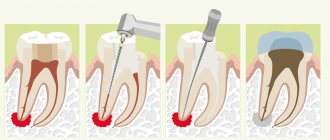
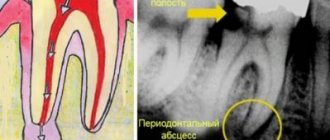
An inflammatory formation affecting the upper part of the tooth root is called granuloma. It is formed during the development of periodontitis. Tooth granuloma is tightly attached to the root, being the initial stage of a granular cyst (cystogranuloma), from which it differs, in fact, only in its slightly smaller size. If the formation is ignored and not treated, it will begin to increase.
Tooth granuloma: symptoms of the disease
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis based on an x-ray, where a darkening will be visible in the root area. Any darkening in the image is a sign of the presence of a cavity, but if a granuloma occurs, it means that periodontitis, which is chronic in nature, begins to develop.
For a long time, the tooth may not bother a person at all. Sometimes pain may occur when biting or when eating hot food: these are the first signs of the development of chronic periodontitis. An exacerbation of the disease is observed during periods of weakening of the body's immunity: then the pain intensifies significantly, which is especially noticeable when biting. During such periods, as a rule, the gums become swollen, and in the area of inflammation it becomes painful to touch.
Granuloma symptoms and complications
Symptoms of dental granuloma are nonspecific. Often the patient is unaware of the disease, since there may be no signs at all. Usually the tooth does not bother you, but moderate pain occasionally occurs when biting, drinking hot drinks or eating food. Such symptoms are characteristic of all forms of periodontitis.
It is worth noting that from time to time the disease may worsen. For example, in case of hypothermia, an infectious disease, surgery - in all cases when the body's defenses are reduced. During an exacerbation, the following symptoms appear:
- sharp pain, intensifying when biting, tightly closing the jaws;
- swelling of the gums in the projection of the root apex;
- pain in the gums when touched.
An exacerbation can go away on its own, and the disease returns to its chronic form. But sometimes inflammation develops before the appearance of purulent contents in the tissues - periostitis or gumboil.
Inflammation can cause resorption or dissolution of a section of jaw bone tissue. The appearance of purulent complications is dangerous due to its consequences: from tooth loss and damage to surrounding units to tissue melting and sepsis. Therefore, it is important to get timely help from a doctor. Treatment of dental granulomas is carried out by a dental therapist, and if removal is required, you need to contact a dental surgeon.
Why does granuloma appear on the root of a tooth?
At the tops of the roots, such formations can appear for several reasons:
- Poorly performed treatment of pulpitis. If caries is started, the affected cavity gradually becomes quite deep. When microorganisms enter the pulp, its inflammation begins, accompanied by acute pain, which may stop over time, indicating the death of the nerve.
But the development of the disease does not end: bacteria through the root canals extend beyond the boundaries of the affected tooth, as a result of which a focus of inflammation appears near the upper parts of the roots, called periodontitis. The further course of the disease can occur according to several scenarios, one of which is the formation of granuloma.
It is necessary to understand that a tooth with a granuloma does not necessarily have to be affected by caries, since the root can become inflamed near a tooth that has already been treated. If the doctor has not completely removed the tissues affected by caries by placing a filling on top of them, then there is a high risk of developing pulpitis with the subsequent formation of granuloma.
- Filling of root canals performed with violations. A granuloma that appears on the root of a tooth whose canals were filled some time ago indicates the unsatisfactory quality of the procedure performed. Due to inattention, haste or inexperience, the doctor could not fill the canals to the very top. Dentists often refuse to admit their own mistake, because in this case they will have to treat the tooth for free. Such unfortunate specialists can evade until the last minute, pretending that they do not understand the causes of pain, recommending taking a course of antibiotics.
Types of X-ray
After the examination, the doctor can prescribe the patient one of four possible types of x-rays
.
Prikusnoy
This method allows you to reflect the crown part of the tooth in the image. It is used to detect periodontitis and interdental caries. Bitewing can be used to obtain images of the upper and lower teeth.
Sometimes such a picture can be taken after prosthetics and crown installation to see how correctly the procedure was performed.
Sighting
With the help of a targeted image, it is possible to discern a specific affected tooth or several. Moreover, such a picture cannot include more than 4 teeth.
Panoramic
Using panoramic images, you can monitor the quality and effectiveness of the treatment already performed. They allow you to see a complete picture of the state of the entire dental system, and this is not only teeth with obvious problems (for example, caries, chips, etc.), but also roots, periodontal tissue, paranasal sinuses and the lower jaw joint.
On a panoramic image, the doctor will be able to see the presence/absence of filling material, hidden carious cavities, inflammation of the peri-root tissues, cysts, tumors, as well as teeth that have not yet erupted.
Digital or 3D X-ray
This type of x-ray is considered the most modern and safe. Using 3D X-rays, you can get a clear image of the entire row of teeth and a specific tooth. The result is a three-dimensional image that is displayed on the monitor.
Diagnosis of granuloma on the tooth root
At the early stage of development of the disease, it will not be possible to notice any visual changes. The first signs of pathology become noticeable as the size of the infected area and the amount of pus increase.
To treat the disease with therapeutic methods, it is necessary to examine the affected area in detail: a complete picture of the granuloma must be obtained, which will allow one to detect key signs of the disease that differ from other diseases.
When suppuration occurs, the gums become very red and swollen, and pain appears, which can radiate to the head area in general and the ear in particular. This is the first symptom that should make you wary.
The following methods can be used to make an accurate diagnosis:
- use of classical x-rays;
- the use of radiovisiography or, in simpler terms, computer x-ray.
In the picture, the affected area looks like a dark spot with a clear border in the upper part of the tooth. The size of the spot indicates the following:
- 5-8 mm – the probability of having a dental granuloma is high;
- more than 8 mm – formation in the form of a cyst.
In rare cases, a large granuloma, up to 1.2 cm in size, may occur. Therefore, X-rays may not be enough for diagnosis: it is recommended to perform a biopsy of tissue cells from the area affected by the disease.
In most cases, granuloma is discovered during treatment of other dental diseases: the doctor may pay attention to increased swelling and swelling of the gums. In addition, the bone tissue near the top of the tooth may also bulge.
An increased risk of developing granuloma is observed in patients with crowns and pulpless teeth. Such people are advised to undergo regular examinations in order to promptly identify any changes affecting the gums and teeth.
Material and methods
To identify patterns in the display of CC, including sealed ones, 374 intraoral periapical radiographs, 53 orthopantomograms (OPMG), 47 CT scans before and after endodontic treatment of 194 patients were studied. Under experimental conditions, 127 intraoral periapical radiographs, 26 radiographs using a parallel technique, 32 OPMG, 1434 CBCT sections were performed on skeletonized jaws with teeth.
CBCT data were compared with the results of endodontic treatment, intraoral imaging and OPMG. The influence of the informativeness of radiological techniques on the quality of endodontic treatment was determined, taking into account the time spent on detecting CD of teeth.
The X-ray examination techniques used were applied according to generally accepted rules of survey geometry.
Intraoral radiography was carried out using dental devices Minrey (Finland) and Heliodent DS (Germany), orthopantomography - using Proscan (Finland) and Orthophos XG5 DS Ceph (Germany) devices. Cone beam computed tomographs New Tom 3G (NIM SrI, Italy) and Vatech Pax Reve 3D (E-WOO Technology, Korea) were used. The shooting conditions on these devices complied with the manufacturer's recommendations.
Tooth granuloma: treatment
Usually treatment is only therapeutic in nature, but its strategy may vary depending on whether the canals have been filled before.
- If the canals have not been filled, the tissues affected by caries are drilled out, and the old filling is removed. This is required to carry out high-quality mechanical treatment of the canals, which are expanded and treated with antiseptic agents. If the granuloma is small (formations up to 3 mm are considered such), then the canal is sealed immediately. If the size of the granuloma exceeds 3 mm, the treatment period increases, since it is necessary to put a medicine into the canal, which includes potassium hydroxide - this substance leads to a decrease in the granuloma or even to its complete disappearance. A temporary filling is placed for the period the medication is placed (approximately 2-3 weeks). Then a repeat x-ray is taken, which should clearly show a significant reduction in the inflammatory formation. If the dynamics are obvious, the canals are sealed and a permanent filling is placed.
- If the canals have been filled, then the first stage of treatment is their unsealing. The further sequence of actions is similar to that described in the previous paragraph. The only thing is that if there is a crown on the tooth, it will have to be removed, and after the treatment is completed, it will have to be made and placed again. Some patients do not want to spend money on re-installing a crown: the solution is to perform a root resection operation, when the upper part with the granuloma attached to it is cut off through a small incision in the gum.
Clinic doctors
If you have extensive carious lesions on your tooth or inflammatory processes (pulpitis, periodontitis), then, unfortunately, removal of the nerve from the diseased tooth cannot be avoided. And at the same time, filling the canals. Root canal filling is a complex and responsible procedure. And not only because the doctor must carry out all manipulations with high precision and caution.
Even if the operation went without surprises, after a while you may encounter very unpleasant complications.
And in 60%-70% of cases, the cause of these complications is poor-quality canal filling!
The consequences of such treatment may be:
- severe toothache due to “overfilling” - when excess filling material extends beyond the upper border of the canal;
- gumboil, the development of acute abscesses, the appearance of cysts on the tooth due to “underfilling” of the canals - then an infection develops in the voids of the canal;
- complete tooth removal , which is caused by inaccurate treatment of the canals before filling and perforation of the root wall.
First of all, let's figure it out -
What difficulties may arise at each stage of canal treatment?
This way you will understand what the dentist does and in what order, and for what reasons complications arise.
After all, the tools and materials that the doctor uses directly affect the success of the entire operation. A minor mistake and the whole procedure will have to start all over again.
In modern dentistry, all manipulations are performed under anesthesia.
1. First of all, the doctor removes the tooth tissue affected by caries.
To open access to the root canals and pulp, diseased and (partially) healthy tissue must be removed.
To do this, the doctor drills the tooth in the same way as when filling.
2. After this, you need to remove the tooth pulp.
This is a bundle of nerves that fills the crown of the tooth and the canals themselves.
It is important to remove the pulp completely, because it is incomplete removal of the nerve that often leads to prolonged pain.
3. Determine and record the length of the root canals.
This is an important stage of treatment, because the correct filling depends on how accurately the doctor determines the working length of the canal.
Incorrectly determined canal length is the main cause of all the complications that you already know.
An unfilled or insufficiently densely filled canal, in the remaining space of which bacteria can multiply.
In this case, you need to reseal the canals as quickly as possible. Otherwise, you risk losing your tooth!
Filling material (gutta-percha or paste) that extends beyond the root apex can lead to severe pain for a month (!) after surgery.
In some cases, the pain will go away on its own, while in others, resection of the root apex and removal of excess material will be required.
In their work, specialists at our clinic use high-precision methods for measuring the length of canals:
- X-ray - based on X-ray images;
- electrometric - using special apex locator devices;
- a combination of both methods.
Today, using an apex locator together with x-rays is the most accurate way to determine the length of the canals.
In this case, much fewer x-rays are needed for diagnosis, which means that your treatment will be more relaxed and comfortable.
Too much canal treatment can lead to post-operative pain. Therefore, having accurately determined the length and shape of the canal, DentaBravo specialists fix it with a limiter, after which all manipulations are carried out within this length.
4. Now let's move on to processing the channel.
As a rule, the channels are too narrow, and their walls have unevenness. Therefore, before filling, the doctor expands and aligns them in order to evenly fill them with filling material.
Our clinic specialists use two types of mechanical canal treatment:
- using hand instruments that the doctor himself rotates in the root canal;
- machine processing using endodontic tips and a special device.
In our work we use both techniques, but we recommend machine processing. In our clinic, the latest tools are used for canal treatment - nickel-titanium files (tapers):
- more flexible and therefore suitable for processing the most complex curved channels;
- more durable , and therefore safer - because they will not break off inside the tooth and the fragments will not damage the tissue;
- more effective due to their special shape, so they clean the channels better.
In addition, in our clinic this is where doctors are extremely careful to prevent such complications.
Careless movement of the instrument can lead to perforation of the canal wall and then the filling material will get inside the bone tissue.
If measures are not taken immediately, further treatment of this tooth will be ineffective!
After preparing the canals, they are treated with antiseptics and filling begins.
5. At this stage, the canals are filled with filling mass.
There are several methods for filling canals, but we will look at the most common of them - the lateral condensation method.
The root canal is filled with a special paste (sealer). Then gutta-percha pins are inserted - first the main one, and then additional ones. As a result, from 8 to 12 pins are tightly placed in one channel.
6. Final control of the filling is carried out and excess gutta-percha is removed.
At the DentaBravo clinic, they first use an X-ray to check that the material densely fills the entire canal. And only after this the remains of gutta-percha protruding above the mouth of the canal are cut off.
7. A temporary filling is installed.
Immediately after filling the canals, the crown of the tooth cannot be restored, so it is carried out at the next visit to the dentist.
And finally, the most important thing...
How can you make sure that the canals are sealed correctly?
There are only two ways.
1. Focus on your own feelings.
You should be wary:
- pain that does not go away after several days;
- excessive tooth sensitivity and discomfort while eating;
- any changes in the color and density of the oral mucosa.
However, pain may be an individual reaction and a variant of the norm, so be sure to consult a doctor. And best of all→
2. Take a control x-ray.
From the image, you can even independently determine how well the dentist did his work, whether there are voids or excess material in the canals. It is clearly visible in the photographs: the sealed canals have a bright white color.
And to finally calm down, come for a free consultation at our clinic with pictures. It’s possible without them - after all, we also have our own state-of-the-art X-ray machine, with which we can check the quality of the previous treatment in a few seconds!
Or immediately in order to fill teeth using 100% reliable methods, using modern equipment and an experienced doctor.
Sign up for a free consultation at the DentaBravo clinic!
Granuloma between tooth roots: treatment with antibiotics
The number of people putting off visiting a doctor until the last minute is large. There are many reasons for this: fear of pain (although modern means of anesthesia make it possible for the patient to feel nothing at all during treatment procedures), lack of free time, and reluctance to part with money. But all these reasons and excuses come to naught when the pain becomes unbearable, becoming chronic. As practice shows, as soon as a person does not sleep for a couple of nights, the issue of the need to visit the dentist is resolved by itself.
However, many people try to cure granuloma on their own using strong antibiotics, which is basically impossible. Antibiotics may be prescribed to relieve inflammation and stop the formation of pus, but nothing more. But the action of antibiotics may not affect pathogenic microorganisms located in the root canals, and it is the infection in their unsealed areas that is the only reason for the formation of granulomas.
If a patient comes to the doctor with a suspicion of granuloma, and the doctor, driven by some of his own considerations, does nothing, recommending taking antibiotics, it is better not to delay time, but to immediately contact another dentist. Some doctors simply do not like to re-treat someone’s poorly treated teeth, since repeating the same operations takes much more time, while others, if the patient comes back again, do not want to admit that they made a mistake, which for them is tantamount to realizing their own lack of competence.
Tooth granuloma: surgical treatment
If therapeutic treatment does not help, then surgery comes into play: the operation is performed in the presence of a destructive process affecting the gums, and anesthesia (both general and local) is used to carry it out.
There are several surgical treatment options.
Root resection
Elimination of granuloma occurs in several stages:
- a passage to the top of the tooth opens by peeling off the gum shell;
- the root canals are cleaned and subsequently filled with medicinal substances;
- excision of the granuloma is carried out;
- the area is filled with synthetic fabrics;
- the tooth is filled.
On average, the operation takes about an hour.
Hemisection
If a tooth has many roots, then this procedure is prescribed (if there are complications that prevent the root from being saved).
The treatment procedure includes:
- removal of roots under the crown;
- filling the empty space between the roots with a special dental product;
- installation of a crown;
- monitoring the condition of the tooth using x-rays.
The method is simple, while the functionality of the tooth is preserved. If necessary, some time after the procedure, the patient can resort to prosthetics, provided that the root system remains healthy.
Cystotomy
The method is used when removal of large granulomas is required.
To implement it:
- a channel is created between the affected area and the oral cavity, through which pus absorbed by tampons is removed;
- after cleaning, the cavity is treated with antibacterial agents;
- sutures are placed;
- the cavity, free from suppuration, is filled with bone cells.
Stages of the procedure
To carry out the procedure, a separate room, equipped accordingly, is required. The procedure itself does not cause virtually any discomfort and consists of several stages.
- The position of the person in the chair, the doctor’s clarification of the location of the problem.
- It is imperative that the patient wears an apron that protects against harmful radiation.
- Fix your head to get a good shot.
- Taking an image with the patient in a stationary position.
The entire procedure from taking a photo to receiving it in electronic or printed form takes a short period of time - about 20 minutes.
Analysis of the finished image
The dentist himself or a radiologist is responsible for describing the image. If the image quality does not meet the required quality, the procedure is repeated. The specialist examines the patient’s teeth, roots, and jaw bones in detail. If there are light and dark areas, this indicates the appearance of inflammation, cysts and other neoplasms.
In the pictures you can see inhomogeneities, damage to bone tissue, damage to the enamel, cement and root part, damage to the septum and other abnormalities that indicate the presence of a particular disease.
Features of performing a targeted shot for children
The younger generation needs this procedure more than adults, because caries develops more intensively in children. Another reason is to identify deviations and defects at an early stage of tooth growth. If any are detected, the necessary preventive and therapeutic measures are taken.
But it is not advisable to use the targeted photo procedure for children under 2 years of age. It is prescribed only in cases of birth or mechanical injuries, or to monitor the development of teeth.
Advantages and disadvantages
Each research endeavor has its pros and cons.
Advantages:
- Safety.
- High image quality.
- A large amount of information received.
- Convenient storage.
- Speed of execution.
Disadvantages for dentists include:
- It is impossible to detect cracks in the roots.
- Pictures of only one plane.
- Small viewing area.
- Narrow survey area.
- Limitations for use
The procedure is considered harmless and therefore has no visible contraindications for its implementation. Considering the minimum level of radiation (the permissible dose is 1000 microsieverts per year, i.e. about 100 images per year), a targeted image can be taken even during pregnancy. But, nevertheless, it is not recommended to resort to the procedure under the age of 2 years, in the presence of bleeding, reduced immunity, or in poor health.
A radiovisiograph provides a lower dose of radiation, an X-ray machine.
Price of the procedure
| Click to sign up for a FREE consultation |
Imaging services are provided in almost every hospital. Its cost will vary from 150 rubles and above. Sometimes the procedure is included in the cost of treatment.
In public clinics, under the compulsory medical insurance policy, you can take an x-ray and print the image for free.
Thus, a targeted image is a safe and effective procedure that can identify problems with the dental elements in the early stages if the patient seeks qualified help in a timely manner.
Measures to prevent granuloma after an extracted tooth
Preventive measures are aimed at preventing the development of the disease. They include:
- high-quality cleaning of teeth and gums on a daily basis;
- timely treatment of bleeding gums;
- regular visits to the dentist at least once a year (it is better to do this twice);
- replacing toothbrushes (old brushes accumulate bacteria that can provoke the development of the disease);
- contacting the dentist at the slightest pain associated with the gums or teeth;
- treatment of caries, periodontitis and pulpitis - quite often these diseases are the catalyst for the development of granuloma;
- the use of medicated toothpastes and herbal decoctions for rinsing;
- eating foods rich in calcium and other trace elements.
Complications after granuloma at the site of an extracted tooth
Lack of timely treatment and hope that the disease will go away on its own is fraught with serious consequences. Among the most common complications it is worth highlighting:
- development of periodontitis and further formation of a fistula;
- the occurrence of alveolitis is a consequence of the presence of an inflammatory process;
- formation of purulent flux;
- suppuration of the perimaxillary tissue;
- entry of pathogenic bacteria into the lymph nodes, from where they penetrate the cardiac system and internal organs (kidneys, liver and brain);
- development of facial asymmetry;
- the emergence of new foci of infection;
- infection of the body due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the blood vessels.
Timely removal of granuloma is a guarantee to avoid unpleasant health consequences.