Tonsil function
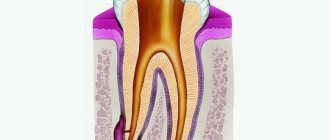
The tonsil is a lymphoid tissue located in clusters in the pharynx. The tonsils are one of the organs of the immune system that protect the internal environment of the body from harmful influences. There are six tonsils in the human pharynx: two paired and two unpaired; together they form the so-called Pirogov-Waldeyer protective ring. The palatine tonsils (popularly called tonsils) are located closest to the entrance of the pharynx, and these tonsils suffer more often than others. The lymphoid tissue of the tonsils supports general and local immunity. Lymphocytes mature in it and antibodies are produced.
The palatine tonsils play a vital role. They are the largest and differ in their structural features. Upon careful examination, it is clear that the surface has depressions or lacunae, smoothly turning into crypts or deep folds lined with mucous membrane. Only the lateral surfaces are covered with a capsule of connective tissue, and all the rest are in contact with everything that enters the pharynx.
At CELT you can consult an otorhinolaryngologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Treatment of complications of dermoid cyst
Complications may require both medication and emergency surgical intervention. For example, during suppuration, the use of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs is indicated, and removal of the dermoid formation is possible only after the inflammatory process has subsided.
In case of necrosis of the formation, its emergency elimination is indicated, since this can lead to serious complications in the form of suppuration, intoxication, sepsis and even death.
Increased or suspected malignancy is also an indication for removal. In this case, there is no need for emergency surgery, but it should be performed as soon as possible after full preparation (additional examination, anesthetic preparation).
Today, refusal from surgical intervention is considered advisable only in cases where the neoplasm is minimal in size, does not manifest itself in any way, and the likelihood of complications is extremely low. In all other cases, it is better to remove the formation at least in order to prevent the development of complications.
Classification
Experts distinguish two types of tonsil cysts:
- Retention - formed after blockage of the ducts of the glands of lymphoid tissue, have a classic round shape, a thin capsule, filled with serous or purulent secretion. After emptying (evacuation of contents or spontaneous breakthrough), they are filled again.
- Dermoid or congenital - formed during intrauterine development, inclusions of embryonic tissue are always found in them. These true tumors, caused by genetic causes or harm suffered by the mother during pregnancy, are very rare. The capsule is usually dense and the contents are viscous.
Types of oral cysts
Based on their origin, mucoceles are:
- true;
- extravasal.
The first ones lack their own membrane and are covered with a gland capsule. They occur due to blockage of the duct and accumulation of mucus. The second are post-traumatic. They are formed when the tightness of certain structures is broken and the mucous secretion enters the surrounding tissues.
According to the localization criterion, the neoplasm is classified into:
- Sublingual. It is located in the hyoid-maxillary muscles or submandibular region. During rapid growth, it grows very quickly and then causes serious discomfort.
- Submandibular. Located in the lower submandibular region. It feels like a dense ball to the touch. Promotes disruption of the natural mechanism of salivary fluid secretion.
- Parotid. Rarely encountered in dental practice. It can be very painful when you open your mouth wide. It is formed due to impacts, injuries, after which the inflammatory process caused the closure of the salivary ducts.
- Extravasal. Most often found on the inner surface of the lip. Occurs due to mechanical damage. The inside is filled with granulation tissue.
Causes of retention cysts
The reasons for the formation of cysts are varied, but more often than others, factors such as:
- chronic inflammation of the tonsils and pharynx with periodic exacerbations - tonsillitis, pharyngitis;
- autoimmune diseases accompanied by the production of a large number of lymphocytes;
- smoking, especially tobacco with a high tar content;
- injuries, including the habit of swallowing small bones;
- hormonal imbalance;
- occupational hazards, inhalation of aggressive aerosols;
- decreased immunity, especially local.
The formation of a cyst is caused by impaired drainage of the mucous lacunae of the tonsils against the background of the inflammatory process.
Localization
The development of a dermoid cyst is possible in almost any organ or tissue, as doctors note. Most often the presence of cysts is found in:
- the ovarian area in women of reproductive age, which can seriously affect the ability of the fair sex to conceive;
- the lower eyelid area (mostly children are affected, but the pathological neoplasm can be easily removed with the help of surgeons);
- the coccyx area, where the size of the ovarian dermoid cyst rarely reaches large sizes, and the formation can go unnoticed for a long time;
- the area of the anus, where without symptoms of inflammation, pathology is generally detected only by digital rectal examination, etc.
The discovery of dermoid cysts in any organ or tissue makes this pathology quite common. Moreover, as doctors note, the presence of dermoid cysts can either not make itself felt for a long time or cause severe discomfort.
Manifestations of tonsil cysts
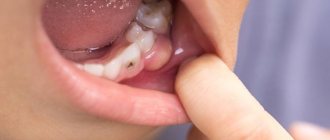
Symptoms of having a palatal cyst depend on its size and location. Cysts up to 1 cm in size usually do not manifest themselves, are invisible and painless. People, as a rule, do not even suspect their existence. Cysts can be discovered accidentally during routine examinations by an otolaryngologist.
You can suspect the presence of a cyst in the tonsil if you have bad breath with healthy teeth and normally functioning digestive organs. The smell comes from food particles that become trapped in the area of the cyst and begin to decompose there. As the size of the cyst increases, a person may experience the following symptoms:
- feeling of constant presence of a foreign body in the throat;
- sore throat or discomfort;
- difficulty and mild pain when swallowing solid food;
- hoarseness of voice.
Young children may begin to choke on food. If the cyst grows towards the pharynx, then a feeling of lack of air may occur, which is especially pronounced in children whose larynx is small. The existence of the cyst itself maintains chronic inflammation. The cyst excludes areas of the tonsil from immune protection.
Content:
- Why does a cyst grow in the oral cavity?
- Types of oral cysts
- Signs of a cyst
- Examination of patients who have a cyst in their mouth
- How to treat
- Treatment of cystic formation at home
- How to reduce the likelihood of developing education
Sometimes, when visiting a dentist, a patient hears a strange diagnosis - mucocele.
More simply, it sounds like an oral cyst. Underneath this disease lies a cavity tumor neoplasm containing mucous contents. It is benign and develops due to obstructed outflow of secretions produced by parenchyma cells. The peculiarity of mucocele is that it does not have a strong epithelial membrane. Usually localized on the mucous membrane of the lower lip or under the tongue. It can also form in the chewing area. Neoplasms of the submandibular zone are very rarely encountered in dental practice.
Conducted studies demonstrate that most often young people under the age of thirty experience mucocele. The disease also occurs in adolescent children.
Diagnosis of a cyst
As a rule, detecting a cyst does not cause any particular difficulties, since the pharynx can be clearly seen even with the help of a backlit frontal mirror. The main thing is to contact an otolaryngologist for examination. ENT doctors use various instruments during examination - spatulas, elevators, and, if necessary, endoscopes.
The cyst is determined in different parts of the tonsils, on the surface or in the depths. It has the appearance of an opaque round formation, similar to a ball, whitish in color, elastic and mobile. There may be no signs of inflammation of surrounding tissues.
You cannot touch or put pressure on the cyst yourself - it can burst, and its contents are unknown. At best, the purulent contents will enter the stomach, and at worst, it will spread to other organs.
The doctor examines cysts larger than 1 cm very carefully, without damaging the surrounding tissues, trying not to touch the capsule.
Diagnosis of a cyst includes puncture (puncture and removal of contents). If necessary, the resulting material is examined in the laboratory to understand the nature of the disease. If a malignant process is suspected or blood is leaking from a cyst, treatment begins immediately, without waiting for the end of the examination.
Depending on age, general condition and concomitant diseases, the doctor may prescribe other clinical tests. The blood coagulation system, the functioning of the heart and lungs are required to be examined.
How to reduce the likelihood of developing education
To minimize the risk of mucocele formation, you need to follow the rules:
- lead a healthy lifestyle, quit smoking;
- carefully observe oral hygiene;
- rinse your mouth after every meal;
- eat a balanced diet;
- do not put foreign objects in your mouth;
- get rid of the habit of biting your lip;
- correct malocclusion;
- undergo oral hygiene every year;
- avoid trauma and chemical burns to the lips;
- promptly replace dentures;
- Follow the rules for wearing braces and caring for them.
People who follow preventive measures are much less likely to need treatment for oral cysts. If a lesion has appeared and is growing in size, there is no need to expect it to disappear on its own. This happens very rarely. It will either “deflate” or be filled again with contents and ultimately may grow to such a size that it will not be possible to do without emergency surgical intervention.
Treatment of palatal cysts
Tonsil removal
- Cost: 75,000 - 105,000 rubles.
- Duration: 30-40 minutes
- Hospitalization: 1-2 days in hospital
More details
Treatment of cysts is determined by many factors, primarily the size of the cyst, its location, growth rate and the age of the patient. At first, they always try to carry out a high-quality course of conservative treatment, especially anti-inflammatory treatment. Treatment is carried out both general and local.
The radical and best way to treat cysts is surgery, which can be performed in different ways. Small cysts located superficially are removed along with the capsule. After this, a slight scar remains on the tonsil, which soon resolves.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia, the patient does not feel anything. In most cases, the intervention is performed on an outpatient basis, and the person goes home the same day.
A cyst of significant size, especially one located deeply, is removed along with part of the tonsil. If there are several cysts or the location is such that it is impossible to get to them, the tonsil is removed completely and a tonsillectomy is performed.
How to treat
It is very dangerous if a person tries to remove a cystic formation on his own and, to do this, puts pressure on it or bites it. Any mechanical influences have a negative effect on the course of the disease. Due to external pressure, the liquid inside the bubble begins to flow beyond its boundaries. Afterwards it accumulates again in the inflamed area. But at the same time, the risk of infection of damaged tissues increases significantly.
Doctors most often treat mucocele surgically. If the “bubble” is localized on the lower lip, two semilunar incisions are made in its projection, after which the internal neoplasm is isolated along with all its contents. Finally, stitches and a sterile pressure bandage are applied.
If the problem concerns the sublingual area, the following can be done:
- cystectomy;
- cystsialadenectomy.
In the first case, only the cyst itself is removed. It is cleaned and cut out. In the second type of surgery, the gland is also removed.
If there is a formation in the parotid zone, a parotidectomy is performed - complete or partial. It involves excision of the cyst and part of the parenchyma. Lesions located in the submandibular area are always removed along with the gland.
If we are talking about treating a child or a weakened elderly person, the dental surgeon may decide to excise only the dome (upper part) of the abnormal structure.
Prevention of palatal cysts
It is important to understand that a cyst is usually formed as a result of a long-term inflammatory process. Carrying a bag of pus in the throat is extremely harmful; it is a source of chronic infection. Microbes have access to the bloodstream; if the body is weakened, this can lead to diseases of the heart, joints and kidneys.
ENT doctors at CELT have extensive practical experience in treating tonsil cysts. Specialists are ready to help people of all ages, including children, as well as those who have unsuccessfully tried treatment in other clinics. The main thing is to cooperate with your doctor to complete treatment until complete recovery. You can safely contact our clinic with this problem.
Treatment of cystic formation at home
Home therapy for oral cysts only makes sense if for some reason you cannot get to a dental surgeon in the next few days. It consists of rinsing with herbal solutions and antiseptics. You can also make compresses with anti-inflammatory herbal medicines.
If the hearth breaks through, it’s too early to rejoice. Most likely, it will soon reappear in its original place. This is how cysts work - their contents expire, but the outer layer remains.
Under no circumstances should you treat a bulge on the gum or mucous membrane as a regular pimple. Any attempts to open it mechanically will not lead to anything good. But the resulting wound can become infected. Then the inflammation will spread to deeper layers in a fairly short time, and it will be much more difficult to cure.
Our services in otorhinolaryngology
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Taking ENT smears | 600 |
| Videoendoscopy of the upper respiratory tract | 2 400 |
| Radio wave removal of skin (mucous) neoplasms of ENT organs | 4 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions