About a century ago, people did not pay much attention to the health of teeth and treated them mainly on the basis of the fact: if something hurts, we try to heal it or pull it out, and if it doesn’t hurt, then we don’t touch it. Not much attention was paid to irregular teeth. But with the development of science, it became clear: dental defects require correction. Only the correct arrangement of teeth in the mouth protects a person from premature destruction of molars and incisors, overstrain of the facial muscles and nearby joints. But even now, not everyone understands what an incorrect bite leads to and what its danger is. Let's look at 19 of the most popular consequences that await owners of teeth with anomalies.
What is overbite
Bite is the relationship between the lower and upper dentitions with full closure and maximum contact. This is the first parameter that a competent orthodontist evaluates in a child or adult. Basic bite problems can be determined even by eye: the doctor just needs to ask the patient to clench his teeth.
There is a correct (normal, physiological) bite, in which the load on the teeth is uniform, and a pathological one. Malocclusion can develop at any age due to various factors. It greatly affects the body and general condition of a person.
Diagnostics
Only a qualified specialist can determine the degree of jaw curvature. This does not require high-tech equipment - the doctor just needs to look at the position of the dentition in several positions.
But, in order to decide which method to use to correct a particular defect, the orthodontic patient will have to undergo a series of examinations, including:
- clinical examination;
- X-ray examination;
- intraoral photographs and facial photographs from various angles;
- measuring the size of the jaws, dentition and teeth;
- assessment of the condition of the muscles of the maxillofacial apparatus;
- deviations in the position of the tongue during swallowing are examined.
In addition, a number of other examinations that are important for making a diagnosis are carried out, which make it possible to accurately and qualitatively determine the degree of neglect of the case.
In particularly difficult situations, radical measures may be required, such as removing several units and even surgery.
What kind of bite should a person have?
Physiological or normal occlusion has the following characteristics:
- all teeth of the upper and lower jaws are in contact with each other, with each tooth intersecting with two antagonists. The exception is the third upper molar and the first lower incisor;
- the midline of the face passes between the central incisors;
- there are no gaps between individual elements of the rows;
- The upper dental arch has the shape of a semi-ellipse, the lower - a parabola.
Correct bite on the sides and front
There are also several types of slight changes in the ideal bite, which, although different from each other, do not require correction:
- orthognathic. The upper incisors overlap the lower ones by a third;
- progenic. The lower jaw is slightly protruded;
- straight. The incisors meet with cutting edges;
- biprognathic. The incisors are inclined towards the vestibule of the mouth, but continue to close.
There are three types of normal occlusion, which replace each other over time:
- Temporary. This is what dentists call baby teeth in children.
- Removable. This is a condition of occlusion when some of the baby teeth have been replaced by permanent teeth, and some are still present.
- Constant. All teeth changed from baby teeth to molars.
Problems with a person’s bite can appear at any stage, but baby teeth are much more susceptible to influence: both negative and positive. That is why the process of treating abnormalities in childhood is faster and easier.
How to identify malocclusion
In most cases, malocclusions are easily recognized by an experienced doctor during a routine visual examination. But there are situations when part of the row has not yet been cut through. In this case, additional examination may be required to find incorrect teeth and determine whether there is any risk of developing serious pathologies.
Teeth that have not fully erupted are called impacted. Read in detail about them in our article: “What are impacted teeth, why do they appear and how to treat them...”
Malocclusion in adults and children is diagnosed using the following research methods:
- panoramic photograph of the jaw;
- CT scan of the jaw;
- teleroentgenogram (TRG image).
The listed materials provide an experienced doctor with enough information to identify bite problems and create an up-to-date treatment plan.
Different types of bite studies
Diagnostic measures
The first doctor you should contact if an abnormality is noticed should be a dentist or neurologist. If you need to connect a doctor of another specialization to the diagnosis - an otolaryngologist, an oncologist, a neurosurgeon - the first receiving doctor will refer the patient to them.
Cosmetologists also claim to be the first to visit, claiming that in case of facial asymmetry caused by hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles, cosmetic procedures alone may be sufficient to solve the problem.
The list of dental diagnostic measures is as follows:
- Survey . The patient's complaints are listened to and the medical history is clarified.
- Physical examination . The degree of anomaly at rest and movement is assessed, probing, palpation and percussion are performed. The clinic of the dentofacial apparatus is assessed (presence of edema, tumors, suppuration, consequences of injuries, condition of the teeth).
- X-ray of the jaws . Photographs of individual teeth, dentition (orthopantomography and teleradiography) and nasal sinuses are taken. If necessary, radiographs of the skull and spine in the neck area are obtained.
- Ultrasound examination. Sonography of sinuses, tissues, salivary glands.
- CT or MRI. Used for detailed study and clarification of symptoms obtained by radiography.
- Orthodontic examination . Cephalography, determination of bite, occlusion, presence of supercontacts, analysis of diagnostic models in the articulator, etc.
When doctors of other specializations participate in the diagnosis, the following examinations may be carried out:
- From a neurosurgeon . A CT scan of the brain is done.
- See a neurologist . The innervation of the facial muscles is checked - by wrinkling the forehead, puffing out the cheeks, raising and lowering the eyebrows, and following the doctor’s movements with the eyes. The exit points of the nerves are palpated.
- See an otolaryngologist . Special examinations are carried out - diagnostic puncture, echosinusoscopy, tuning fork examination, audiometry.
If necessary, general laboratory tests are performed. The blood is examined for the presence of inflammation and bacterial infection. Cytological and histological analysis of punctates and smears is carried out.
Based on the diagnostic results, a conclusion is made about the causes of the anomaly, and a treatment plan is drawn up.
Types of malocclusion
When the dentist discovers the first signs of malocclusion, he tries to understand what kind of dental problems he has encountered. Depending on the characteristics of the development of specific anomalies, several types of pathological changes in teeth are distinguished.
The most popular is Engle’s system, which distinguishes three classes of violations:
- Class I: Includes disorders in which the molars are positioned correctly but there is slight crowding, diastema, or other abnormalities.
- Class II: This includes malocclusions in which the position of the molars shifts and the upper jaw moves forward strongly.
- Class III: Includes anomalies in which the teeth shift and the mandible moves forward.
Each class may include one or more subclasses, which are distinguished depending on the severity of the disease. It is also customary to distinguish the five most popular types of malocclusion: distal, mesial, deep, open, cross.
Distal bite
With a distal bite, the upper jaw is overdeveloped, while the lower jaw remains small and weak. This results in the upper teeth greatly overlapping the lower teeth. The face acquires a slanted profile when a person’s lips are thin, retracted, and the chin often becomes double.
There are two types of distal bite:
- the incisors are inclined forward;
- the incisors are inclined backwards.
Almost always, people with a distal bite have a hunched back and a forward tilt of the head. This happens because in a different position the upper jaw blocks the airways.
Mesial bite
A mesial malocclusion is a protrusion of the lower jaw. It turns out to be more developed than the lower one, so the lower teeth often overlap the upper ones. People with this anomaly have a protruding chin, which makes the profile appear “energetic” and “masculine.” The occurrence of the problem is most often associated with the presence of an extra tooth, too large lower teeth, or incorrect placement of the jaw in space (the upper one is in the posterior position or the lower one is in the anterior position).
Deep bite
A deep bite is a situation where the upper (front) incisors overlap the lower ones by more than half their height. Partial overlap is normal. The upper incisors are usually larger, so they cover the lower ones by a third. With a deep bite, the lower incisors are practically invisible.
Open bite
An open bite is characterized by a lack of closure. People with this type of malocclusion are easy to recognize: they have a clear distance between the teeth of the upper and lower jaw. Usually the problem appears due to underdevelopment of incisors, canines or molars, most often the upper anterior incisors.
Crossbite
A crossbite is an abnormality where one of the jaws narrows and moves to the side, causing the teeth to be unable to find their “mate.” People with this anomaly are characterized by noticeable facial asymmetry.
Features of open, deep, cross, distal and mesial bites
Surgical treatment of mandibular hyperplasia.
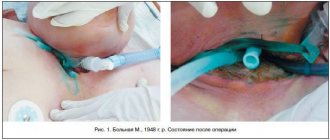
If the height of the mandible is significantly increased, facial symmetry may be improved by surgical reduction of the lower edge of the jaw. High condylectomy surgery effectively stops disproportionate jaw growth while maintaining normal jaw function. Patients with active hyperplasia are treated with high condylectomy, articular disc reduction, and orthognathic surgery. The pathogenesis is most likely related to a disorder of condylar hyperactivity, which can be documented histologically by actively proliferating cartilage. Hyperplasia of the hemimandibular, including the condyle, requires more careful treatment planning compared to these anomalies limited to the ramus and body of the mandible, which require an accurate diagnosis to ensure appropriate treatment.
Causes of pathological bite
There are many reasons for malocclusion. In most cases they are the same for children and adults. A harmful myofunctional habit such as a love of chewing a pencil and many other factors can serve as an impetus for the appearance of disorders.
There is an opinion that dental malocclusion occurs only in children, but it is erroneous. Birth defects usually appear in childhood. In adults, changes are often associated with injuries, unhealthy lifestyles, and advanced diseases of teeth and gums.
In children
The causes of incorrect jaw position and abnormal development of teeth in a child can be called:
- injuries that the baby received during childbirth, if there were complications;
- poor heredity and genetic tendency to an irregular jaw shape;
- malnutrition of the fetus during pregnancy, which may be associated with a woman’s illness;
- the formation of mouth breathing, which not only moves the teeth, but also prevents the nasal sinuses from fully developing;
- Incorrect positioning of the baby during breastfeeding or bottle feeding;
- love for prolonged sucking of collars, fingers, toys, abuse of pacifiers;
- rickets or disruptions in the body’s metabolic processes, as well as poor nutrition, lack of food with fluoride and calcium;
- incorrect position during sleep, thumb sucking during sleep;
- delayed replacement of temporary teeth with molars and too early start of teeth change.
In adults
The appearance of malocclusion in an adult is almost always associated with one or more reasons from the following list:
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx, especially affected by constant nasal congestion;
- multiple carious lesions of teeth, in which a person incorrectly distributes the load on the jaws;
- improper and poor nutrition due to which the teeth do not receive the necessary vitamins and minerals to restore the protective layer of enamel, as well as metabolic failures in which the body cannot extract the necessary microelements from food. The lack of fluoride and calcium has a particularly negative effect;
- injuries of the dental system, etc.
Consequences of malocclusion
Each age has its own critical effects that incorrect teeth can have on the human body. But while in an adult the influence is often unnoticeable, in a child it can lead to developmental anomalies in many systems and organs. That is why it is important to remember what will happen if the bite is not corrected, and to deal with the problem in a timely manner.
Temporary
The temporary bite is formed from 6 months to 6 years. The process usually takes place in two stages: first, the primary teeth erupt. With proper development of the child, this stage ends around 3 years, after which active growth of the jaws begins. This period is a kind of preparation for the eruption of permanent teeth.
Abnormal development of the upper and lower jaw
Incorrect temporary bite usually occurs due to disturbances during pregnancy, birth injuries and poor heredity. Problems also appear if the child does not want to give up the pacifier, replaces it with a finger in the mouth, or has breathing problems.
The most important consequence of malocclusion of primary teeth is underdevelopment of the jaws. The child's body simply does not understand what size they should be and stops jaw growth too early. There is also the opposite case, when the oral apparatus turns out to be overly developed and massive. If left untreated, the problem will cause permanent teeth to erupt improperly.
Removable
A mixed bite is called a removable bite, in which some of the baby teeth have not yet been replaced by permanent ones. There is an early mixed dentition, which is formed at 6-9 years of age. The first to be replaced are the molars, and behind the baby teeth the first permanent molars, the “sixes,” appear. Late mixed dentition begins to form at 10 years of age. At this age, premolars and canines grow. With a correct change of bite, the permanent teeth do not come into contact with the milk teeth and quickly take their place.
Irregular eruption of permanent teeth
Dental disorders in the mixed dentition are caused by elements that fall out or are removed too early: they leave cavities and gaps, which is why the formed permanent teeth grow without the correct orientation. This can cause twisting, incorrect placement of teeth in space and other problems. This is why baby teeth need to be treated rather than removed.
Constant
At the age of 12-15, a person’s milk teeth are replaced by permanent ones, and most of the molars, except for the “eights,” also grow. At this age we can talk about a fully formed permanent dentition. If baby teeth grow correctly, we can hope that the molars will also be positioned correctly. Although this is not a guarantee, this is often the case. But, if a person has developed an incorrect bite, the consequences cannot be avoided.
Decreased chewing activity
Malocclusion almost always leads to a decrease in chewing activity. The teeth do not touch each other, so a person simply cannot provide sufficient force to chew food. He makes a lot of movements without getting the desired result, and as a result, he often refuses to chew properly at all. Because of this, large pieces of food enter the stomach, which are difficult for the body to process; a person does not receive enough nutrients from food.
Temporomandibular joint disease
The temporomandibular joint is one of the most mobile in the human body. But it also cannot withstand too much stress. If the teeth are positioned incorrectly and the chewing function is impaired, overload cannot be avoided. Also, improper bite of the teeth causes disturbances in movement in the joint, the appearance of clicks, and pain. In the most negative version, the TMJ becomes completely stuck: the person opens his mouth, but cannot close it.
Uneven chewing load on teeth
One of the signs of a correct bite is an even load on the teeth. When chewing, each molar and premolar performs its function by cutting or grinding food particles. The absence of an element in the dentition or their weak contact leads to the fact that one tooth “works” and the other does not. This is especially noticeable in an open bite.
Increased enamel wear
Uneven loading invariably leads to frequent use of the same tooth surfaces. Because of this, the enamel suffers, which is damaged in certain places and begins to wear off faster. Weakening and abrasion of enamel almost always causes tooth disease.
Damage to bone tissue
Damage to bone tissue is almost always caused by the absence of one of the elements in the bite. If there is no tooth, the load that it took upon itself falls on the bone. Due to the formation of the cavity, chewing mainly occurs with adjacent molars or canines, but such disorders also have a great impact on bone tissue.
Periodontitis
Gum inflammation is almost always associated with a malocclusion. And the stronger the disorder, the more often inflammation will occur. They are especially familiar to people who have crooked teeth. Periodontitis can also occur due to constant damage to the gums by food or adjacent elements of the dentition.
Early tooth loss
It is possible to lose teeth early even with a normal bite, but due to increased wear of the enamel, the risk of developing caries and other diseases increases. This leads to early destruction of the crown, and even to inflammation of the pulp.
Impaired diction
Diction disorders due to malocclusion are usually associated with the fact that a person cannot ensure the necessary passage of air through the oral cavity. But it is precisely this action that makes it possible to pronounce some sounds correctly. If there is no barrier in the form of teeth, speech sounds incorrect.
Aesthetic violations
While a small deep bite may not be noticeable, a cross bite is immediately visible and looks very unaesthetic. Violations extend not only to the teeth hidden in the mouth, but also to the facial skeleton. Facial asymmetry is a common consequence of malocclusion.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Gastrointestinal diseases most often occur after a long life with dental disorders. The problem is related to insufficient chewing of food. The gastrointestinal tract has to take on the function of teeth, processing too large pieces of food. This leads to rapid wear and tear of organs.
Difficult oral hygiene
Uneven teeth are very difficult to clean. Due to the appearance of too small or too large gaps between the teeth, cavities appear that are inaccessible to the brush, where bacteria accumulate. Only an irrigator or dentist can help ensure an adequate level of hygiene.
Difficult prosthetics and restoration
Most orthodontic surgeries are simply not performed for malocclusions, as there is no point in them. Tooth restoration is available, but chewing disorders and excessive stress will lead to rapid wear of the prosthesis. That is why most dentists first recommend correcting the bite, and then doing restoration.
Breathing problems
The airways are located in the lower jaw area. If it is displaced, then the person cannot breathe fully. This can cause snoring and even nighttime breathing apnea.
Bruxism
Bruxism is excessive clenching of teeth and grinding. It occurs due to problems with the temporomandibular joint, as well as if the dentition is positioned incorrectly. Bruxism is a complex problem and can occur for other reasons, but malocclusions cause it quite often.
ENT diseases
The appearance of various ENT diseases is usually associated with constant inflammation in the oral cavity. Both systems are nearby, so inflammatory processes in the mouth quickly spread to the nasopharynx. And they appear in the mouth due to lack of care and a good environment for the development of bacteria.
Traumatization of soft tissues of the oral cavity
Soft tissue injury usually occurs if one of the teeth is positioned incorrectly. It can be moved forward or to the side. The sharp edge often scratches the mucous membrane, causing non-healing abscesses to appear on it. The problem can be solved locally: just sharpen the tooth.
Gum recession
Gum recession is the exposure of the root portion of the tooth. It usually occurs due to improperly distributed chewing load. Because of this, the teeth themselves become much more sensitive, and inflammation occurs.
Possible complications
The consequences depend entirely on the underlying cause of the anomaly and the timeliness of contacting a doctor. In some cases, the problem can be eliminated without a trace with a quick cosmetic procedure or a light bite correction.
In others, if the problem is ignored for a long time, it can result in significant destruction of the temporomandibular joint, with no guaranteed hope for a complete restoration of its function.
Thirdly, create a serious threat to life itself (in case of malignant tumors).
Only a doctor can give an accurate answer to the question about the consequences of pathology after a thorough examination. In any case, the only correct action for the patient will be to consult a doctor as quickly as possible when a pathology is first detected.
How to correct an overbite
Modern dentistry has come up with dozens of ways to correct malocclusion. Most often, braces are used, followed by retainers to prevent teeth from moving apart. Other adjustment methods:
- wearing trainers;
- use of records;
- aligners and aligners;
- surgical intervention.
An orthodontist is involved in the treatment of malocclusion, about whose work we wrote a separate article. Read more about treatment and diagnostics here: “What an orthodontist treats: what diseases does this doctor treat…”
Conclusions. Expert advice
The correct position of teeth is very important for a person. Bite abnormalities can cause improper development of the jaw, rapid wear of the enamel, and the development of dental diseases, which is why they have to be removed. If you do not pay attention to the problem, it begins to cause disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, breathing problems, and ENT diseases. That is why it is important to diagnose the anomaly in a timely manner and begin treatment for malocclusion. Moreover, you can take care of your smile at any age; modern medicine allows you to do this!
Prevention
As already mentioned, the main reason for the incorrect formation of a crooked jaw is heredity. Therefore, parents need to carefully monitor their child’s oral cavity. Useful tips:
- Natural feeding.
- Timely treatment of a runny nose.
- Proper nutrition for pregnant and nursing mothers.
- Visiting the dentist.
In addition, it is important to rid the baby of his “bad” habits, which can also lead to deformation of the maxillofacial joint.