Dentistry deals not only with teeth, but also with gums. If unpleasant and painful symptoms appear in the oral cavity, we recommend that you sign up for a consultation - it is better to find out from the doctor that there is nothing wrong, carry out a preventive procedure and get advice on home hygiene. For example, a phenomenon such as a hard lump on the gum may not cause discomfort at first, but can later become a serious problem. To avoid having to be treated and operated on, talk to your doctor as soon as you notice something unusual in your mouth or your sensations.
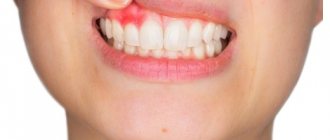
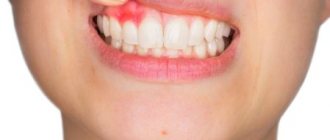
What does a white bump on your gum mean? That there is an infection or injury. This already gives reason to think about treatment. Next, we will talk about the causes of lumps in adults and young patients.
The main advice that can help anyone with any dental problem: do not be afraid or embarrassed by the doctor. At an early stage, all diseases can be eliminated much faster than later, when the process develops and penetrates into the deep tissues of the gum or tooth.
Causes
The causes of lumps in the jaw area are different. But if they appear outside, on the right or left side (closer to the ear) and under the chin, most often this indicates inflammation of the lymph nodes.
When pathogenic bacteria enter the body, the immune system activates the production of lymph. The external manifestation of this process is an increase in the size of the submandibular lymph nodes.
One of the reasons for the development of lymphadenitis is diseases of the oral cavity:
- Pulpitis is inflammation of the dental pulp caused by streptococcal or staphylococcal infection.
- Alveolitis is an acute inflammation of the walls of the socket at the site of tooth extraction.
- Periodontitis is an inflammation of the tissues surrounding the root of the tooth. Its main symptoms are: pain in the area of the affected tooth, swelling of the gums and swelling of the cheek. Can lead to the formation of jaw cysts and osteomyelitis.
- Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa.
- An abscess is an inflammation of the root of a tooth, accompanied by an accumulation of pus.
When signs of lymphadenitis appear, dental pathologies are first excluded. Enlarged lymph nodes are a secondary symptom: it occurs when a visit to the dentist is delayed or after the removal of a tooth affected by a purulent infection. The primary signs of dental disease are gum inflammation and pain.
In 15% of cases, the reasons for the formation of seals in the maxillofacial area are dental. In addition to lymphadenitis, processes occurring in the oral cavity lead to the appearance of bumps on the gums.
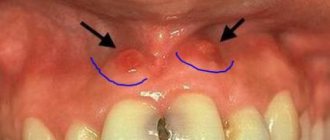
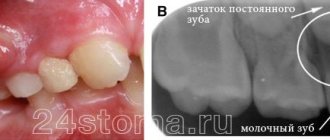
They may be a sign of the growth of a permanent (in young children - baby) tooth or pathology of an existing dentition. The following appear as bumps on the gums near the teeth:
- Exostosis is a jaw abnormality characterized by the appearance of bony protrusions on the gums.
- Epulis is a pink or red mushroom-shaped tumor. Appears when the gums are mechanically damaged by a filling or tartar. Other causes of its occurrence: bruises and burns, congenital malocclusion, the use of low-quality dentures, hormone imbalance.
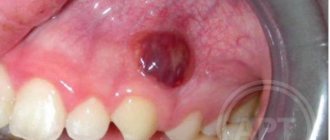
- A fistula is a small seal on the gum with a hole. When an infection occurs, pus flows out of it. The main reason for the formation of fistulas is the granulating form of periodontitis.
On this topic
All about the ball on the frenulum under the tongue
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- September 30, 2022
Benign tumors of bone and soft tissues of the oral cavity have a similar manifestation. The most common are:
- Ameloblastoma - mainly affects the lower jaw. It develops intraosseously and sometimes grows into soft tissues. Diagnosed at the age of 20-40 years. At first, the course of the formation is asymptomatic, but over time it increases. This leads to jaw deformation, swelling, bumps on the face on the affected side, and displacement of teeth.
- Osteoma is a tumor growing from bone tissue. It can form both on the outside of the jaw and on the inside (most often in the area of the upper dentition). With the active growth of the seal, pain appears, jaw mobility is impaired, and facial asymmetry occurs.
- Fibroma is a pathological formation that develops from the connective tissue of the tooth germ. Clinical signs of the tumor are mild: sometimes there is aching pain and inflammation at the site of its location.
- Cementoma is localized, as a rule, on the lower jaw: in the area of the tooth root. When it reaches large sizes, it causes facial deformation.
Malignant tumors of the oral cavity (carcinoma, sarcoma) are rarely diagnosed. But if a lump appears on your gums, you should definitely see a doctor: a dentist and, if necessary, an oncologist.
Non-dental reasons for formation
If the patient does not have pathologies of the teeth, soft and bone tissues of the oral cavity, one should look for another reason for the formation of lumps on the jaw. Inflammation and an increase in the size of the submandibular lymph nodes provoke diseases.
- systemic lupus;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- leukemia.
Traumatic injuries to the lower jaw, head and hearing organs are no less rare causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes and the formation of lumps near the ear, in the chin area. At the site of the bruise, inflammation, swelling or compaction with a dense structure appears.
In the jaw area there are not only lymph nodes, but also blood vessels, salivary and sebaceous glands, bone and soft tissues. Therefore, when lumps appear on the outside of the jaw, the presence of cancer should not be ruled out. Sometimes growths under the skin of the face are benign or malignant neoplasms.
It occurs due to lipid metabolism disorders, clogging of the sebaceous gland, accumulation of toxins in the body
There are many reasons for the formation of lumps on the jaw. It is difficult to independently understand why the lumps appeared: you need to consult a doctor.
Dental causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes on the chin
Since very often in their work dentists are faced with huge lymph nodes in patients, let us dwell in more detail on the diseases that cause this symptom:
- Periodontitis. It can occur in acute or chronic form. Leads to tooth loosening and severe pain. If you do not receive qualified dental care in time, there will be a need to remove the affected unit.
- Stomatitis. Causes painful ulcers to appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth. It is the result of injuries, low immunity, vitamin deficiency. In advanced cases, the entire oral cavity becomes covered with wounds. Then active production of lymphocytes is observed.
- Pulpitis. Inflammatory lesion of pulp tissues. A very insidious disease. Through the pulp, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the lymph nodes and other tissues. It is important to clean the canals and seal them as soon as possible.
- Advanced caries. Despite the fact that many people do not take caries seriously, it is a rather insidious infectious process. If the deep tissues of the tooth are damaged, the lymph nodes come to the aid of the body - they try to neutralize pathological agents by producing lymphocytes. This can be understood by their increased size.
- Periodontal disease. Causes hypertrophy of periodontal tissues, leading to local hypoxia. Periodontal disease does not cause pain, so most often the patient learns about it by chance during a medical examination for some other condition. With periodontal disease, the gums become lighter, the interdental papillae atrophy, and the dental necks become exposed. If treatment is not started in time, the teeth will begin to loosen and fall out.
- Periodontitis. A disease that develops due to metabolic disorders, neurosomatic abnormalities, poor oral hygiene, and deficiency of vitamins and minerals. It manifests itself as bleeding gums, bad breath, and loose teeth.
- Gingivitis. Inflammatory reaction in the gums. Appears against the background of gastrointestinal pathologies, allergies, infections. The patient experiences bleeding gums even with minor mechanical stress. A burning sensation in the mouth bothers me. Ulcerative-necrotic areas may form.
These are not all dental conditions in which the lymph nodes under the chin become inflamed. In medical practice there are many more such diagnoses. This once again proves that the patient himself will not be able to understand why his submandibular area is swollen.
Diagnostics
To find out the reason for the appearance of a lump on the jaw, a comprehensive examination is prescribed. First, the doctor examines and collects the patient’s complaints. If a patient has lymphadenitis, at the initial stage of the disease the following symptoms appear:
- slight enlargement of lymph nodes, their mobility;
- pain of the nodes on palpation, turning the neck (pain can radiate to the ear or other parts of the body nearby);
- general weakness;
- low-grade temperature ;
- decreased sleep quality;
On this topic
What could be a growth on the gum?
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- September 3, 2022
With inflammation of the lymph nodes, accompanied by purulent processes, the patient has complaints of:
- increased pain when moving the jaw;
- redness of the skin in the area where pus accumulates;
- severe swelling of the lymph nodes, their pain even without pressure;
- temperature rise to 38 ºC or more.
In the last stages of lymphadenitis, the patient’s well-being deteriorates significantly: inflammatory processes spread to the neck and shoulders, fever appears, and bluish skin is observed at the site of inflammation.
Since, in addition to inflammation of the lymph nodes, there are other reasons for the appearance of lumps on the jaw, it is impossible to make a correct diagnosis based on the clinical manifestation of the pathology. Therefore, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are used.
- blood test (general, advanced);
- bacteriological examination of mucus from the tonsils and upper respiratory tract;
- radiography of the jaw (in different projections);
- ultrasound examination of pathological formation;
- CT or MRI of the head;
- biopsy (if necessary).
Regardless of the mechanism of occurrence of a lump on the jaw, it is important to begin taking therapeutic measures in a timely manner. The earlier treatment is started, the lower the risk of complications.
How to understand that the problem is in the lymph nodes
Among the symptoms indicating damage to the lymph nodes:
- pain in the area where they are located;
- migraine;
- weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- discomfort under the chin;
- unpleasant pulsation in the lower jaw;
- difficulty chewing food;
- swelling noticeable to the naked eye.
If a purulent process develops, the skin in the area of inflammation becomes red and becomes very hot to the touch. Additionally, symptoms characteristic of the disease that provoked the disorder may appear.
Types of bumps on the face
Subcutaneous formations can be relatively harmless, appear, for example, in the form of acne, or indicate more serious diseases, including cancer. If we consider the main types of pathological processes in connection with which subcutaneous bumps can form on the face, the following stand out:
- Lipoma. Sometimes such seals are called wen, since the formation contains fatty and connective tissue. It is small in size, does not cause pain, and is a benign neoplasm. It forms relatively deep under the skin, a kind of capsule is noted, which can be removed surgically. Squeezing, for example, like a pimple is not only difficult, but also dangerous, as there is a risk of infection.
- Hemangioma. It is most often diagnosed in infants, but is sometimes observed in adults due to injuries and improper skin care. The lump differs in color from the skin, as it consists of accumulations of capillaries that can be compressed and injured. Subcutaneous bumps on the face do not hurt and can go away on their own. If treatment is necessary, physiotherapeutic, medicinal or surgical measures are prescribed.
- Purulent formations, foci of abscess. Such seals are quite painful, especially when pressed. They are formed due to the entry of bacteria and various types of infections into the layers of the epidermis; they can appear in connection with inflammatory processes already occurring within the body.
- Subcutaneous cyst. Refers to benign formations consisting of keratinized epithelium, connective, adipose tissue, and cavity. If the cyst grows rapidly, removal is recommended. A subcutaneous cyst or atheroma can develop together with the inflammatory process and suppuration. Traditional methods for treatment are not used.
- Pimples, boils. The seals have ulcers, inflammation and redness of the skin are even visually noticeable. It is extremely undesirable to squeeze out such formations, although many try to do it on their own. Such actions increase the risk of infection of other tissues, and other complications are possible.
- Oncological formations. It is impossible to distinguish cancerous tumors without appropriate diagnostic measures. Visually, they are similar to other types of cones.
In addition to the above diseases that cause various types of subcutaneous formations, there are others that are less common. In any case, the final diagnosis should be determined solely by the doctor, as well as the choice of treatment methods.
Swelling in the neck
Swelling in the neck - Growths in the neck - Lymph nodes in the neck - Lump in the neck
Patients and their families may notice a lump in the neck area, or it may be discovered during a routine examination. A lump in the neck area may be painless or painful, depending on the cause. When neck augmentation is painless, it may take a long time before patients seek medical attention.
Cause:
There are many causes of cervical mass, including inflammatory diseases, neoplasms, and congenital diseases.
The most common causes in younger patients include the following:
- local and generalized lymphadenopathy - acts as an organizational response to a viral or bacterial infection, usually of the oropharynx, tongue, salivary glands, pharynx and scalp.
- primary bacterial infection
- systemic infections
- some systemic infections (eg, mononucleosis, HIV, tuberculosis)
- congenital disorders can cause a cervical mass (a growth on the neck), usually in the long term. The most common is thyroglossal duct cyst, branchiogenic tumor, etc.
- Neoplastic masses (neoplastic masses) are more common in older patients, but can also occur in younger people. These masses may represent the site of a primary tumor or lymph node metastases from local, regional, or distant cancer. Approximately 60% of the supraclavicular mass is lymph node masses metastasized from distant primary sites. In the neck, 80% of metastatic cervical lymph nodes originate from the upper respiratory and digestive systems. Possible localization of the tumor is the lateral surface of the tongue, floor of the mouth, nasopharynx, pharynx, laryngeal epiglottis and infraorbital region.
- The thyroid gland can dilate in various disorders, such as simple non-toxic goiter, subacute thyroiditis and, less commonly, thyroid cancer.
- The submandibular salivary glands may become swollen if the salivary duct is blocked by a stone, inflammation or tumor.
Reference Information:
As a history of this disease, it should be noted how long the mass has been present, and whether it is painful. It is important to note associated symptoms, which include sore throat, upper respiratory tract infection symptoms, tooth pain, nasal congestion, ear fullness, etc.
Questions about difficulty swallowing or speaking and symptoms of chronic illness (eg, fever, weight loss, general malaise). Peripheral and distant metastases of cancer cause throat symptoms in the swallowing system (eg, cough in lung cancer, difficulty swallowing in esophageal cancer). Because many types of cancer can metastasize to the neck, a complete otolaryngological examination of all systems is important and can help find the cause of the disease.
Your doctor should tell you whether you have HIV or tuberculosis and what risk factors you may be at risk for. Risk factors for cancer include alcohol consumption or tobacco use (especially snuff or chewing tobacco), poor placement of dentures, and chronic oral thrush. Poor oral hygiene can also be dangerous.
Physical examination:
It is necessary to determine the composition of the growth on the neck (that is, whether it is soft, elastic or hard), as well as the presence and degree of sensitivity. If the mass is freely mobile or stable, it appears only under the skin or the depth must be determined.
The scalp, ears, sinuses, mouth, nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx and larynx are closely associated with possible infection and any visible damage. The base of the tongue, the base of the oral glands, the thyroid gland and the salivary glands should always be palpated for possible involvement.
The mammary gland and prostate gland are palpated for possible hypertrophy, palpation of the spleen, and examination for splenomegaly. The presence of blood in the stool indicates gastrointestinal cancer.
Other lymph nodes are palpable (eg, armpits, groin).
Attention:
The following signs are of particular concern:
- Rigid, immovable mass
- Elderly patients
- Presence of oropharyngeal lesions (other than simple pharyngitis or dental infection)
- History of chronic hoarseness or dysphagia
Interpretation of results:
Significant differentiation of factors by neck mass (including severity, pain, mobility, size and location).
A new mass (that is, swelling of the neck just a few days old), especially after symptoms of an upper respiratory tract infection or pharyngitis , signifies benign reactive lymphadenopathy .
Chronic neck swelling in young patients may suggest a congenital cyst .
A lateral cervical mass in elderly patients, especially those with risk factors, should be considered cancer until proven otherwise!
The midline mass is likely a thyroglossal duct cyst.
Pain, tenderness, or both with cervical swellings indicates inflammation (especially infection), while a painless mass is a cyst or tumor. A tough, hard, painless mass suggests cancer , while an elastic texture and mobility suggest the opposite.
Generalized lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly may be found in infectious mononucleosis . Only generalized adenopathy may indicate HIV , especially in individuals with risk factors.
Red and white mucous membrane ( erythroplakia and leukoplakia ) in the oropharynx may be a malignant change that is responsible for metastases in the neck. .
Difficulty swallowing may be noted with a thyroid tumor or cancer in various areas of the neck. Hoarseness may be due to cancer of the larynx or paresis of the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
If nasal endoscopy shows changes in the nasopharynx , then tests may include CT or MRI, and a fine needle biopsy of the lesion.
In older patients, especially those who have a risk factor for cancer, additional tests must be done first to determine the underlying cause: a biopsy of the mass may simply reveal undifferentiated squamous cell carcinoma without telling us the source of the disease. These patients should undergo direct laryngoscopy, bronchoscopy with biopsy, and esophagoscopy of all suspicious areas.
CT scan of the facial region of the skull, neck and chest is necessary. If the primary tumor is not found, a fine aspiration biopsy of the mass should be performed.
If the neck mass has been identified as a metastatic and primary tumor, then it should be considered necessary for general anesthesia - biopsy of the nasopharynx, tonsils, base of the tongue, pyriform fossa, larynx, esophagus and bronchoscopy.
Treatment:
Key points:
- A neoplasm on the neck in young patients is usually benign.
- New growths on the neck in old age usually cause cancer.
- The first and main test that guides the otolaryngologist in the right direction for diagnosis in a clinic or hospital is flexible endoscopy using a rhinolaryngoscope with or without local anesthesia. This test is painless and allows the otolaryngologist to examine the nose, nasopharynx, hypopharynx and larynx in detail using video imaging. Read more
- If you have a lump in the neck with a firm, painless, unilateral structure and a diameter of more than 2 cm, urgently consult an otolaryngologist or go to the nearest hospital for examination and diagnosis of possible malignant transformation.
Causes
There is an opinion that dermatological diseases occur mainly due to insufficient or improper skin care, but this is not entirely true. This reason is one of the common ones, but there are others. These include:
- Hormonal disorders, diseases of the endocrine system.
- Lifestyle, nutrition, bad habits.
- Use of low-quality cosmetics and care products.
- Metabolic disorders, including chronic diseases, such as diabetes.
- Infectious, viral diseases.
- Injuries. Subcutaneous bumps on the face after a blow can occur not only in the form of bruises, but also as other structural seals. These can be infectious formations, cystic, and so on.
Treatment
Conservative or surgical methods are used to treat subcutaneous lumps. Defining
factors are the size of the compaction and the reason for its development. If the formation is benign, small in size and does not cause any physical or emotional discomfort, then you can only observe it. If the lump grows, symptoms of inflammation and other signs of activity, measures are taken to eliminate the problem area.
Conservative therapy is used only if there is a possibility that the lump may disappear over time. To do this, antibiotics or antivirals are selected, external agents are prescribed, the action of which is aimed at the problem area. If necessary, antihistamines, antiallergic drugs, and hormonal drugs are taken.
For each patient, depending on the clinical picture, an individual treatment regimen and surgical options are determined.
What kind of education is this
A lump is a lump on the face in the form of a ball under the skin. They can be found on the forehead, chin, and cheeks. Such lumps are often found in the area of the corners of the eyes and lips. There are many reasons for lumps to appear. Depending on them, all such formations are divided into groups. It is necessary to consult a doctor so that, after conducting a diagnosis, he can determine why the lump appeared.
Important! To accurately understand the cause of the lump under the skin on the face, you need to undergo a short examination, take a blood test and take a smear of the dermis. After receiving the results, it will be possible to clearly say what caused the disease.
Types of formations and reasons for their appearance
An abscess is a lump under the skin that forms after infection. The formation in this case is very dense, since there is a clot of pus in the lesion. This lump is red around its entire perimeter, and very often patients experience an increase in temperature. It will not be possible to surgically remove or simply squeeze out such a lump without consequences; it will form in the same place again. This will continue until the infection is eliminated.
An intradermal cyst is a solid formation, which is accompanied by regular discharge from it onto the surface of the skin. Such a compaction can occur as a result of disturbances in the body and the secretion of the sebaceous glands of the dermis: around the ear, in the auricle, on the nose, on the neck, and also on the face. This disease is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs, which are prescribed by the doctor in accordance with the examination results.
Dense lump under the skin of the face
Rheumatoid nodes are the result of an inflammatory process in the lymph nodes. If the disease is not treated correctly, deformation may occur in the joints, which stand out on the face in the form of lumps.
Lipomas are spherical lumps that can move under the skin if you press on them with your finger. They can often be seen in the area near the eyes, as well as on the cheeks. By themselves, if they are small in size, they are painless, but in cases where lipomas grow, discomfort sets in, and they can even ache a little when pressed. They can damage other tissues, as well as organs if they are located near the formation.
The reasons for the appearance of such wen can be varied:
- swipe;
- smoking;
- alcohol;
- disorders of the nervous system;
- disorders of the secretion of the sebaceous glands.
Cancerous lump - in shape it can be similar to any formation described above. At the beginning of the development of the disease, no symptoms may appear; in many cases, the lumps are difficult to detect visually. When the formation grows inside the dermis, damaging a fair amount of tissue, it may appear on its surface in the form of a small reddish pimple. Subsequently, it can grow very quickly or, conversely, slowly, and the formation is accompanied by unpleasant sensations and sometimes pain.
What formations hide danger?
The following types of neoplasms require urgent medical intervention:
- Atheroma is similar to a lipoma, but unlike it, it often becomes infected and turns red, and can also increase in size. It is this moment that poses a health hazard, since there is a danger of fistula formation and pus leaking into nearby tissues.
- A median cyst is a congenital benign round formation located on the front of the neck. Up to a certain point, it may not bother the child, but in 60% of cases it becomes inflamed with the formation of a fistula, causing pain and discomfort when swallowing. In addition, the cyst is prone to degeneration into cancer.
- Neurogenic tumors are formed at the ends of nerve trunks and represent a wide range of neoplasms. They can be safe, but malignant formations can also occur. Under no circumstances should they be left without the attention of a doctor.
- Lymphogranulomatosis (Hodgkin's lymphoma) is cancer of the lymph nodes. The first symptom of this cancer is expressed in enlarged lymph nodes, but they do not hurt and slowly enlarge.
The otolaryngologist makes conclusions about the safety of formations only after conducting a comprehensive examination. It is impossible to do this on your own.
Common Causes of Bumps
Most formations on the face are a consequence of an unhealthy lifestyle
Most of the reasons that lead to the formation of a tubercle are a consequence of an unhealthy lifestyle, regular stress, and bad habits. Some of the most common causes of bumps:
- hormonal disbalance;
- violation of diet and sleep patterns;
- poor nutrition;
- allergy;
- bad habits;
- injuries;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- malfunctions of the nervous system.
- infections.
- incorrect selection of cosmetics and skin care.
About the subcutaneous boil
A boil is a purulent inflammation of the skin. There are many reasons for its appearance:
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- metabolic disorders;
- intestinal disorder;
- abrasions and cuts.
Boils are painful subcutaneous pimples on the face that are accompanied by pain at the slightest touch. At the base of this formation there is a purulent rod, and at its tip there is a head filled with purulent fluid. Often they try to remove it to remove the pus, but this only leads to worse consequences: the boil begins to increase in size, damaging more and more tissue. Many, not understanding the danger, try to squeeze out the unfortunate pimple, enduring extreme pain when pressed. But the inflammatory process can only deepen into the skin with such actions.
Under no circumstances should you apply compresses; they only create excess moisture, which contributes to the development and enlargement of acne. To reduce the size of the formation, it is necessary to dry the skin; even heating helps to reduce the inflammatory process and its faster maturation. An abscess will gradually form, which should be lubricated with a special ointment with the addition of an antibiotic; you must first consult a doctor. He will analyze the condition of the pimple and give recommendations for its removal.
Important! Subcutaneous boils on the face are treated comprehensively. It is mandatory to prescribe a course of medications for external and internal use, as well as a complex of vitamins to cleanse the blood. A preliminary examination is carried out, which is aimed at finding out the cause of the disease.
Benign formations
Relatively safe are:
- Lipoma (wen) is a formation consisting of adipose tissue covered with a fibrous membrane. It does not pose a threat to health if it is not inflamed, and is more of a cosmetic defect. Occurs due to disruption of lipolysis processes in adipose tissue.
- A furuncle is an inflammation of the hair follicle, which is a cavity in the skin filled with pus. The causative agent of this inflammation is staphylococcus. Untimely surgical treatment can lead to blood poisoning.
- Fibroma is a benign formation of connective tissue that forms at the site of an injury or scratch. Fibroma is completely painless and does not degenerate into malignant, but nevertheless, it must be kept under control.
- Inflamed lymph nodes are a constant companion of infectious diseases. As you recover, the seals decrease and return to normal.
- An enlarged thyroid gland is a consequence of impaired hormone production. The thyroid gland changes in size due to iodine deficiency or in case of genetic predisposition. The danger of nodular or diffuse goiter is that it can develop into a malignant tumor.
- Inflammation of the submandibular salivary glands can occur if it is blocked by a stone. As a result, saliva accumulates in the gland, causing pain and swelling. Infection may also be the cause of the increase.
Treatment options
Many small formations can appear during a cold, so there is no need to make hasty conclusions and resort to treating them. The body itself will cope with the underlying disease, and then begin to fight the pimples; they will gradually begin to dissolve on their own. They are most often flesh-colored and can appear in the forehead area, along the jaw. The patient may experience discomfort, as such pimples may peel and itch.
Flesh-colored bumps may be the result of a cold
Other types of bumps on the face need to be shown to doctors so that they can prescribe treatment. It will not be possible to get rid of them by squeezing out - this will only lead to damage to the cover, and the compacted lesion itself will not be removed. This may lead to the need to resort to surgery, after which it will be necessary to treat the skin for a long time from the consequences of the patient’s incorrect actions.
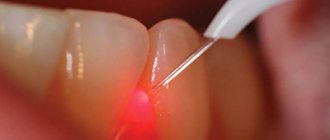
Laser removal of cones allows you to painlessly remove them from the surface of the dermis, while the beam penetrates to the depth of the entire formation and reduces it, pushing the pus out. The use of injections and ointments can help get rid of acne. Most often, this method is used in combination with surgery.
Important! It is worth remembering that after each treatment procedure, redness and induration may persist on the face for another 6-8 days. This is why many people think that the course is not suitable for them or there is no result.
Further skin care
Before resorting to your usual skin care, you should visit a cosmetologist. He will select gentle care that will help restore the skin, and gradually the ulcers will stop hurting. For the first week after treatment, you should care for your skin only with water and a cotton pad; you should avoid all kinds of cosmetics, as they can cause acne to reappear.
After treating subcutaneous diseases, it is worth visiting a cosmetologist
Over the next couple of weeks, you need to use products that will protect your skin from exposure to sunlight. They will also gradually relieve itchy skin after bump treatments.
Preventive measures
In diseases that lead to the formation of acne, improper care, frequent bruises and untreated wounds lead to the appearance of knobby formations. To avoid health problems, you should adhere to preventive measures:
- remember the rules of personal hygiene and follow them. Change your razor in a timely manner, use decorative cosmetics as little as possible, which leads to clogging of pores;
- monitor your diet. It is worth minimizing the consumption of alcohol, sweets, marinades, preservatives, sausages and sauces;
- undergo a complete examination by doctors once a year.
Getting rid of bumps under the skin on your face is difficult on your own. This is best done in beauty salons. Specialists will be able to do this practically without damaging the surface of the dermis.
Gum cancer
Description
A rare dangerous disease. It is characterized by the formation of a dense lump on the gum at the root of the tooth; it can develop asymptomatically for several months.
Treatment
Requires serious medical intervention, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, long-term recovery and follow-up.
Gum cancer, if detected early, is curable, otherwise it ends in death. Red and white bumps on the gums appear in both adults and children. Only a doctor can correctly identify the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. The sooner you see a dentist, the greater the chances of a quick recovery.
Don't self-medicate! If a ball is inflated on your gum and you don’t know what to do, contact a dentist in Odintsovo. The doctor will conduct a full examination of the oral cavity, accurately diagnose the disease, and prescribe effective treatment.
You can make an appointment for a consultation, as well as find out the cost of admission and treatment by calling the clinic in Odintsovo.