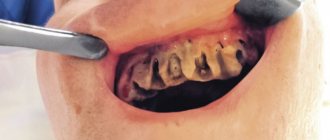
What do we do when a tooth is pulled out? Even under the office, many examine the traces of the operation, fearing for its consequences. The fear intensifies after the end of the painkillers: how long should the wound hurt, and when will the bleeding stop?
Blood clot after tooth extraction
On the first day, a blood clot appears at the site of the pulled out tooth - an important condition for high-quality wound healing. In order for recovery to proceed without serious consequences, it is important to know what the wound should look like during extraction, what should and should not be done with it during the recovery period.
A few words about the procedure
Tooth extraction is a full-fledged surgical procedure. The operation consists of four stages.
- Treatment of the area around the tooth that is to be removed.
- Anesthetic injections - ampoules in carpules, where an anesthetic is combined with drugs to constrict blood vessels. Usually local anesthesia is used in the area where the nerve that innervates the problem tooth exits; if this is not enough, anesthetics are added without additional effect. When the medicine is injected into the inflamed gum with an acidic environment, part of it is inactivated, so additional anesthesia is used.
- Tooth extraction after the anesthesia has started working (the gums become numb, the blood vessels narrow). A scalpel is used to cut off the ligaments that fix the tooth. The choice of instruments and duration of the procedure depend on the condition of the tooth.
- Treatment of the oral cavity after removal: sutures (if the wound is torn or its edges are located far from each other) and a gauze swab soaked in a hemostatic agent (it must be held in the teeth for 20 minutes, since the effectiveness of the hemostatic drug increases compression of the wound). Do not rush to remove the tampon.
Gum section
Preparing for removal
Removal of a tooth
Installing a tampon
Stitching
Bleeding from the hole itself does not pose a mortal danger. In medical practice, only one case of death was recorded when blood from a wound entered the respiratory tract because the patient was intoxicated. The bleeding was complicated by cirrhosis of the liver, which interferes with clotting, and the woman had three teeth removed at once.
The main causes of bleeding gums
There may be several reasons - from gum disease to an incorrectly selected brush and stones on the teeth.
- A common cause of bleeding from the gums when brushing teeth is a common disease in children and adults - periodontal disease. Dental bacteria infect the oral cavity and then penetrate into the periodontal pockets. The gums in the affected area may be sore and swollen, and blood may appear when brushing your teeth. Treatment of periodontal disease will help you get rid of this problem.
- Another fairly common reason why gums bleed and become inflamed is the formation of stones on the teeth and under the gums due to poor oral hygiene. You need to clean plaque at least once a year, this is done by your dentist.
- Pregnancy and the resulting hormonal changes cause gum pain and bleeding.
- A hard brush is a common cause of bleeding when brushing your teeth. The best option is a brush with soft bristles or medium-hard bristles.
- Infectious diseases of the throat and nose can also cause the gums to become swollen, painful, and bleeding.
- Avitaminosis. Due to a lack of vitamins and microelements, not only the body as a whole suffers, but also the oral cavity.
- In fairly rare cases, bleeding can be caused by smoking.
After operation
After three hours, the painkillers are still strong, so patients do not feel pain or it is mild. All this time, pure blood or ichor may be released from the hole. If a figure eight was removed, this can last all day, since the surgical area of the wisdom tooth is larger than that of other teeth.
Bleeding from the socket
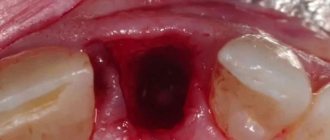
On the second day, the hole has an unattractive appearance: a blood clot with a grayish coating. It looks like pus, but you shouldn’t be afraid of it: it’s fibrin, a substance that facilitates wound restoration. If everything goes well, the pain will be aching and will subside by the end of the day. If the nature of the pain is different - sharp, pulsating, and there is scarlet blood from the wound, you should urgently see a dentist.
At first, the hole may smell foul. There is no need to be afraid of this: blood accumulates there, and since it cannot be rinsed out, bacteria settle in the wound. If you feel normal, there is no fever, there is no reason to worry.
The rehabilitation process is normal if:
- What medicine is put into the hole after tooth extraction?
- when touching the wound, the ichor does not appear;
- the aching pain gradually disappears;
- feeling normal (temperature up to 38° is possible only in the first two hours);
- swelling on the cheek decreases (if it was not there before extraction, it should not appear at all);
- after 3 days the wound no longer bleeds.
2 weeks after removal
To reduce bleeding, you can make a tampon yourself. Positioning it so that the edges do not injure the blood clot, hold the napkin for half an hour. In the pharmacy chain you can buy a hemostatic sponge, which can be used in cases of heavy bleeding, for example, in liver failure.
Hemostatic sponge
The hole is closed with a hemostatic sponge.
You can take one or two tablets of Dicinone or Etamzilate (no more than 8 pieces per day).
Dicynone tablets
You cannot experiment with hydrogen peroxide: it reacts with blood components, destroying the blood clot and increasing blood flow.
How does the healing process work?
Even if there are no complications, the wound heals completely within four to six months.
- On the 2nd day, a blood clot appears in the socket - a protective gate against mechanical damage and infections.
- If healing proceeds normally, on the third day you can already see granulation tissue at the operation site.
- In the second week, the epithelium actively grows, and granulation tissue appears instead of a clot. Primary restoration of bone structures occurs.
- In 2-3 weeks, it displaces the blood clot and bone tissue is visible around the perimeter.
- Recreation of new tissues takes 30-45 days.
- In about 60 days, the hole is closed by osteoid tissue impregnated with calcium.
- After 4 months, the bone becomes an “adult”, with a porous structure.
- When the bone is fully formed, the wound should resolve to a third of the length of the root.
- After extraction, the gums atrophy and the process of subsidence continues for 6-12 months.
Stages of tissue healing after tooth extraction
Surgical preparation for prosthetics
The reasons for removal are varied - from banal caries to the roots of a decayed tooth and age-related diagnoses that cause a general deterioration in the condition of the oral cavity. Injuries, gum disease, genetic predisposition are on the list of existing prerequisites.
Simultaneously with the removal, a good doctor will definitely suggest considering the possibilities of restoring the bite - installing an implant with a crown, a full-fledged bridge, or a permanent artificial jaw. Within the framework of such a task, removal is considered as surgical preparation of prosthetics:
- tooth extraction, root extraction;
- increasing the volume of bone tissue by building up;
- cutting off altered areas of the mucosa;
- implant installation.
In the absence of aggravating diagnoses, the surgeon is limited to removal, in other cases he requires additional operations. Next, the issue of installing artificial units is resolved. And here the patient’s choice is especially important.
What determines the rate of tissue regeneration?
The indicated time frames are indicative information, since the restoration process is influenced by many factors:
- doctor's qualifications,
- condition of the roots,
- hygiene procedures,
- gum health
If a tooth is removed during an exacerbation of the disease, healing slows down. A lacerated wound also tightens it, especially during operations on figure eights. Particular attention is paid to high-quality treatment after the procedure. If tooth fragments remain in the hole, they will interfere with the formation of a protective blood clot, and in the end everything will end in an inflammatory process, lengthening the recovery period.
Healing socket in place of a wisdom tooth
After removal, the surgeon will definitely give advice on proper care of the wound. If you ignore advice or follow it irregularly, complications are inevitable.
Since the blood clot covers the vulnerable hole, it is important not to disturb it. If you rinse immediately after visiting the dentist, you can wash it. An unprotected wound easily becomes infected.
Rinsing after tooth extraction is prohibited
If there are problems with changes in blood pressure, sometimes the wound bleeds for a long time. Once the blood pressure normalizes, bleeding usually stops.
Recommendations from experts
If the pain does not go away for a long time, there is no need to guess what exactly caused the discomfort. It is better to consult with highly qualified dentists to exclude serious complications and consequences. Experienced doctors with many years of experience accept Cerekon dentistry. Doctor's appointments are carried out by appointment. To make an appointment, contact us at +7(495)-105-92-30. Be healthy!
Sign up for a free consultation:
Enroll now
Complications during extraction
All unfavorable conditions lead to alveolitis - inflammation that develops after infection of the wound. Most often, problems begin after a blood clot falls out. Sometimes a clot does not form at all.
- Ear hurts after wisdom tooth removal
Alveolitis of the tooth socket
If you rinse your mouth, alveolitis is diagnosed after 1-3 days. The water pressure washes away the protection and inflammation is guaranteed. Its signs:
- increasing pain, gradually affecting neighboring areas;
- as inflammation spreads, general signs of intoxication intensify: fever, aching joints, loss of strength;
- swelling spreads to nearby areas;
- the mucous membrane turns red-blue due to impaired blood supply;
- bad odor from the problem area in which food debris accumulates.
All other complications also develop after the wound becomes infected. It is convenient to present their features in a table.
| Type of complication | Description |
| Dry socket | The blood clot has not formed, recovery time is delayed, and there is a risk of alveolitis. Most often it happens during active rinsing. A dry socket should be shown to the dentist. |
| Osteomyelitis | A serious consequence when alveolitis spreads to the jaw bone. Inpatient treatment is required. |
| Nerve damage | If the tooth has massive roots, there is a possibility of nerve damage. All tissues near the tooth lose sensitivity. For treatment, a vitamin complex and medications are used that accelerate the transmission of nerve impulses to muscle tissue. |
| Cyst | A serious complication requires surgical methods of elimination. |
After recovery, there is no need to delay prosthetics, since the absence of any unit of the dentition has a bad effect on the condition of the entire oral cavity.
Prosthetics