Author:
- Elena Vitalievna Naumova, otolaryngologist, leading doctor of the clinic
2.81 (Votes: 16)
If the temperature exceeds 38°C, the lymph nodes are inflamed, white plaque has spread to the tonsils, the back wall of the pharynx, then antimicrobial therapy cannot be avoided. To prevent purulent tonsillitis from developing into a chronic process, taking antibacterial drugs is mandatory. Medicines suppress the growth of bacteria, prevent infection of family members, and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Only an ENT doctor can figure out which antibiotic is effective and safe for purulent sore throat.
Main groups of drugs
Sore throat is provoked by different types of opportunistic microorganisms and treatment depends on the specific causative agent of the disease. First of all, the ENT doctor will give a referral for a blood test and bacterial culture from the tonsils to detect antibiotic resistance.
Most often, purulent tonsillitis is treated with systemic antibiotics:
- Penicillin series. They have fewer contraindications, so they are often prescribed to children and adults with intolerance to other groups of antibiotics. Penicillins are effective only at the initial stage, when ulcers have not formed. It is worth noting that they are not prescribed if the patient has a history of bronchial asthma or urticaria. During pregnancy, they are prescribed only when absolutely necessary in the early stages.
- Cephalosporins. They are beneficial in severe cases of the disease. They are low toxic and effective from the first day of use. Can be prescribed to pregnant women.
- Macrolides. Prescribed if there is no effect from taking medications of the first two groups. Macrolides have an extended list of contraindications and are taken in a short course. It is worth noting that they are prohibited during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Lincosamides. Used for frequent exacerbations of purulent tonsillitis.
General therapy should be comprehensive, i.e. It is possible to speed up recovery and remove the pathogen with oral antibiotics and local treatment. Local antibiotics for purulent sore throat are prescribed to young children and pregnant women.
Sore throat - symptoms and treatment
The incubation period is up to 2 days. The beginning is acute.
Syndromes:
- general infectious intoxication;
- tonsillitis (acute, purulent);
- anglemaxillary lymphadenitis.
Fever, chills and general fatigue
The first signs of a sore throat are an increase in body temperature to 38-40°C, chills, weakness and sweating. Fever of a constant type. Heart rate corresponds to body temperature. The skin of the face is hyperemic, the eyes are shiny.
Headaches and muscle aches
With a sore throat, a headache appears (dull, without clear localization) and severe aches in the muscles and joints.
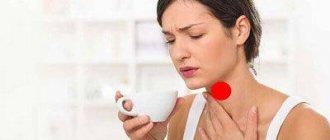
Sore throat
On the first day of the disease, sore throat appears when swallowing, then becomes a permanent manifestation and can radiate to the ear.
Enlarged and painful lymph nodes
The maxillary lymph nodes enlarge, become very painful, have a dense elastic consistency, and are not fused to each other and the surrounding tissues.
The data obtained during pharyngoscopy are very characteristic:
- mouth opening is free;
- the palatine arches, uvula, tonsils and soft palate are clearly hyperemic in the first days.
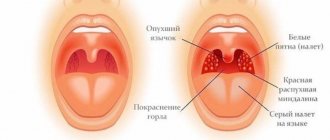
Main manifestations of tonsillitis
Enlargement and redness of the tonsils. The tonsils are swollen, red (“juicy”), which corresponds to catarrhal tonsillitis. Usually this stage of the disease is not recognized (they do not have time) and bright visualization occurs on the second day of the disease, when white follicles 2-3 mm in size form in the tonsil tissue, rising above the surface of the tonsil tissue - follicular tonsillitis develops.
From the third day, a yellow-white discharge (pus) appears in the lacunae - follicular-lacunar tonsillitis.
What does a throat look like with a sore throat?
Further, in severe forms, necrotizing tonsillitis occurs: the tonsils are dark gray in color, after the purulent-necrotic masses are rejected, tissue defects remain.
It must be remembered that purulent plaque in case of tonsillitis does not spread beyond the tonsils, is easily removed, and does not sink in water - the appearance of any other variants of the course is a reason to doubt the diagnosis.[2][3][5][6]
Phlegmonous tonsillitis
Phlegmonous tonsillitis is the most severe form of tonsillitis. It is characterized by the development in the tonsil tissue, often of a unilateral purulent focus without clear boundaries. Intoxication sharply increases, severe pain on the affected side and swelling occurs, and it becomes difficult to open the mouth. The disease requires urgent surgical treatment.
Ulcerative-membranous form of tonsillitis
With the ulcerative-membranous form of tonsillitis, ulcerations occur on the surface of the tonsil tissue, severe pain and plaque, which is easily removed with a spatula.
How does viral and herpes sore throat occur?
“Viral sore throats” have nothing to do with classic streptococcal sore throat. They are only separate syndromes for viral diseases: adenovirus, cytomegalovirus and enterovirus (herpangina) infections and many others. The term “tonsillitis” applies only to diseases caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. All other inflammations of the tonsil tissue should be called acute or chronic tonsillitis.
For this reason, it is incorrect to distinguish herpetic sore throat, sore throat due to diphtheria , influenza , scarlet fever and infectious mononucleosis .
How does angina occur in children?
In children, the symptoms of sore throat are more pronounced than in adults. Intoxication is more severe, the child is lethargic, refuses to eat, possible abdominal pain, severe headaches, nausea and vomiting.
What symptoms of sore throat should you sound the alarm about?
When to see a doctor:
- when the temperature rises above 37.5 °C;
- severe and painful sore throat;
- severe intoxication;
- soreness of the mandibular lymph nodes.
Reception features
Each antibacterial drug is taken differently. The dosage, regimen, and duration of therapy are selected by the ENT doctor individually for each patient. Penicillins are usually eliminated from the body quickly, so treatment with drugs of this group involves frequent taking of tablets. Cephalosporins in tablet form are taken every 6-12 hours.
Uncontrolled use of antibiotics entails a decrease in the sensitivity of bacteria to the drug and a lack of treatment effect, and subsequently to the development of persistent resistance of the patient's microflora to antibacterial drugs.
Antimicrobial agents are taken one hour before meals or two hours after meals. Thus, the absorption of the active substance is higher.
How to treat purulent sore throat
The list of therapeutic measures is as follows:
- gargling with antiseptic solutions to flush out pathogenic microorganisms. For this purpose, furatsilin, hydrogen peroxide, chamomile and calendula decoctions, and rotokan are used.
- antibiotics of the cephalosporin and macrolide groups kill pathogenic flora. They are prescribed by the doctor individually according to the scheme.
- symptomatic therapy is aimed at alleviating the general condition of the patient. These include antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, antihistamines, and vitamins.
Release form
Depending on the stage of development of the disease, the ENT doctor prescribes different types of antibiotics:
- Tablets and syrups. Used as the disease progresses. Usually the drug effect is noticeable 2-4 days after the start of administration.
- Local medications (sprays, lozenges). They are used as an addition to the main therapy, since they only relieve acute pain when swallowing saliva, and do not kill completely pathogenic bacteria.
- Injections for intramuscular and intravenous administration are prescribed for advanced stages of angina, when the patient cannot swallow a tablet. Basically, antibiotics of the bicillin group are used as active substances once. The effectiveness of injections is much higher, since the active substance is evenly distributed throughout the tissues. A high concentration of the drug lasts longer, so the result is visible faster.
Important to remember! The earlier the diagnosis is made and rational therapy for acute purulent tonsillitis is prescribed, the greater the chances of curing the disease without developing serious complications. At the first manifestations of purulent tonsillitis, do not waste precious time self-medicating, consult a doctor! This will save you and your loved ones from serious consequences!
Sore throat: main complications
Everyone has probably encountered tonsillitis, or, as it is also called, acute tonsillitis. Some heard about the disease from a friend, while others themselves felt the characteristic symptoms - high fever with chills, severe weakness and a sharp pain in the throat when swallowing. What is a sore throat and why is it so dangerous?
Angina and its treatment
Acute tonsillitis is an infectious disease that can be caused by various types of pathological microorganisms, but most often the causative agent of sore throat is beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
Once upon a time, sore throat was considered a fairly serious disease, which in some cases could even lead to death, but the situation has changed radically since the discovery of antibiotics. Nowadays, sore throat responds well to treatment with antibacterial drugs, provided that the medicine is correctly selected and the treatment regimen is followed.
Treatment for sore throat
The patient is hospitalized in the infectious diseases department only in complicated cases. Most often, angina can be treated on an outpatient basis. The treatment method consists not only in eliminating the general symptoms of angina, but also in influencing the causative agent of the disease. The patient is prescribed:
- Regular gargling with saline solution or special antibacterial agents. During treatment, the deep parts of the pharynx should be affected, so when rinsing, it is recommended to tilt your head back.
- Local preparations with antibacterial and analgesic effects: tablets, sprays, lozenges.
- Treatment with antipyretic drugs if necessary.
- Antibiotics, which are prescribed only after evaluating the results of laboratory tests of blood and smears. Antibacterial drugs may have varying degrees of sensitivity to a specific group of pathogenic microorganisms. When treating a bacterial infection, antibiotics of the penicillin group, macrolides or cephalosporins can be prescribed.
During treatment of angina, the patient should be kept in bed. It is recommended to eat gentle foods that do not irritate the throat, mainly vegetable and dairy products. Due to the high prevalence of sore throat, a sick person should use separate personal hygiene products and utensils, and limit contact with others.
It should be remembered that at the first signs of the disease you should consult a doctor. Ignoring the symptoms of sore throat or poorly treated disease can provoke complications and also contribute to the development of a chronic latent form, which will enter the acute phase when the immune system is weakened.
Preventive measures consist of increasing the body's defenses by taking vitamin complexes and a balanced diet, daily walks in the fresh air, eliminating irritating factors, quickly responding to characteristic symptoms, and limiting contact with infected people.
Symptoms of the disease
Depending on the form of the disease, the type of pathogen and the degree of angina, the general clinical symptoms will differ:
- Catarrhal. With this form of sore throat, the infection spreads to the mucous membrane of the tonsils. The main symptoms are: sore throat, which reaches maximum strength during swallowing, redness and swelling of the tonsils. Against the background of the inflammatory process, an increase in temperature is observed.
- Follicular. With angina, not only the mucous membrane is affected, but also the lymphoid follicles. The primary symptom is a sore throat, which begins acutely and is accompanied by a sharp rise in temperature to high levels. A person feels weakness, aches in muscles and joints, and headaches. On the tonsils, festering follicles measuring 1–3 mm appear, which open on the second to fourth day.
- Lacunar tonsillitis, which is characterized by a deep degree of damage to the tonsils, accompanied by the accumulation of pus in the lacunae. The tonsils become bright red, with a yellow-white coating clearly visible on them. Sore throat is accompanied by general intoxication of the body.
- Necrotizing tonsillitis is quite rare and is characterized by the presence of necrotic areas.
The onset of symptoms begins after the end of the incubation period. Against the background of elevated temperature, febrile convulsions may occur - severe tension in the muscles, followed by shuddering and twitching.