13579
The expression “jaw asymmetry” is often used as a synonym for a broader concept – facial asymmetry. In fact, these are different, although closely related, pathologies.
An anomaly should be discussed when a violation of the proportions of the lower third of the face is caused by the dental factor. According to research, such cases account for 80% of the total number of imbalances in the space from the chin to the nose.
General information
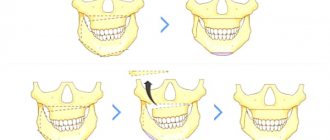
Jaw asymmetry is a pathology expressed in visually visible asymmetry of the lower third of the face. Displacement away from the midline of the entire upper or lower jaw, their segments or individual areas of the face - lips, chin, branches of the upper and lower jaw.
In addition to the above features, pathology can manifest itself as drooping corners of the lips, disruption of the oval of the face, widening or narrowing of the eyes, smoothed lip folds, and some specific features, for example, a pained expression.
To see whether there are deviations or not, you need to imaginarily draw the central line of the face - a vertical straight line passing strictly along the space between the central incisors of the upper and lower jaw. A wide smile makes asymmetry more pronounced.
Strictly speaking, there is no complete correspondence between the left and right parts of the face (ideal symmetry). A certain disproportion of them is present in all people.
The physiological norm is considered to be a position in which the asymmetry in the linear value does not exceed 2-3 mm, in the angular value - 3-5°. If these values are exceeded, they talk about pathology and look for the reasons for its occurrence.
To a greater extent, asymmetry is characteristic of the lower jaw. This is explained by the fact that it is located movably relative to the skull, and has more factors influencing its position than the upper jaw. This is the type of bite, the condition of the TMJ, habitual postures, manner of chewing food, etc.
Dental problems solved with mandibuloplasty and the results achieved.
Come here if you are wondering why your jaw clicks when chewing.
According to this address https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/chelyustey/smeshheniya-sredney-linii.html we will discuss how to correct the displacement of the midline of the teeth.
Stars with facial asymmetry
If all our celebrities had perfectly symmetrical faces, they would be boring to look at. However, it is doubtful that they would have become famous then. Slight asymmetry adds charm and makes the face special and recognizable.
Look at Meryl Streep: her nose is slightly tilted to the side, as is the oval of her mouth. We see the same thing with Harrison Ford, in addition, his ears are not on the same line. Handsome Jim Morrison had an uneven lip line: on the right they are much thinner.
And even the most famous models in the world - those who have become famous throughout the world - have asymmetrical nuances in their faces, despite their almost perfect appearance.
Just evaluate Cindy Crawford's face: her wonderful smile is far from the mathematical ideal of symmetry. A rather large mole on the lip also adds piquancy.
So you should never strive for a faceless ideal. And it’s better to always remain yourself, correcting only what really interferes with your life and feeling happy. Read this blog - let's learn to enjoy life together!
Reasons for the formation of anomalies in children
Often, an orthopedic doctor immediately after birth notes asymmetry of the skull in newborns. It is determined by the factors of the child’s development in the womb and the conditions of birth (the position of the fetus in the uterus, its passage through the birth canal).
Usually after 2-3 days the newborn’s skull takes the correct shape. If this does not happen, a thorough examination of the baby is necessary to identify the causes of the deformities.
In addition to the birth anomaly, most children under one year of age have facial disproportion due to infants being in one position for a long time.
Birth and infant asymmetry are natural types, and in most cases do not require medical intervention, except perhaps massage.
The pathological anomaly is more often observed in preschool children. It can be congenital or acquired, right-sided or left-sided.
Congenital asymmetry is a consequence of genetic factors and abnormalities in fetal development caused by the condition of the mother and embryo during pregnancy (intrauterine infections, abnormal position of the fetus, asphyxia, lack of nutrients, etc.).
These factors lead to disruption of the formation of soft tissues, cartilage and bones of the skull, uneven healing of sutures, etc.
The specific, most common congenital causes include the following:
- Hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles.
- Muscular dystonia (involuntary muscle contractions leading to impaired development of the TMJ and, often, crossbite).
- Crossbite (due to muscular dystonia or accelerated/slow development of one of the jaws).
- Cleft lip. An anomaly manifested by the presence of 1 or 2 clefts in the upper lip, leading to disruption of the shape of the nose and a depression in the middle area of the face.
- Stigmas of embryogenesis. Various etiological malformations of the fetus. They disrupt the symmetry of the dentofacial apparatus, nose, and skull.
- In addition to pathological factors associated with pathologies of the dentofacial apparatus, there are many other congenital diseases that lead to disruption of facial symmetry.
- These are torticollis, Sturge-Weber syndrome, craniofacial microsomia, etc. The dentist’s task is to differentiate them from pathologies of the dentofacial apparatus, and refer the patient to a doctor of appropriate specialization.
Acquired jaw asymmetry develops in the postnatal period under the influence of various external and internal factors:
- Malocclusion. The most common cause is crossbite, which develops due to bad habits and incorrect positioning of the child in the crib, stroller and at the table. A crossbite can result from slower or faster development of the upper or lower jaw.
- TMJ pathologies.
- Odontogenic and non-odontogenic tumors in the jaws (hard and soft odontoma, osteoma, salivary stones, etc.)
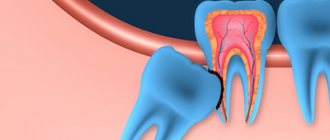
- Impacted teeth.
- Injuries to bone (fracture of jaw bones, skull and face) or muscle tissue.
- Birth injury.
- Periostitis.
- Periodontal inflammation.
Among the non-dental acquired disorders that can lead to an anomaly, the following should be mentioned: diseases of the ENT organs, eye pathologies, curvature of the spine, paresis of the facial nerve, stones in the salivary glands, tumors in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses.
Provoking factors in adults
The cause of the anomaly in adults is acute and chronic diseases of the dentofacial apparatus and its injuries:
- Congenital pathologies of the dentofacial apparatus that were not corrected in childhood.
- Arthrosis of the TMJ (dystrophic destructive changes in the joints). They manifest themselves as a displacement of the LF towards the diseased joint, stiffness in the morning, and pain.
- TMJ ankylosis (joint immobility due to cartilage degeneration). The anomaly is noticeable at rest and increases when the mouth is opened, which in case of severe pathology does not exceed 1 cm.
The line drawn between the lower central incisors shifts towards the damaged joint. Movement of the jaw in the horizontal direction becomes impossible. - Contracture (restriction of movement) of the LF muscles. The midline is shifted towards the affected muscle.
- Odontogenic benign tumors (odontoma, ameloblastoma, steoma, osteoblastoclastoma). The jaw bones are destroyed by neoplasms, deformation occurs, which usually becomes the first manifestation of the disease.
- Malignant tumors of the upper and lower jaw (sarcomas, carcinomas). The resulting deformation is caused by tumor growth.
- Jaw defects (reduction in the volume of dental tissue) due to osteomyelitis, syphilis, tuberculosis, surgical interventions for oncological diseases. Bone deficiency causes receding of the cheeks and disruption of the oval in the lower jaw area. As the mouth opens, the asymmetry increases.
- Micrognathia – due to underdevelopment of the jaw or damage. Micrognathia HF manifests itself as a reverse overlap, LF - with a slanted chin.
- Diseases of the salivary glands.
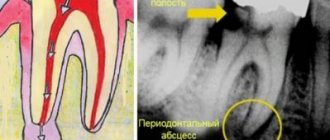
- Periostitis. Asymmetry is caused by swelling and/or abscess under the periosteum.
- Periapical (at the root of the tooth) and periaxillary abscess. Facial deformation is caused by swelling that has spread to adjacent tissues. The pathology manifests itself as throbbing pain.
- Crossbite (transversal displacement of the jaws relative to each other). The chin appears to the side, the lip sinks on one side.
- Facial injuries, fracture of the lower or upper jaw. Temporary asymmetry occurs due to soft tissue swelling and/or displacement of the jaw bones.
In addition to the above pathologies, the anomaly can be caused by many other diseases that are not related to the dentofacial apparatus:
- Damage to the brain and meninges (meningitis, encephalitis, stroke).
- Nerve diseases (Bogorad syndrome, facial nerve damage).
- Pathologies of the salivary glands (mucocele, purulent parotitis, adenoma).
- ENT diseases leading to unilateral deformation (sinus cyst, atelectasis (collapse of the paranasal sinus)).
Facial asymmetry can occur due to hydrogen peroxide poisoning, botulism, actinomycosis (infection with actinomycetes fungi).
Treatment methods for small lower jaws in children and adults.
In this publication, read how to expand the dentition with braces on one side.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/chelyustey/ukorochenie.html we will consider the reasons for shortening the dentition and methods for its correction.
Habit of chewing on one side
Most often, this is again a consequence of the loss of a tooth (or teeth). We chew on one side of our mouth because there is simply nothing to chew on the other. As a result, the facial muscles on the one hand, not receiving the proper load, weaken, while on the other they become hypertonic. Overstrained muscles literally pull on facial tissues, creating creases and visible asymmetry. It should be noted that the risk of developing an aesthetic defect is especially high if you like chewing gum. In this case, the chewing muscles experience uneven load for a long time.
Diagnostic measures
The first doctor you should contact if an abnormality is noticed should be a dentist or neurologist. If you need to connect a doctor of another specialization to the diagnosis - an otolaryngologist, an oncologist, a neurosurgeon - the first receiving doctor will refer the patient to them.
Cosmetologists also claim to be the first to visit, claiming that in case of facial asymmetry caused by hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles, cosmetic procedures alone may be sufficient to solve the problem.
The list of dental diagnostic measures is as follows:
- Survey . The patient's complaints are listened to and the medical history is clarified.
- Physical examination . The degree of anomaly at rest and movement is assessed, probing, palpation and percussion are performed. The clinic of the dentofacial apparatus is assessed (presence of edema, tumors, suppuration, consequences of injuries, condition of the teeth).
- X-ray of the jaws . Photographs of individual teeth, dentition (orthopantomography and teleradiography) and nasal sinuses are taken. If necessary, radiographs of the skull and spine in the neck area are obtained.
- Ultrasound examination. Sonography of sinuses, tissues, salivary glands.
- CT or MRI. Used for detailed study and clarification of symptoms obtained by radiography.
- Orthodontic examination . Cephalography, determination of bite, occlusion, presence of supercontacts, analysis of diagnostic models in the articulator, etc.
When doctors of other specializations participate in the diagnosis, the following examinations may be carried out:
- From a neurosurgeon . A CT scan of the brain is done.
- See a neurologist . The innervation of the facial muscles is checked - by wrinkling the forehead, puffing out the cheeks, raising and lowering the eyebrows, and following the doctor’s movements with the eyes. The exit points of the nerves are palpated.
- See an otolaryngologist . Special examinations are carried out - diagnostic puncture, echosinusoscopy, tuning fork examination, audiometry.
If necessary, general laboratory tests are performed. The blood is examined for the presence of inflammation and bacterial infection. Cytological and histological analysis of punctates and smears is carried out.
Based on the diagnostic results, a conclusion is made about the causes of the anomaly, and a treatment plan is drawn up.
Treatment methods
The variety of causes and nature of the disease determines a wide range of possible treatment methods - from cosmetic to surgical.
Depending on the root cause, cosmetic, conservative, orthodontic and surgical treatment can be used. As well as massage and therapeutic exercises.
Massage
Massage has multiple therapeutic effects:
- Relaxes and tones muscles, relieves hypertension.
- Activates blood and lymph circulation in the affected area, relieves swelling and inflammation.
- Stimulates nerve fibers.
- Reduces pain.
Manual therapy in children is more effective than in adults due to the plasticity of children's muscles. The earlier the anomaly is diagnosed, the more effective manual therapy is.
Cosmetology procedures
Cosmetic treatment consists of getting rid of hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles, which causes facial asymmetry. Technologically, the procedure involves injections of Botox into the masticatory muscles.
The drug relaxes overstrained muscle fibers, straightens the face, returns it to harmonious proportions, and gives a calm and confident expression.
Conservative therapy
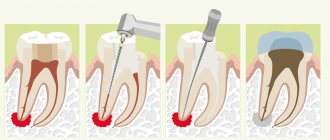
Conservative therapy is determined by the nature of the pathology and provides for the treatment of pulpitis, caries, periodontitis, periodontitis and other diseases of the teeth and periodontium, which make it possible to do without surgical intervention.
Analgesics (for pain), antibiotics (for infections), antiseptics (for local inflammation and wounds on the mucous membranes), NSAIDs (for severe inflammation) may be prescribed.
Orthodontic correction
Orthodontic treatment is used for crossbites, narrowing of the jaws, and other dental anomalies. Treatment is carried out with the help of splints, mouthguards, extra- and intraoral devices, braces and other fixed and removable orthodontic appliances.
Surgical intervention
The type of surgical intervention is determined by the nature of the disease and is divided into:
- for dental (removal of tumors and cysts, removal of teeth, opening of abscesses);
- maxillofacial (lavage, arthroscopy, phlegmonectomy, TMJ endoprosthetics, rhinocheilognatoplasty);
- eliminating the consequences of injuries (splinting and regeneration of jaw bones, tying with a ligature);
- otolaryngological (ectomy of paranasal sinus cysts, etc.).
If asymmetry is caused by damage to the brain and meninges, according to indications, ectomy of tumors and abscesses, transcranial or endoscopic removal of hematomas, areas of the brain crushed by TBI, and other surgical protocols are performed.
How to correct facial asymmetry
What to do if a stroke or nerve inflammation has caused part of the face to lose sensation and a clearly visible curvature?
First of all, we go to the doctors to accurately determine the cause and agree on treatment.
You should consult with the following specialists:
- dentist;
- orthodontist;
- ophthalmologist;
- maxillofacial surgeon;
- neuropathologist.
If surgical correction of the pathology is not prescribed, massage and special facial exercises will most likely be indicated, which I want to tell you about in as much detail as possible in this article.
Possible complications
The consequences depend entirely on the underlying cause of the anomaly and the timeliness of contacting a doctor. In some cases, the problem can be eliminated without a trace with a quick cosmetic procedure or a light bite correction.
In others, if the problem is ignored for a long time, it can result in significant destruction of the temporomandibular joint, with no guaranteed hope for a complete restoration of its function.
Thirdly, create a serious threat to life itself (in case of malignant tumors).
Only a doctor can give an accurate answer to the question about the consequences of pathology after a thorough examination. In any case, the only correct action for the patient will be to consult a doctor as quickly as possible when a pathology is first detected.
Preventive measures
Prevention of any dental diseases consists of following a number of rules that are relevant for almost every person. And although, unfortunately, they do not provide a complete guarantee of preventing dental diseases, they reduce the risk of their development. And if they have already appeared, they speed up and facilitate treatment.
This is the fight against bad habits of children, teaching them proper oral care. Quitting smoking and foods that are harmful to teeth. Using mouthguards when playing sports. And, perhaps most importantly, regular visits to the dentist for preventive purposes.
In the video, experts talk about the causes of asymmetry of the face and jaws.
Habit of sleeping on one side
Sleep, as you know, is a necessary condition for beauty. However, if you are used to sleeping on one side, you risk losing your beauty while sleeping. The fact is that the tissue on the side of your face, with which you press against the pillow, slowly but inevitably deforms. The oval gradually changes, a network of small wrinkles forms around the eye, deeper folds lie between the eyebrows, and vertical lines form on the cheeks and chin. As cosmetologists say, if you prefer to sleep on one side, then it will quickly become clear which one. The best way to avoid asymmetry and wrinkles while sleeping is to eliminate any contact between your face and your pillow. You can do this by training yourself to fall asleep lying on your back. This way you will not only avoid prolonged pressure on the muscles and skin, but also maintain normal fluid flow throughout the night.