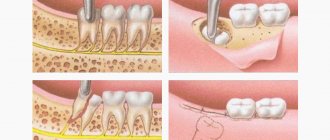
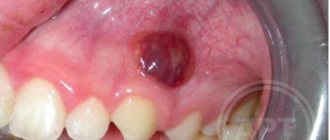
If not treated promptly, caries under the gum can lead to severe tooth decay and even loss. The enamel at the base of the tooth darkens noticeably, and it begins to react painfully to cold and hot food and mechanical stress. Read the article about the causes of subgingival caries and methods of treating the disease.
In this article
- Causes of caries in the gums
- Additional reasons for the development of caries under the gum
- Features of the disease
- Symptoms of root caries
- Treatment of cervical caries
- Consequences of cervical caries if left untreated
- Features of filling caries near the gums
- Prevention of subgingival caries
Causes of caries in the gums
The main cause of the disease is cariogenic microbes that cause damage to enamel and dentin. They exist in everyone, but they begin to develop only when favorable conditions are created: consumption of large amounts of carbohydrate foods, poor oral hygiene and due to some other reasons. The development of caries at the base of the tooth is associated with its localization and is caused by the following factors:
- Due to the characteristic structure of the tooth, plaque constantly accumulates in the root area, which cannot always be removed even with a toothbrush. If you do not make an effort when cleaning, then gradually the neck of the tooth will begin to collapse under the influence of cariogenic bacteria contained in plaque.
- In the depressions near the gums, the so-called “pockets,” food debris accumulates. If oral hygiene is not sufficiently thorough, food decomposes and lactic acid is formed, which destroys tooth enamel.
A risk factor that provokes the development of cervical caries may be the consumption of large quantities of too acidic foods that contain quickly fermentable carbohydrates. As a result of their fermentation, organic acid is released, which corrodes tooth enamel and washes away calcium.
Additional reasons for the development of caries under the gum
In addition to factors directly related to the impact on the teeth, there are also third-party causes that can provoke the occurrence of a carious process between the gum and tooth.
Let's name the most common ones:
- hormonal or endocrine disorders in the body;
- use of medications that increase enamel porosity;
- lack of certain vitamins, especially group B;
- poor quality of drinking water;
- heredity;
- increased acidity of the body;
- age factor and others.
Taking into account these additional reasons, the treatment of gum caries should not be limited only to the work of the dentist. In this case, it should be comprehensive with the involvement of several specialists, for example, an endocrinologist and others. If the cause is not eliminated, the pathology will return again and again.
Features of the disease
This type of caries is especially dangerous and unpleasant, as it has some peculiarities in its course and location. Its manifestations are associated with the following factors:
- Carious lesions are localized in the weakest area near the neck of the tooth (this is the part covered by the gum). In this zone, the enamel is also weakly mineralized, and this factor enhances the development of caries.
- Circular distribution. Cervical caries affects the tooth in a circle, covering increasingly larger areas. As a result, part of it may break off, since the integrity will be broken in many places.
- Damage to the front teeth. An unpleasant feature of gingival caries is its frequent location on the incisors. A person experiences psychological discomfort when he has to talk, smile, laugh.
Under the influence of the bacteria Streptococcus Mutans, which causes the development of the disease, the enamel and dentin underneath are actively destroyed. Inflammation can spread to the pulp and ultimately lead to pulpitis or periodontitis.
Other symptoms of inflammatory diseases
Swollen, loose gums may not be the only sign of periodontal disease. In most cases, other symptoms and manifestations are observed:
- dry mouth - viscous thick saliva, lack of proper hydration of the mucous membranes, which can also indicate systemic diseases (for example, diabetes) and diseases of the salivary glands;
- burning, itching, sensitivity of the gums - may be a consequence of an inflammatory, infectious-inflammatory disease;
- bleeding - this symptom is observed in acute forms of gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease;
- bad breath - often observed in infectious and inflammatory diseases, the presence of tartar and a large amount of plaque;
- formations on the gums - in the absence of severe pain, they can be a sign of cysts, granulomas, periodontitis, chronic inflammation of the periosteum, etc.;
- exposure of the necks of teeth and the appearance of periodontal pockets are a sure sign of periodontal disease.
Loose gums are a reason to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Symptoms of root caries
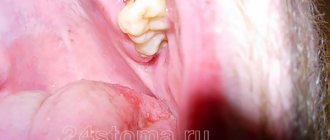
Pathology has the same symptoms as caries of other classifications, but its impact is more destructive, and the consequences are more unpleasant and more dangerous for dental health. Carious lesions can spread deep inside, gradually destroying all the canals. Here is what the main signs of cervical caries look like:
- increased reaction of teeth to cold, hot, sour, sweet foods;
- the appearance of dark spots on gums with carious lesions;
- pain when chewing food and while brushing teeth.
All of these symptoms indicate the development of a disease that consists of several stages.
- Chalk stain. At this stage, a slight dark spot appears on the surface of the enamel without changing its shape or size. Particular sensitivity to acidic foods may occur. At the matte spot stage, caries under the gum is eliminated without the use of a drill.
- Superficial stage. The spot becomes rough, and gradual destruction of the enamel begins. A diseased tooth reacts to various irritants, in addition to sour: hot, cold, including cold air, mechanical stress. The pathology begins to actively progress.
- Middle stage. Cavities form in teeth as dentin is destroyed. The defect is already becoming clearly visually noticeable.
- Deep stage. The process spreads deep into the tooth, reaching the roots and nerve endings. The pain can be very severe, especially at night, and discomfort occurs when inhaling cold air.
There is no clearly defined boundary between the listed stages; the transition from one to another is so smooth that it is almost impossible to track it. In an advanced stage, serious consequences can develop: for example, circular caries, when the process already covers the entire gingival area of the crown in a circle. Teeth at this stage break off easily.
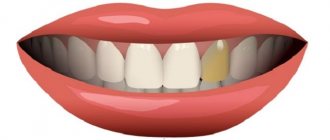
Causes of darkening of teeth near the gums
The condition of teeth and enamel is affected by many everyday factors, as well as various dental diseases.
Household factors include:
- abuse of coffee, tea, red wine;
- smoking;
- frequent consumption of natural juices (for example, grape or tomato);
- taking certain medications that contain ferrous gluconate.
Coloring drinks provoke the appearance of enamel pigmentation, which is easily eliminated with professional teeth cleaning.
Pathological processes that provoke the accumulation of dark plaque on the enamel in the gum area:
- cervical caries;
- tartar;
- fluorosis (a disease characterized by a high content of fluoride in the human body).
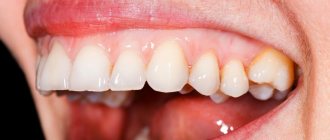
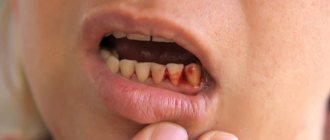
Cervical caries is the most common cause of dark spots on teeth. Pathology is one of the most dangerous types of the carious process, since it occurs in a hidden form, and the destruction of enamel occurs very quickly.
The disease develops in stages:
- A small pigment spot appears in the area of the tooth neck near the gum;
- Then the darkened area of enamel becomes rough;
- The tooth begins to react to external stimuli (sour, sweet, hot, cold), painful sensations appear;
- The stain on the enamel changes color from light brown to black.
The deep form of cervical caries is accompanied by severe destruction and most often turns into pulpitis.
Treatment of cervical caries
It is very important to contact your dentist for help while the process has not yet become global. A competent specialist knows how to effectively treat this disease in order to save teeth and eliminate the consequences. At the initial stage, you can still do without the use of a drill and filling, which allows you to significantly save your budget. The doctor determines treatment methods depending on the degree of pathology and the general clinical picture. Each stage requires its own approach to therapy.
Treatment at the spot stage
In this case, remineralizing therapy and additional means of protection are used. The doctor removes tartar and plaque from the teeth, then applies fluoride strips to the affected areas. This element helps regenerate enamel layers and stop the carious process. At home, you can use herbal decoctions, solutions of fluoridated salt and water to rinse the mouth, use pastes and threads containing fluoride.
How to treat cervical caries of the superficial and middle stages
At these stages, the doctor removes the damaged tooth tissue and polishes the carious area. The procedure is completed with remineralizing therapy. If necessary, a filling is placed.
Method for treating deep caries
At this stage of the disease, coping with it is not an easy task. The treatment consists of several sessions. Here are the procedures the dentist performs:
- Anesthetic injection. When treating cervical caries, the doctor must provide anesthesia, since the area near the gums is very sensitive to action.
- Cleaning enamel from plaque and tartar. This is necessary to prevent infection from reaching the affected area.
- Selecting the color of the filling material.
- Removing carious tissue using a drill.
- Treatment of the cavity with an antiseptic and adhesive material.
- Filling. The composite material is applied in layers, each of them is treated with a photopolymerization lamp for hardening.
- Grinding and polishing the tooth surface. The dentist gives the surface the correct shape and makes sure that he has achieved the correct bite.
Thus, each carious tooth is treated. The process can take a long time and cost a lot of money - another argument in favor of regular prevention.
Causes of darkening after implant installation
Hematoma
Darkening of the gums after implantation may be due to the formation of a hematoma. Hematoma is a common postoperative symptom, which is a natural reaction of the body to the presence of a foreign body. Most often it appears a few hours after implantation and goes away within a week. The hematoma reaches its greatest development on the fourth day after the intervention.
Blue discoloration on the gums can occur from an injection of anesthesia. With a favorable prognosis, such darkening is not dangerous and will disappear within a few days, like a hematoma.
Illumination of titanium elements
Even successful placement of dental implants can result in blue gums. When installing an implant and abutment, a blue highlight is possible; the blue color is especially clearly visible on the front teeth. To avoid such an unpleasant effect, when installing implants on the front teeth, you need to opt for zirconium abutments rather than titanium abutments.
Complications during prosthetics
Often darkening is observed after installing crowns on the implant. First, the gums turn red and swell, later they darken and bleed. The cause of the complication is an incorrectly formed gingival contour, if a former was not installed after the implant was implanted. The edges of the crown put pressure on the gum, disrupting blood circulation in it, causing swelling and blue discoloration. Stagnation of blue venous blood especially stands out against the background of white teeth and healthy areas of the gums.
What to do if your gums are darkened
Darkening is a sign that the installation of an implant or subsequent dentures has caused irritation and bleeding of the gums. Therefore, medication administration and monitoring should be carried out by a doctor.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the cause of the pathology. It may be necessary to adjust the implant superstructures or replace the crown or bridge fixation system. At the same time, the doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory therapy. Massage and physiotherapeutic treatment methods are also indicated.
In case of color change, you should not self-medicate. Immediately contact a specialist to determine the pathology.
The most effective drugs:
- Rotokan . Black gums are rinsed with the solution three times a day.
- Metrogil Denta . Antibacterial gel is applied to the affected area for a month.
- Chlorhexidine bigluconate 0.5% . Rinse the mouth with the solution up to six times a day for several days.
- Vinylin . A compress with balm is applied to the darkened gum and kept for 20 minutes.
Before using folk remedies, consult your doctor because medicinal herbs have serious side effects.
The oral cavity is rinsed:
- a decoction of mint, sage, oregano, lemon balm;
- a decoction of St. John's wort, thyme, chamomile, sage;
- soda solution;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- sea salt;
- infusion of oak bark.
Comment from an implant surgeon with 12 years of experience: “Darkening can be caused by injury to blood vessels during implantation. If the operation is successful, there should be no severe pain, swelling or darkening. Standard complications: pain of moderate intensity, small hematomas, a feeling of fullness in the maxillary sinus, low-grade body temperature, inflammation of the soft tissue in the area of implantation, temporary bleeding.”
Consequences of cervical caries if left untreated
Advanced caries near the gums is very dangerous, it can progress quite quickly and cause complications such as:
- periodontitis;
- pulpitis;
- inflammation of the gums;
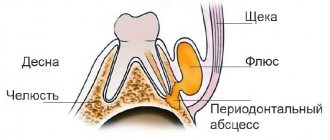
- an abscess or a well-known flux.
In addition, the development of caries in the gums is often associated with pathologies of the thyroid gland and diabetes mellitus. It is necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis to determine the exact cause of the disease. After the therapy prescribed by the endocrinologist, the disease may recede.
Features of filling caries near the gums
Placing fillings in the area near the gums is much more difficult than with other types of caries - approximal or fissure. This is due to some factors that arise during the work process:
- the area near the gums is inconvenient for filling, especially on the upper teeth;
- Saliva gets on the affected area all the time, even placed cotton rolls do not help;
- During the treatment process, blood is always released, which also enters the working area.
The closer to the root a tooth is damaged, the more difficult it is to treat. Due to the fact that cervical caries most often affects the front teeth, you need to choose the color of the material with special care - it should ideally match the color of the enamel, since the aesthetic visual effect plays a role here.
Prevention of subgingival caries
The development of the disease is provoked by many external and internal factors. And even if caries has never bothered you, preventive measures will help prevent its occurrence and development. Here are some simple rules doctors recommend following:
- Brush your teeth with toothpastes high in minerals.
- After each meal, use a mouthwash and dental floss - it will help effectively remove pieces of food stuck between your teeth. Oral irrigators can also be used.
- Half an hour after eating, brush your teeth if possible. This should be done twice a day for a couple of minutes.
- Include in your mandatory daily diet foods rich in fluoride, calcium and other beneficial microelements to strengthen enamel, eat more solid vegetables and fruits.
- Avoid excessive consumption of sweets, flour and sour foods.
- Periodically massage the gums: it improves blood circulation in the gum tissues, protects against the formation of deep periodontal pockets and the accumulation of deposits in them, which reduces the risk of caries formation at the neck of the tooth.
If the enamel is thin and susceptible to the rapid formation of tartar on it, regular remotherapy helps a lot - this is the name for applying fluoridating compounds to the teeth. The procedure reduces the risk of enamel destruction and improves the condition of hard tissues. To further strengthen the enamel, you can periodically take special vitamin complexes containing useful minerals. In addition, it is necessary to visit the dentist’s office at least once every six months for a dental examination. The doctor will make sure that everything is fine with them, or will prescribe additional diagnostics using x-rays. Once every 6-9 months, it is recommended to carry out professional enamel cleaning using ultrasound or other methods. During the procedure, plaque and tartar are removed from the surface of the teeth. It polishes and becomes smoother, and less deposits accumulate on the enamel. During cleaning, the doctor can also clean periodontal pockets if plaque and deposits accumulate under the edge of the gums.
People who are at risk for endocrine diseases need to be especially attentive to pain in their teeth. With them, teeth are often affected by cervical caries. Treatment must be comprehensive and systemic to prevent caries from damaging the tooth root. Gingival caries is a dangerous pathological process if it is started, but it can be successfully treated in the early stages.
Modern dentistry eliminates caries of various types, but it also happens that if the stage of the disease is too deep, some teeth cannot be saved. We have to remove them and resort to various methods of restoring the dentition. You just need to be attentive to your oral health, taking simple preventive measures, so as not to have to deal with expensive treatment later. With regular dental examinations, you will be able to detect the problem in time and solve it.
Treatment of loose gums (gingivitis or periodontitis)
- In dentistry, a periodontist will perform a complete cleaning of the teeth using a mechanical method or using ultrasound.
- Be sure to carry out an anti-inflammatory course of treatment of the whole body according to the recommendations of a dentist.
- Agree to undergo a curettage procedure, during which the cavity formed due to inflammation is completely cleaned and treated with antiseptics. It is better to use ultrasonic cleaning.
- In advanced forms of the disease, when treatment is already overdue, perform a splinting procedure. In such cases, the teeth are fixed together using fiberglass.