- Questions and answers
- Stock
- Reviews
- Causes
- Types of cysts
- Symptoms
- Treatment
| Prices | Causes | Types of cysts | Symptoms | Treatment |
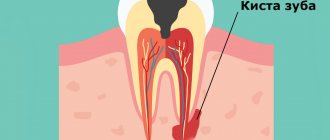
A dental cyst is a pathological neoplasm that occurs as a result of the body’s defensive reaction to infection or injury. A cyst occurs when pathogenic microorganisms that cause inflammation enter the jaw bone tissue through the root canal. Gradually, the cells involved in the disease process die, forming a cavity in the bone tissue. To prevent the spread of the process, our body forms a capsule with dense walls around the necrosis zone.
The resulting neoplasm contains inflammatory fluid, dead cells, decay products and bacteria. Sizes range from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Small ones (less than 5 mm in diameter) are called granulomas. Granuloma, cystogranuloma and cyst are stages of the inflammatory process in the bone tissue of the jaw. As long as it is small, there will be no manifestations. The number of microbes in it continues to grow, but since this happens under the control of the immune system, the process develops unnoticed. Immune cells are sent to the cyst through the blood vessels that feed the bone tissue. This is how the body tries to cope with the problem. But, if the immune system weakens, the disease enters the acute phase.
The development of the disease can lead to serious consequences. An increase in size threatens a fracture (especially of the lower) jaw, loss of teeth involved in the inflammatory process, and degeneration into a malignant tumor. Exacerbation of the disease leads to the development of periostitis, purulent abscess or even osteomyelitis. If at this stage the patient does not receive qualified medical care, sepsis may begin. This is an extremely serious condition, characterized by infection entering the blood and subsequently spreading throughout the body.
Types of cysts
Root cyst
Develops from granuloma as a continuation of pulpal necrosis (death of pulp tissue) and as a result of periapical inflammation. It is located in the apical (apical) third of the tooth root and sometimes has a transverse orientation due to additional canals, the initial paths for the spread of pulpous necrosis.
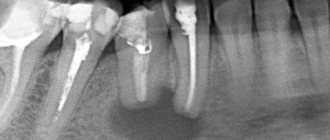
Root cysts are radiolucent capsules with well-defined boundaries. They can vary greatly in size from 2-3 mm to 2-3 cm. In the absence of secondary inflammation, the roots develop asymptomatically. Even the largest neoplasms do not displace teeth or expand bone tissue.
Once diagnosed, treatment requires eliminating the underlying cause. The most common treatment for pulp necrosis is endodontic treatment. If it is unsuccessful, a decision is made on surgical curettage or enucleation.
Residual
Remains after removal of the pathology. It can form in the granuloma left after tooth extraction or around the left apex of the root.
The residual cyst is clearly visible on x-ray. Its dimensions range from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
Follicular cyst on the gum
A cyst in the gum develops from a follicular sac that encloses each unerupted tooth. This is a capsule clearly visible on an x-ray, most often surrounding the crown of an unerupted tooth. May cause extensive tooth damage. It has a rapid growth rate, can move to adjacent teeth and lead to expansion of the cortical plate.
Clinically, a follicular cyst always occurs in the area where the enamel meets the cementum of the tooth (the place of attachment of the follicle). Due to its growth, adjacent teeth may tilt, and in rare cases, resorption (destruction) of tooth roots occurs. Unerupted teeth can also become displaced due to aggressive growth. If a follicular neoplasm has been identified, its treatment may include surgical curettage (curettage).
Eruption cyst
This is a fluid-filled follicular sac that usually occurs during teething. It covers the erupting tooth and often contains blood. Outwardly it looks like pronounced swelling of soft tissues of a bluish color (due to the presence of blood). Most often it occurs due to slow tooth eruption and can rupture spontaneously. However, in some cases where it is found, treatment may include surgical resection to help the tooth erupt faster.
Primordial (keratocyst)
Develops from the tooth germ as a result of degeneration of the stellate reticulum during tooth development before the onset of calcification of its tissues. Keratocysts can arise from any developing tooth germ, but most often they are localized in the area of premolars and the third molar of the mandible.
Clinically very prone to relapse. If the patient is diagnosed, treatment consists of careful curettage and close follow-up to ensure early detection of recurrence of pathology.
Lateral periodontal
The exact reasons for their occurrence are not fully known. They are rarely large. They are clearly visible on an x-ray and are most often closely associated with the lateral surface of the tooth root. Typically, teeth associated with these cysts have normal pulp. When a lateral periodontal neoplasm (cyst) is detected on the root of a tooth, treatment consists of surgical curettage without compromising the integrity of the tooth. It is important that the removed tissue is sent for histological analysis to rule out more serious pathologies such as early adamantinoma.
Calcifying odontogenic
Their etiology is also completely unknown. They can be found in any area of the supporting surface of the jaws, most often in the lower part. Morphologically they are quite diverse. Clearly visible on x-ray and may contain various opacities depending on the degree of calcification of the tumor. Once diagnosed, treatment consists of surgical curettage or resection.
Symptoms of a dental cyst
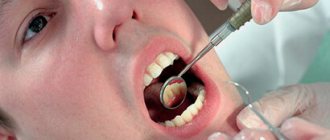
Most often it is formed as a result of traumatic injury or infection, for example, due to poor-quality root canal filling in the sinus of the tooth. Often this pathology occurs against the background of frequent sinusitis. Treatment should begin with a visit to the dentist and an x-ray. At an early stage it does not manifest itself in any way. The primary symptom is discomfort when chewing solid food.
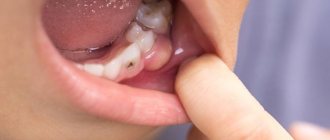
As it develops, a protrusion of bone tissue or a fistula on the gum in the area of the apex of the damaged tooth may be observed.
When the disease worsens, patients complain of acute pain. The reason for the transition of the disease to the acute phase may be a weakened immune system, relapses of chronic diseases, hypothermia, infectious diseases, or the use of certain medications, such as immunosuppressants (drugs that artificially suppress the immune system). An exacerbation may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the face in the area of the damaged area;
- increased body temperature;
- general malaise;
- enlargement and tenderness of the submandibular cervical lymph nodes;
- pain in the area of the damaged tooth, intensifying when chewing.
You should not ignore these symptoms if you want to undergo treatment without tooth extraction. When the first signs of illness appear, you should immediately seek help from a dentist.
Development mechanism
A cyst is a tumor-like disease and is found quite often in dentistry. It appears in the form of a small ball with a dense connective tissue membrane. It occurs as a result of an infection, the development of which leads to the destruction of the dental or bone tissue of the jaw. The infection spreads very quickly and the body, in order to protect itself and prevent further destruction, surrounds the lesion with a capsule, thus protecting healthy tissues from infection. As a result, a cavity with purulent contents is formed.
All of the above processes take a very long time to occur, and therefore the disease does not manifest itself immediately. The main symptoms usually appear when the cyst becomes inflamed or filled with pus. And to get rid of it, a fistula tract is formed. It can appear both on the gum and on the cheek. It is through this passage that the pus comes out.
Treatment of a cyst without tooth extraction
The success of treatment directly depends on how early it was detected. Therefore, dentists recommend that patients undergo regular preventive examinations and seek help at the first signs of illness. More recently, therapy necessarily involved tooth extraction. Of course, this approach did not suit either the doctors or especially their patients. Today, dentists' methods have changed significantly, and it is possible to get rid of a cyst without losing the beauty of your smile.
Treatment of the cyst can be surgical or conservative. The choice of therapy method depends on: the type, age of the patient, personal wishes and is determined for each patient.
Effective alternative medicine
As mentioned above, the use of traditional methods must be combined with taking medications, but this must be done correctly. Therefore, if a cyst appears in the gum, treatment at home should only occur after prior consultation with a specialist. He will tell you which folk remedies will be most effective in your case and how to use them correctly.
Salt mouthwash
You can get rid of a cyst using saline solutions. They have numerous medicinal properties, including:
- Aseptic.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Painkillers.
- Antibacterial.
- Wound healing.
All these qualities of saline solutions make it possible to relieve inflammation and purulent processes in the cyst without drugs. They are prepared simply: take a glass of chilled boiled water, in which 0.5 tsp is stirred. finely ground table or sea salt. You need to rinse your mouth with the resulting solution every 1.5 hours until the signs of the cyst completely disappear.
Herbal infusion
Treatment of cystic formations on the gums at home can also be done with the help of medicinal infusions. To prepare them, you can use herbs, for example:
- chamomile;
- calendula;
- yarrow;
- sage;
- eucalyptus.
All these plants have a powerful antibacterial effect and make it possible to eliminate the purulent processes occurring in the cyst, even in the later stages of the disease. Infusions are used to rinse the mouth. To prepare them, take any herb mentioned above in the amount of 2 tbsp. l., pour a glass of boiling water and infuse in a thermos for 10 hours.
After this, the infusion is filtered, diluted with chilled warm water in a ratio of 1:10 and rinsed with it 3-4 times a day.
Alcohol tinctures
When a cyst appears, treatment can also be carried out using alcohol tinctures. They have a disinfecting effect, prevent the spread of infectious and purulent processes, as well as the development of sepsis and abscess. The most effective in this regard are tinctures based on horseradish and ficus.
To prepare the first tincture, you need to take a three-liter bottle, fill it halfway with finely grated horseradish root and fill it to the top with vodka or medical alcohol. You need to infuse the product for at least 3 days in a cool place. After this, strain it.
To prepare the second tincture, you will need 30 - 50 ficus leaves, which must be crushed and poured into 1 liter of vodka. Place the resulting mixture in a cool, dark place for a week, and then strain.
These tinctures are used as a mouth rinse. To do this, they are diluted in half with water. Therapeutic measures need to be carried out at least 3 times a day.
Sesame oil
You can also treat cysts at home using sesame oil. It has the following properties:
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Aseptic.
- Antibacterial.
In addition, the oil saturates the gums with useful micro- and macroelements, which ensures the restoration of metabolic processes in them and accelerates the regeneration of damaged tissues.
Treatment with sesame oil is as follows: oil in the amount of 1 tbsp. l. hold in the mouth for 10 - 15 minutes, then spit out. These manipulations are carried out 5 – 6 times a day. After them, it is not recommended to drink or eat food for 30 minutes.
Garlic
Garlic has a powerful antibacterial effect, and therefore is suitable for treating festering cysts in the oral cavity. It is used in several ways:
- Rub the gums in the projection of the location of the cyst 3 – 5 times a day.
- Apply garlic pulp to the site of inflammation and keep it in the mouth until completely absorbed 2 - 3 times a day.
You should not use garlic too often, as this can cause gum irritation and other unpleasant symptoms. To prevent this, after medical procedures, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with herbal infusions or vegetable oil.
Clove oil
Clove oil has also proven itself in treatment. It perfectly relieves inflammatory processes, prevents the development of infection and provides pain relief. It is used as compresses, which are placed on the gums 2–3 times. To do this, soak a small piece of gauze in oil and apply it to the cyst for 15–20 minutes.
Lemon
Lemon contains a lot of vitamin C, which is necessary to improve immunity, as well as other beneficial substances that relieve inflammatory processes and improve the regeneration of damaged tissues.
It is used as follows: squeeze the juice from ½ lemon and dilute 1:1 with chilled boiled water. Rinse the mouth with the resulting solution every 2 hours.
It is necessary to understand that alternative medicine does not help to completely get rid of the cyst. Their use can only reduce the clinical manifestations of the disease and prevent the development of complications. Only surgery will help cure the cyst and forget about it once and for all.
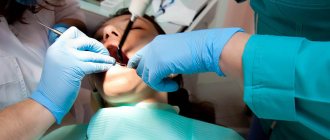
Surgery
Most often, a cystectomy procedure is performed to surgically remove a tumor. It involves removing the cyst and damaged root tip. The advantage of this method is its high efficiency. Its disadvantages include the fact that cystectomy is a rather complex operation, and not every surgeon decides to perform it.
A more complex method is hemisection. This operation is performed when one of the roots is completely destroyed. During surgery, the doctor removes the disease-causing capsule, damaged root and part of the tooth crown. The defect resulting from surgical resection is eliminated using composite materials or a crown.
Much depends on at what stage the capsule was discovered. Treatment can be accompanied by tooth extraction only if it is entirely located in the capsule of the cyst or its tissues are almost completely destroyed.
Conservative treatment
This type of therapy allows you to be cured without surgery. In this case, an incision is not required to gain access to the tumor. At the initial stage of treatment, the dentist drills out and cleans out the affected root canal. The apex of the tooth root connects to the cyst, so once the root canal is opened, the contents flow out. After cleaning and disinfecting the root canal, the doctor introduces antibiotics and substances into the cavity that destroy its capsule.
After this, the doctor fills the resulting cavity with a special paste that will help restore bone tissue. The hole is then filled. If after 6 months the cyst is not detected on an x-ray, the treatment can be considered successful. This method helps in about 75% of cases.
An innovative treatment method without surgery
is depophoresis. It helps eliminate infection in all root canals without drilling them. The dentist exposes the mouth of the canal and inserts an electrode into it. Another electrode is pressed against the surface of the cheek, which produces a weak current discharge. Together with the discharge, copper-calcium hydroxide is passed through the root canal, which penetrates into all hard-to-reach areas, destroying all bacteria, microorganisms and dead cells.
After three sessions of depophoresis, the damaged tooth is filled and its crown is restored. Regardless of what type of tumor was detected, treatment with depophoresis allows you to get rid of it in almost 100% of cases.
Cost of treating a cyst under a tooth
The price of dental services for the treatment of cysts in our clinic is about 8,500 rubles. and depends on the following factors:
- type;
- complexity of the disease;
- method of treatment (surgical or therapeutic);
- use of complex equipment;
- expenses for surgical or dental supplies;
| Service | Price |
| Consultation | |
| Orthopantomogram OPTG of the jaw | from 1,100 ₽ |
| Cystectomy | 5 300 ₽ |
| Hemisection | 3 300 ₽ |
Look at the detailed price list for dental treatment at NovaDent dentistry in Moscow and the pain-free region.
If you have been diagnosed with a dental cyst, it should be treated by a qualified dentist. Many patients do not fully understand the danger of this disease. Photos of the cyst can be found on the Internet. From them it can be understood that this can cause the destruction of large areas of bone tissue. And this, in turn, poses a risk of jaw fracture and tooth loss.
Expert of the article you are reading: Svetlana Viktorovna Derevyakina Chief physician, doctor of the highest qualification category, therapist, periodontist, leading specialist of the NovaDent network
28 years
Clinical experience
Petrovsko-Razumovskaya
Verkhniye Likhobory
st. Dubninskaya, 27, building 1
+7
Free consultation with this specialist
Complications
If you do not know how to treat a cyst and do not take any measures to eliminate it, this can lead to serious consequences. The most common of them are:
- Tooth loss.
- Jaw deformation.
- Sinusitis.
- Osteomyelitis.
- Abscess.
- Sepsis.
- Jaw fracture.
- Decreased quality of hearing or its complete disappearance (the occurrence of this complication is caused by the spread of purulent processes to the hearing aid).
Considering the high risks of developing all these complications, it is necessary to treat this disease as soon as the first signs of its occurrence appear.