Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
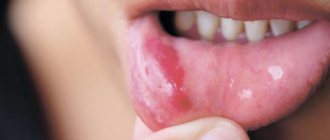
Purulent pulpitis (also called pulp abscess) is a disease of the dental pulp, which is characterized by the presence of pus in the pulp chamber. Most often it occurs due to improper or unqualified treatment by a doctor.
When the amount of serous matter in the pulp increases, oxygen deficiency occurs. As a result, metabolic processes and acid-base balance are disrupted, which ultimately leads to the accumulation of lactic acid and a decrease in the protective activity of cells. The tissue disintegrates and an abscess forms. When the doctor opens the pulp chamber, the exudate is able to outflow, the pressure in the chamber decreases and the pulp restores its regenerative functions. If the purulent cavity opens spontaneously, then the pus enters the carious cavity, and the pulpitis becomes chronic.
This disease can also be caused by various pulp irritants: strong antibiotics, medicinal pastes, filling materials. In some cases, a broken tooth may be to blame for pulp damage if the fracture line is near the tooth cavity.
Tooth granuloma
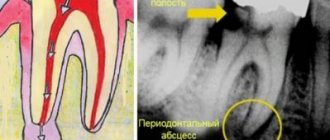
Granuloma on the root of a tooth - what is it and why does it appear? Granuloma is an inflammatory formation that affects part of the root. It is the initial stage of a granular cyst and differs from it only in its smaller size. The disease is characterized by the formation of a purulent sac of granular tissue. The sac is surrounded by a fibrous capsule that connects to the apex of the tooth root.
The appearance of a granuloma under a tooth indicates that an inflammatory process is underway. Before installing dentures, it must be eliminated, otherwise the granuloma will grow under the crown.
The formation of a focus of inflammation in the jaw bone is the body’s defensive reaction to the attack of pathogenic microbes. A dense connective capsule is formed around the lesion, isolating it from the healthy bone. But this protection does not last forever, so granuloma is often compared to a time bomb.
Surgery to remove a cyst in the gum
If therapeutic procedures do not help, then surgical intervention is used to treat cysts in the gums, and in most cases this is what happens, since patients seek the help of doctors when the disease is in an advanced stage. First, an x-ray is taken, based on the results of which the method of removing the cyst in the gum is determined:
- cystectomy - complete removal of the cyst and part of the root;
- hemisection – the disease, part of the tooth and root are removed, restoration is performed using a crown.
If the root and tooth are not damaged, then superficial surgical intervention is used, that is, the cyst is incised and all the pus is sucked out, the wound is disinfected and sutured.
Symptoms
Even having an idea of what dental granuloma is, its symptoms are not so easy to determine. The fact is that the disease may not manifest itself for a long time. The tooth under which the formation is located may not outwardly stand out in the dentition. The gums may also look quite healthy.
In some cases, the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of facial tissues;
- swelling of the gums;
- slight increase in temperature;
- the occurrence of flux;
- acute pain in the area where the granuloma has formed;
- slight discharge of pus between the tooth and gum;
- pain in the eyes, migraine, dizziness;
- On palpation there is acute pain.
Good to know. Granuloma often makes itself known if a person has had a cold, flu, pneumonia and other diseases that lead to a decrease in immunity.
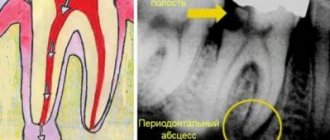
Diagnosis of purulent pulpitis
First of all, the dentist listens to the patient’s complaints and examines his oral cavity. If during the examination the patient experiences a painful reaction, there is a smell of pus from the oral cavity, and the dentin in the cavity of his tooth is softened, this is a reason to send the patient for an x-ray, which will confirm or refute the diagnosis, and will also allow one to assess the depth of the process. Also, the dentist should be alert to the light shade of dentin or its pigmentation. Often, a diseased tooth and the mucous membrane around it are covered with a white coating, swelling is observed in the transitional fold, and if you press on the tooth, pus may be released.
It is very important to correctly diagnose a disease such as purulent pulpitis, because it is quite easy to confuse it with other dental diseases. Among them:
- Diffuse or focal pulpitis in acute form. This disease is characterized by the absence of pus when opening the dental cavity and not so long-lasting pain.
- Purulent periodontitis. In this case, the patient will experience short-term sharp pain in the tooth, especially when biting.
- Trigeminal neuralgia. Pain at night is not typical for this disease, and it is not aggravated by various temperature stimuli. Most often, painful sensations with this disease appear as a result of touching the skin of the face in certain places.
Causes of granuloma
What causes dental granuloma? Among the main factors provoking the formation of a focus of inflammation, the following should be highlighted:
- treatment of pulpitis was carried out poorly (for example, tissues affected by caries were not completely removed);
- the dentist filled the root canals in violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis;
- the tooth was injured directly due to damage to the maxillofacial area, unsuitable orthodontic design or for other reasons.
Complications
Untimely treatment of apical granuloma leads to the following consequences:
- Transformation of a granuloma into a cyst, the treatment of which is more difficult. The cyst can degenerate into a malignant neoplasm.
- Tooth loss. This leads to aesthetic discomfort, disruption of chewing and speech functions, and necessitates prosthetics.
- Due to the spread of infection through the bloodstream, there is a high risk of infectious myocarditis, an inflammatory lesion of the heart muscle.
- The development of pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys, which is also caused by the spread of infection from the focus at the apex of the tooth root.
- The threat of odontogenic sinusitis - inflammation of the maxillary sinuses due to infection from the root of the tooth.
- The development of osteomyelitis – purulent-necrotic inflammation of the jaw bone.
- The appearance of odontogenic subcutaneous granuloma is a change in the subcutaneous fat layer under the influence of microorganisms that have penetrated from the source of inflammation. As the disease progresses, fistulas appear on the skin of the buccal and submandibular areas, from which bloody-purulent discharge is observed for a long time, sometimes for several months.
How is dental granuloma diagnosed?
Diagnosis at an early stage is almost impossible. Even a dentist with extensive experience will not always be able to visually determine the occurrence of a granuloma under a tooth; this will require additional research. Most often, a neoplasm is discovered completely by accident during radiovisiography, which was prescribed for a completely different purpose.
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed radiography. Using this study, it is possible to differentiate dental granuloma from other diseases. In the picture, the source of inflammation and its location will be clearly visible. Based on the results of the study, the most suitable treatment method is prescribed.
In the photo you can see what granuloma of the gums and teeth is and what it looks like.
It is important to know. Unfortunately, it is not always possible to save a tooth under which a cyst has formed. If the tooth is already partially destroyed or has a vertical crack, it must be removed.
Prevention
There is no unique prevention for granuloma. Basically, the dentist recommends the same measures as for the prevention of other dental diseases. You should adhere to the rules of oral hygiene, brush your teeth morning and evening. It is imperative to promptly treat diseases of the teeth and gums - such as caries, pulpitis, periostitis and others. It is necessary to visit the dentist regularly, preferably twice a year. All this will help prevent the occurrence of lesions, and if they occur, diagnose the disease in a timely manner.
Treatment options for granuloma
Treatment of the tumor consists of eliminating the source of infection and preventing relapse. Therapeutic and surgical techniques are used.
Therapeutic method
It will bring results only if the disease is detected at an early stage. The patient is prescribed antibiotics and sulfonamide medications. Timely treatment will help eliminate the infection and save the damaged tooth.
Non-surgical method
It appeared relatively recently, the essence of the method is as follows: the affected tooth canal is expanded and a substance is introduced into it that destroys the infection.
Surgical method
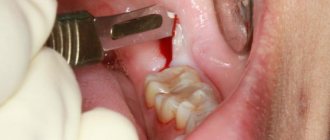
It is used if the granuloma has grown greatly and the use of drug therapy will be ineffective. During the operation, the dentist cuts the gum to allow pus to come out. Then a drainage is installed in the tooth, which the patient must endure for three days. Also during this period, drug therapy is carried out. After three days, another operation is performed, during which purulent sacs, tumors, or a tooth root with a cyst are removed. Then the doctor makes a decision about the fate of the tooth: it is either left or removed.
Removal is necessary in the following cases:
- the tooth is so damaged that it can no longer be restored;
- root canals cannot be treated;
- the cause of inflammation was problems in the periodontal pocket;
- the patient is undergoing a prosthetic procedure;
- cracks have formed in the area of the tooth or its root;
- There are multiple perforations of the tooth.
In other cases, doctors try to save the tooth.
Why did an abscess appear on the gum?
The main, main cause of abscesses is the penetration of infection into the gum tissue. In this case, a reaction of the body’s defenses occurs: leukocytes that destroy hostile cells die, and a large amount of pus accumulates at the site of infection. As a result, a pus-filled sac forms in the gum tissue, which can gradually increase in size and eventually rupture. Infection can enter the gum tissue in a variety of ways. In addition, the formation is promoted by the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, immune system, permanent plaque on the teeth and tongue, and smoking.
There are many factors that increase the risk of developing abscesses inside the oral cavity, but ultimately all the reasons come down to two main ones:
- Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a disease in which a focus of infection forms at the very root of the tooth (usually at the apex). The development of periodontitis is caused by untreated caries and advanced pulpitis (inflammation of the soft tissues of the tooth). Often, the infection penetrates into the tissue surrounding the tooth root during dental procedures and manipulations - for example, when the dental canals are not completely cleaned during the treatment of pulpitis or when the filling is not dense enough. The development of periodontitis is also facilitated by the presence of chronic infectious diseases that cause a steady decrease in the activity of the body's defenses, stress and overwork, and the presence of bad habits. Infectious foci often arise under crowns when they are installed poorly.
Sometimes periodontitis can affect two teeth at the same time. Most often, when this disease occurs, patients complain of severe pressing, aching, acute pain and swelling, but in some cases these symptoms may be absent. Over time, pus accumulates inside the gums, and the cavity containing it expands to the boundaries of the outer mucous membrane of the gums. As a result, an “abscess” or fistula (a small hole through which pus comes out) may form on its surface.
A common result of periodontitis is the appearance of cysts or granulomas - benign formations associated with changes in the structure of the tissues of the oral cavity. To diagnose such conditions, X-ray examination is used, which often makes it possible to detect the disease in the early stages of development and prevent the formation of an abscess. However, due to the latent course of the disease in the initial stages, diagnosis is sometimes difficult: often the presence of infection in the root apex is discovered by chance, when examining other teeth.
The release of pus to the surface of the gum and the formation of an abscess on the gum in the mouth is most often accompanied by acute pain. However, if inflammation on the gums does not hurt, this does not mean that the disease is progressing favorably and you can postpone a visit to the dentist. The absence of pain is usually due to the fact that when a fistula or abscess forms, the pressure of pus on the root and nerve of the tooth decreases. But the main cause of the disease, the focus of chronic infection, still persists. In addition, ulcers without pain often turn out to be formations of other types - for example, wen or benign tumors.
If a white abscess forms on the gum, this usually indicates the presence of a focus of inflammation deep in the gum, at the root of the tooth. Due to the deep location of the infectious focus, characteristic signs of inflammation are often absent.
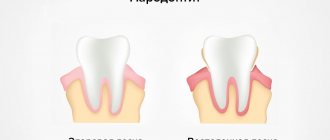
- Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a disease in which “pockets”, areas of sagging gum tissue, form between the lower edge of the teeth and the gums. As a result, cavities are formed in which food debris and bacterial mass accumulate. All this creates the most favorable conditions for the emergence of a focus of infection, which subsequently leads to inflammation.
As a result of the constant presence of pathogenic microorganisms, the part of the gum adjacent to the tooth becomes inflamed, becomes red and swollen, and may bleed when brushing or applying pressure. The deepening of the gum pocket against the background of the constant presence of a source of infection leads to the accumulation of pus in it, as a result of which an abscess is formed.
Unlike periodontitis, with periodontitis the source of inflammation is not deep in the gums, but on the surface. Therefore, even with a simple examination, you can detect characteristic signs of inflammation: swelling and redness. Since periodontitis pockets often form on several or even all teeth of the jaw, the abscesses caused by this disease can also be multiple.
Expert advice and recommendations
Having figured out what kind of disease this is - dental granuloma, you can protect yourself from it. To do this you need to follow a few simple rules:
- undergo preventive examinations every 6 months;
- contact your dentist in a timely manner if any unpleasant symptoms from the dental system occur;
- treat caries at an early stage;
- carry out hygiene procedures regularly;
- change the brush monthly.
Dentists at the Saint-Dent Clinic in Moscow will offer patients a modern and comprehensive approach to the diagnosis and treatment of dental granuloma. Only the most effective treatment methods and high-quality materials are used. You can find out the cost of services here PRICES. The contact section is located here CONTACTS.
How to cure an abscess on the gum?
Treatment for this disease should include not only the elimination of inflammation, but also the causes that caused it: periodontitis, periodontitis, tartar or plaque, and somatic diseases. The treatment regimen largely depends on the reasons for the formation of an abscess on the gum and the presence of concomitant diseases.
The first stage of treatment consists of sanitation of the oral cavity. The dentist conducts a thorough examination of the abscess and opens it surgically to ensure the drainage of pus (if the abscess on the gum has ruptured, this procedure is not required). The operation is usually performed under local anesthesia. The cavity is cleaned and treated with disinfectants. If possible, other sanitation procedures are also carried out at this stage: caries is treated and carious cavities are filled, plaque and tartar are removed, and sometimes professional teeth cleaning is performed. This is necessary in order to eliminate all sources of infection inside the oral cavity, which may cause re-infection and the formation of new abscesses.
If the source of infection is a focus of inflammation in the root apex, additional surgical treatment may be required: removal of the granuloma or cyst, refilling of the canals, or resection (removal) of the root apex. In the most severe cases, the tooth that served as the source of infection is removed. If there are signs of periodontitis or periodontal disease, the patient is referred for consultation and treatment to a specialist - a periodontist.
After opening and disinfection, the patient is most often prescribed antibiotics and disinfectant rinses to prevent secondary infection and allow the cavity to heal. Drugs that accelerate tissue regeneration can be added to the treatment regimen.
The best way to avoid lengthy and costly treatment is to take preventive measures. You can significantly reduce the risk of ulcers forming on your gums by regularly brushing your teeth with a brush and floss, and using disinfectant rinses. It is necessary to conduct regular preventive examinations at the dentist, as well as independently monitor the condition of the gums.
ASEPTA Active mouth rinse will be a reliable assistant in the treatment of gum inflammation. This unique product contains:
- Benzydamine, which has anti-inflammatory and local anesthetic effects, which may be accompanied by a feeling of numbness. Benzydamine is absorbed through mucous membranes and penetrates into inflamed tissue. Reduces pain sensitivity at the site of inflammation.
- Chlorhexidine, active against vegetative forms of gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms, yeast, dermatophytes and lipophilic viruses.
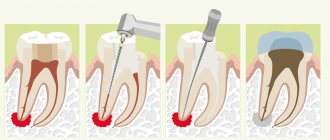
Conservative and drug treatment
Timely detection of a granuloma on an x-ray allows the dentist to apply the most loyal approach to the treatment of this pathology. Here are the actions that will be taken then:
- cleaning and antiseptic treatment of tooth root canals,
- placing a drug based on calcium hydroxide inside the channels,
- applying a temporary filling,
- installation of a permanent filling.
The second and third points can be repeated repeatedly until the formation finally resolves. Additionally, the doctor prescribes home therapy for the patient, which consists of taking antibiotics and painkillers, and performing antiseptic mouth rinses, for example, with Chlorhexidine.
The photo shows the process of conservative treatment
Many doctors believe that this measure is not always effective; often, after conservative therapy, the disease can recur. But patients do not always like that treatment can last for 4–6 months. However, if you don't want to resort to more radical solutions, then it's worth a try.
“A year ago, I began to notice that when I chew on one tooth, it hurts, but after eating, the pain goes away immediately. I didn’t think that I needed to go to the dentist with such a problem: the tooth was treated and filled. But one fine day he began to get so sick, even regardless of food intake, that he ran to the doctor. A diagnosis of granulomatous periodontitis was made. They treated him for a very long time, put medicine inside him for almost a year, but the tumor at the root did not resolve, and it had to be removed surgically. I don’t know, maybe I should have deleted it right away instead of suffering like that...”
Helga32, review from the dental portal gidpozubam.ru
Physiotherapeutic methods
In some clinical cases, when the granuloma is small and the inflammatory process is not acute, treatment is possible using the following methods.
Electrophoresis
This procedure involves introducing iodine-based medications into the infected canals using current pulses, designed to kill bacteria and also promote the resorption of the formation. True, physiotherapy requires patience and a lot of free time, because it will take about 10–20 procedures performed daily or every other day to get rid of the pathology.
Depophoresis
Another physiotherapeutic method is depophoresis. The principle of introducing medication into the root canals here is similar to that of electrophoresis. Copper/calcium hydroxide is used only as the main drug. Depophoresis can only be performed on teeth that lack pulp. The number of procedures is usually three, with a break of a week between them.
This method does not require complex surgical procedures.
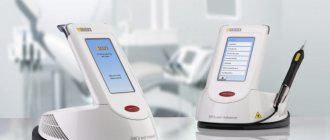
Destruction of granuloma with laser
The method is more expensive, but fast and effective. Suitable even for curved root canals. Before this, the specialist cleans the canals and sterilizes them. Penetrating through the root, the doctor treats the granuloma with a laser, and it resolves. The laser has a powerful disinfecting effect, does not injure surrounding tissues, on the contrary, promotes their rapid healing, stops bleeding, because cauterizes blood vessels. Doctors who practice this type of innovative equipment claim that relapses of the disease are excluded.
The laser has a powerful disinfecting effect
Contraindications to the use of laser: oncology, cracks and fractures at the root.