Catalog: Dental handpieces / Help in choosing
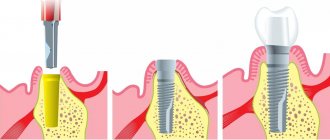
Fig.1. Turbine and micromotor dental handpieces
Handpieces for dentistry can be divided into groups:
- Turbine FG Friction Grip
- Corner RA Right Angle
- Direct HP Handpiece
- Special (endodontic, surgical, for removing dental plaque, for dental work)
Dental handpieces from time immemorial
The history of the development of dental handpieces as an independent tool designed to convert the energy of a compressed air flow, rotation of a micromotor or electric current into the movement of a dynamic working tool fixed in the handpiece began in ancient times with a primitive bur, which was driven by a rope-arc stretcher.
In subsequent centuries, doctors attempted to create a tool suitable for preparing teeth, but lack of knowledge and the low level of technical progress did not give them a chance. And only in the middle of the 14th century did things get off the ground...
How it was in the 19th century
The prototype of a dental handpiece with a fixed steel bur can be considered the first automatic drill, powered by a spring mechanism that wound up for two minutes. This invention, made in 1864, belongs to the English doctor George Fallows Harrington. The bur speed reached 100 revolutions per minute, but the design was extremely inconvenient for the doctor. In the early 70s of the 19th century, American dentist James Morrison patented a drill with a foot pedal drive, where a sleeve with a tip was put directly on the output shaft and the torque reached 2000 rpm. It was this design that not only marked a revolutionary breakthrough in the development of dental equipment, but was also actively used in medical institutions in developed countries until the first quarter of the 20th century.
Russia, XX century
In Russia in the 30s of the 20th century, with the active development of dentistry as a practical discipline, industry began to produce several types of dental machines in which the dental handpiece was already a separate part and performed the same functions as the most modern handpieces. Only the speeds are incomparable: straight and contra-angle handpieces of those years had speeds from 3,000 to 30,000 per minute, the turbine handpiece invented in 1957 reached 45,000 rpm and was in great short supply, and the modern turbine handpiece reaches 500,000 rpm.
TOP 5 popular models
To choose a dental handpiece, you need to clearly understand for what purpose it is being purchased. Given the multidirectional activities of specialists, several tips are required. The advantages of some complement the positive aspects of others.
Today, German and Japanese handpieces, as well as budget models from Russian manufacturers, are popular among dentists. Chinese tips appeared on the market quite recently, but they also managed to conquer their segment. Disposable ones are especially in demand - they are used during one dose.
NTKS-300-01 M4, Micron
Turbine push-button handpiece with standard head for therapeutic work.
NTS-300-05 M4, Micron
Friction bur clamp with standard head for therapeutic work.
Hunan Jinme Dental Handpiece (China)
The handpiece with M4 key is intended for orthopedics.
Standard RT07 with NSK rotor, Rito Dental
The turbine tip with fiber optics guarantees constant visibility of every area of the surface being treated.
TC-40P B, 2-channel BORDEN
Reference!
The quality of a dental turbine handpiece is reflected in its cost. Products from Russian manufacturers will cost between 2-12 thousand rubles, European ones - from 10 to 60.
Source
Straight and contra-angle handpieces
Straight handpieces are low speed. A conventional handpiece paired with a micromotor provides bur rotation speeds from 1000 to 30,000 rpm. Due to certain design features, they are most often used in surgical and orthopedic practice, as they allow significant pressure to be applied to the cutting tool without vibration. For comparison: the standard pressure on dentin for a steel bur at a rotation speed of 18,000 rpm is 500 grams, and for a tungsten carbide bur at 450,000 rpm is 2 grams. . Dental technicians also work with them in the manufacture and fitting of dentures, implants and other orthodontic structures.
Contra-angle handpieces are also low-speed and have a wide range of bur rotation speeds, making them a versatile tool. Contra-angle handpieces are used by dentists of all specialties. Its shape is convenient for working in hard-to-reach areas of the oral cavity, it can withstand significant lateral loads without vibration and easily works with various cutting tools. The following types of contra-angle tips are distinguished:
- Standard contra-angle handpiece with 1:1 gear ratio and bur rotation speed of 1,000 - 40,000 rpm. (blue markings).
- The overdrive contra-angle with gear ratios from 1:2 to 1:10 reaches speeds of 5,000 - 230,000 rpm. (red marking).
- Reducing tips have reduction ratios from 4:1 to 20:1 and speeds from 2,000 to 10,000 rpm. (green marking)
Straight and contra-angle handpieces from all manufacturers have a standard micromotor mounting (ISO 9001). According to the cooling system, tips are distinguished:
- No cooling. They are used extremely rarely and only for low speeds due to the risk of overheating and damage to enamel and dentin.
With external cooling. Used mainly in dental surgery.
With internal cooling. Used with air and electric micromotors and is the most common and effective type of cooling.
The backlight can be implemented through fiber optics or a built-in LED and light generator.
TG 656 EASY
TG 656 EASY
An elegant and powerful turbine handpiece without backlight, with a push-button bur clamp and a side 5-channel cooling system from the legendary company CHIRANA Medical - a world-famous manufacturer of high-quality medical equipment since 1935 in Stara Tura (Slovakia).
TG 656 EASY is a handpiece with air supply and is intended for drilling tooth enamel, dental cavities and grinding crowns.
The handpiece has a 5-channel cooling system with push-button fastening. The casing is made of brass with surface treatment. Connection type using 4-ISO MIDWEST.
The main advantages of the handpiece are low weight, easy movement in the patient’s mouth and ventilation of the tooth cavity. At the same time, despite its dimensions, the device is quite powerful.
Characteristics:
- Working pressure: recommended 0.21 to 0.23 MPa
- Speed: from 342,000 to 418,000 rpm. /minute
- Bur stopping time: up to 2 seconds. An undeniable advantage in terms of patient safety and hygiene, because when the rotor rotation is quickly stopped, it is impossible to harm the patient, and microscopic contaminants from the patient’s mouth are not sucked into the turbine head
- Air consumption: 38 l/minute ±2 l/minute
- Used burs: shank diameter 1.59-1.6 mm, length maximum 25mm
- Cutting diameter maximum 2.1 mm
- Collet force: minimum 35 N
- Sterilizability: AUTOCLAVE 135°C
- Power: 18 W
- Noise level: 60 dB
- Hose connection: ISO 4 MIDWEST
- Bearings: ceramic (made in Germany)
- Spray: 5-jet spray
- Weight: 46 grams
WHERE CAN I BUY
Turbine tips
In clinical practice, turbine handpieces are most often used by dental therapists. Turbine tips differ significantly from angled and straight tips in their technical characteristics. There are two main factors:
- High bur rotation speed, which is 150,000 - 500,000 rpm.
- Low mechanical power, due to which increased force on the tip leads to a decrease in the speed of the bur and its possible stop, as well as to rapid wear of the rotor group.
Working with a turbine handpiece requires a certain skill and constant control of the pressing force, since excessive or insufficient force on the drill reduces the efficiency of cutting hard tissue.
Connection Standards
The turbine tip can be directly screwed onto the mouthpiece of the installation hose or you can use a quick-release adapter to which the tip can be attached by simply snapping it into place. There are five standards for hose connections, the most common being the 2-channel Borden, 4-channel Midwest (non-illuminated), and 6-channel Midwest LUX with fiber optics. As a general rule, if you want to use quick-release adapters, then you need to buy them of the same brand with the tip.
Classification by type of hose
If we take into account the second type, then the question of choice depends on the dental unit itself. To select a turbine tip, a photo will clearly not be enough. It is necessary to review its technical data. It all depends on the hose to which this part will be connected. Recently, four-channel tips have become increasingly used, although two-channel ones also exist. The latter type is still used only in offices run by experienced doctors who give preference to time-tested items. Depending on the method of connection to the installation, the turbine tip can either be screwed onto the hose or simply snap onto a special adapter. Naturally, the price of the second option is slightly higher, but it guarantees excellent performance for a long time. Such an adapter needs to be cleaned much less frequently, which means there is no need to constantly remove the tip.
Head dimensions
Turbine tips are available with heads of 3 sizes:
- Standard head (std). A universal model for therapeutic treatment.
- Small head (mini). Designed for children's use and light work that does not require pressure on the bur. The power is slightly less than standard.
- Large head (midi). Mainly used in orthopedic practice, it has increased power and bearings with a large margin of safety.
Illumination of the working area is implemented in the same way as in straight and angled handpieces: through fiber optics or a built-in LED with a generator. The bur clamp is most often push-button, but inexpensive models may use a latch or a special key. Tips are available with ceramic and metal bearings. Ceramic bearings are more expensive and more durable, but with proper care, metal bearings are just as durable.
Classification by additional functions
There are a number of additions that can greatly simplify the doctor’s work. First of all, the conversation is about light support for the operation. A turbine handpiece with illumination is much more convenient, especially if the lighting in the office is not powerful enough. The operation of such an element is most often carried out in the presence of fiber optics or a generator with an LED. The second type is undoubtedly more convenient, because the necessary electricity is generated autonomously, and such a system costs much less than an installation with fiber optics.
An additional function for cooling the working area is available in all types of tips. There are single-point, three-point and five-point sprays, which are used to cool boron. It is customary to distinguish them by price range. The most popular are five-point turbine tips, reviews of which are always full of praise. The spray of such a turbine allows you to use freezing even during the main operation of the dental machine.
Based on the type of bearings, a distinction is made between metal nozzles and the ceramic ones that replaced them. The service life of the latter is still longer, but the rules for caring for them should always be remembered. Any mistake may cause the bearing to be scrapped.
You can notice that turbine tips are much better quality than their mechanical counterparts. The choice of working element of a dental machine depends on many factors, so it is worth carefully studying all the proposals put forward by medical equipment manufacturers.
Our recommendations
So, to select a specific turbine tip model, you should pay attention to the following points:
- Hose Connection Standard (Borden, Midwest, Midwest LUX, Siemens)
- Presence/absence of quick-release adapter
- Head size (std, mini, midi)
- Bur clamp type (button, latch, key)
- Lighting (fiber optics, built-in light generator)
- Cooling (1-point, 3-point, 5-point spray)
- Bearings (ceramic, metal)
Specifications
When choosing, pay attention to several important points. The main characteristics of dental handpieces include:
Bur fixation
A screw collet that secures the bur in the tip is considered more reliable. The disadvantage is the inconvenient replacement of the cutting tool. The collet can be easily damaged if over-tightened. The push-button collet is extremely convenient to use.
Connector for connecting to the drill
Thanks to the connector, it is attached to the hose of the dental unit. They can be six, four, three or two-channel. Four-channel (without electrical wiring) are popular. Midwest-connected handpieces provide greater comfort and precision. Two and three channel TVs are now considered obsolete.
Type of working head
When choosing the type of working head, there are 3 generally accepted standards: for children's appointments (Mini), medium or standard (Std, the most popular) and large (Midi) for orthopedics.
Work area illumination
A turbine handpiece equipped with its own light source will cost significantly more, but it has many advantages. Additional lighting guarantees safe and precise work in the patient's mouth. In addition, the strain on the dentist’s eyes is reduced several times.
Cooling system
The rotation speed of the turbine is high, so it is impossible to do without a spray as a cooling system. There are tips with separate supply of water and air. These include the three-hole Midwest and Borden. There are tips where two functions are combined into a common one (Borden). A cooling system is installed in each turbine, but with one difference - the number of nozzles cooling the boron changes.
Dimensions: weight and size
The average tip head size is 15.5 mm. Weight - 82 grams.
Ergonomics: how it fits in the hand
The handle and working part of the tool should not touch. The ring finger becomes the axis of rotation and support: it rests against the tooth, which makes it possible for effective work. The ring and middle fingers are pressed together: this provides support. The little finger is not involved: it should be relaxed and not bent.
Turbine power
Handpieces vary in power level: the more powerful the tool, the more pleasant it is to work. If there is not enough power, the drill stops and the treatment time increases. The speed of all turbines is almost the same. Manufacturers of handpieces make them according to approximately the same pattern, and the turbine will in any case slow down when it comes into contact with hard tissue.
Bearing type
The tip has 2 miniature bearings built into it: the axis with the turbine impeller rotates on them. The following types are distinguished: metal and ceramic. Ceramic is much lighter than steel and quieter in operation, and has less wear and tear.