug should be discontinued at the first signs of intolerance to the drug.
Studies have shown a negative effect of the drug when taken together with anticoagulants, since the active substances of Metrogyl can enhance their effect, which can cause bleeding.
Experts recommend careful use of the drug, since, for example, swallowing the gel can have serious consequences:
- nausea;
- dizziness,
- which is facilitated by metronidazope, which is part of the product.
Drug interactions Metrogyl vaginal gel
When using Metrogyl vaginal gel topically, the interaction with other drugs is insignificant, however, when administered simultaneously with certain drugs, caution should be exercised: metronidazole enhances the effect of indirect anticoagulants, leading to an increase in prothrombin time; simultaneous use with disulfiram can lead to the development of neurological symptoms, so Metrogyl should not be prescribed to patients who have taken disulfiram over the past 2 weeks; Cimetidine inhibits the metabolism of metronidazole, which may lead to an increase in its concentration in the blood serum and an increased risk of side effects.