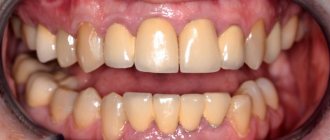
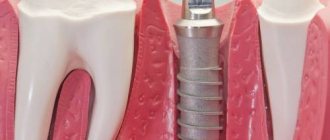
Dental implantation is an operation to restore lost teeth. Instead of a lost tooth, an implant (artificial root) is inserted into the jawbone, and a crown is fixed on top. Like any surgical intervention, implantation has contraindications and limitations. They are absolute and relative. Taking them into account, the doctor reduces the likelihood of complications after the procedure, which speeds up the healing of the implant.
Indications and contraindications for dental implantation
When is implantation indicated?
- Missing one or more teeth in a row. In case of a single defect and the absence of 2 teeth in a row, implants are implanted in place of each tooth with separate crowns. If 3 or more teeth are missing, it is not necessary to restore each tooth with a separate implant - it is possible to install a smaller number with a fixed bridge.
- Absence of terminal teeth. Implants replace lost units and serve as support for prostheses.
- Edentia (absence of all teeth). The situation is diagnosed in older people who did not seek medical help in time. The dentist may suggest installing dentures on 4 or 6 supporting implants.
- Intolerance to traditional dentures. Removable structures cause discomfort in the mouth and irritate the mucous membrane. Structures with extensive defects are not held in place. If the use of dentures is not possible, dentists recommend implantation.
- Malocclusion. With some congenital or acquired defects in the structure of the jaw, the bite is disturbed and the teeth take an incorrect position. If treatment cannot be carried out in any other way, implants are installed.
General restrictions on the operation
- Blood clotting disorders, taking anticoagulants (blood thinners);
- poor oral hygiene;
- bruxism (uncontrollable grinding of teeth);
- diseases that impair the regeneration of bone and soft tissue;
- infectious diseases of the oral cavity (gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis);
- metabolic disorders that slow wound healing and bone restoration;
- insufficient occlusion;
- therapy aimed at suppressing the immune system (radiation, chemotherapy);
- insufficient amount of bone or soft tissue.
Related articles:
- Guarantees of our center
- Possible complications
- Indications for implantation
Types of dental implants
In modern dentistry, different types of dental implants are used. High-quality structures are made from titanium alloys or pure titanium. This material has decent strength, a high percentage of survival in the body and virtually eliminates the risk of allergic reactions.
Dental implants vary in design features and location in the structures of the oral cavity.
Types of dental implants
:
- intraosseous root-shaped;
- intraosseous lamellar form;
- combined;
- subperiosteal;
- zygomatic;
- implants for insertion into the mucosa.
After the engraftment of the titanium root, a permanent crown is installed: zirconium, ceramic, porcelain and others - at the patient’s choice.
Absolute and relative contraindications
Absolute contraindications are those that make the procedure impossible. These include:
- mental disorders characterized by inappropriate behavior of the patient;
- diseases of the blood, hematopoietic organs;
- tuberculosis in the acute stage;
- connective tissue pathologies;
- malignant tumors on the head, neck;
- slowing down blood clotting, complicating stopping bleeding and wound healing;
- chronic alcoholism, drug addiction;
- diseases of the immune, central nervous system;
- impossibility of anesthesia due to allergic reactions;
- congenital anomalies of the jaw that prevent the implantation;
- age under 18 years;
- renal failure.
Relative diseases include diseases and conditions that can be eliminated and then implanted:
- poor nutrition;
- venereal diseases;
- endocrine pathologies;
- diseases of the temporomandibular joint that interfere with opening the mouth;
- anemia;
- viral infections;
- smoking;
- regular stress, exhaustion;
- diseases eliminated by dental treatment;
- insufficiency of bone tissue.
Relative contraindications include chronic diseases that require regular monitoring by doctors (compensated diabetes mellitus, HIV, hepatitis).
Risk factors
These are conditions that are not contraindications, but may reduce the effectiveness of the intervention, require parallel treatment, or for which implantation is considered as a method of intervention.
In these conditions, it is more difficult to achieve a positive result, additional efforts are required, the rehabilitation stage is longer, and the success rate is lower.
The list includes: dysfunction of the maxillary joint, periodontitis, periodontal disease. This also includes smoking and age.
Obstacles to implantation in the upper and lower jaws
The main obstacle to implantation is atrophy of the bone of the upper or lower jaw. After the root of a natural tooth is removed, the alveolar process becomes thinner over time. If you install an implant into atrophied bone tissue, over time it will deteriorate even more, and the metal part of the artificial tooth will be exposed. To prevent complications after implantation, jaw bone augmentation is performed.
Problems when installing an implant in the upper jaw are caused by sinusitis - an inflammatory process in the maxillary sinus of the nose. The infection that causes the disease weakens the immune system and complicates the operation. Since the implants are located near the sinuses, pathogenic bacteria can spread to the jaw tissue. The inflammatory process that develops leads to rejection of the metal part of the implants.
Average cost of treatment in Moscow
| Service | price, rub. |
| Consultation with specialists: | |
| dentist | 600 |
| periodontist | 740 |
| implantologist | 820 |
| Services for the treatment of complications: | |
| laser therapy of the gum mucosa | 490 |
| periodontal applications in the area of one tooth | 370 |
| removal of dental plaque in the area of one tooth | 180 |
| implantation of osteoconductive material in the area of one tooth | 10900 |
| implantation of a protective membrane | 12900 |
| application of a protective periodontal bandage | 400 |
| implant removal | 6900 |
The cost of treating complications after implant placement varies depending on the severity of the consequences , extent of spread and treatment methods .
What explains the restrictions in case of illness?
Diabetes
The disease is characterized by impaired absorption of glucose in the body, which leads to a number of irreversible changes. Diabetes mellitus damages blood vessels, complicates wound healing, and slows down the healing process of the implant. Bone tissue becomes thinner and thinner. This fact further complicates the operation.
But diabetes is not an absolute contraindication to implantation. The procedure is carried out if the patient is receiving treatment and blood sugar levels do not exceed 6 mmol for the last 2-3 months. In this case, if there is a sufficient amount of bone tissue, dentists choose a one-stage implantation method that does not require massive incisions in the jaw tissue. But if diabetes has led to damage to internal organs, excess weight, high blood pressure, implants are not installed due to the risk of heavy bleeding.
Thyroid diseases
Thyroid diseases lead to hormonal imbalance and affect the structure of bone tissue. With hyperthyroidism (excess hormone), mineralization is inhibited and cells do not receive enough nutrients. With hypothyroidism (lack of hormones), the process of bone tissue restructuring slows down.
Both conditions affect the survival rate of implants and create a risk of rejection of the metal part. But if the patient is undergoing treatment, surgery is possible depending on the patient's condition.
Oncology
For malignant tumors, surgery is performed after the patient has recovered. The risks of developing complications from cancer are too great. Surgery is prohibited if:
- there are metastases;
- neoplasms are located in the face, neck, head (damage to the tumor during surgery leads to further metastases);
- chemotherapy and radiotherapy treatment are carried out (the procedure slows down cell regeneration and interferes with healing).
Hepatitis
The disease is caused by viruses, the most dangerous of which are hepatitis B and C. The disease is not considered a contraindication to implantation, but dictates restrictions. They are associated with possible complications after implantation:
- difficulties in stopping bleeding (increased bleeding develops against the background of damage to liver cells, leading to a decrease in the concentration of coagulation factors);
- risks of developing an inflammatory process against the background of a weakened immune system;
- additional burden on the patient's body.
Implantation is possible after therapy aimed at eliminating inflammation. The patient is given an extended list of tests that he needs to undergo before the procedure.
HIV infection and AIDS
HIV is an immunodeficiency virus that attacks cells of the immune system. As a result, the body becomes unstable to infections; even a cold can be deadly.
Implantation for HIV diseases is possible only in the initial stages, if the patient’s immunity is still strong. In the later stages of the pathology, there is a high risk of infection during surgery, which can lead to the death of the patient. Even ordinary bacteria that live in the mouth often provoke the development of inflammation.
Rheumatoid arthritis
This is an autoimmune disease that causes a number of pathological conditions in the oral cavity:
- formation of cysts and gaps between teeth;
- disturbances in the functioning of the parotid glands;
- the appearance of disocclusion of the dentition;
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve;
- destruction of bone tissue;
- deformation of the head of the temporoinferior joint.
Rheumatoid arthritis is not a contraindication to implantation, but the patient will have to undergo a number of tests. Based on the results obtained, the doctor determines the size of the bone structures, the condition of the jaw tissue, and makes a conclusion about the possibility of installing implants. After the operation, the process of engraftment of artificial roots lasts from 3 months to a year . During this time, the patient undergoes regular tests and receives dental consultations.
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the number of red blood cells (erythrocytes) decreases. The consequence is a low level of hemoglobin, which is responsible for the delivery of oxygen to tissues and organs. Since the transport function of the blood is impaired, complications may arise during the operation.
When assessing the condition of a patient with anemia, the doctor pays attention to the rate of development of the disease. If the decrease in hemoglobin levels occurs slowly, the body adapts and does not experience a lack of oxygen. In this case, surgery is possible if the hemoglobin level is at least 90 g/l . If anemia develops rapidly, implants are introduced only after the patient has recovered.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
If a person suffers from cardiovascular pathologies, implantation is contraindicated:
- when using general anesthesia or local anesthesia with epiniphrine;
- with a pacemaker installed;
- at risk of cardiac arrest or heart attack.
If a patient suffers from hypertension, before surgery he visits a cardiologist and undergoes a course of treatment to reduce blood pressure. For such patients, we recommend implantation during sleep under sedation - the person does not experience stress and is calm. Along with the sedative, drugs are administered that reduce blood pressure and correct the functioning of the heart. These measures help minimize blood pressure spikes.
Periodontal disease and periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammatory process in the soft tissues surrounding the tooth. With this disease, the alveolar process in which the tooth root is fixed is destroyed. At a late stage of the disease, the tooth becomes loose and falls out. Implantation for periodontitis is carried out after treatment and elimination of the cause of the disease.
Periodontal disease is a pathology in which the bone tissue of the jaw is slowly destroyed, but there is no inflammation. At an early stage, the tooth remains fixed and does not wobble, so it is not advisable to introduce implants. In the later stages, the root gradually becomes exposed, the tooth becomes loose and falls out. In this case, the only way to restore lost teeth is implantation.
Why is this possible
Thanks to technologies, materials and the skillful hands of doctors, the ROOTT MCDI performs the most complex operations with a high success rate.
Implants
Swiss implants ROOTT - a line of more than 250 types of products
, which can be selected for any clinical case. With this choice, it is easy to combine different models. All elements of implantation systems are made of the same alloy, so complications in the form of galvanosis are excluded.
The hydrophilic coating ensures rapid survival, and the special thread ensures initial stability.
Trate AG is one of the few that produces basal and pterygoid models - dental implants, the contraindications for the installation of which are very limited. They are longer than usual and have a special design. This allows installation into the deep, cortical layers of the jaw, which are not subject to bone tissue atrophy. Basal implantation and installation of pterygoids have a high survival rate, over 98%
.
Technologies
The clinic uses innovative methods for installing dental implants:
- One-step protocol. Temporary dentures are installed simultaneously with the implants, without waiting for engraftment.
- Transgingival method of installation. A minimally invasive operation in which a pin is screwed through a puncture in the gum. Allows you to avoid cuts and seams.
- Single-stage implantation. The pin is inserted immediately into the socket of the extracted tooth, without waiting for the wound to heal.
Contraindications to simultaneous implantation, transgingival and one-stage, are not so extensive. Patients with severe chronic diseases receive good results.
With the participation of implantologists from the ROOTT MCDI, an innovative ReSmile protocol was developed, in which it is possible to restore the entire dentition in 4 days
. Prosthetics are performed on an unlimited number of implants, immediately after implantation. 14 teeth are restored, just like in a natural jaw.
The clinic’s doctors also use other protocols: All-on-4 (jaw on 4 pins) and All-on-6 (jaw on 6 implants).
That is why operations have become possible in patients with infectious, endocrine diseases, serious heart diseases and in the elderly.
What other conditions affect the possibility of installing implants?
Features of implantation in women
The female body is characterized by a number of conditions that cannot be called pathological, but they become temporary obstacles to the implementation of implants:
- Menstruation. Doctors recommend refraining from surgery during menstrual bleeding. The main danger is excessive blood loss and the possibility of uncontrolled bleeding. The operation is complicated by the high risk of blocking blood vessels, since during menstruation the blood in the female body has increased clotting. During menstruation, patients are susceptible to nervous breakdowns: the procedure can harm the woman’s morale.
- Pregnancy. Anesthetics and other medications, X-rays have a negative effect on the unborn child. Also, during pregnancy, the immune system is weakened and cannot fully resist pathogens, which creates a risk of developing inflammation.
- Breast-feeding. During breastfeeding, medications administered to the patient pass into the milk. Toxic substances cause allergies and other undesirable consequences in the baby.
A woman needs to wait until these conditions pass. Then it will be possible to install implants.
Are there any restrictions for older people?
Older patients must be sent for examination of the state of their health. If older people do not have general obstacles to the procedure, implantation is not contraindicated, but the recovery period takes longer. This is due to a slowdown in regeneration processes in old age. To reduce the risk of complications, dentists carefully prepare the patient’s oral cavity and choose minimally invasive surgical methods.
Is implantation performed for children?
in children under 18 years of age . As a child grows, jaw bones grow and teeth change. If an implant is placed in childhood, over time it will become too small and will have to be reinstalled. If the baby does not have dental units, dentures are used. The issue of implantation is decided upon when the child reaches the age of 18-22 years.
Is it possible to install implants for smokers?
Smoking increases the risk of implant failure. One cigarette smoked after surgery reduces tissue repair by 30% . But this is not the only danger. When smoking, the mucous membrane burns and the wounds heal slowly. A bad habit leads to disruption of saliva production. The mouth constantly feels dry, the mucous membrane is not cleared of pathogenic bacteria, and the risk of infection increases.
Possible mistakes of surgeons
Negative consequences can occur even during careless operation. Let's name a few medical errors that, unfortunately, although rarely, happen.
Sometimes the doctor inadvertently overheats the head of the titanium root. This occurs due to overheating of the bur and hollow in the jaw bone. The reason for this is untimely irrigation of both.
If the doctor begins to tighten the implant screws while the cement is hardening, this ultimately leads to incorrect root installation, since the cement in this case cracks.
If the doctor does not place the head of the implant tightly in the hollow of the jaw bone, there is a risk of inflammation occurring, as bacteria enter the gap. In addition, loose placement of the head can lead to an imbalance of mechanical load on the entire prosthetic structure. This can cause peri-implantitis.
Correct diagnosis and planning are the key to success
For the procedure to be successful, the patient needs to carefully prepare for it. An important role in the process is played by examination to identify contraindications and possible limitations.
Diagnostics is carried out in 3 stages:
Initial examination of the patient
It includes a conversation between the dentist and the patient to collect anamnesis, and an examination of the oral cavity. The doctor informs the patient about the obstacles to the procedure, talks about methods of treating diagnosed diseases, features of implant installation, and possible complications.
Analyzes
After the examination, the dentist prescribes a number of tests for patients with a history of diseases that may become an obstacle to implantation. They are necessary to assess the patient’s health status and identify diseases of internal organs. Before installing implants, it is recommended to undergo a general and biochemical blood test, urine test, and tests for viral hepatitis and HIV. Women take a pregnancy test.
CT
Computed tomography is prescribed before surgery for a detailed study of the structure of the teeth, identifying the remains of the root of a destroyed tooth, etc. After the introduction of an artificial root, research is necessary to monitor the engraftment process and prevent complications.
If the patient's condition is satisfactory, a treatment plan is drawn up. At the preparatory stage, the patient needs to take future surgery seriously. Do not hide conditions from your doctor that may lead to complications. Honesty in your relationship with your doctor ensures a quick recovery period.
Research and diagnostics can be performed at our Center for Private Dentistry “Doctor Levin”. The surgical department staff includes a neurologist, anesthesiologist, therapist and otolaryngologist. Laboratory tests can be taken without leaving the clinic.
EARLY COMPLICATIONS
It is necessary to distinguish between complications and consequences of the operation. Complications require rapid intervention by specialists; the reason for their development often lies in problems of the body or incorrectly performed surgical intervention. While the consequences of the operation are the inevitable result of tissue injury, which always appears and, as a rule, does not pose any threat to the patient’s condition, but is a normal reaction of the body.
Consequences or normal processes that occur after implantation and do NOT require prompt contact with a specialist:
- bleeding, which gradually decreases and goes away on its own within a day,
- pain due to tissue injury, the intensity of which also gradually decreases,
- swelling of tissues,
- temperature rise to 38 degrees
- slight numbness of the jaw in the area of installed implants.
The following are complications that arise during the installation of implants or a few weeks after (symptoms of problems may arise a little later - after the anesthesia wears off and even 2-3 days after the operation). The important thing is that problems that arise in the first few days or weeks after the installation of implants are quite easy to solve. The main thing is to contact your implantologist in time.