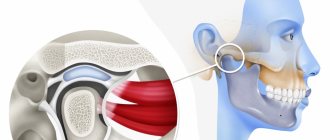
Stiffness in the movements of the lower jaw, pain, cracking and crunching – all these are signs of TMJ pathology, requiring prompt treatment to a dental clinic. Arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint is one of the types of diseases in this category, caused by dystrophic changes developing in the structure of the tissues.
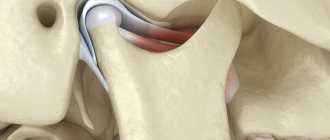
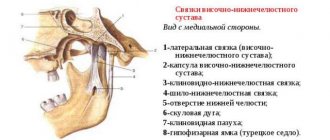
From a medical point of view, arthrosis is a chronic pathology that affects the junction of the mandible and the temporal cranial bone, leading to joint dysfunction. The problem is widespread - according to statistics, signs of the disease are observed in more than half of patients over fifty, and in 90% of patients over seventy years of age. However, the disease also affects representatives of the middle age category, mainly the fair sex. Treatment of arthrosis and restoration of functionality of the temporomandibular joint is a complex process that involves specialists from various fields of medicine, including not only orthodontic dentistry, but also maxillofacial surgery, physiotherapy, rheumatology and traumatology.
Symptoms, causes, classification
Due to the hidden development of the pathology, symptoms are characterized by a gradual increase. In the early stages, the patient does not attach importance to individual changes caused by arthrosis, such as a slight feeling of stiffness, clicking and a slight crunch in the morning. As it progresses, pain occurs associated with mechanical stress on the joint - chewing or speaking. The development of pain from dull to aching indicates the development of synovitis, which increases sensitivity to temperature and time factors.
At later stages, the amplitude of jaw movement is noticeably reduced. Deforming arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint leads to changes in the structure of the head, which manifests itself in the form of a shift towards inflammation and pronounced asymmetry of facial features. Hearing problems, pain in the fundus, migraines and tissue numbness occur.
The list of factors contributing to the development of pathology includes:
- Chronic predisposition;
- Defects in bite formation;
- Partial edentia of the lower dentition;
- Bruxism and vulnerability of the enamel layer;
- Errors in prosthetics and fillings;
- Consequences of operations and injuries of the TMJ.
According to the accepted classification, there are four stages of the disease:
- Initial manifestations are characterized by narrowing of the joint space and instability of the joint;
- Pronounced changes – there are extensive symptoms;
- Late stage – joint dysfunction occurs, cartilage degeneration is diagnosed;
- Advanced stage – fibrous ankylosis develops.
Arthrosis of the TMJ, both in sclerosing and deforming forms, is a good reason for visiting a dental clinic.
Predictions and prevention
Joint arthrosis is a multifactorial disease, that is, it develops against the background of systemic problems and local pathologies. Often tissues are destroyed due to malocclusion, complications of arthritis. At risk are people suffering from bruxism, pathological abrasion of enamel, and with previously incorrectly performed prosthetics. Increase the risk of developing this disease:
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- rheumatism, gout, arthritis of various types;
- vascular diseases, circulatory disorders;
- pathologies of the endocrine glands.
Treatment prognosis is good, but in the chronic form only maintenance therapy is recommended. Preventive measures are also necessary, which include periodic examinations, physiotherapy sessions, massage, and the elimination of bad habits.
About Us
The clinic of orthodontics, gnathology, and aesthetic dentistry MY ORT offers treatment for arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint. We provide our Patients with the following benefits:
- modern methods of therapy and certified materials;
- diagnostics and laboratory research methods;
- treatment control;
- comfortable conditions and individual approach to everyone;
- affordable prices.
You can make an appointment by phone. Leave a request on the website, choose a convenient time to visit, or send your question to our specialists by email [email protected]
Diagnosis and treatment methods
The difficulty of identifying pathology is determined by the anatomical specificity of the joint structure, as well as the polyetiological nature of the disease. It is important not only to identify the presence of arthrosis, but also to determine the cause of its occurrence. Diagnostic methods include:
- Conducting an initial visual inspection;
- Instrumental examinations of the oral cavity;
- X-ray and computed tomography;
- Collection of samples for laboratory research.
The treatment plan is drawn up based on the results obtained during the formation of the clinical picture, and may include drug treatment, physical therapy (including electrophoresis), orthopedic treatment, as well as surgery.
During the treatment period, it is recommended to establish a dietary regimen that reduces the overall load on the jaw joint. As part of dental intervention, the causes that influence the formation of excess jaw pressure are eliminated, including bite defects and dentition anomalies.
How dangerous is the disease?
Often, arthrosis of the jaw in the first stages is asymptomatic, which leads to prolonged inactivity in the treatment of the pathology. However, ignoring the disease is dangerous. If you notice at least one of the symptoms, you should visit a doctor. In advanced forms of pathology, medications, orthopedics and even surgery are used.
The risk group includes persons:
- over 50 years old;
- females who have reached menopause;
- those who have had injuries and surgeries of the jaw;
- with malocclusion, diseases in the jaw area;
- with damaged or missing teeth;
- with chronic inflammatory diseases;
- with arthrosis of other joints;
- whose family members suffer from jaw joint dysfunction.
Should you decide to undergo arthroscopy of the jaw joint?
| The operation is recommended if: | Arthroscopy is not performed in the following cases: |
| The patient has a chronic pathology leading to temporary disability; | Acute pain of a new nature with the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy for several months; |
| Pain interferes with eating; | High probability of deterioration in articular function after arthroscopy; |
| The articulation elements are constantly shifting; | Patient's reluctance to undergo surgery; |
| Significant destruction of the articular surfaces is recorded; | Low probability of successful treatment; |
| The dysfunction developed after a jaw injury and does not respond to therapy; | The possibility of scar tissue growing during the healing process (this will subsequently reduce the range of movements in the joint); |
| There are chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system: osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and others; | Presence of contraindications to the operation. |
| Partial or complete immobilization of the jaw joint is observed. |
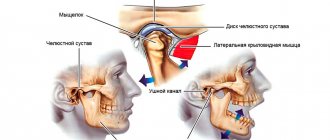
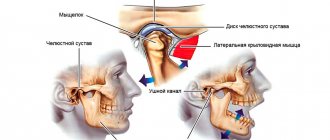
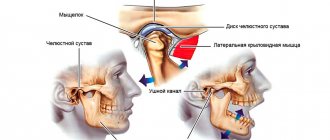
Signs of TMJ pain dysfunction syndrome
In the clinical picture of the disease, 2 periods are distinguished: dysfunction and painful spasm of the masticatory muscles. At the initial stage of the disease, patients complain of joint noise, crunching and clicking in the joint. They are bothered by pain when palpating the masticatory muscles.
The following symptoms are noted:
- deviation of the lower jaw to the side when opening the mouth;
- S-shaped movements of the lower jaw;
- feeling of stuffiness in the ear;
- ringing and noise in the ears;
- hearing loss.
There are no radiological changes in the joint. During the period of painful spasm, a sharp restriction in mouth opening and severe muscle pain of a neuralgic nature suddenly appear in the face and head. In some patients, in the early stages of the disease, periodic exacerbations occur, followed by spontaneous cessation of pain and dysfunction. An exacerbation of the disease often occurs with a sharp overload of the masticatory muscles (opening the mouth wide, chewing solid food) or during an emotional crisis. Over time, the number of muscle trigger zones in spasmed muscles increases. They become sharply painful, the pain begins to radiate to various areas of the head.
Therapeutic measures for diseases of the temporomandibular joint
When an accurate diagnosis of TMJ dysfunction is established, the doctor prescribes a course of therapeutic measures, the features of which are determined by the degree of the pathological process and the etiological factor. The disease requires complex treatment. The most lasting effect in restoring the functions of the maxillofacial apparatus is provided by the following recommendations, methods and means:
- complete exclusion of solid food, which will make it possible to maintain conditional rest for the mandible joint;
- maximum restriction of mobility (no yawning, no talking);
- alternating warm and cold compresses in combination with certain exercises to warm up the joints, which is performed under the supervision of a physiotherapist;
- for pain relief, the doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in a certain dose and at the recommended dosage interval;
- in case of extremely severe pain, it is possible to take narcotic analgesics;
- muscle relaxants are used to eliminate tension in the muscles of the face, neck and shoulder girdle, if any;
- to restore harmony in the patient’s psycho-emotional background, it is possible to take antidepressants in small dosages;
- physiotherapeutic procedures (laser, electrophoresis with novocaine, ultrasound, radio wave therapy, neurostimulation);
- installation of a special design on the teeth (mouthguard, orthopedic splint), which allows you to prevent the closure of the dentition as much as possible, correct the bite and restore the movement of the TMJ joint in the physiologically correct position;
- orthopedic treatment involves the installation of crowns and bridges to align the dentition and ensure comfortable static and dynamic occlusion;
- avoidance of foods that irritate tooth enamel to prevent relapse of exacerbation;
- a slightly open position of the mouth, which is carried out using the tongue located between the front teeth, will ensure relaxation of the masticatory muscles and jaws;
- in some cases, doctors use the injection of analgesic drugs into the muscle tissue of the projection of the pathological joint.
Complex treatment using the listed methods and means, in most cases, gives a positive effect and long-term remission.
Folk remedies
With the permission of a doctor, non-traditional methods of treating arthrosis of the jaw joint can be used. There are both simple and complex traditional medicines to prepare. For example, warming with salt or sand is a great way to cope with pain. They need to be warmed up, poured into a textile bag and applied to the affected jaw for 1.5-2 hours until completely cooled. Another simple recipe is to use raw egg whites. At night, apply it to the entire jaw and the area behind the ears.
Among the more labor-intensive, but also more effective folk remedies, the following can be distinguished:
Drops based on celandine
- Mix crushed and squeezed celandine through cheesecloth with honey in a 1:1 ratio.
- When the honey is completely dissolved, the medicine is ready.
- Place 1 drop in each nostril before bedtime. In the first few days, this treatment may cause discomfort, but over time the effect will be noticeable.
Solution for compresses
- Mix 5 g of the following components: rhizomes of elecampane, burdock and horseradish, leaves and flowers of mint, St. John's wort, lemon balm, celandine, calendula, eucalyptus, plantain, juniper fruits.
- Grind the raw materials and pour in hot corn oil.
- After cooling, the solution is freed from all solid ingredients.
- Add 5 g of bee bread and propolis to the resulting liquid.
- Infuse the medicine in a warm place for about 20 minutes.
- At this time, mix 100 g of gum turpentine with 15-20 g of gum rosin.
- After 20 minutes, mix both solutions.
- Use the resulting mixture as compresses at night.
Development factors
In infectious arthritis, pathogens affect the joint in several ways:
- contact (for otitis, osteomyelitis, furunculosis of the external organs of hearing, etc.);
- direct (infection enters the joint due to puncture of the TMJ, fracture of the movable jaw, injury, etc.);
- hematogenous (for sore throat, tuberculosis, measles, diphtheria and other infectious diseases).
The reactive form of arthritis is observed with chlamydia, rubella, viral hepatitis and other infections. Rheumatoid arthritis can spread to other joints. An acute traumatic form of pathology can develop due to mechanical damage to the joints.
How to treat TMJ arthrosis
If the diagnosis is confirmed, it is necessary to treat TMJ arthrosis under the supervision of a specialist. Physiotherapeutic methods at home will not give the desired result and will not stop degenerative changes in cartilage. Long-term use of painkillers will not help if the problem is not solved radically.
Complex treatment is aimed at stopping the inflammatory process, relieving pain and stopping the destruction of cartilage tissue. If all measures are completed, the functionality of the joint will be restored: the person will be able to talk, eat and smile without pain and discomfort.