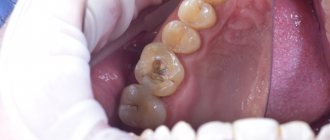
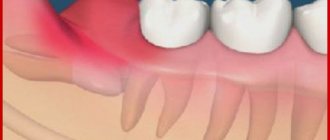
Teeth can hurt for various reasons. Often toothache occurs from cold. The following factors influence dental hypothermia:
- The tooth is affected by caries or an inflammatory process has begun in the deep layers of dental tissue and affected the nerve. If the immune system is weakened, the nerve may become inflamed from the cold.
- Cold causes active activity of pathogenic bacteria.
- Due to hypothermia, pathogenic bacteria begin to multiply intensively in the nasal cavities. The inflammatory process can spread from the nose to the teeth. Cold is a favorable environment for the life of pathogenic microorganisms.
- If inflammation of the trigeminal nerve occurs from hypothermia, it is difficult to distinguish it from dental diseases.
- Herpes, which occurs on the lips from hypothermia, can cause inflammation of the nerve endings of the teeth.
Why do teeth hurt from cold and hot?
The most obvious causes of pain when eating cold and hot foods are:
- Regular exposure of enamel to acids
. Remember, do you eat too many lemons and oranges, do you like sweet carbonated drinks and especially Coca-Cola? - Microscopic enamel injuries
. Tiny cracks are not uncommon among those who like to chew nuts, seeds, caramels, and other hard foods. For the same reason, the habit of biting your nails and clenching your teeth is also dangerous for your teeth. - Abuse of whitening pastes
. They can be used in short courses. It’s better to seek help from professionals - home whitening does not provide a long-lasting effect, but it seriously damages the enamel. - Using a brush that is too hard
. Such a personal hygiene instrument provokes atrophy of the soft tissues of the gums and ultimately leads to exposure of the neck of the tooth. - Development of caries
. Hyperesthesia in this case signals the development of erosion and the appearance of wedge-shaped defects. - Exposure of the neck of the tooth
. There is no enamel at the base of the tooth, so patients with this problem react particularly acutely to cold and hot foods, and even to a flow of cold air when inhaled.
Body problems that, at first glance, are in no way related to dentistry can also deprive you of the pleasure of eating ice cream. These include:
- Endocrine disorders
. Problems with hormones change the acid-base balance in the mouth, which in turn affects the condition of the enamel. - Acute respiratory diseases
. Bacteria and viruses during acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections and influenza can easily provoke hyperesthesia. One thing is good: with recovery, excessive tooth sensitivity also goes away completely. - Bacterial gastritis
. Increased acidity causes heartburn, which in turn increases acidity in the mouth. A too acidic environment inevitably leads to the destruction of enamel and the development of hyperesthesia. - Stress
. When we worry about problems in the family or at work, we unconsciously trigger a complex mechanism, one of the manifestations of which is increased nervous excitability. They respond with excessive sensitivity to global stress and nerve roots in the tooth. - Lack of magnesium, calcium or phosphorus
. Without getting enough of these minerals, tooth enamel begins to break down, nerves become exposed, and sensitivity to the temperature of food and drinks increases. - Toxicosis during pregnancy
. The first trimester is a difficult period during which a woman often develops stomatitis and periodontal disease, and all dental problems, including hyperesthesia, worsen.
Some medications, such as hormonal contraceptives, can also cause problems. As well as constant inhalation of chemicals, which is typical for workers in the food and chemical industries. Situations in which teeth react only to hot or only to cold deserve special attention.
A painful reaction only to hot foods is most often a sign of an exposed nerve. By the time pain appears, the culprit tooth is already practically dead due to lack of tissue nutrition. But decomposition inside the tooth is in full swing with the simultaneous release of methane gas. When eating hot food, methane expands and puts pressure not only on the inflamed nerve, but also on the main one, passing through the entire dentition. Thus, due to the disease of one tooth, hyperesthesia of the entire jaw can develop.
The cause of tooth sensitivity to cold foods, drinks and even air often lies in inflammation of the soft tissues of the tooth - pulpitis. And also in the exposure of the neck: in those areas that react to cold, you can usually easily see the peeling of the gums from the neck of the tooth.
Systemic reasons
- Hormonal imbalances. Often observed with improper use of hormones, pregnancy or menopause;
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals. Products must contain magnesium (Mg), phosphorus (P), calcium (Ca);
- Stress. Depression, psychological fears, and increased anxiety can provoke hyperesthesia;
- Regular contact with chemicals (for example, when performing professional activities in production).
Initially, high sensitivity manifests itself to cold and hot drinks, while the pain lasts no more than 30 seconds. Later (in the absence of professional treatment!) discomfort becomes the norm when eating sweet, spicy and salty foods.
What diseases provoke the development of hyperesthesia?
Did you bite into a cold apple, take a sip of hot coffee, eat some ice cream and feel pain? This means that you have a high sensitivity to hot and cold foods (drinks), which can be caused by certain diseases.
Among them:
- Caries. It leads to exposure of the pulp (the “dental nerve”). Externally, this can be determined by a dark-colored hole located on the tooth enamel. Typically, pulpitis causes acute pain when consuming cold foods (drinks), while such a reaction is not observed with hot dishes;
- Bleaching. The use of whitening pastes with large abrasive particles and unskilled mechanical whitening at the dentist provokes a violation of the sensitivity of tooth enamel. It reacts to cold and high temperatures, sweet and sour;
- Filling. After installing a temporary or permanent filling, tooth sensitivity increases, BUT it usually lasts no more than 2-3 days. No special treatment is required, but if hyperesthesia does not go away after some time, seek qualified dental care;
- Periodontitis. Inflammation of the periodontal tissues, accompanied by bleeding of the mucous membranes, exposure of the necks and roots of the incisors, subsidence of the gums, the formation of large pockets, suppuration, leads to increased sensitivity and the formation of a reaction to hot and cold.
If your teeth are absolutely healthy, but begin to hurt under the influence of irritants, then it is recommended to refrain from sweet, sour and spicy foods. Replenish your diet with healthy foods that help restore tooth enamel (fish, milk, cottage cheese, fresh vegetables, fruits and berries).
Formation of hyperesthesia
The high sensitivity of tooth enamel to external irritating factors develops gradually, going through several stages:
- The first pain signals. Occurs when taking cold or hot food or drinks. The pain is “aching” in nature, there is no pulsation.
- Expanding the list of irritants. It includes sweet, salty and spicy foods. The pain lasts longer and makes eating irritating foods impossible.
- Reaction to all stimuli. Even cold air becomes a factor causing acute throbbing pain. Pain syndrome is a constant concern.
Treatment of hyperesthesia
How to restore normal tooth sensitivity so that eating does not bring pain and suffering, but pleasure? Immediately go to the dentist - no one can solve the problem better than him.
Do not delay contacting a specialist and do not hope that hyperesthesia will go away without treatment. Perhaps the pain will subside and not bother you, but it will arise again - it’s only a matter of time, and it will be much stronger and longer lasting.
The dentist will carefully examine the oral cavity and, if abrasion of tooth enamel, cracks, chips, caries or inflammatory processes is detected, he will make a diagnosis and then prescribe the correct treatment using one of the methods:
- medicinal (medicinal),
- hygienic,
- physiotherapy,
- surgical.
Attention! To test the sensitivity of teeth, a stream of water is directed from the tip onto the enamel, the temperature of which is about 30 oC.
If hyperesthesia is accompanied by caries, periodontitis, pulpitis or other diseases, then they are quickly treated (if possible), and then the normal sensitivity of the tooth enamel is restored. For general therapy, use soft brushes and stop smoking.
TOP 3 toothpastes for hyperesthesia
At home, it is recommended to use special toothpastes to reduce the sensitivity of enamel and restore its sensitivity:
- Sensodyne paste. The active elements are zinc and sodium fluoride, which ensure 100% elimination of bacterial plaque and increase the protective properties of teeth. The result of regular use is a decrease in enamel sensitivity.
- Pasta "Lacalut". Contains active fluoride, which promotes rapid restoration of tooth enamel. Additionally, it provides remineralization of tissues (gums and mucous membranes of the oral cavity).
- Pasta "Silca". The active ingredients are fluorides, urea and potassium citrate. They reduce tooth sensitivity and stop calcium leaching. Additionally, the paste eliminates the negative effects of acids.
TOP-3 gels for hyperesthesia
Special gels will help enhance the therapeutic effect of toothpastes. Their regular use helps reduce the reaction of teeth to temperature changes:
- Gel "ROCS". It contains calcium, phosphorus and magnesium, which create a protective film on the enamel and prevent the negative effects of various irritants. The result of use is a decrease in tooth sensitivity and lightening of the enamel.
- Gel "Emofluor". The content of stannous fluoride ensures the effectiveness of the product against bacteria and bacterial plaque. Providing a cariesostatic effect, the gel reduces the sensitivity of the enamel and prevents the development of periodontitis.
- Gel "Fluoridex". Recommended for use together with regular toothpaste. The active element is sodium fluoride, which strengthens the enamel and reduces the sensitivity of teeth to irritants.
Pain after dental treatment
Sometimes the start for the development of hyperesthesia is a visit to the dentist. The doctors themselves admit: the insufficient level of professionalism is entirely to blame for the development of this situation. Teeth may hurt after:
- hygienic cleaning and polishing;
- whitening procedures;
- installation of a photopolymer filling;
- tooth extension, or rather, due to etching of tissues with acid-containing gels.
In the vast majority of cases, an experienced dentist would be able to avoid the development of hyperesthesia. For example, a whitening service in modern clinics necessarily includes a preventive procedure for protecting the enamel. And the development of tooth sensitivity after filling indicates a gross mistake by the doctor. Possibly during treatment:
- not all inflamed tissue was removed by the dentist;
- a burn of the pulp occurred, and as a result, inflammation developed;
- an air bubble remains in the treated cavity;
- the doctor damaged the integrity of the seal;
- individual intolerance to the composite material made itself felt.
Unfortunately, the pain will not subside over time, but will only intensify. Therefore, if the sensitivity of tooth enamel remains unchanged for 7-10 days, it is better to schedule an examination with the dentist again. If the pain increases, you cannot postpone the visit: you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Diagnosis and treatment
As a rule, it is possible to determine the presence of numbness and find the cause of this ailment already at the stage of conversation with the patient. The dentist must conduct an in-person examination, on the basis of which he may prescribe the following studies: radiographic, tomographic, and Dopplerography of the vessels of the jaw. Unfortunately, without a thorough preliminary diagnosis, making a correct diagnosis and prescribing a treatment regimen is impossible. That is why, if necessary, it is not recommended to refuse to do some tests.
Most often, therapy is limited to the use of certain medications without the need for surgery. Sometimes it is necessary to perform an operation using one of the methods of jaw microsurgery. In both situations, the doctor’s main goal is to relieve the patient of discomfort and return the tissues to their former sensitivity.
It is important to understand that timely seeking help guarantees the fastest possible cure. A disease whose duration exceeds 3 months will be much more difficult to overcome. If numbness persists for a year, then it will be almost impossible to regain sensitivity. After treatment, the following therapeutic procedures may be prescribed: UHF, electrophoresis, laser therapy, exposure to diadynamic currents, etc.
Why does a tooth without a nerve hurt from cold and hot?
It is generally accepted that after the nerve is removed, the tooth will no longer be able to hurt. In fact, the reaction of a dead tooth to temperature is rather normal, and there is no need to worry. Over time, the pain will subside on its own, because most often the cause lies in microtraumas to the enamel of neighboring teeth that were received during treatment.
If after a few days the reaction to hot or cold does not decrease, but intensifies, you should not hesitate! It is likely that the dentist did not completely remove the nerve, and the inflammatory process was not stopped. Such mistakes are extremely rarely made by dentists with extensive experience, but among beginners it is not at all uncommon.
There is no point in blaming the aesculapians: what we are accustomed to calling a nerve is, in fact, a branched system of tiny hairs, spreading in all directions of the tooth. It is sometimes impossible to see all the “tentacles” even on an x-ray. And only with experience comes an intuitive feeling of how the “labyrinth” of nerves is located in a particular patient.
In the practice of Western dentistry, a separate specialty has long been distinguished: an endodontist, a specialist in root canal treatment. In Russia, only large, well-equipped clinics can afford specialists of such a narrow profile.
Symptoms and causes
The scientific name of this pathology is paresthesia. The main symptoms by which one can suspect the onset of the disease are: a burning sensation, the appearance of goosebumps and slight tingling in the soft tissues, numbness of part of the dentition or the entire jaw at once. This condition can be caused by many reasons. It is important to understand that numbness is not always a sign of a developing disease, but it is still worth seeing a doctor.
The main factors that provoke the loss of usual sensitivity: inflammatory processes in the root system, for example, periodontitis, severe injuries to the jaw, problems with the temporomandibular joint and malocclusion, disruption of the work algorithm during installation of implants, poor-quality dental treatment, stress and tension, violation integrity of nerves, etc.
Less common causes today are allergic reactions (to medications used by the dentist or to a sudden change in air temperature) and a significant outflow of blood from the head.
How exactly does pain occur?
To understand the mechanism of pain when eating cold or hot food, it is enough to remember the structure of the tooth. We call the topmost, visible layer enamel. This is the most durable tissue of the human body, which reliably protects the more sensitive tooth tissues from any irritants, including thermal ones.
But if you neglect your health or due to chronic diseases, the enamel becomes thinner, exposing dentin. It, in turn, is permeated through and through with hollow tubules, which begin at the pulp itself. And without a barrier in the form of durable enamel, irritants: cold air, cold and hot drinks easily pass through the tubules of the dentin and begin to directly affect the nerve endings. The patient experiences a sharp attack of pain.
Forms and degrees of hyperesthesia
Most often, hyperesthesia is of a generalized nature, when the entire dentition reacts equally to cold and hot. This form of the disease is associated with a general deterioration in health or with a passion for whitening procedures. But after treatment at the dentist or injury, a localized form of the disease may occur. It captures only one tooth, less often – several.
Hyperesthesia develops gradually:
1st degree
. Often ignored by patients who are in no hurry to pay attention to the reaction of the tooth when it comes into contact with hot and cold. At this stage, brushing your teeth and eating foods with a bright taste does not yet cause discomfort.
II degree
. The irritants in the form of extreme temperatures are accompanied by tastes: sweet, salty, spicy. And the unpleasant, but still painless reaction is replaced by pain when eating.
III degree
. Now, it seems that the teeth react with unbearable pain to literally everything: hot and cold, spicy and sweet, sour and salty. And just the thought of using a toothbrush plunges the patient into horror: touching the teeth hurts even with a finger.
When erosive processes are slowed down, for example, due to the use of high-quality toothpaste or when adjusting the diet, tooth sensitivity can significantly decrease. But as soon as the underlying disease worsens or medications are resumed, hyperesthesia reasserts itself.
How to reduce the likelihood of developing hyperesthesia - preventive measures
High sensitivity is a condition that can be avoided in most cases. To do this you need:
- Brush morning and evening, using a medium-hard brush and high-quality toothpaste.
- Use dental rinses on a regular basis.
- Carry out a home course of enamel remineralization two to three times a year. For this purpose, you should use a special strengthening gel.
- Undergo professional hygiene procedures annually. During this procedure, the upper layers of the crown are cleared of plaque and stone. Due to this, they begin to better absorb beneficial microelements.
- Eat properly. You can’t eat a lot of sweets or drink carbonated drinks.
- Periodically take a complex of vitamins and minerals, selected by your doctor.
If you properly care for your teeth, the risk that they will react sharply to cold, hot, sour, and sweet foods will be minimal. Pay enough attention to the health of your smile and you won’t have to suffer from severe pain.
What can you do to relieve pain?
If the pain is severe and it is impossible to get to the dentist in the next few days, hyperesthesia can be pacified for a short time. The simplest, but, alas, not always effective way is to rinse your mouth with a soda solution: 1 teaspoon of soda per glass of warm water.
Painkillers based on ketoprofen: “Ketonal”, “Flexen” and ibuprofen: “Nurofen”, “MIG” relieve symptoms of hyperesthesia well. They act quickly and allow you to completely forget about pain for 5-6 hours.
Local anesthetics in the form of gels give an even stronger effect: “Cholisal”, “Kamistad”, “Dentinox”. These drugs contain lidocaine, so they begin to act instantly. The effect, however, does not last long - for 2-3 hours, after which you can apply another drop of the product to the surface of the teeth.
Traditional medicine gives its own recipe for pain relief: rinsing the mouth with warm water with the addition of 3-4 drops of clove oil or tea tree oil.
Is it possible to cure sensitivity on your own?
If the process is not too advanced, you can cope with hyperesthesia at home. First, you should review your diet and remove from it all those foods that cause pain: sour fruits and juices, hot drinks and dishes, iced cocktails and soda, sweets and ice cream. This alone can soothe aching teeth for a long time.
To speed up the process, you can purchase special gels and ointments, for example, Fluokal, GS Tooth Mousse, President. Their task is to create a thin film on the surface of the tooth that will protect the enamel from destruction by acids and close the exposed dentin tubules. The dental film Diplen Denta F also showed good results. It is fixed on the teeth for 7-8 hours so that the film has time to saturate the enamel with fluoride.
An excellent folk remedy for tooth sensitivity is tea tree oil. To treat hyperesthesia, 3 drops of it should be diluted in a glass of warm water and rinsed 1-2 times a day. After such rinses, it is important not to eat for 1.5-2 hours.
Self-treatment of tooth sensitivity can be quite effective. But only if the cause of the problem is thinning of the enamel. If the measures taken do not produce any results over the course of several days, and the pain intensifies, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Choosing toothpaste
For increased tooth sensitivity, desensitizing pastes containing a lot of fluorine, potassium and calcium are recommended. In addition, they contain components that fill microcracks in the enamel and restore its structure. Sometimes the composition contains a long-acting anesthetic. Such pastes can simply be spread on the teeth to get a quick pain-relieving effect.
The best on the Russian market are SILCA Complete Sensitive and LACALUT Extra Sensitive, Sensodyne F and Blendamed Pro-Expert. The popularity of these products has played a cruel joke on them - there are a huge number of fakes on store shelves. Therefore, you need to buy medicinal paste only at the pharmacy.
Despite the fact that the use of desensitizing pastes is no different from the use of conventional ones, the former are classified as medicinal. Therefore, you cannot use them constantly, without a break: a course of 4-5 weeks is enough, after which you need to return to regular hygienic toothpaste.
In order for the components of the medicinal paste to bring maximum benefit, you need to brush your teeth with special care, and for at least 3-5 minutes 2 times a day. Brushes for hyperesthesia should be selected with medium hardness. So that they can successfully cope with the removal of food debris, but cannot injure the gums.
15% discount on emergency care for acute pain!
Moscow
Sensitive teeth react to cold: what you need to know
Increased sensitivity of teeth (hyperesthesia, dentin hypersensitivity), especially to cold, is a very common problem. According to Russian researchers, it is observed in 40–70% of our country’s residents aged 20 to 65 years. Fortunately, dental hypersensitivity is easy to get rid of, and today we have many options at our disposal for this. Many find salvation in special toothpastes, but sometimes dentist intervention is required.
Causes of tooth sensitivity
As dentists explain, dental hypersensitivity can be caused by a number of factors. In most cases, the neck of the tooth, the area at the gingival margin, reacts to cold. This is often due to exposure of dentin due to abrasion of the protective layer in the form of enamel and cement. Increased sensitivity can also occur as a result of the formation of a carious cavity, loss of a filling, or exposure of the tooth root due to receding (recessive) gums. Most often, the cause of dental hypersensitivity is the latter factor.
What causes the tooth root
Human teeth are covered with a layer of enamel, which is considered the hardest substance in our body. The enamel protects the crown - the visible part of the tooth located above the gum line, but the root, lacking such a strong coating, may suffer when exposed for one reason or another. The outside of the root is covered with cement, under which there is dentin. The latter is permeated with microscopic tubules, through which the temperature signal from food and drinks is transmitted directly to the nerve cells inside the dental pulp. So, your tooth has suddenly become sensitive to cold. Perhaps there was a loss of enamel or a root was exposed? Dentists cite factors such as:
- Incorrect teeth brushing technique
- Clenching or grinding teeth
- Erosion caused by contact with acids
- Orthodontic treatment
- Tooth injury
- Dental procedures, such as teeth whitening, professional teeth cleaning
- Receding gums due to periodontal disease
Ways to combat hypersensitivity to cold
The choice of strategy depends on the degree of tooth sensitivity and a number of other conditions. Contact your dentist or hygienist to assess the condition of your tooth and suggest the best methods to combat hyperesthesia in your case. Treatment at home or in a clinic may include several elements:
- Professional fluoridation of teeth
- Daily use of toothpaste for sensitive teeth
- Changing your diet
- Placing a crown or filling on a tooth to protect the exposed area
- Gum tissue transplantation to correct recession
- Root canal treatment
Fluoride helps reduce tooth hypersensitivity. These substances are found in a variety of products, from special professional pastes and varnishes used in the clinic to over-the-counter mouth rinses. Fluorides reduce dental hyperesthesia by strengthening enamel and dentin. Their use as part of professional dental products is minimally invasive; it must be combined with proper self-care for the oral cavity, that is, regular and thorough brushing of teeth using toothpaste and a soft-bristled brush. A technology that combines the action of arginine and a calcium source, which instantly and permanently seals open dentinal tubules and creates a protective layer on the surface of exposed dentin, is very effective in combating hypersensitivity. Proper nutrition plays an equally important role, since our regular diet often includes acidic foods and drinks, which can increase tooth sensitivity.
Most ways to combat hyperesthesia involve medical assistance, which consists of restoring the lost tooth structure and providing protection to the exposed root. The dentist will recommend the most effective treatment for you and, if necessary, refer you to the appropriate specialist.
Increased sensitivity of teeth to cold, as well as hot, sour, sweet foods and drinks is an extremely common problem. Because of it, many people are afraid of dental treatment, eat poorly - and suffer in vain, because thanks to new research and modern means, this condition can be alleviated or completely eliminated very quickly. First of all, you should visit a dentist who has all the necessary knowledge, tools and materials to assess the problem and effectively combat it. Reducing or eliminating dental hypersensitivity will benefit your dental health and overall health.
Treatment in the clinic
Advanced cases of hyperesthesia require the intervention of a dental therapist. Its main task is to identify the cause of increased sensitivity. And based on this, solve the problem:
- if sensitivity occurs as a result of caries , the affected tooth is filled;
- in case of severe receding gums , the soft tissues are surgically raised to the proper level;
- if the gums are inflamed , the patient will be offered medication;
- In case of severe tooth wear, an orthodontist consultation is indicated.
The initial stage of hyperesthesia is perfectly treatable with fluoridation. It consists of applying calcium and fluoride salts to damaged teeth. Usually, after 5-7 sessions the patient feels much better, and after 10-15 procedures the hyperesthesia completely subsides.
Unfortunately, if you do not adhere to a gentle diet and do not follow the dentist’s recommendations, enamel sensitivity may return after six months to a year. And the course of treatment will have to be repeated.
Iontophoresis helps enhance the effect of fluoridation. This is a physiotherapeutic method, which consists of introducing therapeutic solutions into tooth tissue using numerous but small discharges of galvanic current.
What complications may arise?
The main thing to remember is that tooth sensitivity does not go away on its own. If you do not fight it, the disease will progress quickly. Unpleasant sensations will soon be replaced by outbreaks of pain when the enamel is irritated by hot and cold drinks. Then you will not be able to eat sweet and sour, salty and spicy. And at the last stage, short-term pain transforms into constant pain, and its intensity will be such that just touching the tooth will seem unbearable.
At the last stage of the disease, fluoridation will no longer help. It will be lucky if the dentist agrees to cover the patient’s own enamel with composite materials. But in most cases, the doctor will insist on the removal of diseased teeth and subsequent prosthetics.
Prevention
Unfortunately, modern dentistry has not come up with any special preventive measures aimed at reducing the risk of dental numbness. This is explained by the fact that the main causes of pathology are usually severe trauma and mechanical damage to the nerve during surgical procedures. However, it is still possible to minimize the risk of the disease; to do this, you should adhere to several rules.
If you need to undergo treatment or install an implant in place of a missing tooth, you need to choose a truly experienced specialist. After surgery, it is very important to give the body time to fully recover, so do not neglect rest. It is also not recommended to stay outside for a long time, especially in severe frost or gusty winds.
Teeth numbness is a rather unpleasant syndrome that can cause a lot of inconvenience to its owner. In most cases, the pathological process requires specialist supervision, as it does not go away on its own. If the problem is not properly addressed, numbness can develop into a more serious dental disease.
previous post
How to overcome your fear of dentists?
next entry
Prevention of tooth sensitivity
The best prevention of hyperesthesia is daily care of tooth enamel:
- Thorough brushing of teeth 2 times a day.
- Periodic use of preventive pastes and complete avoidance of bleaching products containing abrasives.
- Mandatory presence in the diet of foods containing calcium and phosphorus.
- Minimum consumption of sweets.
- The habit of drinking juices and carbonated drinks through a straw.
- Avoiding foods that are too hot or too cold.
And most importantly: if the tooth’s reaction to an irritant occurs abruptly, and the painful sensations do not go away within 3-4 days, contact an experienced dentist. Don't wait for the problem to become rampant.
Author: Elena Grunina Dentist-therapist, endodontist. Work experience more than 9 years.
The information is for reference only. Before treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
How to solve a problem
Firstly, there is no need to aggravate the situation. “Some have the habit of clenching their teeth in the cold, this leads to abrasion of the enamel and increased sensitivity of the teeth,” notes Alexander Akhtanin. - There is no need to do this. Monitor the position of your teeth if you go out for a walk in cold weather, and be sure to dress warmly - if you don’t get cold, the desire to clench your teeth will disappear.”
Secondly, try to breathe outside through your nose and not through your mouth (this way your teeth will not be damaged by temperature changes). Also, you should not drink hot drinks in the cold - this increases tooth sensitivity.
Thirdly, use toothpastes for sensitive teeth. As a rule, they contain fluoride.
Well, in general, reconsider your diet towards a healthier one: reduce the content of sugar and acids in it, add more fresh vegetables.