Vitamin A
Vitamin A or retinol enhances the protective properties of the skin and mucous membranes. With its deficiency, yellow pigmentation and hypoplasia of the hard tissues of the teeth may appear on the teeth, if this deficiency in the vitamin is revealed during the period of their development. If a deficiency of vitamin A occurs after teething, a disease such as hyperkeratosis and proliferation of the base layer occurs.
With an excess of vitamin A, an anomaly in the development of the jaws and tongue occurs, as well as an anomaly in dentin density.
Bleeding gums
Hepatitis
8249 09 March
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Bleeding gums: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition _
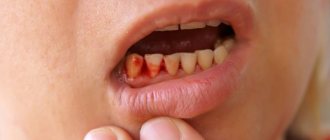
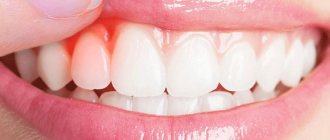
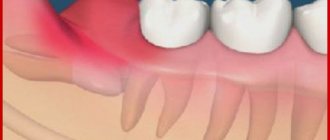
Bleeding gums occur when brushing teeth or chewing hard foods, such as apples or raw carrots. It should be remembered that in some cases this condition may be a symptom of serious oral diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis.
In addition, a large amount of data has now been accumulated proving the relationship between diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular pathologies with inflammation of the periodontium (tissues surrounding the teeth).
Types of bleeding gums
According to the frequency of manifestations, bleeding gums can be chronic, that is, occurring regularly, or be situational in nature - usually in response to gum injury.
Possible causes of bleeding gums
The causes of bleeding gums can be divided into two main groups:
- Pathologies of the oral cavity.
- Pathologies of body systems.
Pathologies of the oral cavity
- Gingivitis
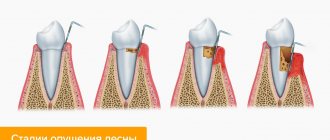
. This disease is characterized by the development of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gums. Symptoms of this condition include redness or bluishness of the gums, swelling and bleeding. In advanced cases, manifestations of the disease interfere with eating and disturb even during sleep.
- Periodontitis
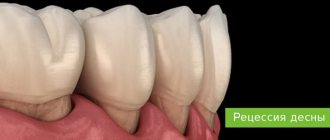
is a disease that requires a visit to the dentist. It is characterized by severe bleeding gums, loose teeth, the necks of which are exposed, resulting in teeth falling out. Periodontitis is often accompanied by severe inflammation, up to the discharge of pus from the pocket that forms between the tooth and the gum.
- Tartar
is hardened food debris and waste products of oral bacteria. It injures the gums, which leads to their bleeding. There are subgingival stones (outwardly invisible) and supragingival stones (visible to the naked eye).
In addition to bleeding, all gum diseases are characterized by the following symptoms:
- unpleasant and painful sensations when touched (pressing on the gums, brushing teeth);
- bad breath;
- increased salivation not associated with other diseases of the oral cavity or gastrointestinal tract;
- dental plaque and calculus;
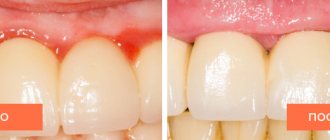
- change in the appearance of the gums (swelling, redness or cyanosis);
- change in the appearance of the teeth (exposure of the neck, change in color due to the deposition of tartar).
Another, albeit rare, cause of bleeding gums is the increased content of fluoride in drinking water.
After water analysis has confirmed the high content of this element, it is recommended to use various filters to purify running and drinking water. The most common pathologies of the body leading to bleeding gums
are vitamin deficiency
. The well-known disease scurvy is associated with insufficient intake of vitamin C in the body, this is manifested by increased bleeding of the gums, impaired collagen synthesis, as a result of which the connective tissue cannot fully perform its functions.
The cause of bleeding gums may be insufficient intake of vitamin A (retinol), riboflavin and pyridoxine (B2 and B6), calciferol (vitamin D, in particular, its variety - vitamin D3), tocopherol (vitamin E), nicotinic acid (vitamin PP ) and vitamin K. The latter not only affects the structure of tissues, but also participates in blood clotting processes.
Hormonal changes in the body
, which occurs during pregnancy and puberty in adolescents, may also be accompanied by bleeding gums.
For diabetes
Small vessels throughout the body are affected, including the oral cavity, retina, etc.
Hepatitis
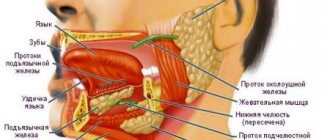
of various etiologies is also characterized by the development of bleeding gums, since many blood clotting factors are synthesized in the liver . Taking into account the fact that the human blood coagulation system works on the principle of a cascade, a deficiency of at least one element leads to impaired hemostasis. Hepatitis is characterized by a mixed type of coagulation disorder, caused by a lack of many vitamins as a result of impaired absorption, a decrease in platelet levels, and damage to the liver as a source of coagulation factors.
Leukemia
, as well as
blood diseases of various types
, leading to a decrease in the number of platelets, or vice versa, increasing blood viscosity, can manifest as increased bleeding of the gums. With these diseases, attention is drawn to pallor of the skin and visible mucous membranes, the appearance of bleeding in various locations, bruises, increased fatigue, and weakness; Night sweats and fever not due to any other reasons are possible.
Which doctors should I contact if I have bleeding gums?
First of all, patients with bleeding gums turn to the dentist.
If the doctor cannot find the root cause of the bleeding, consultation is necessary, or.
Diagnosis and examinations for bleeding gums
If diabetes mellitus is suspected as the cause of bleeding gums, it is necessary to prescribe a glucose tolerance test, determination of glycated hemoglobin in the blood, determination of blood glucose levels on an empty stomach and during the day.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D - regulates the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body, stimulates the growth and formation of bones, and participates in the formation of tissue respiration. With a lack of vitamin D, the well-known rickets develops, as well as dental caries. In addition, a lack of vitamin D leads to a primary state of calcium metabolism. There is an increase in the volume of the organic dentin matrix. Osteoporosis of the bone tissue of the alveolar process may develop, and in severe cases, enamel hypoplasia occurs. With a lack of vitamin D, as well as calcium and phosphorus, rickets occurs in children, and osteomalacia (mineralization disorder) develops in adults.
With insufficient amounts of vitamin D and normal levels of calcium and phosphorus, osteoporosis and resorption of dental cement develop.
With a lack of vitamin D and calcium, but with a normal amount of phosphorus, resorption of the jaws and hemorrhages into the bone marrow spaces may occur.
With a lack of vitamin D along with phosphorus, with a sufficient amount of calcium, rickets occurs.
With a lack of calcium and phosphorus and with normal vitamin D levels, alveolar bone resorption occurs.
With a lack of phosphorus and with normal levels of vitamin D and calcium, there is slow growth of the jaws, delayed teething, which subsequently leads to bite pathologies.
Hypervitaminosis D also leads to negative consequences. First, osteosclerosis occurs, then osteoporosis and resorption of the alveolar process. In addition, intensive formation of tartar occurs, hypercementosis and ankylosis occur. It should be noted that death can occur when large doses of vitamin D are administered.
Why is a child bleeding from his gums - what to do?
Children often suffer from gingivitis. The main prerequisites for the occurrence of the disease are poor oral hygiene, consumption of large amounts of sweets, accumulation of soft and hard deposits, and drinking sugar-containing carbonated drinks. This affects not only the coronal part, but also the mucous membranes. Also, the child’s body is especially vulnerable during the eruption of milk and permanent units. Dentists will advise you on all questions and help you get rid of problems of any etiology.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C - normalizes the permeability of the vascular wall, its strength and elasticity, and also increases its resistance to infection.
The human body is unable to synthesize vitamin C, so it must be obtained from food. With a lack of vitamins B and C, a disease such as scurvy or scurvy develops. In this case, bleeding, hemorrhages in the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles, joints are observed, and degenerative processes develop. Collagen formation is also disrupted and bone tissue formation slows down. Hemorrhagic gingivitis, rapid-onset periodontitis, occurs directly in the oral cavity.
Methods for diagnosing gingival bleeding
Before determining what to do if the gums are bleeding, inflamed and painful, or why there is bleeding between the teeth, the doctor must prescribe certain diagnostic tests to determine the causes of the disease and identify systemic diseases. For this, the following are shown:
- visual and instrumental examination of the oral cavity;
- general blood test, urine test;
- coagulogram;
- stool examination;
- X-ray, CT.
Examining the mucous membranes, the specialist assesses their condition. What is important is the neglect of the inflammatory process, swelling, the severity of redness, the presence of plaque and stone.
In medicine, there are 6 degrees of bleeding (starting from zero and higher as the pathology develops). The method for determining the PBI index (from 0 to 4) is also used.
Local pathologies
Often the answer to the question why gums bleed heavily can be pathological conditions and inflammation of the oral cavity, among which the following diseases should be highlighted:
- Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that weakens the protective functions. Tartar and plaque provoke the proliferation of bacteria, resulting in inflammation, which manifests itself often and this is just the beginning.
- Periodontitis is the spread of inflammation in the internal periodontal tissues, which causes disruption of the tissues between the gums and teeth. Important! If the disease is not stopped at this stage, the inflammation will become chronic and lead to tooth loss!
- If you understand why gums bleed, the reasons may be hidden in periodontal disease. The disease changes the structure of tissues and blood circulation, teeth become mobile.
Causes of vitamin deficiency
Accordingly, the following factors lead to vitamin deficiency.
Nutritional factors. Here we can highlight:
- predominant consumption of foods in which vitamins are present in insufficient quantities and are absent altogether;
- malnutrition. Passion for fasting and other “folk” methods of weight loss often cause hypovitaminosis;
- excess sugar consumption;
- culinary processing or storage conditions that contribute to the destruction of vitamins in foods. The diet must include fresh fruits and vegetables;
Digestive disorders, in particular:
- defects in the mechanisms of vitamin absorption;
- dysbiosis – a disruption of the normal microflora in the intestines (for example, as a result of an infectious disease or antibacterial therapy);
- activation of pathogenic microflora;
- intestinal parasites;
Factors that affect the body as a whole and suppress the immune system. This is, first of all:
- unfavorable environmental conditions (increased background radiation, ingestion of heavy metals, pesticides and other highly toxic substances);
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
Uncompensated increased need for vitamins. The body requires more vitamins than usual when:
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- stress;
- significant physical activity;
- work in low temperature conditions, etc.
Preventive measures
In order not to wonder why gums bleed and what to do, it is necessary to regularly carry out preventive maintenance of the oral cavity and teeth. It is necessary to visit a specialist twice a year for an examination and dental cleaning to detect when inflammation is just beginning. It is necessary to ensure hygiene at home, brush your teeth twice a day, use dental floss and mouth rinses. It is also worth paying attention to your diet, making it balanced and nutritious.
What to do with your teeth if your gums bleed and bleed during pregnancy
The problem can bother women at different gestational stages. It is important to understand that many medications should not be taken by a pregnant woman because they are likely to harm the fetus. The cause of unpleasant symptoms is usually accumulated plaque due to changes in hormonal levels, toxicosis, etc.
Local remedies, as a rule, are not contraindicated. Treatment takes place in several successive stages:
- removal of deposits;
- rinsing with anti-inflammatory compounds;
- establishing a proper diet;
- regular special hygiene.
In the first trimester, intervention should be minimal; if possible, you should avoid any medications, even external use. The dentist will describe in detail what remedies for bleeding gums to buy at the pharmacy, and how to remove dangerous manifestations at the very beginning of gestation. Mid-pregnancy is the optimal time for therapy. Immediately before childbirth, any intervention can lead to increased uterine tone and premature delivery.