Author: Brodsky Sergey Evgenievich Deputy Chief Physician, Candidate of Medical Sciences in the specialties: dentistry and medical microbiology A cyst on the root of a tooth under the crown is one of the fairly common and most dangerous dental diseases. Dentists consider it difficult to treat, and until recently such a diagnosis threatened to remove the tooth, but modern methods of dental treatment provide a fairly high chance of saving it.
Deputy chief physician
Brodsky Sergey Evgenievich
Sign up for a free consultation
+7
What is a tooth root cyst?
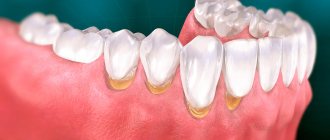
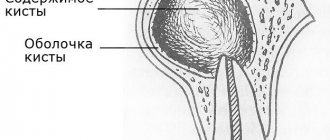
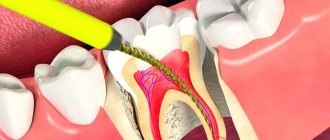
A cyst on a tooth under the crown is a benign neoplasm localized at the apex of the tooth root, in its bone tissue. The cystic structure has the appearance of a round cavity, covered from the inside with a fibrous membrane and filled with purulent exudate. First of all, a cyst under the crown of a tooth indicates that the treatment at the stage of preparation for prosthetics was carried out in bad faith, with poor-quality filling of the root canals.
Treatment methods for dental cysts
Some experts claim that they can treat a dental cyst without removal - simply by pumping out the purulent fluid from the cavity of the tumor. In some clinics, they can charge up to 30,000 rubles for the procedure, while presenting this manipulation as the “latest technique.”
However, you should not believe empty promises! Six months later, pus and inflammation appear again. Thus, it turns out that the patient is again and again forced to pay a lot of money for a dubious treatment, who receive regular income from this; it is not profitable to cure a person, but it is profitable to treat him endlessly.
Meanwhile, in order to get rid of a dental cyst once and for all, it is necessary, firstly, to properly treat the dental canals, and secondly, to remove all infected tissue, and not just pump out the pus. At the same time, only in the most extreme cases is tooth extraction required! Today, specialists are able to treat a complex multi-channel tooth in just three visits. Only after endodontic treatment, which is necessarily carried out under a microscope, is the patient at the disposal of the surgeon. And this whole set of measures, which will rid you of the problem once and for all, costs significantly less than one-time dubious procedures.
Signs of development of cystic formation
The initial symptoms of a dental cyst under the crown are completely absent or barely noticeable and are expressed in slight pain when pressing on the gum or tooth, discomfort when chewing food and slight darkening of the enamel. Such minor signs are usually not given importance, so a cystic neoplasm becomes an incidental finding when taking an x-ray, which is necessary to prescribe treatment for other teeth. By the time specific signs of a tooth cyst appear under the crown, the cystic sac usually grows in diameter to 1 cm in diameter. At this stage, patients complain of the following negative symptoms:
- Increased body temperature, weakness and general malaise due to the development of pathogenic microbes in the cystic cavity.
- The appearance of a nagging or aching pain in the area of inflammation, which is very difficult to get rid of with conventional analgesics.
- Hyperemia and swelling of the gums around the causative tooth, swelling of the face and inflammation of the lymph nodes from the developing cystic formation.
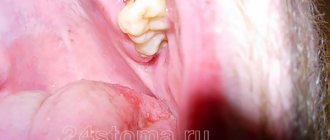
External manifestations of a cyst formed on the root of a tooth can be gumboil, suppuration and fistulous tract. All signs that accompany this type of cystic formations tend to worsen when a person’s immunity decreases. These symptoms cannot be ignored, because if the cyst under the tooth crown is not treated, it will provoke the development of serious, often life-threatening consequences.
Treatment of dental cyst without removal
It is not possible to carry out tooth-preserving cyst removal in only one situation - if we are talking about a formation that has formed on the surface of a wisdom tooth. Such complex cases are quite rare and are accompanied by severe pain. Here, removal of a cyst on a tooth is carried out in a radical manner. In other cases, tooth-preserving techniques are used - this is an immutable rule. Therefore, before you go to a doctor who suggests pulling out a tooth with a cyst, think a hundred times. Perhaps this is simply profitable and convenient, since implantation can then be offered. Installing an implant is the best method for restoring lost teeth, but throughout the world, tooth-preserving principles are paramount in dental treatment. If a doctor can save a tooth, it is his medical duty to do so.
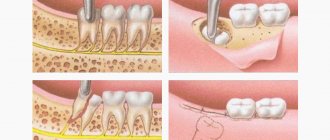
Stages of formation of a dental cyst
Causes of a cyst on a tooth root
There are also several other reasons why, after installing a crown on a tooth, a cyst appears on the root:
- Getting under the crown, into the root canals, infections, as a complication of systemic diseases, for example, sinusitis.
- An accumulation of organic residues between the tooth and the crown that are difficult to clean out during traditional hygiene procedures.
- A tooth cyst under a dental bridge may appear due to the penetration of bacterial flora through the gaps left between the gum and the crown due to poor quality work by the dentist.
Ask a question!
8
We'll call you back in 1 minute
Surgery to remove a dental cyst
There are three ways to remove a cyst: cystotomy, hemisection and cystectomy.
Cystotomy
Cystotomy is used for large cysts. The doctor removes only those parts of the formation that do not come into contact with the vessels, after which he installs an obturator - a device that prevents tissue fusion - into the resulting cavity. After some time, the remaining portion of the cyst connects with the epithelium of the oral cavity, changes its structure and ceases to be dangerous to the body.
Hemisection
Removal of a tooth root cyst is carried out through hemisection. During the operation, the formation, one of the roots and the adjacent coronal part are removed. The resulting space is restored with an orthopedic design. However, the above method is quite traumatic, so it is considered outdated.
Cystectomies
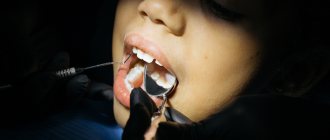
The operation to remove a dental cyst is performed using the most modern technique - cystectomy. The method allows you to remove the tumor once and for all without affecting healthy dental tissue. The operation to remove a dental cyst takes place under local anesthesia in a surgical office and involves the use of a microscope. First, the specialist determines where exactly the patient’s tumor is located, “opens” it, cleans out the contents with special tools, leaves an antiseptic inside and stitches it up. After some time, the cavity remaining after the operation heals on its own, which does not require additional replanting of bone blocks. A cystectomy takes from 15 to 40 minutes, depending on the size of the cyst and bone structure. An hour after the operation, the patient can go home.
Cyst under the crown: how to recognize, treat and prevent complications
If you have recently had a tooth treated and restored with a prosthetic structure, then very soon or after a few years it may come as a complete surprise to you that there is a cyst under the crown. Unfortunately, it is sometimes impossible to insure against this pathology even for those who have undergone expensive treatment. Despite the fact that the situation is quite common in medical practice, it is considered one of the most insidious, difficult to diagnose in the early stages and, in the absence of timely treatment, can harm the patient.
In order not to miss a tumor under the crown and know what to do, be sure to continue reading today’s useful material.
Types or types of neoplasms
| Type of cyst | Peculiarities |
| Radicular | Localized in the root area, it occurs as a result of insufficient treatment |
| Paradental | Occurs next to a wisdom tooth that has difficulty erupting |
| Residual | This is a formation that remains in the bone tissue of the jaw after tooth extraction. It can manifest itself, for example, after prosthetics with bridge structures |
On a note! Doctors also identify other types of cysts, but they no longer appear on teeth with prosthetic structures. For example, a follicular formation may appear when the buds of a baby or permanent tooth become infected. The primary cyst occurs against the background of complex eruption of individual units.
Diagnostic measures
Here, the most effective diagnostic method to this day remains x-ray examination. After all, it is with the help of an image that the doctor can best assess the extent of the inflammatory process and confirm the diagnosis. In the photographs, the cyst appears as a black, rounded spot located near the apex of the root.
“Many patients panic, suspecting a cyst under the crown. After all, in their minds they immediately begin to replay a situation in which in any case they will have to get rid of the prosthetic structure, remove it, treat it, and then install a new one. All this costs significant costs, and no one wants to pay twice. It is important to emphasize here that the less the inflammatory process, the greater the chance of getting by with therapeutic measures, medications, and even in some cases you may not have to remove a previously installed crown. Therefore, it is important for patients not to delay treatment, but to immediately consult a doctor at the first suspicion. This is a real chance to save money and nerves,” says dentist-therapist O.A. Belyaeva.
What complications may arise if the problem is not resolved in time?
The consequences of lack of treatment can be the most tragic: jaw fracture due to the formation of large tumors and abscesses, phlegmon, osteomyelitis. Also, the inflammatory process may not be limited to just the tooth on which the crown is installed; it can go further and reach its neighbors. When affected by infection, neighboring teeth may change color and become mobile (these symptoms can be easily detected if there is no artificial crown), become loose and fall out.
The presence of a cyst can contribute to the release of purulent masses and their spread throughout the body, throughout the hematopoietic system, sepsis, as a result of which the functionality of vital organs will suffer: kidneys, heart, liver and even the brain. Also, lack of treatment can provoke the appearance of malignant cancer tumors.
Development factors
A detailed analysis of the factors contributing to the appearance of cysts allows us to draw a conclusion about the influence of granulomas - small nodular elements formed as a result of pathogenic microflora entering the tissue structure. As granulomas develop, they transform into a cyst - the causes of the pathological process include:
- Incorrect performance of dental prosthetics;
- Violation of the dental canal treatment protocol;
- The presence of dental diseases that have not been completely cured;
- Allergic reaction to composite filling material;
- Mechanical damage to the structure of gum tissue;
- Complications that develop after infection;
- Chronic forms of periodontitis;
- Exacerbations of systemic or chronic diseases;
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards for oral care.
It is worth noting that the connection between prosthetics and the development of cysts can be traced in most diagnosed cases. Moreover, the first negative symptoms may appear only 2-3 years after the placement of the replacement structure.
Why does pathology occur?
The culprit is infection of the root canals. But pathogenic microorganisms can get there in completely different ways:
- chronic periodontitis of neighboring teeth or a treated tooth, but if the inflammation has not been eliminated,
- violation of the technique of preparation and treatment of root canals before prosthetics: for example, the specialist used an unsterile instrument, injured the canals or root, used an allergenic material that caused irritation and inflammation of periodontal tissues. Also, the doctor could not complete the root canal, poorly disinfect it or seal it tightly enough, overlook incompletely cured caries, pulpitis, periodontitis,
- insufficiently high-quality prosthetics: for example, the doctor who initially installed the prosthetic structure for you could not fit it tightly enough to the gum, as a result of which you did not even notice how the smallest food debris and bacteria began to get under the crown, and, accordingly, the inflammatory process began ,
- chronic sinusitis: in this case, the infection from the nasal sinuses could have gotten not from the outside, but from the root, hematogenously, i.e. through lymph and blood,
- injury and inflammation of the gums,
- advanced diseases localized on adjacent teeth,
- eruption of adjacent (usually impacted) teeth: these are those that do not fully penetrate the surface and occupy an incorrect position in the bone. They can put pressure on neighbors, destroy them and thereby cause an inflammatory process around them,
- untreated systemic and chronic diseases: especially in the acute stage, they can reduce the overall immune status of the body and lead to the appearance of similar problems.