I recommend placing a crown on a living tooth if:
- Destruction of
the crown part of the tooth
more than 55%
(trauma, caries, large chip, crack) with normal pulp condition. - Intensive abrasion of enamel
. - The tooth serves as a support for attaching the bridge.
In addition, orthopedic structures using crowns are placed on loose teeth during the treatment of the underlying disease that caused tooth mobility. Sometimes it is possible to place crowns on severely crooked teeth.
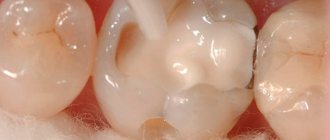
Crown for a living tooth
When to place a crown on a living tooth
Stages of installing a crown on a living tooth
Types of crowns. Their pros and cons
When does pulp need to be removed?
Myths about dental crowns
The question of whether it is possible to put a crown on a living tooth has gathered many myths and prejudices and divided people into two camps. When you can put a crown on a living tooth, and when not, what are the pros and cons of both methods, we will consider in this article.
First, let's figure out what a living tooth means. A tooth is an organ consisting of a protective layer (enamel, dentin, cement) and a neurovascular bundle (pulp). A tooth is considered alive if the pulp is preserved, and dead if the pulp is removed - this procedure is usually carried out in the treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis.
Reasons for installing a crown without removing the nerve
To preserve the tooth, dentists try to maintain blood supply and innervation. After removing the nerve, the enamel is quickly destroyed, exposed to external influences, and caries appears. Whenever possible, the tooth is left alive.
Cases of crown installation without pulp removal:
- destructive gum diseases that lead to loose teeth;
- grinding of teeth located next to problem ones for further installation of crowns, bridges, clasp dentures;
- partial destruction of the crown as a result of mechanical trauma;
- installation of veneers for aesthetic purposes;
- the tooth has changed color and is very different from the others;
- destruction is less than 50%.
Please note: Sometimes patients complain that after installing a crown on a living tooth, pain and swelling of the gums remain. These symptoms are not directly related to the procedure. The main causes of negative consequences are the abnormal location of the channels. Violations of the preparation technique are observed less frequently.
When to place a crown on a living tooth
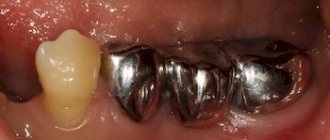
A crown is a permanent cap-shaped structure that is similar in appearance to a natural tooth. Typically, a crown is installed on severely damaged teeth, when restoration with conventional filling materials is impossible or ineffective, since due to heavy loads, cracks may appear on the filling.
Indications for crown installation
- the tooth is destroyed by caries by more than 50%;
- the tooth is destroyed as a result of injury;
- the tooth has become gray or yellow, and stands out strongly against the background of other teeth.
Often, before installing a crown, the tooth is depulped, that is, the neurovascular bundle is removed from the root canals. However, in some cases this procedure is not carried out. The decision whether to perform depulpation or not is made by the doctor, based on clinical indications.
Cases when a crown is placed on a living tooth:
- the tooth is healthy, but due to destruction it cannot perform its functions;
- demineralization and fragility of enamel;
- using a tooth as a support for a bridge;
- destruction of the crown as a result of mechanical trauma;
- tooth loosening due to gum disease.
Why put a crown on a living tooth?
The neurovascular bundle (pulp) is the tissue that is located inside the tooth. It performs several functions: it delivers nutrients to the tooth and protects it from pathogenic microorganisms. After removal of the pulp, the tooth becomes fragile and vulnerable, as it is left without protection and does not receive nutrition, which leads to the destruction of enamel and the rapid development of caries. Therefore, preserving the pulp is a guarantee that the tooth can serve for many more years.
Sometimes after prosthetics, patients complain of toothache and swelling of the gums. This has nothing to do with the fact that the tooth was not pulpless. The main reasons are untreated diseases, incorrect technique when grinding down the enamel, and damage to the canals during preparation. If you experience these symptoms, you should make an appointment with your doctor.
Why do you need a crown?
A dental crown is a microprosthesis that is used to eliminate dental defects and restore the shape and chewing function of the tooth. It looks like a cap that is put on the tooth and completely conveys the color, shape and position of the teeth.
Most often, a crown is installed on a tooth when it is badly damaged and a regular filling is not enough. But this process has its own nuances, the main one of which is the fact that the tooth must be ground (filed) so that the crown is well fixed. Such grinding used to lead to the fact that the tooth had to be depulped, in other words, to make it dead by removing the dental nerve. However, there are cases when this process can be avoided and the tooth can be left alive.
It is worth remembering that the decision about whether the nerve needs to be removed or left is made only by the doctor, based on your clinical indications.
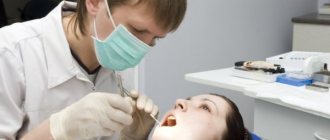
Stages of installing a crown on a living tooth
Installing a crown will require several visits to the dentist
Table 1. Stages of installing a crown on a living tooth
| Stage name | Procedures |
| Initial examination and diagnosis | Consultation with an orthopedist, examination of images, development of a treatment plan |
| Preparing to install a crown |
|
| Preparing a tooth for a crown | Using a drill, the doctor shapes the tooth so that the crown can be firmly attached to it. To do this, a layer of enamel is removed, the thickness of which depends on the thickness of the future crown. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. |
| Making crowns | After preparation, the doctor takes impressions. Based on them, a plaster model is first made in a dental laboratory, and the crown is cast from it. If making a crown takes several days, the patient is given a temporary crown, which protects the tooth from bacteria and mechanical damage. |
| Fitting and fixation | Before installation, the doctor tries on the crown on the tooth. If the patient does not feel discomfort during fitting, the crown is fixed to the tooth using dental cement. |
Materials used
In dental prosthetics today, several types of materials are used, which make it possible to create structures that differ in cost and purpose, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Plastic
Due to its financial accessibility, plastic has long remained the most popular material. But its main indicators are significantly inferior to innovative materials, which is why it is used mainly only for temporary prosthetics.
Plastic dentures are short-lived - they quickly change shape and collapse. It is almost impossible to make such crowns aesthetically pleasing and comfortable. They absorb all kinds of odors well and can be colored with food dyes.
Plastic is a porous material in structure, which makes it favorable for the active reproduction of pathogenic microflora.
Important! The only way to protect yourself from the occurrence of pathologies and at the same time extend the life of a plastic prosthesis is regular and high-quality cleaning of the structure itself and the teeth.
Ceramics
The main advantage of ceramics is its high aesthetics due to the closeness of its shade to the color of the enamel coating.
Visually, crowns made of this material are indistinguishable from natural teeth, i.e., in color and transparency they match natural dental units. Modern technologies have made it possible to increase the strength of ceramics, which makes it possible to use it in the restoration of chewing elements.
Another advantage of the material is its lightness, i.e. the dentures are almost imperceptible in the oral cavity. Preference should be given to ceramics for those patients with a predisposition to allergies.
Important! Ceramics are safe for allergy sufferers. It leads to redness of the gum tissue, bleeding, swelling and inflammation in exceptional cases.
Disadvantages of the material include fragility and high cost. In addition, ceramic dentures require compliance with safety rules and careful care when worn.
Zirconium dioxide
Prostheses based on zirconium dioxide are considered the most advantageous method of dental reconstruction due to the following advantages of the material:
- High aesthetics. Dentists recognize zirconium dioxide as the best material for creating dentures. Artificial teeth made from it are visually indistinguishable from anatomical organs in color, transparency and structure.
- Incredible strength. After firing, this material acquires strength comparable to that of metal.
- Possibility of gentle grinding of teeth for a crown. A zirconium prosthesis is thinner than a metal-ceramic one, which means you can preserve more of your own tooth tissue.
- Biocompatibility. There are no manifestations of an allergic reaction or galvanism.
- Long service life, reaching up to 20 years if certain requirements are met.
Prosthetic structures made of zirconium dioxide have virtually no restrictions on installation, are characterized by an ideal fit to the gums, and are resistant to constant chewing loads.
The disadvantages of such crowns include:
- high cost;
- are not very suitable for prosthetics of anterior teeth due to the smaller choice of shades (than with ceramics);
- insufficient strength of the connection between the frame and the facing layer of porcelain, which is why chips occur on the porcelain;
- acceleration of physiological wear of antagonist teeth.
For many patients, these disadvantages are significant and are a strong argument for refusing to place zirconium dioxide crowns in favor of other materials.
What are ceramic composite crowns, their advantages and disadvantages.
In this publication, we will find out why there is an unpleasant odor from under the crown and what to do in such a situation.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/protezirovanie/nesemnyie-p/koronki-np/dostoinstva-farforovyih.html we will look at the technology for making a porcelain crown.
Types of crowns. Advantages and disadvantages
Metal-ceramic crowns are rarely installed on a living tooth, since before installing such products, a significant layer of enamel must be removed. Therefore, metal-free structures are most often used: ceramics and zirconium dioxide.
| Ceramic crowns ➕ High aesthetics. Such crowns are indistinguishable from natural teeth. They are very light and almost imperceptible in the mouth. Ceramics can be used for people prone to allergies. ➖ high cost and fragility of the product. Ceramic crowns are not suitable for chewing teeth. |
| Zirconium dioxide crowns ➕ Considered the most in demand. Zirconium dioxide is a very strong and durable material. Just like ceramics, it looks natural, does not require significant grinding of teeth, and is hypoallergenic. ➖ high cost, not suitable for restoration of anterior teeth. |
Materials
The choice of materials for making a replacement crown is determined by both medical indications and the wishes of the patient. Today, clinics have a variety of options to choose from, among which the most popular are:
- Polymers - plastic is still an economical and affordable option, but its performance characteristics leave much to be desired;
- Ceramics is an aesthetic, but fragile material, the advantages of which include the lightness and hypoallergenicity of prostheses;
Zirconium dioxide is an option recommended by most clinics, characterized not only by its biological compatibility with oral tissues and a visually attractive structure, but also by its long service life.
When does pulp need to be removed?
Depulpation is not a mandatory procedure before prosthetics, but it cannot be avoided if there are the following indications.
- Advanced caries or caries at the very root of the tooth.
- Pulpitis or periodontitis.
- Partial exposure of nerves during grinding of enamel.
- Anatomically incorrect position of the tooth.
- Tooth injury, which may result in partial death of the nerves.
- Hypersensitivity.
- Low landing crown.
If there is a need to remove the nerve after the crown has been installed on a living tooth, then depulpation can be carried out without removing the crown. The doctor makes a hole, removes the nerve, and then fills the hole with polymer. After such a procedure, the prosthesis does not lose its performance properties.