Causes Symptoms Treatment Possible complications Prevention
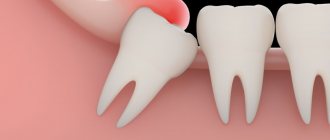
Gum hyperplasia is a condition in which tissue begins to grow excessively. They hang over the teeth, forming false pockets, covering most of them, interfering with hygiene procedures. There are several terms in the literature that describe this condition: gingival overgrowth, hypertrophy, or hypertrophic gingivitis.
The main danger of tissue proliferation is that it promotes the proliferation of bacteria, causing serious diseases such as periodontitis.
Causes of gum hypertrophy
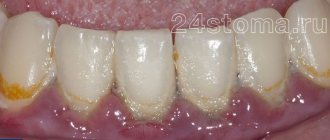
The main reason for tissue hypertrophy in the mouth is poor hygiene. Remains of food and decay products settle on the enamel of the teeth. They accumulate, causing inflammation of the mucous membrane, one of the manifestations of which is hyperplasia.
Other reasons include:
- Taking certain medications
A side effect of some anticonvulsants and immunosuppressants, and some heart medications, is gum overgrowth. However, you should not stop taking them or reduce the dosage if your gums have increased in size and began to bleed, without consulting a doctor.
- Genetic predisposition
Most people experience tissue growth during puberty. In most cases, after the end of hormonal changes, spontaneous reduction is observed. But in some patients, the gums do not shrink and may even increase in size. This phenomenon is characteristic of hereditary fibromatosis.
- General diseases
Leukemia almost always provokes tissue hypertrophy because they are saturated with dense masses of immature leukocytes. The gum turns into a hard surface on which wounds appear at the slightest pressure. This problem is also typical for sarcoidosis.
- Hormonal instability
Pregnancy and diseases of the endocrine system, such as diabetes or hypothyroidism, disrupt metabolic processes in tissues and lead to inadequate growth.
- Crowded teeth
If teeth creep onto each other and overlap surfaces, this interferes with proper cleaning of surfaces and contributes to the formation of microbial plaques. They, in turn, provoke inflammation.
Consequences
If the root and part of the tooth are left inside the gum tissue, some complications may occur. Inflammation in the pulp chamber can begin as a result of dirt and infection; this process is accompanied by severe pain, the appearance of purulent discharge, rotting, etc. To avoid sepsis, surgical removal of the root and nerve endings is recommended.
Another dangerous disease is periodontitis. In the absence of timely treatment, the unit can become very loose; it is surrounded by voids where germs, food particles, and infection can get in. In this case, the root moves away from the coronal part quite quickly and it becomes almost impossible to save it. If the problem is not corrected in time, there is a high risk of damage to other organs and even blood poisoning. The latter threatens with very serious complications and is dangerous to human health.
Another common occurrence is when a previously filled tooth breaks and particles of the composite get into the hole. These particles can react with tissues, which leads to the development of inflammation. In this case, not only the root of our broken tooth can become inflamed, but also nearby units. If inflammation is left unattended by a specialist for a long period of time, a cyst may appear.
Symptoms
The growth of the mucous membrane is a gradual process. There are 3 degrees:
- The gingival papillae increase in volume. The gingival contour is disrupted and hangs over the tooth.
- The growth progresses, the tissue covers up to half of the coronal part. Bleeding and discomfort when brushing teeth and eating food develop.
- The gum covers the tooth by two thirds, sometimes completely. Folds form in which microflora accumulate, causing inflammation.
The process is generalized
when the entire gum on the jaw suffers.
Focal
hyperplasia is located around one or more teeth.
The edematous form is characterized by the presence of plaque, there is a lot of it, it is quite soft, but covers the enamel with a thick layer. Gum pockets form. The papillae turn red and bleed when pressed.
Patients complain of itching, discomfort in the mouth while eating, and an unpleasant odor.
With fibrous gingival hyperplasia, patients are only concerned about the unusual appearance of the mucous membrane. There is usually no pain or bleeding, but there are complaints of an unpleasant odor.
Gum grafting: healing after surgery
Depending on the type of gum grafting, complete recovery takes from several days to several weeks. Your doctor will give you a list of recommendations to follow after surgery. He will also prescribe painkillers. In general, the recommendations boil down to the following: it is necessary to remain calm and reduce physical activity, eat soft foods at room temperature and avoid spicy foods until the gums are completely restored, and carefully carry out oral hygiene, including rinsing. Until complete healing, you will have to wear a special mouthguard that protects the affected areas from external factors and promotes faster and safer healing.
Swelling after surgery lasts for several days. As a rule, on the third day the swelling may increase, and then subside. If swelling does not go away, severe pain, bleeding or other frightening symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Gum grafting is a surgical procedure, and like any other, it has certain risks. The most common are allergies to the anesthetic and recurrent gum recession. In order to avoid allergies, you should notify your doctor in detail in advance about the presence of any diseases and the occurrence of allergies to medications in the past. In case of relapse, the procedure can be repeated no earlier than six months after the previous one.
Treatment of gum hyperplasia
Any medical intervention is preceded by diagnosis. The clinic conducts a visual examination using dental instruments. An X-ray is taken and, in some cases, a tissue biopsy. Collect information about current diseases and what medications the patient is taking.
Gingival hypertrophy is differentiated from papillomas, granulomas, epulis (neoplasms) or swelling of the gums as a result of periodontitis.
The treatment plan is drawn up taking into account the degree, course and reasons for which the gums have grown.
For concomitant diseases, procedures should be agreed with the attending physician. Sometimes, simply changing the drug leads to a reduction in overgrown tissue.
Therapeutic methods
They are used mainly after replacing the drugs that caused hyperplasia.
- Decoctions and applications
from oak bark, chamomile, St. John's wort, calendula. Tannins in these plants narrow and strengthen the walls of blood vessels, reducing their permeability. As a result of combining with proteins, tannins form an insoluble film on the mucous membrane. This protects nerve endings from breakdown products and reduces pain.
- Installations in gum pockets.
Plant-based preparations are placed in pockets for 15-20 minutes, for up to 3 weeks.
- Dorsenval therapy.
After the elimination of the inflammatory process, physiotherapy is carried out to strengthen blood vessels.
The main treatment measure is professional teeth cleaning.
If the effect of the procedures is insignificant, as well as with fibrous hyperplasia, gingivectomy
.
Surgery
In cases where the gum has grown on the tooth so much that it covers half of the surface or more, the excess tissue is removed. For fibrosis, therapeutic treatment is not used at all; in other cases, the decision depends on the clinical picture.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Apply:
- Classic way
. The tissue is excised with a scalpel. The surface of the roots is polished with instruments, and the wound is treated with an antiseptic. Finally, a special bandage is applied (septopak, vokopak). - Laser
removal of overgrown gums . This is a minimally invasive operation, after which healing occurs much faster. During surgery, the vessels are sealed with a laser beam, which eliminates bleeding. At the same time, pathogenic flora is destroyed. Complications after such operations are extremely rare.
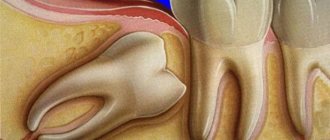
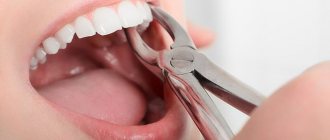
How is removal carried out?
Before the operation, an x-ray is prescribed and a diagnosis is made based on laboratory tests. From the image, the doctor determines a certain type of growth, an abnormal location of the wisdom tooth. It also examines infectious and inflammatory foci in this area and prescribes preliminary treatment. The dental surgeon performs the operation under local anesthesia, which begins to take effect within 10 to 15 minutes. After exposure to anesthesia, he begins to excise the excess mucous membrane hanging over the tooth with a scalpel. Removing a wisdom tooth hood involves several main steps:
- Disinfection of gums and segments of the oral cavity;
- Excision of the “hood” with a scalpel;
- Rinsing the cavity with an antiseptic;
- Stopping bleeding and disinfection with iodoform turunda;
- The use of anti-inflammatory drugs, wound healing ointment.
Complications
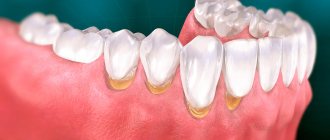
Hyperplasia is dangerous because without treatment it provokes inflammatory processes in the periodontium: gingivitis and periodontitis. This leads to loosening of teeth and their loss.
Due to the fact that it is impossible to clean teeth well, caries often develops. Enamel demineralization occurs. Metabolic processes are disrupted.
Due to increased sensitivity, patients try not to chew on the side where the gum has grown. The chewing load is distributed unevenly, and the risk of losing teeth increases.
The procedure for plastic correction
With any type of surgical intervention, the technology remains unchanged and consists of the following stages:
- examination of the general condition of the gums, preparation of the oral cavity for surgery: elimination of caries, plaque, tartar;
- injection of an anesthetic;
- removing or cutting part of the gum using a scalpel or laser. If there is a shortage of gum tissue, it is transplanted from another place;
- suturing.
After the procedure, the doctor prescribes further treatment and indicates recommendations that should be followed.
Prevention
Simple measures will help prevent gum overgrowth. Dentists recommend brushing your teeth with a soft brush, using dental floss or interdental brushes. Using a rinse aid reduces the number of bacteria settling on the enamel. But all these measures will not help if there is plaque on the teeth. Therefore, professional teeth cleaning in dentistry is where the prevention of hyperplasia begins.
Author of the article Voznyuk Vladimir Aleksandrovich Maxillofacial surgeon-implantologist of the highest category
Work experience: 28 years.
Non-inflammatory pain syndrome -
If the pain syndrome is not associated with the development of inflammation, but is the result of pressure from the wisdom tooth on the teeth in front, this is an indication for taking analgesics from the NSAID group, for example, based on ibuprofen. Of course, there are also pain-relieving gels for topical use (Cholisal, Kamistad, etc.), but the effect of their use in this case will not be long or pronounced. Again, in this case, we recommend contacting a dentist (24stoma.ru).
If the wisdom tooth does not have enough space to erupt, it can cause displacement of the teeth in front, which will lead to crowding of the front teeth. The second variant of the problem is that the pressure of the wisdom tooth when erupting on the 7th tooth can lead to the destruction of the crown of the latter. Therefore, if pain occurs during teething, it is better to immediately assess the need to preserve the wisdom tooth, and in some cases it is better to remove it immediately.
→ Indications for saving the eighth teeth
Complications of wisdom tooth eruption –
- Crowded teeth – if there is not enough space for the erupting wisdom teeth, the latter begin to shift the remaining teeth towards the central incisors, causing crowding of the teeth in the frontal area of the dentition. Therefore, it is very important to assess in advance whether the length of the body of the lower jaw is sufficient for the eruption of the eighth teeth. If there is not enough space, it is better to remove these teeth preventively, otherwise you will likely need orthodontic treatment in the future.
- Destruction of the tooth in front - wisdom teeth often erupt in such a way that they have an inclined position, resting the front tubercles of the crown on the seventh tooth in front.
Constant, prolonged pressure will eventually cause the enamel and dentin to break down. As can be seen in Fig. 7, the seventh molar has a darkening in the crown area, which corresponds to the area of tooth destruction. Preservation of the seventh tooth and its full treatment in this case is impossible without removing the wisdom tooth. Figure 8 shows the same picture - number (1) shows a small area of destruction of the hard tissues of the seventh tooth, and number (2) shows the area of bone tissue destruction. In Fig. 9 you can see significant destruction of the coronal part of the seventh tooth (the area of destruction looks like a dark spot against the background of the crown, and is limited by white arrows). At the same time, the amount of destruction of the crown of the 7th tooth indicates that it must be removed.
How to ease the eruption of wisdom teeth -
If the crown of the wisdom tooth is already close to the surface of the gum, then to speed up eruption and reduce symptoms, the gum above the crown of the wisdom tooth is usually excised. That is, they make a so-called “window”. The decision about the possibility of such an intervention should be made by the dentist, taking into account the X-ray data.
In some cases, pain-relieving gels for the oral mucosa can also be recommended, for example:
- Cholisal-gel applications,
- Kamistad gel applications.
Miller classification
Today, the generally accepted classification of gum recession is the Miller classification, which is divided into 4 classes
.
First and second classes
according to Miller - root closure is 100 percent possible.
Third class
according to Miller, 100 percent root closure is impossible.
And fourth grade
according to Miller, he is not even being treated.
What treatments are available for each stage of gum recession?
For the first, second and third classes according to Miller - only surgical closure of the exposed necks of the roots of the teeth. The fourth class according to Miller is not treatable, that is, it cannot be treated.
Is there an age limit for treating gum recession?
No.
There is no age limit for treating gum recession.