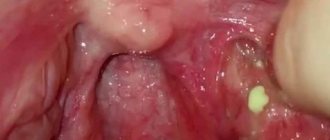
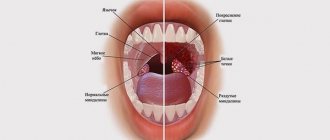
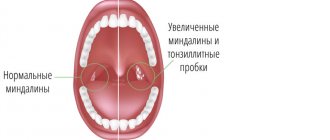
Allergic laryngeal edema is a pathological condition characterized by inflammation of the mucous tissues of the larynx and narrowing of its lumen (stenosis). It occurs due to the body’s contact with factors hostile to it – allergens.
Author:
- Sadykhov Rahim Agalarovich
ENT pathology expert
2.45 (Votes: 38)
Allergic laryngeal edema is a pathological condition characterized by inflammation of the mucous tissues of the larynx and narrowing of its lumen (stenosis). It occurs due to the body’s contact with factors hostile to it – allergens, which cause a negative immune reaction. The main danger of edema is depression of respiratory function. As the lumen of the larynx narrows, breathing becomes difficult, which provokes oxygen deficiency, which is life-threatening.
Causes of swelling
Laryngeal edema occurs as a response of the body to an allergen irritant. This reaction is individual - under the same conditions, the same stimulus can cause a serious condition in one person, but not affect another in any way. It depends on the characteristics of the immune system.
Allergens may be the following:
- medications, especially when administered intravenously and intramuscularly;
- pet hair;
- insect bites;
- fungi, mold;
- food (often nuts, milk, eggs, fish, some vegetables, fruits);
- chemical substances;
- dust, pollen.
Reasons and factors
The circumstances that cause the persistent desire to scratch the roof of the mouth include both harmless factors and chronic pathologies requiring medical intervention:
- Infections of mucous tissues in the oral cavity;
- Development of inflammatory processes;
- Failure to comply with recommendations for hygienic care;
- Receiving mechanical injuries when processing food;
- Pathological processes, including caries and pulpitis;
- Damage to the nervous structure of the TMJ;
- Reaction to the replacement structure, including in the form of allergies;
- Neuralgic manifestations, etc.
A comprehensive clinical diagnosis using dental equipment that meets industry standards allows us to determine the root cause of the problem.
Types of allergic laryngeal edema
There are acute and chronic allergic edema.
Acute allergic edema
In this case, you must call emergency assistance. Difficulty breathing is obvious and sudden, the condition is rapidly deteriorating. A person breathes intermittently and frequently; the muscles of the shoulders, head and back are involved in breathing, the supraclavicular fossae are sunken, and the intercostal spaces are drawn in. The skin turns pale, blue, the pulse increases, and the patient may begin to panic. In the absence of medical assistance, the lumen of the larynx closes completely, which causes asphyxia and death.
Before the arrival of medical workers, those close to the patient should be advised by telephone what to do. Emergency tips for breathing problems:
- interrupt the person’s contact with the substance that caused such a reaction (if this can be determined);
- in case of food poisoning, rinse the stomach;
- free a person from being squeezed by clothing;
- provide a flow of fresh air;
- give an antihistamine.
Chronic allergic edema
In this case, discomfort in the throat and breathing problems occur periodically, without getting worse, but giving the person very unpleasant sensations. This condition is a consequence of certain diseases or systematic contact with an allergen (for example, mold or animal hair in the house). Its symptoms are as follows:
- swelling and redness of the tonsils, uvula and palate;
- difficulty inhaling more than exhaling;
- rapid breathing;
- dyspnea;
- sensation of a foreign body in the throat;
- inability to exercise due to worsening breathing problems.
If you have these symptoms, be sure to consult an otolaryngologist to cure the underlying disease or remove the allergen from your environment.
Chronic allergic edema of the larynx is dangerous because it can sharply and suddenly develop into Quincke's edema - when the increase in clinical manifestations occurs within a few minutes. Quincke's edema is characterized by severe swelling of the neck and face and can spread to the mucous membrane of the larynx, causing severe stenosis. If signs of Quincke's edema appear, you should urgently call an ambulance.
In cases of chronic allergies, the person is usually aware of their condition and should always keep antihistamines on hand to stop the progression of the condition. Such drugs are prescribed by the doctor individually - there are different types of antihistamines, and it is important to choose the ones that suit you.
When the causes of itching are ENT diseases
The most common causes of severe itching in the throat are associated with diseases of the ENT organs:
- sinusitis;
- tonsillitis;
- pharyngitis;
- fungal infection of the pharynx (mycosis).
In each of the above diseases, itching inside the throat is a consequence of exposure to foreign agents on the human mucous membranes.
In case of sinusitis, tonsillitis and pharyngitis, such agents are pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate the larynx, pharynx or nose from the outside. The causes of fungal infection, respectively, are pathogenic fungi.
Bacteria and fungi often inhabit human mucous membranes, but for them to become more active and trigger the inflammatory process, it is enough for favorable conditions to arise for their reproduction. Such “favorable” factors are decreased immunity, hypothermia, stress, and the presence of chronic diseases. Also, a common cause of the development of diseases of the ENT organs is infection of one person from another by airborne droplets or contact-household methods.
Tonsillitis is caused primarily by streptococci. Pathogenic microorganisms settle in the palatine tonsils, causing severe inflammation in them. At the same time, the throat not only hurts greatly, but also itches and itches.
With pharyngitis, the inflammatory process covers the mucous membrane of the pharynx. In this case, the patient complains not only of an itchy throat, but also of a strong dry cough and a feeling of a lump in the throat.
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. A feeling of severe itching in the throat occurs when mucous masses flow from the nasal cavity along the back wall of the pharynx and irritate its mucous membrane.
The main sign of mycosis (fungal infection) is a white coating on the surface of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx. Inflammation is caused mainly by fungi of the genus Candida. Mycosis can be provoked by a sharp decrease in immunity, frequent diseases of the pharynx, diabetes mellitus, and taking antibacterial and hormonal drugs.
The variety of diseases of the ENT organs that cause a feeling of severe itching is quite understandable: all ENT organs are interconnected with each other, and an infection from the nose, for example, easily spreads to the pharynx or ear.
Therefore, it is necessary to treat an ear, nose or throat disease in a timely manner to prevent the development of complications.
Diagnosis and treatment
At the appointment, the doctor collects anamnesis, examines and palpates the larynx. If necessary, bronchoscopy and laryngoscopy procedures, X-rays, and computed tomography are performed.
Allergic swelling of the larynx is treated with medication or surgery. Medicines include antihistamines, which suppress the action of histamine, and glucocorticosteroids, which block the inflammatory response and swelling and suppress the immunological response to the allergen. Surgical intervention is a tracheostomy, an emergency measure when a person is at immediate risk of suffocation - inserting a breathing tube into the trachea through a small incision in the throat.
Doctor MOM® for the treatment of cough and sore throat
In the complex treatment of cough and sore throat, the use of herbal medicines from the Doctor MOM® line - syrup and herbal cough lozenges - is indicated. Thanks to the unique1 “FITO BRONHO formula”2 based on medicinal plant extracts, the products in the Doctor MOM® line have a complex effect, helping to both relieve unpleasant symptoms and eliminate their cause - inflammation.
The main actions of Doctor MOM® syrup and herbal cough lozenges are:
- Eliminating the cause of cough – inflammation;
- Removing infection from the body3;
- Combating unproductive and unproductive cough.
Prevention
As preventative measures, as well as after an attack, it is recommended:
- strengthen immunity;
- perform moderate physical activity;
- use halotherapy and climatotherapy (stay at sea and in the mountains);
- use air purifiers;
- adhere to a diet excluding highly allergenic foods and products containing preservatives and chemical additives.
If you are concerned about breathing problems of any kind, we are always ready to provide assistance, make the correct diagnosis and begin treatment immediately. Call and make an appointment at the Ear, Nose and Throat Clinic!
Treatment options
To effectively treat dryness, sore throat and cough, it is necessary first of all to act on the cause of their occurrence - inflammation. To make an accurate diagnosis, you should consult a doctor who, depending on the anamnesis (history of the development of the disease), complaints and examination, will immediately suggest a particular disease or prescribe additional examinations and consultations. Since dryness, tickling and cough are not a diagnosis, but only one of the symptoms of the disease, it is necessary to carry out comprehensive treatment, and not limit ourselves to just eliminating unpleasant symptoms. Elimination of pathogens.
In case of infectious origin of tickling and cough, therapy is prescribed that acts on the pathogen - antiviral, antibacterial or antifungal drugs for systemic use (orally or by injection, in the form of rectal suppositories). The selection of an antibiotic or antiviral agent is carried out by a doctor. Under no circumstances should you independently cancel and replace one drug with another or stop taking it earlier - this can lead to the progression of the process or its transition to a chronic stage.
Pain relief
. However, cough and severe sore throat, as a rule, are subjectively difficult for patients to tolerate, causing severe discomfort and disrupting their usual way of life. Therefore, it is difficult to do without the use of symptomatic medications to reduce the severity of complaints. For this purpose, a variety of local remedies are used: tablets and lozenges, sprays, rinsing solutions. If your throat is very sore, frequent warm drinks, warming and distracting procedures can help soothe the irritation of the mucous membranes. If you have a painful, obsessive, prolonged non-productive cough, you may need to prescribe antitussive drugs.
“Throat and stomach hurt,” or what do you know about adenovirus
During seasonal ARVI, cough and sore throat are an “expected” phenomenon. But what if traditional respiratory symptoms are combined with diarrhea or vomiting? Perhaps it is an adenoviral infection.
Special signs
Adenovirus, unlike many respiratory viruses, affects not only the respiratory tract, but also the mucous membrane of the small intestine. In addition, the conjunctiva of the eye comes under attack.
It leads to:
- copious mucous discharge from the nose,
- sore and sore throat,
- cough (first dry, and later with sputum),
- symptoms of conjunctivitis, such as redness of the eyes, watery eyes, a feeling of dryness and “sand” in the eyes,
- as well as abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting
- and fever, the duration of which can reach 2 weeks.
Moreover, if intestinal symptoms may not develop during the entire infection, then the “characteristic” eyes are an important distinguishing feature of the adenovirus.
Where can you get infected?
Adenovirus is extremely infectious and resistant in the external environment. And the source of infection can be sick people or household items on which the virus remains active for up to 8 days.
You can become infected:
- when the patient coughs and sneezes,
- consuming food prepared without sanitary standards (thorough hand washing is required),
- and even through contact with the feces of an infected person (for example, when changing a diaper for an infected child).
You can “catch” the virus even in a swimming pool if the water is not properly disinfected. And, obviously, this viral infection is not uncommon in children's groups.
How dangerous is this?
Adenovirus infection, in most cases, does not pose a threat to health or life. And it usually ends without consequences after 7-14 days. Whereas in weakened patients, the infection can drag on and reach 6 weeks.
This same category of patients most often develop complications in the form of:
- pneumonia,
- otitis,
- bronchospasm
- severe keratoconjunctivitis.
However, Rospotrebnazor experts note that complications of adenoviral infection are always associated with the addition of pathogenic bacterial flora (staphylococci, streptococci and others).
How to identify adenovirus
The classic symptoms of adenoviral infection, as a rule, do not require additional tests. And the help of laboratory diagnostic methods is mainly resorted to at the earliest stage of the infectious process or in case of doubt about the diagnosis.
The most informative analysis in this case is PCR diagnostics of the material (throat swab or feces) for adenovirus.
The study can be ordered separately or immediately in combination with other ARVI viruses (for example, “ARVI-Screen”), which will allow you to immediately carry out a differential diagnosis. True, the PCR technique sharply loses its reliability if treatment, both local (rinses, sprays) and general, has already begun.
A blood test for IgA antibodies to adenovirus does not have these shortcomings.
They appear in the blood during the initial period of the disease, and continue to circulate for some time after recovery.
However, children, as you know, “don’t like” blood tests, so this examination format is more suitable for adults.
Causes of a red throat
| CAUSES | A COMMENT | ||
| causes: | Infectious causes | a comment: |
|
| causes: | Non-infectious causes | a comment: |
|
In 70% of cases, inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa is caused by ARVI viruses (rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, coronaviruses, influenza and parainfluenza viruses), as well as other viruses (enterovirus, herpes virus, Epstein-Barr virus for infectious mononucleosis, and others).
The cause of inflammation can be bacteria:
- group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS)
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenza
It should be remembered that a red throat can be a manifestation of infectious diseases such as measles, scarlet fever, and rubella. In some cases, differential diagnosis with other infectious diseases is required.