Sometimes we experience a special kind of discomfort - it seems that either our head or our eyes hurt. This pain occurs in the sinus area or at the back of the eye. Sometimes it is pulsating, sometimes it is constant. This condition frightens us very much and we want to know what causes this pain? What can be done to alleviate it? Could there be something wrong with my vision?
Let's first answer the last question.
Scientists from the American Academy of Ophthalmology defined "eye pain" as "physical discomfort caused by an eye or other disease." But scientists emphasize that “the location of the pain does not necessarily indicate the cause of the pain.”
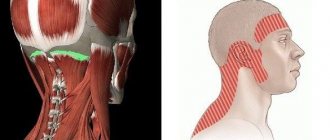
In most cases, the cause of a headache felt in the eyes may be hidden in a completely different place. We feel pain in this particular location because of a network of interconnected sensory nerves that penetrate all tissues of the body.
“Almost every pain-sensitive structure in the head transmits the sensation of pain to the eye area,” says Dr. Mark W. Green, MD, professor of neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City. “Just because the eye hurts does not mean that the problem is in the eye itself. In fact, this happens quite rarely."
Green advises to remember one useful rule: if the white part of the eye (sclera) is not red, and there are no complaints about vision - a blurred or distorted picture, it is very unlikely that the headache is associated with the eyes themselves.
Symptoms of pain under the eye
Note! Painful sensations in the infraorbital area are often perceived as pain in the bone, but in most cases (excluding traumatic ones) soft tissues hurt.
Depending on the disease, tingling may vary in nature and intensity. Most often, such sensations are caused by the development of sinusitis in the acute stage.
In this case, the aches are felt even without pressure, and symptoms such as:
Where is an MRI of the sinuses done?
Targeted scanning is necessary if the degree of complexity of the disease cannot be determined by other instrumental methods, if the drug treatment did not help, and as monitoring of the instrumental treatment performed. Screening is carried out in specialized tomography centers with the necessary equipment.
A complete list of medical institutions in the city can be found on the unified registration service of St. Petersburg. To do this, select a service on the top panel of the page, the type of study and study the list of clinics distributed in the regions of the Northern capital. Mark the best offers, sign up for diagnostics immediately directly through the portal and receive a guaranteed discount. The telephone number of the consulting service is also posted on each page of the service.
Possible reasons
Tingling under the eye may be a symptom of one of the following conditions::
- Sinusitis . The pathology is an inflammation of the nasal sinuses, which communicate with the lacrimal canals. With this disease, the maxillary sinuses, which are located under the eye sockets, become clogged with purulent discharge. The pathology in its advanced form can progress to the chronic stage, and inflammatory processes can spread to the upper respiratory tract. Treatment in this case is carried out by an otolaryngologist, who prescribes appropriate anti-inflammatory and, if necessary, antibacterial drugs.
- Osteomyelitis . A purulent-necrotic process in the bones, which can develop against the background of complications of dental diseases, when infectious processes from the teeth of the upper jaw spread to the infraorbital bones. Treatment consists of taking immunostimulating and antibacterial drugs, vitamins, and in severe cases, blood plasma transfusion to detoxify the body.
- Mechanical damage to the periocular area. Painful sensations in such cases require, first of all, symptomatic treatment and the use of painkillers. And with concomitant damage to the eyeball and penetrating wounds, antibacterial treatment and surgical intervention are necessary.
- Neuralgic pathologies. Such disorders are usually accompanied by a complex of symptoms, including disturbances in facial expressions, numbness of the facial, hypoglossal and pharyngeal nerves. Often the patient experiences tingling sensations in the temples, shoulders or neck.
- Disturbances in the activity of the vascular system of the organs of vision . In such cases, the patient may feel pain in the bone under the eye, but this syndrome only affects the blood vessels and soft tissues.
Only a specialist can determine what exactly causes such a symptom after conducting an appropriate examination.
Treatment is determined solely by the origin of the pathology and its severity.
Symptoms of sinus inflammation
The pathological process in the paranasal area occurs for various reasons, among which are a decrease in the immune response to the pathogenic effects of infections of various natures, as well as allergic reactions of the body. The main signs of the anomaly, in addition to pain and discomfort, are:
- difficulty breathing, stuffy nose;
- pain in the head, heaviness in the area of the cheekbones, brow ridges;
- discharge of a purulent substance, possible bloody spots;
- swelling of the face, dry mouth and throat;
- increase in body temperature;
- malaise, fatigue.
Any inflammatory process is dangerous if it spreads to adjacent areas. From the paranasal cavities, pathogens can infect the meninges and lead to critical consequences. To prevent complications, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible. Based on the nature of the disease and the cause of infection, a personal treatment regimen is developed and prescribed by an ENT specialist.
Diagnostic methods
It is worth noting! The exact cause of pain can only be determined after a detailed examination, including:
- donating blood for general and biochemical tests;
- rhinoscopy (examination of the nasal cavity);
- nasal swab to analyze the discharge for the presence of pathogenic microorganisms;
- CT scan;
- radiography of the upper jaw area;
- dacryocystography (examination of the tear ducts using x-rays);
- puncture of the maxillary sinus (if sinusitis is suspected).
How are sinuses treated?
The use of traditional methods to restore breathing and other methods of self-medication is not recommended unless the manipulations are prescribed by a doctor.
At the first signs of the disease, you can use the usual nasal medications to alleviate the symptoms, but only until, in consultation with an otolaryngologist, specific targeted drugs that affect the root cause of the pathology are prescribed. In case of a complex anomaly, hardware diagnostics is first performed using MRI. In complex therapy the following are used:
- intensive nasal rinsing sprays;
- antibacterial drugs (after identifying a pathogenic bacterium, virus or fungus);
- local vasoconstrictors;
- surgical intervention for congenital or acquired anomalies of the upper respiratory tract.
Instrumental endoscopic treatment is used in cases where traditional therapy has proven ineffective. To determine the feasibility of surgery, it is necessary to undergo an MRI in advance. During surgical treatment, mechanical expansion of the cavities is carried out, which helps the purulent substrate to naturally exit the respiratory canals. During the manipulation, the patient does not experience discomfort, since the procedure is performed using anesthesia.
Prevention
Prevention involves compliance with hygiene standards , which will eliminate the risk of infections in the eyes.
It is necessary to keep your hands clean (especially after going outside or visiting public places), but even with clean hands you should not rub your eyes too much.
You should also follow a sleep schedule, avoid getting too cold, and include more healthy foods in your diet (including fruits and vegetables).
This is necessary to maintain immunity at a high level and will avoid the development of diseases even when pathogenic microflora enters the body.
Where does it hurt?
First, the doctor will ask you which area of the eye hurts. Pain can be localized in a variety of places:
- cornea - the transparent membrane through which light passes;
- sclera - the white shell of the eye;
- conjunctiva - a thin film on the surface of the sclera under the eyelid;
- iris - the colored part of the eye surrounding the pupil;
- orbital socket - the depression in the skull where the eyes are located;
- external eye muscles, which are responsible for eye movements;
- nerves that transmit visual information from the eye to the brain;
- eyelids - the outer membranes that protect and moisturize the eye.
Why does my eye hurt?
Main reasons:
- blepharitis - inflammation of the edges of the eyelids when ingested by mites, fungi or bacteria;
- conjunctivitis - inflammation of the conjunctiva due to an allergy or infection caused by a bacteria or virus. Due to infection, the blood vessels of the conjunctiva become inflamed, the eye turns red, and the eyelid begins to itch;
- corneal erosion - injury or damage to the cornea due to a foreign object or mechanical pressure on the eye;
- Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea due to a bacterial or viral infection. Occurs if you do not clean your contact lenses well or do not remove them at night;
- a foreign body in the eye that causes pain and irritation. Usually washed away with tears, but if this does not happen, the foreign body scratches the eye;
- Glaucoma is increased eye pressure due to fluid accumulation in the eye area. If left untreated, you can go blind in one eye;
- Iritis or uveitis is inflammation of the iris or choroid of the eyeball due to injury, infection, or diseases of the immune system. The pain is accompanied by redness of the eye and blurred vision;
- Optic neuritis is an inflammation of the nerve that connects the eye to the brain. The cause of inflammation may be multiple sclerosis. Pain is accompanied by decreased visual acuity and discomfort when moving the eyes from left to right;
- sinusitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses;
- stye - inflammation of the eyelid as a result of infection in the sebaceous gland or hair follicle;
- chalazion - inflammation of the meibomian gland in the eyelid area;
- dry eye syndrome - a feeling of dryness and burning due to insufficient production of tear fluid;
- migraine - pain behind the eye and in any part of the head, rolling in waves; goes away after the attack stops;
- general fatigue, eye strain - when working for a long time at the computer or with small objects.
Symptoms
With the development of edema, the integrity of the nasal mucosa is always compromised, resulting in the area of damage expanding over time.
Keep in mind! As a result, swelling spreads to the periocular area and appears in the form of reddened swelling.
The following symptoms are typical for edema that occurs precisely because of sinusitis :
- rapid breathing due to partial narrowing of the airways;
- redness of the lower (less often upper) eyelids ;
- change in voice timbre;
- swelling of the eyelids and parts of the cheeks directly under the eyes ;
- headache;
- accumulation of pus in the maxillary sinuses , which is periodically discharged through the nose.
The severity of the pathology can be judged by the swelling.
The stronger these symptoms are, the further the disease progresses.
Therefore, if symptoms increase and home methods at hand are ineffective, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Useful video
First aid for eye injury. Algorithm of actions before contacting a specialist.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2100
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 2 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Why does the eye under the lower eyelid hurt?
The causes of pain under the lower eyelid are the same as under the upper , and in most cases it is chalazion and stye .
But with the disease “ endophthalmitis,” the pain syndrome often manifests itself under the lower eyelid. This is a purulent inflammatory lesion that spreads to the vitreous body of the eye and, if left untreated, endophthalmitis leads to loss of vision.
Know! Pain under the lower eyelid in this case can be explained by the fact that this is a pathology of traumatic origin (including it can develop after unsuccessful surgical operations), and sometimes it develops with ulcerations of the cornea.
And in all these cases, the nerve endings are affected, of which there are more in the lower part of the visual organs.
A complete cure for endophthalmitis can only be guaranteed in a hospital setting, so at the first manifestation of symptoms of such a disease (swelling of the eyelids, headaches, the appearance of a white or yellowish stripe at the lower edge of the iris, lacrimation), you should consult a specialist .
Treatment options
Elimination of pain under the upper eyelid require symptomatic therapy, but complete treatment of the underlying disease , therefore, after examination by an ophthalmologist, additional diagnostic measures are possible from other specialists.
In cases where the cause of pain is a foreign body getting under the eyelid , you can cope with the problem yourself if you follow this simple algorithm:
- A clean scarf or napkin is folded into a triangle to form a sharp edge. After which, with this sharp edge, the foreign object is gently pushed towards the inner corner of the eye (if the object has not dug into the conjunctiva to a great depth, it can be immediately picked up with the corner of a napkin);
- when the speck reaches the corner of the eye, you can remove it from there with a cotton swab ;
- After the procedure, antibacterial drops can be dropped into the eye .
At home, you can take emergency measures for chemical burns.
Treatment
Elimination of pain in the corners of the eyes is possible only after identifying the cause that caused it. Only a specialist can help with this during a diagnostic examination of the organ of vision. To relieve discomfort, you can independently apply moisturizing drops and cold compresses to the eye area.
However, it is necessary to remember that you should not delay your visit to the doctor, and pain in the eyes, accompanied by decreased visual acuity, redness of the eyes and photophobia, require immediate attention.
In the medical department, everyone can undergo examination using the most modern diagnostic equipment, and based on the results, receive advice from a highly qualified specialist. The clinic provides consultations to children from 4 years old. We are open seven days a week and work daily from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. Our specialists will help identify the cause of vision loss and provide competent treatment of identified pathologies.
You can find out the cost of a particular procedure or make an appointment at the Moscow Eye Clinic by phone (daily from 9:00 to 21:00, free for mobile phones and regions of the Russian Federation) or using the online registration form.
Yakovleva Yulia Valerievna