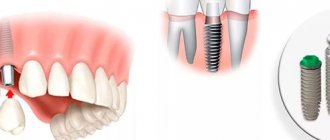
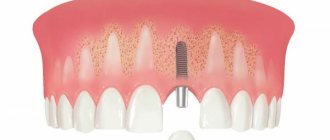
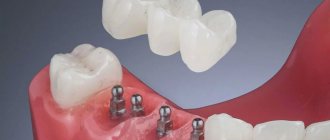
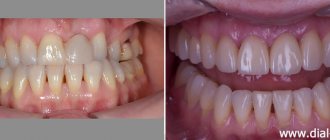
Dental implantation for diabetes mellitus has become possible in modern dental practice. The patient needs to visit an endocrinologist in a timely manner, monitor the amount of glucose in the blood and prevent the disease from moving into an acute stage. However, most of the responsibility lies with the implant surgeon. Qualified professionals at the Implantmaster clinic will select the necessary technique for performing surgery and recovery afterwards.
Many people with diabetes believe that implantation is completely contraindicated for them. However, studies performed in this area have shown the success of implantation of titanium rods. Of course, an important aspect is preparatory measures, supportive therapy, close attention at all stages of the operation by the doctor, and medical equipment. institutions.
In innovative dental implantation for diabetes, it is carried out by qualified doctors who regularly improve their operational skills and knowledge from the best European lecturers. Our doctors master the latest modern implantation techniques. They use specialized diagnostic technologies to place implants, setting loyal prices for services. We solve difficult problems in a short time.
In the article you will learn about the peculiarities of the effect of diabetes mellitus on dental units and the installation of implants. We will tell you in detail about the stages of surgical intervention, indications and limitations for the procedure. We will introduce you to the cost of manipulations and restoration measures.
Get a consultation
We will answer all your questions before visiting the clinic!
+7
Online registration
Content
1 The impact of diabetes on dental health
2 Is it possible to get implants for type 1 and type 2 diabetes? 2.1 Contraindications to implantation in diabetes
2.2 Indications for installation of implants for diabetes
3 Stages of dental implantation for diabetes
4 Conditions for successful implantation for diabetes at the Implantmaster clinic
5 Rehabilitation after dental implantation for diabetes
6 Cost of dental implantation for diabetes
7 Alternatives to implantation for diabetes
How the disease affects teeth - dangers
Systemic metabolic failure, which is what diabetes mellitus is, in addition to its destructive effect on the entire body, also affects the health of teeth, soft and bone tissue. That is, dangers can arise not only during implantation (complex surgical intervention), but even on previously healthy teeth. The disease affects the following processes:
%akc54%
- mineral metabolism and absorption of calcium: their disruption leads to fragility and thinning of the enamel and the subsequent development of caries,
- change in the chemical composition of saliva: “sweet” and viscous saliva does not perform the function of cleansing teeth from bacteria, but itself serves as a medium for their development,
- blood circulation in the gums: due to vascular pathologies caused by excess glucose, blood flow is disrupted, gum nutrition is significantly deteriorated, which leads to tissue inflammation and the development of periodontitis,
- blood clotting and weakened immunity: gum inflammation in diabetics is often accompanied by candidiasis and the appearance of sores in the mouth. Poor clotting interferes with healing, and weak immunity does not fight infections that arise.
In Russia, according to WHO, the prevalence of the disease is about 10%. The connection between diabetes mellitus and the development of periodontitis as its complications has been proven. Patients with diabetes are 2 times more likely to experience periodontitis than those who do not suffer from it[1].
All this significantly increases the likelihood of complications after implant installation, and also increases the risk of rejection of structures and the development of infectious diseases.
Read more about the reasons for implant rejection and the development of peri-implantitis on our website in the “Complications during implantation” section.
The impact of diabetes on dental health
“Are implants used for diabetes?” - This is a question asked by all patients with this disease. The answer is “YES,” but the patient needs to monitor the development of the pathology, and the doctor needs to monitor the preparation, performance of the operation and recovery.
When the glucose level in the blood increases, its negative effect on the body increases - conditions are created for the occurrence of certain pathological conditions of the oral cavity:
- Hyposalivation (little salivation). Dry mucous membranes and insufficient formation of pellicle (protective film) lead to the destruction of enamel and the development of caries.
- When the values are too high, acetone is released, which increases the disturbance of mineral metabolism in the enamel.
- Inflammatory processes in gingival tissue. The tooth's hard tissue structures, ligamentous apparatus (mobility), and bone tissue are destroyed. Wound healing takes a long time, and with the addition of infection, pus forms.
- Fungal infections (Candidiasis). As the fungus spreads, everything in the mouth and nasopharynx becomes covered with a film (whitish coating).
- Accumulation of bacteria. Generalized (multiple) caries develops.
- Regeneration failed. Wounds heal slowly, ulcers and pockets of chronic infection form.
Postoperative period
In order to minimize the risk of developing infection in the postoperative period, it is especially important for patients with diabetes to follow the rules of oral hygiene: brush your teeth twice a day, use dental floss, and rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution. You must follow and cooperate with your dentist's instructions. This will increase your chances of success!
For diabetic patients with complete absence of teeth on one or two jaws, All-on-four implantation is recommended. This is the least traumatic method of implantation, which means healing will be faster. In addition, when choosing an all-on-4 implant, bone grafting is usually not required, which reduces the number of surgical interventions and the overall time spent on restoring the dentition. Read more.
Is it possible to get implants for type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Diabetes is a pathological condition that arises due to disruption of the endocrine system and is associated with a lack of insulin. This hormone is responsible for the processing of glucose: if the pancreas does not produce a sufficient amount of insulin, or it is not properly perceived by the cells of the body, then the amount of glucose in the blood increases.
Dental implantation for diabetes mellitus is directly dependent on the type and stage of the pathology. Diabetes has a negative impact on oral structures and the healing of dental implants.
- Diabetes mellitus type 1 (insulin dependent). In most clinical cases, it occurs at a young age due to viral diseases and heredity. With this type of pathology, the pancreas does not produce insulin at all or not enough. The disease is a complicated type, so dental implantation is not performed for type 1 diabetes.
- Diabetes mellitus type 2 (non-insulin dependent). An acquired disease that develops in adults due to poor nutrition and an unhealthy lifestyle. The cellular apparatus does not perceive insulin, which leads to an increase in sugar levels. Therapy consists of normalizing nutrition and taking glucose-lowering medications. In the advanced stage, type II can turn into type I, and the patient can become insulin dependent. Dental implantation for type 2 diabetes mellitus is performed without controlling the disease with hormonal drugs. Favorable materials used for dental implants for type 2 diabetes are 100% titanium or an alloy that does not interact with organic structures.
Contraindications to implantation in diabetes
Dental implantation cannot be performed if you have diabetes mellitus if the following conditions exist:
- Dental implants cannot be installed if you have type 1 diabetes;
- the patient was diagnosed with a decompensated form of the pathology (disorder of fat metabolism, causing an increase in glucose);
- there are blood and cardiovascular diseases;
- there is no regular monitoring and consultation with an endocrinologist;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages and smoking.
Indications for implant placement in diabetes
Conditions under which implants can be placed for diabetes:
- Dental implantation can be performed for type 2 diabetes mellitus (without taking hormonal medications);
- the presence of a compensated form (glucose 7–9 mol/l before and after surgery);
- the patient receives the necessary medicinal hypoglycemic support and follows a low-carbohydrate diet;
- healing proceeds normally (damage to soft tissue structures does not lead to complications);
- bad habits are excluded;
- there are no concomitant pathologies of the blood, endocrine and cardiovascular systems;
- The patient is registered with an endocrinologist and visits him regularly.
In what cases is implantation impossible?
The operation is not performed in the decompensated (uncompensated) stage of the disease or insulin-dependent diabetes, since in this case it is impossible to maintain the required level of health.
Installation of implants is prohibited if the medical history additionally includes:
- tuberculosis;
- bleeding disorders, blood diseases;
- mental disorders;
- arthritis or rheumatism;
- severe pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- oncology;
- low level of immunity;
- bruxism, pathological bite;
- chronic alcoholism;
- active smoking with the inability to give up cigarettes for a long time.
Temporary restrictions include acute infections, exacerbation of chronic diseases, dental diseases and a number of other pathologies that can be eliminated.
Stages of dental implantation for diabetes
In order for the result of implantation surgery for type 2 diabetes to be successful, it is necessary to make some modifications to the manipulations and the procedure itself. The main changes concern the timing of wound healing, engraftment of the titanium rod and permanent prosthetics. A patient undergoing dental implantation for type 2 diabetes usually requires more visits to the dentist.
Diagnostic measures
At this stage, according to the standards, a CT scan of the jaws is performed and a general blood test is taken. In patients with diabetes, the number of examinations is increased.
At the consultation appointment, the dentist will collect important information:
- taking an anamnesis;
- formation of a complete picture of the disease;
- patient monitoring of blood sugar levels;
- whether any surgical intervention has been performed previously;
- undergoing tissue regeneration.
Important additional factors when deciding whether to undergo implantation will be the form and duration of diabetes. It has been proven that patients with type II diabetes and only recently developed pathology tolerate the intervention better.
In the Implantmaster clinic, in order to avoid such complications, a number of preparatory measures are carried out. CBCT is performed, which produces more accurate images and less Rg radiation. Also, we have the opportunity to use the 3Shape trios scanner. 3D modeling of implantation and new smile is performed. The patient can see the future result. Our appointment is led by a neuromuscular dentist. Using specialized equipment, the tone of the chewing muscles is revealed, and when they relax, the true relationship of the jaws is determined. If necessary, it is possible to change the bite with temporary plastic structures and adapt to the natural muscle tone. On the recommendation of the attending physician, in order to achieve an optimal result, it may be necessary to perform preparatory treatment measures.
Preparation
During this period, an important goal will be to stabilize blood sugar levels with medications or diet. Also, to minimize the risk of infection during or after implantation, infectious foci are treated:
- treatment of ENT organs;
- complete sanitation of the oral cavity;
- performing sinus lift or osteoplasty (if necessary);
- atraumatic removal (in the presence of destroyed units and remaining roots), reducing the occurrence of complications and pain in postoperative rehabilitation;
- prophylactic use of antibiotics.
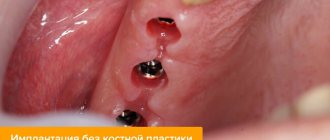
Installation of implants
Depending on the clinical situation, a specialist can install 1-6 implants during one surgical intervention. Also, it is possible to perform removal at the same time, and then install the implant. There are two types of surgical intervention: stage 1 or stage 2.
The placement of the implant is performed by a maxillofacial surgeon under the control of a navigational surgical template. With a large number of implants, the template helps to maintain the location of the artificial roots in the jawbone. Our specialists use the latest techniques and technologies. Premium class implants - Straumann, osseointegration of which takes about a month, and installation is possible even with low bone level. The best budget option is the Dentium implant system (Korea).
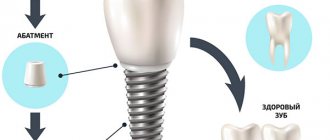
Prosthetics
With a one-stage operation, after a couple of days it is possible to install a temporary plate prosthesis. With a two-stage procedure, prosthetics are performed after 2–3 months, depending on the degree of healing and the jaw.
Zirconium dioxide crowns are used on all groups of teeth, and e.max are the most aesthetic and are used only on the anterior group of teeth from canine to canine.
Possible risks
In patients with diabetes, metabolic processes are disrupted, hormonal levels are unstable, injured tissues regenerate slowly, and blood supply to blood vessels is difficult. These factors explain the increased risk of complications after implantation. Possible consequences include:
- allergic reaction;
- complicated engraftment;
- implant rejection.
The risk of complications increases as the diabetic’s experience increases—the longer the patient is sick, the higher the risk of implant therapy.
Conditions for successful implantation for diabetes at the Implantmaster clinic
- Maintain complete oral hygiene for the entire period of preparation, implantation and recovery. The oral cavity must be clean to prevent the occurrence of infectious processes.
- In diabetes, surgery should be atraumatic due to complicated healing. Single-stage implantation is considered the least invasive, but it is not always possible to immediately carry out an orthopedic load. With the standard two-stage technique, the use of laser and other technologies may be necessary.
- Engraftment of artificial roots takes a longer time: six months in the lower jaw and up to 9 months. on the upper jaw. In the upper jaw, the healing of implants with diabetes is more difficult.
- Strict requirements for materials and implants must be met. Medium implants (10–12 mm) made of pure titanium or specialized alloys are installed. Prosthetic structures must be bioinert, and crowns without a metal base.
Features of the procedure
Preparation
To ensure a successful operation and minimize the risk of complications, the patient should undergo preparatory measures:
- take a urine, saliva, blood test (including sugar levels), visit a therapist and endocrinologist;
- undergo oral sanitation at the dentist, intensify tooth brushing several weeks before surgery;
- undergo diagnostics of the condition of the jaw bone.
What methods can be used
Implantation in diabetics is carried out extremely carefully, with minimal tissue trauma, so that healing takes place without complications. The operation can be performed using one of the following methods:
- Simultaneous with immediate loading
The implant is implanted in place of the newly removed unit. The tissues are not re-injured, healing occurs naturally. A temporary prosthesis with immediate loading is installed immediately, a permanent one - as soon as the implants take root. - One-stage (express implantation)
The implant is implanted in place of the missing tooth when the socket is healed. A rod with a special thread is screwed into the puncture in the gum. The implants have good primary stability. A temporary prosthesis can be installed immediately. - Classic
The prosthesis is fixed after completion of the implant healing stage. The rod fuses with the tissue in an unloaded state; it is covered with a gingival flap. Classical implantation is rarely performed for diabetics: a prolonged process increases the risk of complications.
Osseointegration of a titanium pin with bone in diabetes mellitus is a slow process and lasts at least six months. The probability of successful implantation in the lower jaw is higher than in the upper jaw.
Requirements for implants and prostheses
Patients with diabetes are recommended to have titanium implants without impurities or products made from specially manufactured alloys. The average length of the pins is 10-12 mm.
Prostheses for diabetics - designs with crowns made of an alloy of chromium with nickel or cobalt, metal-free zirconium crowns. When selecting a denture, it is important to achieve uniform distribution of the chewing load.
Rehabilitation after dental implantation for diabetes
The successful result of implantation in the postoperative period very much depends on the actions of the patient. Certain recommendations must be followed:
- take prescribed antibiotics 10–12 days after the intervention;
- control blood glucose levels;
- maintain ideal oral hygiene;
- Visit your doctor every 2-3 days a month. When the implant is implanted, you can go to the dentist once a month;
- give up bad habits.
Memo to the patient after surgery
For diabetics, a more strict approach to the postoperative period. Antibiotic intake is increased to a week or more (depending on the patient’s condition), rinsing with chlorhexidine and other antiseptics is done more often and for longer. It is necessary to keep the injured area clean, so brushing your teeth, using mouthwash, diet, and relative rest in this case are not just words, but a factor influencing the success of the operation.
The purchase of an irrigator will be justified by the cleanliness and health of the oral cavity after its use.
Cost of dental implantation for diabetes
The price of implantation for diabetes mellitus is almost the same as standard intervention. But additional consideration should be taken into account. expenses for a full examination, sanitation of the oral cavity, medications.
| Implant Straumann SLA (Switzerland) | -15% 50 000 42 500 ₽ |
| Implant Straumann SLActive (Switzerland) | -15% 55 000 46 750 ₽ |
| Implant Astra tech (Sweden) | -15% 55 000 46 750 ₽ |
| Implant Nobel Biocare (Sweden) | -15% 55 000 46 750 ₽ |
| Anthogyr implant (France) | -15% 40 000 34 000 ₽ |
| Dentium implant (South Korea) | -15% 35 000 29 750 ₽ |
INSTALLING THE GINGIVAL FORMER
| -100% 5 000 0 ₽ |
| Complete list of prices for dental implants » |
To find out exactly about the possibility of implantation with diabetes in your clinical case, as well as about preparatory measures, you need to make an appointment with an Implantmaster specialist.
What implants are used and requirements for systems
Patients with diabetes are at high risk of developing allergic reactions, so it is recommended to choose only high-quality implants made of pure titanium without added impurities. Titanium is a biocompatible material that is completely accepted by the body.
In addition, implants with a special ultra-hydrophilic surface are used. Its properties ensure accelerated implant healing and tissue rehabilitation. An additional layer of phosphorus on the surface activates the growth of tissue surrounding the implant. Among the manufacturers of such structures are Nobel Biocare and Straumann.
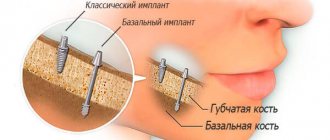
Also, in case of diabetes mellitus, additional operations to build up bone tissue in case of its atrophy are undesirable, since the result in this case is difficult to predict. To solve this problem, elongated structures are used for basal implantation, which are fixed in dense parts of the bone that are not subject to atrophy. This allows you to completely abandon bone grafting and perform the operation quickly, bypassing the stage of bone grafting.
After implantation, the patient must be monitored by an endocrinologist during the entire period of implantation. Also, his support and consultation will be required before the operation.
DENTAL PROSTHESIS WITH 4 OSSTEM IMPLANTS - RUB 170,000!
Implantation even with bone tissue atrophy. Work guarantee! Save RUR 20,000.
on promotion >> Free consultation with an implantologist +7 (495) 215-52-31 or write to us
Alternatives to implantation for diabetes
If implantation for a patient with diabetes cannot be performed, one of the following types of prosthetics may be a justified alternative:
1. Removable prosthetics. Complete removable dentures made of hypoallergenic materials (nylon or acrylic) are used even for uncompensated diabetes. The disadvantage is the uneven distribution of the chewing load, which causes bone loss.
2. Fixed prosthetics. Bridge-like structures that are conveniently fixed and evenly distribute the load. For installation, there must be healthy support units in the jaw. Material: ceramics or zirconium dioxide.
Author:
Requirements and conditions for dental restoration
There are special requirements for patients with diabetes both at the preparation stage and in the post-implantation period. Let's look at these conditions in more detail:
- A glucose level of up to 7 mmol/l (sometimes up to 9 mmol/l) is a mandatory and most important condition for a diabetic.
- Maintenance therapy for diabetes (possibly additional therapeutic measures to stabilize sugar levels during dental treatment).
- Regular monitoring by an implantologist, endocrinologist and therapist (if necessary).
- Strict adherence to all recommendations for oral care after installation of implants. Hygiene should be given special attention, since diabetics have a high likelihood of developing infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
- Balanced diet, optimal level of physical activity and avoidance of stress.
Rules for oral care during the rehabilitation period
If a patient with diabetes mellitus follows simple rules for oral care after implantation, then the risk of complications now and in the future is virtually eliminated. Proper care includes the following:
- immediately after surgery and during the first 3-5 days, only oral baths are allowed; you cannot use a brush due to the risk of damage to sutures and injured tissues: after each meal, you need to put a little clean warm water or an antiseptic solution prescribed by your dentist into your mouth, and hold the liquid for about a minute,
- regular use of brushes and pastes, starting from 3-5 days after implantation: you will have to carefully brush not only the remaining teeth, but also the denture. There are special pastes for this. You can alternate pastes labeled “for dentures” and “for diabetes.” It is better to buy a new brush, of medium hardness and with a large number of bristles. This tool will have to be changed every 2-3 months, because... plaque and microbes accumulate in the pile,
- use of an irrigator after 2 weeks and thereafter: this device, using a narrowly directed stream of water, perfectly rinses the interdental and subprosthetic space, and also removes plaque from teeth and dentures.
It is important to take all medications prescribed by the implantologist during the rehabilitation period. Moreover, it is better to take this list BEFORE the operation and agree with the endocrinologist. Of course, you need to control your glucose levels, eat properly and nutritiously, and take medications for the underlying disease. Every 6-12 months you should visit the dental clinic for a professional examination and cleaning of dentures.
[1] Grossi SG, Zambon JJ Assessment of risk for periodontal disease. Risk indicators for attachment loss // J Periodontol, 1994.
[2] Matyuta M.A. [and others] Dental implantation for type II diabetes mellitus / International Student Scientific Bulletin. – 2016.
Author: Namdakov N.V. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)
Features of implant healing and how to reduce the risk of complications
If patients have controlled diabetes mellitus, the survival rate of implants remains the same as in standard situations – at the level of 96–99%. However, there are points that need to be paid close attention to, both by the patient and the doctor. Increased risk of rejection in diabetics is possible during two transition periods - in the first weeks of engraftment and at the time when the prosthesis is installed on the implants. With one-stage implantation, the prosthesis is installed, as a rule, already on the 3rd day. And the most critical stage occurs in the first weeks and months of implant healing. That is, in the compensated stage of diabetes, implants take root as standard and can last a long time.
Careful preparation and a competent choice of methods in each specific situation are important for a successful outcome. Concomitant body problems that arise with diabetes mellitus automatically place patients at risk. Therefore, in this situation, you need to understand that there are unfavorable factors for such patients, but they can be minimized.