Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Today, almost everyone knows that teeth need especially careful care. We buy expensive pastes and use special thread. But, unfortunately, when taking care of our teeth, we completely forget about the tissues surrounding them, while the health of our gums needs to be monitored no less carefully.
Many people are familiar with the symptoms when the gums begin to hurt when pressing between the teeth. And many, unfortunately, ignore this unpleasant pain. Let's figure out what can cause it, what these sensations indicate, and how to relieve unpleasant symptoms.
Causes of pain in the gums when pressing
Remember, discomfort in your gums is a reason to see a dentist. No matter what kind of pain you feel, relatively mild or severe, you need to determine the cause of the problem as soon as possible and begin treating it.
As a rule, pain in the gums when pressed is provoked by three diseases:
- Gingivitis. This disease is accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane and bleeding. Inflammation is provoked by microbial plaque, which occurs due to non-compliance or improper oral hygiene.
- Periodontitis. The disease, as a rule, is accompanied not only by unpleasant sensations, but also by a general deterioration in well-being. The patient feels which tooth is bothering him, as his “elevation” is felt above the other teeth.
- Periodontitis. The disease occurs due to untreated gingivitis. With periodontitis, the necks of the teeth open, pus oozes from the gums, and the teeth become mobile. The problem affects the entire cavity and can lead to tooth loss.
Gum diseases
There are 3 gum diseases that can cause pain. These include:
- Gingivitis.
- Periodontal disease.
- Periodontitis.
The main cause of gum inflammation is poor hygiene and the formation of stone and plaque, which activates the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Inflamed gums begin to swell, turn blue or red. In advanced cases, tooth mobility appears, which can later cause tooth loss.
Gingivitis
Gums with gingivitis
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums, which most often causes pain between the teeth. It is superficial in nature, and at an early stage a person experiences the following symptoms:
- Redness and swelling.
- Bleeding.
- Itching.
- Unpleasant smell.
- The pain intensifies after eating.
As it progresses, small ulcers may form on the gums, which are particularly painful. Subsequently, the gum tissue decreases, which leads to exposure of the tooth root. There is severe discomfort while eating.
- Pocket in the gum between the teeth - how to treat
Important! The main cause of gingivitis is the formation of plaque due to poor hygiene.
Treatment is carried out by a dentist and depends on the severity of the gingivitis. Initially, plaque removal is required, and hygiene products are selected individually. In severe cases, overgrown gum tissue is removed.
Types of gingivitis
The standard treatment regimen includes the use of:
- Anti-inflammatory gels (Cholisal, Mundizal-gel, Kamistad).
- Paste (Lacalut fitoformula, Parodontax F, PresiDENT exclusive).
- Rinse aids (Lacalut “aktiv”, Paradontax, President profi).
- Vitamins (B1, C, A, E).
Treatment lasts 10 days. Treatment of gums with gels is carried out 2 times a day. Rinse aids are used after meals. During treatment, it is necessary to use a soft brush to avoid further trauma to the gums.
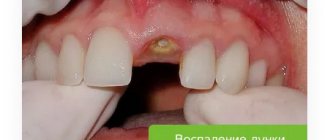
Periodontitis
Inflammatory gum disease, which is characterized by damage to periodontal tissue. It is a consequence of untreated gingivitis.
Gums with periodontitis
The symptoms are similar to gingivitis, but other unpleasant signs appear:
- Severe swelling and suppuration.
- Pain when touched.
- Gaps between teeth and their loosening.
Periodontitis can be caused by failure to comply with hygiene rules, deficiency of vitamins and beneficial microelements, and improper bite and tooth shape. The treatment regimen coincides with therapy during gingivitis. After removing plaque and stone, a person needs to carefully maintain hygiene for 2 weeks.
Stages of periodontitis
Important! Advanced stages of periodontitis require cutting the tissues surrounding the tooth and removing deep stone.
Local treatment includes the use of anti-inflammatory gels (Acepta, Cholisal, Mundizal-gel). If tooth mobility occurs, the installation of temporary splints is required, which can be replaced with a prosthesis if necessary.
Periodontal disease
Damage to periodontal tissue. Pain occurs not only between the teeth, but also around them. The disease occurs rarely - no more than 8% of dental patients. Leads to increased tooth mobility and does not relate to inflammatory pathologies. Symptoms:
- Bleeding.
- Exposing the neck of the teeth.
- Severe pain.
- Tissue atrophy.
Periodontal diseases
The main reason is poor circulation in the periodontal tissues. Periodontal disease is often a consequence of systemic diseases of the body (diabetes, atherosclerosis, hypertension). It can occur in people with a hereditary predisposition.
- Caries between teeth - why I have it and my neighbor doesn’t
The treatment is long-term, and at the first stage includes the removal of tartar. Severe stages require the use of gels, ointments and rinses with an anti-inflammatory effect. If there are carious teeth, they are treated.
Local treatment includes:
- Rinse with 0.05% Chlorhexidine solution.
- Applications "Cholisal gel".
Dental gel Cholisal
The average duration of treatment is 10 days. Rinsing with Chlorhexidine solution should be done in the morning (after breakfast) and in the evening. Then the teeth and gums are dried with a cotton swab and the gel is carefully applied to the marginal part of the gum. After using medications, it is not recommended to eat for 2 hours.
Treatment of gum pain
It is important to treat gum disease as soon as possible. Any, even the most harmless pathology, can turn into periostitis with high fever, swelling of the mucous membranes and loose teeth. Moreover, inflammation in the gums releases toxins that provoke the development of blood poisoning.
You should not discount the possibility of pain in the gums when pressing due to illiterate treatment by a dentist. Normally, pain after treatment persists for 1-2 weeks. If the pain continues longer and does not subside, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. It happens that after poor-quality dental canal filling, bacteria appear in the voids, which provoke an infectious process.
The dentist may also leave the edges of the filling uneven, causing damage to the gums. In this case, you should definitely consult a doctor so that he can improve his work.
Attacks of pain when pressing on the gums are also common with increased sensitivity of the teeth and gums. However, with proper care, this pain goes away quite quickly. When it occurs, you should use toothpastes and rinses for sensitive teeth.
For example, ASEPTA Sensitive preventive toothpaste allows you to perform oral hygiene without irritating sensitive gums. The combination of 3 desensitizing components - potassium citrate, hydroxyapatite, thermal mud - significantly reduces the sensitivity of teeth and gums.
For more effective prevention of pain in the oral cavity, it is recommended to use ASEPTA gum gel with propolis. In this product, propolis is produced in the form of a gel, which makes it easy to apply to the gums. Prolonged contact with the painful area of the gum allows the gel components to penetrate deeper and promotes rapid healing.
The cause of pain when pressing on the gums can also be various injuries to the gums and teeth, received, for example, when trying to crack nuts or toffee. Such injuries also need to be shown to the dentist as soon as possible, otherwise there is a possibility of an inflammatory process.
Reasons why a dead tooth hurts
Pulp removal is a traumatic procedure after which the tissues need time to recover. During the first two weeks they may go away on their own. If the pain does not go away for a long time or occurs a year or more after removal of the nerve, then the reasons may be:
- poor quality treatment;
- some pathologies;
- individual characteristics.
It makes sense to consider all the reasons why a dead tooth hurts in more detail, so that, if necessary, you can seek dental help in time and prevent complications.
You might be interested in:
Dental treatment
Inflammation of the tooth root
Tooth inflammation
Tooth abscess
Poorly performed treatment
In this case, pain may be a consequence of:
- Root perforation
. Incorrect treatment resulted in the filling material extending beyond the apex of the root and into the tissue of the jaw bone. The body perceives it as a foreign body and, as a result, inflammation appears, accompanied by bursting and throbbing pain. - Incomplete depulpation
. Painful sensations when pressed may also be evidence that the pulp was poorly removed and there are remnants of living tissue in the canals. - Incomplete closure of root canals
. If the doctor incorrectly determined the length of the canal, then part of it may not be filled with filling paste. And this is a reason for infection to develop in the voids and such a dead tooth hurts when pressed. - Poor insulation during channel cleaning
. If during work the doctor poorly or insufficiently isolated the tooth from saliva, then pathogenic organisms enter the canals along with it, infecting the tissues and causing pain. - A piece of tool left behind
. To inspect the canals, special ultra-thin needles are used. Careless or inept handling of them can lead to breakage of the tip, which remains inside, causing the development of infection. - Poor/incomplete removal of caries
. If not all affected tissues are drilled out, then a dead tooth may hurt even under a filling, since pathogenic microflora continues to develop there.
Less critical reasons include installing a filling that is too high. At the same time, there is an increased load on the ligaments, they stretch causing discomfort and pain.
Some pathologies
Among them, a dead tooth most often hurts due to:
- Cysts
. Since the indication for pulp removal is infection, any extraction of root nerves increases the likelihood of an apex cyst. Symptoms may appear a year or even more after treatment and depulpation. - Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
. If pain is observed when pressing or biting, this may indicate trigeminal neuritis. The reason is the treatment process itself (not the dentist’s mistake). To eliminate the pathology, you need to contact a neurologist.
It will not be possible to diagnose and eliminate these pathologies on your own, therefore, at the first symptoms, you should make an appointment with a dentist and, after an examination, receive high-quality, professional help.
Individual characteristics
The causes of discomfort caused by a dead tooth can be not only pathologies and incorrect treatment, but also the individual characteristics of a person. These include:
- Allergies
. Expressed in the form of intolerance to certain filling materials. Accompanied by pain, swelling and other unpleasant sensations. - Anatomical features of the bite
. An incorrect bite can cause overload of individual teeth, which leads to leaks, injuries and cracks through which infection can enter. - Specific root structure
. If a patient has a non-standard root structure, in some cases it cannot be seen even on an x-ray. Then the doctor relies only on his own feelings and works as if blindly, and the risk of incomplete treatment of the canals increases.
Sometimes, when pressed, a dead tooth hurts not for one reason, but as a result of a whole complex of dental problems. In this case, it will take more time to eliminate pathologies and discomfort in general.
How to relieve pain when pressing on the gums
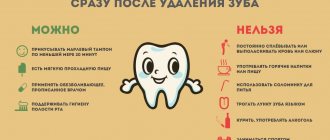
Remember, only a dentist can help eradicate the pain experienced when pressing on the gums or teeth. It is important to quickly determine the cause of the discomfort and prescribe proper treatment. However, to eliminate discomfort before visiting a doctor, you can try the following methods:
- Take painkillers, such as paracetamol or analgin. The main thing is not to overdo it with such drugs, as they can be addictive and negatively affect the functioning of internal organs.
- Brush your teeth properly, trying to free the inflamed cavity from plaque and food particles.
- Rinse your mouth with a solution of baking soda, furatsilin or potassium permanganate.
Remember, it is strictly forbidden to warm your cheeks and gums or apply warm compresses to the sore spot. Heat can trigger more severe inflammation. Also, you should not take antibacterial or anti-inflammatory drugs without a doctor’s prescription.
It is also prohibited to put analgesics into the cavity of a diseased tooth. This popular method is far from safe: you can not only cause an infection, but also get a serious burn to the mucous membrane.
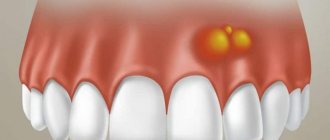
Pain due to hematoma
If the gums hurt for a long time after removal, the body temperature rises, the gums swell and suppuration begins in the place where the dead tooth was, then this indicates a hematoma. A characteristic sign is the bluish color of the gums in the place where the tooth was.
Why a hematoma occurs: an incorrectly performed operation, during which the doctor damaged a blood vessel, general ailments of the body. For example, a hematoma often appears in people with diabetes or hypertension. A weakened immune system increases the risk of hematoma.
The only way to get rid of toothache due to a hematoma is surgery. During this process, an incision is made in the gum flesh and the accumulated pus is released. After this, the wound is washed and a course of drug treatment is prescribed, which includes rinsing with dental antiseptics and taking antibiotics.
Treatment for gum pain
The treatment tactics for pain in the gums when pressing depends on the cause of the disease. If the pain appears due to problems with the teeth, the canals are filled or refilled. The doctor removes the source of inflammation. Advanced stages of the disease are treated with surgery and removal of the diseased tooth.
If the cause of pain in the gums when pressing is their inflammation, it can be relieved with medications prescribed by the dentist. As a rule, in such cases, the doctor prescribes antibiotics or other penicillin drugs. Rinse must be prescribed.
Folk remedies – decoctions of medicinal herbs – also help relieve pain and inflammation. Oak bark, chamomile, and sage perfectly remove unpleasant sensations. A solution of baking soda with a few drops of iodine also helps relieve inflammation.
Other popular methods for treating inflammation at home are:
- Propolis tincture
has antibacterial and antimicrobial effects. To prepare it, dilute a teaspoon of tincture in 200 ml of water. You need to rinse your mouth with propolis up to five times a day. - Massage with oils
has a beneficial effect on the gums. It is not at all difficult to do: apply a few drops of tea tree, eucalyptus, juniper or fir oil to the pads of the thumb and index fingers of one hand. You need to massage the gums gently for 5-10 minutes. After the massage, you should not rinse your mouth. - Aloe
also contains many anti-inflammatory components. For gingivitis or stomatitis, you can chew a fresh leaf of this plant a couple of times a day.
Treatment of gingivitis
For minor gum damage, anti-inflammatory gels such as Metrogyl Denta, Kalgel, Hyaludent, and Cholisal help well. Doctors advise using toothpastes: Asepta, Paradontax. They have a special composition that helps eliminate plaque and helps strengthen the enamel.
If the gums with gingivitis hurt not only in the upper jaw, but throughout the entire mouth, you need to contact a qualified specialist. Severe inflammation requires medical treatment with antibiotics . The doctor must prescribe a specific pill regimen. In this case, you should not self-medicate to avoid complications.
When deposits become lodged under the gums, periodontal pockets form. In modern medicine, plaque is removed using a curettage procedure. There are open and closed curettage.
Open type manipulation is an operation during which the gum canals are cleaned. This type of curettage is used if periodontal pockets are deeper than 0.5 cm. During the procedure, the source of inflammation is removed.
Closed curettage is a more simplified dental procedure. Cleaning the gum pockets does not disturb the tissue. The procedure uses special equipment; the dentist performs professional ultrasonic cleaning, which does not cause pain.
You can visit the dentist and install a splinting clasp prosthesis. This is worth doing for those who not only have severe gum pain, but also have pronounced gum pockets. This is a very reliable method of combating gingivitis.
If severe pain in the gums is accompanied by displacement of the teeth, they can be fixed with crowns or bypass surgery. The second method allows you to connect several loose teeth into one group. Loosening can also be eliminated by using fiberglass prosthetics.
Nutrition: prevention of inflammation
If gingivitis is the cause of pain when pressing on your gums, it is important to review your diet by including healthy foods in your diet. To prevent future diseases, first of all, you need to consume plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables:
- Apples and pears contain a lot of pectin, which helps accelerate tissue regeneration.
- Citrus fruits are a real storehouse of vitamin C, which also helps reduce bleeding and inflammation.
- Black currants, blackberries, and raspberries contain a large amount of minerals and vitamins that increase the body's resistance.
- Carrots, cabbage and zucchini are valuable fiber and vitamins that enhance metabolic processes in the body and accelerate tissue regeneration.
To prevent gum inflammation, professional teeth cleaning is also recommended. The procedure is carried out by a dentist and allows you to eliminate all accumulated deposits and tartar.
So, now you know the most common causes of pain in the gums when pressing. Remember: when your gums or teeth bother you, you should never put off visiting the dentist. The sooner the doctor determines the cause of the problem and begins treatment, the greater your chances of saving your teeth, gums and avoiding possible complications.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
Why does pain occur?
Gums don’t hurt out of nowhere, which is why they need to be treated in the dentist’s office and not at home. All kinds of folk recipes are only suitable for alleviating symptoms, but they do not eliminate the cause of the manifestation.
Pain in the gums occurs for the following reasons:
- Due to the development of a cyst.
- After tooth extraction.
- Against the background of inflammatory processes.
- Due to an incorrectly selected toothbrush.
- Due to a carelessly installed filling or crown that touches the gums.
- The main reason why the marginal part of the gum may hurt is the eruption of a wisdom tooth.
If a person’s gums hurt throughout the entire oral cavity, this indicates a serious inflammatory process. When the pain is localized near one or several teeth, the cause should be sought in them.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis can be caused by irregular teeth brushing. Neglect of oral hygiene standards leads to the formation of plaque, which turns into tartar. The latter provokes the development of an inflammatory process in the soft tissues, as a result of which the mucous membrane of the gums becomes inflamed.
Symptoms of gingivitis:
- accumulation of plaque on teeth;
- specific odor from the mouth;
- the gums swell and become purplish-red;
- bleeding;
- pain often spreads throughout the entire oral cavity;
- the upper part of the gum adjacent to the tooth hurts;
- The acute form of the disease is manifested by pustules and severe itching.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a consequence of untreated gingivitis. The disease is chronic, inflammation affects everything that surrounds the tooth.
Symptoms:
- with periodontitis, the tooth begins to loosen;
- the gums near the tooth hurt a lot;
- suppuration and bleeding appear;
- body temperature may rise;
- there is a general weakened state of the body;
- tooth sensitivity increases;
- gums become red.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis should not be confused with periodontitis. Although the symptoms of these diseases are similar, the first disease is a consequence of the second. The inflammation is first localized in the gums, but if the disease is advanced, the deep tissues that hold the tooth root in the bone fossa are affected.
Aesthetic consequences of loss of bone volume due to missing teeth
The facial changes that naturally occur with age can be exacerbated and accelerated by tooth loss. Pronounced aesthetic consequences result from loss of alveolar bone. Patients do not even suspect that all these changes in soft tissues are associated with tooth loss:
- Reduction in facial height occurs due to disturbances in the vertical dimension of the alveolar bone.
- A change in the labiomental angle and deepening of the vertical lines in this area give the face a rougher appearance.
- A malocclusion develops. As a result, the chin turns forward.
- The corners of the lips droop, the patient's face has an unhappy expression.
- Due to poor support of the lip by dentures and loss of muscle tone, the border of the red border of the lips becomes thinner.
- Age-related deepening of the nasolabial philtrum and other vertical lines on the upper lip is more pronounced with loss of bone volume.
- In edentulous patients, the decrease in the tone of the facial muscles that support the upper lip occurs faster, and the lengthening of the lip occurs at an earlier age. As a result, the smile ages.
- Bone atrophy has a negative effect on the attachment of the mental and buccal muscles to the body of the mandible. The fabric sags, creating a double chin. This effect is caused by decreased muscle tone when teeth are lost.
Nature of pain
In the first 3-5 days, pain after the installation of dental systems is a normal reaction of the body to surgical intervention. Analgesics prescribed by a doctor help cope with discomfort. If it hurts under the implant after the first week, after six months, a year or later, you will need the help of a doctor.
To identify the causes of pain, its type plays an important role:
- by nature - pressing, pulsating, dull, cutting;
- according to the degree of localization - within a certain area, diffuse, irradiating;
- according to the presence of additional symptoms - swelling, itching, redness, mobility of the structure.