What is tooth flux?
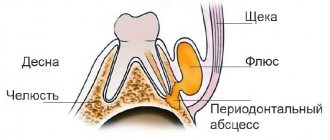
Flux, or, in dentist's language, periostitis, is a very unpleasant pathology, which is characterized by inflammation of the periosteum and soft tissues. The causes of flux on the gums can be different: trauma, gum disease, poor-quality dental treatment - all this can lead to a complication in the form of periostitis. The localization of the disease does not depend on the area of the jaw: flux of the upper and lower teeth occurs equally often.
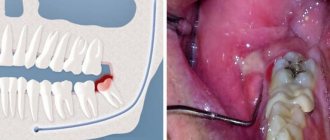
Flux under a tooth (or above a tooth, if we are talking about the upper jaw) visually resembles an inflamed sac. However, this is far from the only possible manifestation of periostitis. There is also a serous form, when the periosteum becomes inflamed as a result of trauma and damage, as well as one of the most unpleasant types - diffuse, when the infection is localized in different parts of the jaw, which requires extensive surgical intervention with the participation of a maxillofacial surgeon.
What to do if your cheek is swollen after tooth extraction?
Often after a tooth extraction procedure, many people experience swelling that may persist for some time.
Its appearance is natural, since tooth extraction is essentially a surgical operation, after which the wound remaining in the oral cavity remains open. It recovers fairly quickly, but damaged gum tissue will remain swollen for some time. The size of the tumor may depend on several factors, such as the complexity of the removal procedure, the individual characteristics of the person, and the professionalism of the dentist.
Symptoms of gumboil
Flux on the gums in adults occurs much more often than in children (approximately 80-90 percent of all cases). A characteristic feature of the pathology is that it does not go unnoticed. This is one of the most unpleasant diseases, causing severe discomfort. The most striking symptoms are the classic purulent flux.
Symptoms
- Severe throbbing pain.
- Inflammation and swelling of soft tissues. At the advanced stage, the side of the face on which the flux is diagnosed swells.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Discomfort and pain when eating and talking.
- Flux of the lower tooth (in the molar area) can lead to numbness of the lip and part of the chin.
- Weakness, headache, fever.
How to remove swelling of the cheeks and gums
If the tumor does not cause particular concern, then it is a natural phenomenon after tooth extraction.
There are ways to relieve pain and reduce swelling, as long as it is not harmful to health.
- It is necessary to apply cooling compresses to the inflamed cheek several times during the day, this can be a bottle of cold water, ice in a cloth, a damp towel, which should be kept for twenty minutes, periodically cooling it in cold water. You will immediately feel relief and notice how the tumor decreases in size.
- People with high blood pressure are more susceptible to post-operative swelling. They are recommended to take sedatives and blood pressure-normalizing medications after tooth extraction.
- Conventional anti-edema products can relieve swelling well - gels, creams, ointments that can be applied to the outside of the cheek.
- To relieve pain, which is inevitable after complex removals, you can take a painkiller (except aspirin) or an anti-inflammatory drug and lie down to rest.
How many days does tooth flux last?
Waiting for the flux to disappear on its own is, to say the least, naive. Some patients believe that if the flux bursts and pus comes out of the wound, then further treatment may not be carried out at all. This is a big mistake, since complete removal of pus requires special drainage, as well as complex therapy and subsequent treatment in the dentist’s chair. With timely and correct treatment, the flux disappears on average in 12-14 days; rehabilitation after severe periostitis can take more than a month.
Treatment methods
The attending physician should tell you after the examination how to treat gumboil and what measures need to be taken to achieve a successful result. The mechanism is approximately the same, but each clinical case has its own nuances. Today, several techniques are used aimed at eliminating the disease and its manifestations. As a rule, they come together.
Antibiotics for gumboils
Antibiotic treatment is an important stage of rehabilitation. The most effective antibiotics for fighting inflammation and infection are Metronidazole, Lincomycin, Amoxiclav and their analogues. Any tablets and antibiotics for tooth flux should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor!
Physiotherapy
Used as an additional measure to reduce inflammation and speed up recovery. Recommended procedures include electrophoresis, laser and ultrasound therapy.
Therapeutic treatment
It is carried out if it is decided to save the tooth. This includes endodontic treatment and filling of root canals, as well as resection of the root apex if necessary. If the cause of the flux is periodontitis, then a series of manipulations are carried out to eliminate the accumulation of bacteria in the periodontal pockets.
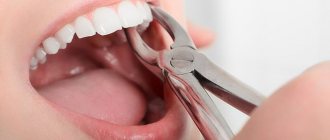
Surgical procedures
This includes tooth extraction and periostotomy - the main procedure for treating flux. The doctor makes an incision into the purulent sac, and then installs a drain through which the purulent exudate comes out.
Local therapy and rinsing for tooth flux
For better release of pus, pain relief and reduction of swelling, gels and ointments are used topically: Metrogyl Denta, Levomekol, Cholisal. Many people are interested in how to rinse gumboil on the gums. Miramistin and soda solution are usually used for rinsing. As an alternative, you can use folk remedies: decoctions and tinctures of propolis, chamomile, sage or calendula. A tooth after gumboil is still very vulnerable: to minimize the risk of re-infection, these treatment and preventive procedures are very important.
Possible causes of gum swelling
Depending on the location of the tumor, its nature, the presence or absence of pain, we can talk about the following causes of the disease:
- Caries or pulpitis. Negligence towards oral health leads to inflammation spreading from the tooth tissue to the gums. Most often, both caries and pulpitis are accompanied by constant pain (sharp, aching, throbbing), but sometimes the process is painless. So, for example, if a neurovascular bundle was removed during a previous intervention, there may be no pain. In this case, tooth decay continues and over time, inflammation affects the gums.
- Gingivitis or periodontitis. Improper oral hygiene leads to an increase in the number of pathogenic microorganisms. Gingivitis is an inflammation caused by bacteria and occurs without disruption of the periodontal bonds, and often without pain. However, if you do not pay attention to the problem, the disease progresses to the stage of periodontitis, which is characterized by destruction of the alveolar part of the bone tissue. Both gingivitis and periodontitis are accompanied by redness and swelling of the gums.
If the gums are swollen at the root neck of the tooth, and the shape of the swelling is elongated (along the border of the gums), we can most likely say that the cause is gingivitis or periodontitis. In this case, pain is mild, and at the initial stage of inflammation is completely absent. Bleeding gums can be considered an additional symptom of these diseases, but it does not always occur.
- Abscess (flux). If swelling of the gums affects a large area, is localized at a distance of 10-15 mm from the neck of the tooth and is accompanied by throbbing pain that intensifies with pressure, the cause is almost certainly purulent inflammation. If you do not consult a doctor, the abscess gives rise to various complications, including phlegmon - acute purulent inflammation, which in advanced cases can be fatal.
In addition to the above reasons, swelling can be caused by gum injury, wisdom tooth eruption, or surgery. It is important to understand that slight swelling of the gums, which persists for 1-2 days after tooth extraction or other dental surgery, is normal. However, if the swelling does not go away within this time or becomes more extensive, you should see a dentist.
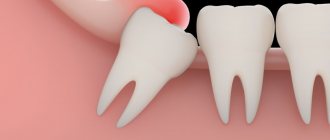
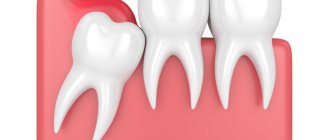
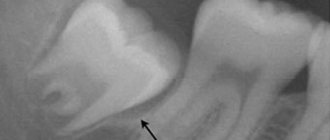
As for wisdom teeth, it is better to immediately consult a doctor without waiting for swelling to appear. This is due to the fact that very often the “eights” have certain defects that interfere with their eruption and cause inflammation of the gum tissue. The decision on the advisability of preserving a wisdom tooth is made after an X-ray examination, which makes it possible to identify certain pathologies in its development. If swelling has already appeared, but the tooth can be saved, most often a hood resection is performed, that is, the upper part of the gum that covers the crown is removed.
Swelling of the gums when wisdom teeth erupt is a common problem.
Is a tooth removed during gumboil?
A tooth can be removed due to flux, but in modern dentistry the emphasis is on tooth-preserving manipulations. This also applies to flux. A tooth must be removed when its crown is seriously damaged and cannot be restored with a pin or inlays. If an infection occurs under the crown, then re-prosthetics are often difficult. In some cases, a tooth has to be removed because it is impossible to unfill the canals after a previous unsuccessful treatment, but this happens extremely rarely. In any case, the doctor makes the decision to remove a tooth based on the clinical picture.
Contraindicated actions for swelling:
- Under no circumstances should you heat the swollen area, or touch the wound with your hands and tongue;
- rinsing on the first day after tooth extraction is not recommended, as it can wash away the blood clot that protects the socket from infections. In the future, you can rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions - miramistin, furatsilin, or decoctions of chamomile, sage;
- the first two to three hours after the removal operation, you should refrain from smoking, drinking and eating;
- Until the wound is completely healed, you should not consume solid food, hot and carbonated drinks, or alcohol.
If you follow these simple rules, the swelling will go away quickly enough and there will be no need to visit the dentist.
Why is tooth flux dangerous?
An inflammatory process of this type tends to develop and, as it spreads, affects deeper layers of tissue. If left untreated, flux often develops into phlegmon - a serious purulent inflammation that has no definite boundaries. The most severe forms of flux provoke the development of sepsis, which can lead to infection of the entire body and even death. It is important not only to know how to cure gumboil and visit the dentist on time, but also to follow a number of preventive measures so that the likelihood of complications developing is minimal.
- Regular and high-quality hygiene.
- Treatment of caries at the initial stage. Flux, dental cysts and other complications often arise due to untreated pulpitis and periodontitis.
- Preventative visits to the clinic to assess the condition of the oral cavity and carry out professional cleaning.
Associated symptoms
Often gum swelling is accompanied by other symptoms:
- swelling of the cheek;
- fistula formation;
- tooth pain;
- bleeding gums;
- sensation of a metallic bite;
- redness of the gums;
- discharge of pus from the carious cavity;
- loosening of the crown;
- the appearance of ulcers;
- increase in general body temperature;
- the appearance of white plaque on the gums.
If there are signs of a purulent process, then contacting a dentist should be done immediately. Complications can lead to serious consequences not only for the oral cavity, but also for the entire body.