Reasons for the appearance of a lump
A tumor can appear for various reasons. If the pain is not severe, temporary, and goes away on its own within a day, there is nothing to worry about. And when the appearance of a growth causes significant discomfort and lasts for several days, you should be alarmed. A growth under the tongue near the frenulum can be caused by the following factors:
- Condylomatosis, that is, papilloma virus. In this situation, the cell growth mechanism is disrupted. The early phases of the disease have no obvious symptoms. The virus is actively transmitted through household and sexual contact, especially with weak immunity. The nature of warts is such that they act selectively. HPV is distinguished by genotypes. There are benign and life-threatening strains. Warts may rise above the muscular organ. Keratin, which is produced in such cells, gives the balls rigidity.
- Inflammation often appears when the frenulum is short from birth. It is better to correct the problem in childhood.
- The process of inflammation appears with vitamin deficiency, gastrointestinal diseases, allergies, abscesses in the oral cavity, and injuries.
- A pimple on the frenulum under the tongue is formed during tonsillitis, when streptococci and staphylococci are activated and the lymph nodes are affected.
- The problem occurs when the salivary duct is blocked. Mineral or mucus plugs can become an obstacle. This interferes with patency. In this situation, a ranula is formed, which contains liquid exudate. The bubble may be clear or cloudy. It can burst, then build up again. Provoking factors include stomatitis, herpes, candidiasis, and lichen planus.
Since the mucous tissues of the oral cavity are sensitive, they can be damaged by hot food or drink. In the burn area, bacterial microflora feels comfortable, which contributes to the formation of salivary plugs in the ducts.
Treatment of ulcers under the tongue
If a parent discovers a sore in the child’s tongue area, he should immediately take him to a dentist for examination. This is the doctor who deals with such diseases. He will conduct an examination and, if necessary, ask the patient to see a doctor of another specialization.
Traumatic ulcer during teething
To make a diagnosis, the doctor must talk with the patient. This will allow us to understand the nature of the lesion in the oral area. A microscopic examination will also be required.
The easiest way to understand how to treat ulcers that appear as a result of mechanical damage. As a rule, they heal fairly quickly if the affected area is provided with suitable care. To quickly get rid of a sore that has formed under the tongue, you must immediately treat it with an antiseptic. Can be used:
- hydrogen peroxide;
- brilliant green;
- propolis spray;
- soda solution.
Propolis spray effectively heals wounds
This antiseptic treatment is usually prescribed for stomatitis. Additionally, vitamin complexes are prescribed.
Individual therapy must be selected for each patient. In addition to treatment with an antiseptic, the attending physician may prescribe:
Painkillers. They contain benzacaine or lidocaine. Ointments and gels based on corticosteroids. Flucinocide is especially in demand. In particularly severe cases, corticosteroid drugs are used. They are necessary for patients who suffer from recurrent aphthous stomatitis.
Squamous cell carcinoma at the bottom of the tongue
If the ulcers were caused by herpes, the patient is prescribed the use of local medications, this may be Acyclovir ointment. Candidal stomatitis cannot be defeated without antifungal drugs, which are used in local and internal treatment.
When stomatitis is accompanied by deterioration in health, namely fever, inflammation of the lymph nodes and exacerbation of a number of diseases, then the patient is immediately sent to the hospital. It is very difficult to cure a patient, especially a child, at home in such a situation.
Tongue herpes in a child is very painful
Which doctor should I contact?
If a lump appears under the tongue on the frenulum, you need to find out what factors provoked its formation. Only a doctor can correctly determine the cause. After all, the ball can be filled with liquid or consist of epithelial cells. The degree of discomfort depends on the size of the formation. When papillomas are soft, the patient may not feel them, but large inflammatory growths interfere and begin to hurt. Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- The mucous tissues of the oral cavity constantly dry out;
- The deficiency of saliva and its composition is clearly expressed;
- The taste sensations have changed a lot;
- Increasing pain appeared;
- Swelling on the face increases;
The affected tissue around the lesion may become red and begin to bleed. First of all, you should consult with your local therapist. To confirm the suspected diagnosis, it is most often necessary to visit a dermatologist, dentist, otolaryngologist, venereologist, or gastroenterologist. If the need arises, the patient is referred to a surgeon or oncologist. During the examination, the doctor collects anamnesis, conducts a thorough examination, and performs laboratory diagnostics and histology. In complex cases with abscesses, patients are referred for ultrasound examination, as well as computed tomography. The pathogen is detected using a cytological analysis of saliva.
Why do ulcers appear under the tongue?
An ulcer under the tongue occurs due to an inflammatory process of an erosive nature. An abscess can be caused by various factors. It is very important to identify the cause that provoked the disease. After all, this is the only way the doctor will be able to prescribe effective treatment to the patient.
The most common causes of mouth ulcers include:
Leukoplakia under the tongue - the spot cannot be removed
Development of stomatitis
It can be of three types, namely candidal, aphthous and herpetic. The second option is more common. This stomatitis is chronic, so it cannot be completely cured. Therefore, from time to time the patient will experience a sore under the tongue and in other parts of the oral cavity.
Mechanical damage to the oral mucosa
This reason is often explained by the appearance of ulcers on the frenulum of the tongue in a child. He may get hurt on cutlery or scratched by candy. Simply biting your tongue is enough to create a wound on it.
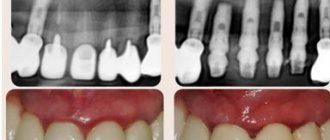
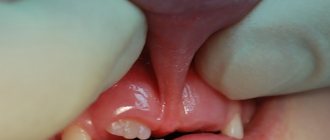
Frenum injury - rupture
Just one microcrack can cause serious inflammation in the mouth. It develops into an abscess due to the active activity of bacteria. Within a few hours, the first symptoms of the disease will begin to appear in a child or adult. If you do not provide first aid to the patient, the infection will spread throughout the entire oral cavity.
Hematoma on the frenulum after trimming
Somatic disease
Often a white sore is one of the symptoms of a dangerous disease that affects the human immune system. These diseases include tuberculosis and HIV. Ulcers will begin to appear due to poor personal hygiene, as well as decreased immunity.
Varicose veins under the tongue with inflammation
To find out why ulcers appeared under the tongue in an adult or child, you need to ask the patient about his health and find out if he was injured several hours before the onset of the inflammatory process.
Treatment and removal methods
The treatment regimen is drawn up depending on what factors caused the anomaly. But treatment is necessary so that the acute stage of the disease does not develop into the chronic phase. If this happens, the exacerbation will recur from time to time. This form of the disease is more difficult to treat. If necessary, laser treatment of gums should be carried out on time. A healthy oral cavity is the key to the overall well-being of the body.
- The doctor selects medications based on the underlying pathology. The initial manifestations of the disease are successfully eliminated with medications and local applications. According to indications, medications are recommended that stimulate saliva production. This may be Galantamine, Pilocarpine, Potassium Iodide. To maintain general condition, the doctor selects means to stimulate the immune system.
- Serious blockage of the salivary glands is eliminated by mechanical cleaning of the ducts. Today, sialoscopy, a minimally invasive procedure for grinding mineral deposits, is widely used.
- Purulent papules are opened, after which the exudate is removed. Surgical technologies such as galvanocaustics, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser beams, and radio waves are used.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity to accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissue includes rinsing with Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, Rotokan, Miramistin.
To prevent pathology, you need to regularly carry out hygiene procedures with a brush and toothpaste. In addition, floss and irrigator should be used. It is necessary to visit the dentist every six months, and other doctors when the initial symptoms of the disease appear.
Classification and photo of stomatitis in the tongue
The classification of stomatitis in the tongue is based on the causes of the development of the pathological process in the oral cavity. The disease is divided into the following types:
- Bacterial. Glossitis develops due to the activation of staphylococcal or streptococcal microflora. A characteristic feature of this form of pathology is its rapid development. Symptoms of the disease appear in the form of small ulcers, which over time turn into ulcers. Stomatitis on the frenulum of the tongue occurs more often precisely because of the activity of bacterial microflora.
- Herpetic. Glossitis occurs due to activation of the herperovirus, which also occurs against the background of weakened immunity. A photo of herpetic stomatitis on the tongue shows the main signs of pathology: small blisters filled with clear liquid. The herpetic form appears in the form of small blisters.
- Candida. The causative agent of the pathology is fungi of the genus Candida. The latter are constantly present in the human body, localized mainly on the mucous membranes. More often, candidal glossitis develops against the background of decreased immunity caused by long-term use of antibacterial drugs or the course of pathologies of internal organs. In adults, stomatitis also occurs due to severe stress.
- Traumatic. The cause of the development of this form of glossitis is considered to be mechanical damage to the tissues of the tongue (bites, poor-quality dentures) and thermal burns.
- Allergic. Occurs when consuming food or due to orthodontic structures, the materials of which caused an allergic reaction in the patient. This form of stomatitis goes away immediately after the influence of the provoking factor is eliminated.
- Ray. Appears due to radiation therapy prescribed for the treatment of cancer. The peculiarity of pathology is the formation of small and large ulcers on the tongue.
- Catarrhal. It is the mildest form of stomatitis in terms of clinical features and duration.
- Ulcerative. Characterized by deep damage to soft tissues. The disease is accompanied by intense pain, which intensifies while talking or eating. Ulcerative stomatitis occurs as a complication of the catarrhal form of pathology.
- Aphthous. It manifests itself in the form of characteristic ulcers (ulcers) with smooth edges that penetrate deeply into the soft tissues. In the affected area, the mucous membrane becomes bright red. The plaque has a white or yellow color. Successful treatment of stomatitis on the tongue in adults is possible if its current form is diagnosed.
Diagnostics
In the early stages, the disease is difficult to detect, since the lump is small and does not show symptoms. A preliminary diagnosis is established based on the patient's complaints and visible signs. The doctor carefully examines the tumor to determine its characteristics.
For confirmation, a histological examination is prescribed. To do this, cells from the tissue of the cone are collected with a special instrument, and then the sample is sent to the laboratory.
In some cases, consultation with other specialists, such as an oncologist, may be necessary.
Possible complications
Typically, glossitis occurs without complications, even if the patient has not undergone treatment for the pathology. However, under certain conditions, stomatitis acquires an ulcerative-necrotic form, characterized by the gradual death of tissues and cells. As this disease progresses, the affected area extends to the jaw bones. As a result, the ulcerative-necrotic form can cause periodontal disease and tooth loss.
If left untreated, chronic glossitis also occurs. It is dangerous because it causes the formation of ulcers in the oral cavity.
To avoid negative consequences, it is important to promptly treat stomatitis on the tongue and eliminate associated pathologies. In order to prevent glossitis, it is necessary to follow the rules of oral hygiene, replace orthodontic structures that injure the mucous membrane, and avoid contact with allergens. At the same time, the immune system should be strengthened.
Additional recommendations
For bacterial stomatitis, antibiotics are used. However, such medications must be used with extreme caution. Antibiotics negatively affect the immune system and digestive organs. Therefore, excessive use of antibacterial drugs leads to increased intensity of glossitis. In addition, antibiotics are not prescribed in cases where stomatitis occurs against the background of viral pathologies.
The allergic form of glossitis is treated with antihistamines:
Antihistamines suppress the intensity of pain and eliminate rashes on the mucous membrane.
Antiviral drugs are used in the treatment of herpetic stomatitis:
In addition to the above-mentioned drugs, medications are prescribed that accelerate tissue regeneration processes:
- "Solcoseryl";
- Shostakovsky balm and others.
In addition to vitamin complexes, immunomodulators are used to strengthen immunity (general and local).
If stomatitis occurs due to severe stress, the doctor prescribes sedatives.