General information
Of all patient visits to a surgeon, 70% are for purulent diseases of soft tissues. Patients present with a mild to moderate infection— boil , hidradenitis , abscess , or carbuncle —referring to these conditions as “abscesses.”
In most cases, these are advanced processes due to “wait-and-see” tactics or unsuccessful self-medication. Most patients turn to the surgeon on the 4-6th day after the first symptoms of inflammation appear, which indicates a frivolous attitude towards their health. Wikipedia gives the following definition: “an abscess (abscess) is a limited accumulation of pus in organs or tissues that occurs during inflammation caused by pyogenic microbes.” Purulent inflammation is most often caused by streptococci and staphylococci, affecting not only the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but also the organs of the abdominal cavity and mediastinum. The high incidence is associated with the widespread distribution of staphylococci and streptococci . Microbes penetrate through the skin and mucous membranes, which are damaged, multiply and cause inflammation with the formation of a purulent focus. Inflammation develops when the body's defenses and sensitivity to pathogens decrease.
Services
Opening of abscesses - a puncture, an incision of the abscess with a scalpel, followed by cleaning the wound.
An abscess is a formation on the skin and mucous membranes of various sizes and shapes with purulent contents.
At the “My Doctor” medical center, the following types of ulcers are opened:
- carbuncles
- boils
- acne
- abscesses
- hidradenitis
- panaritiums
- paronychia
- phlegmon
EXAMINATION BEFORE OPENING UPSURES
Express test for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B, C (blood test is performed in our laboratory within 30 minutes).
Carbuncle is an acute purulent inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue around several adjacent hair follicles and sebaceous glands. The opening of the carbuncle is carried out in case of necrosis (death) of tissue.
HOW IS THE CARBUNCLE OPENED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the carbuncle. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, a cross-shaped incision is made with a scalpel at the site of the formation, dead tissue is removed, and the leaks are opened. The wound is cleaned of pus and treated with an antiseptic.
After the procedure, an aseptic bandage is applied for 2 days. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes.
A furuncle or boil is an acute purulent inflammation of the hair follicle, sebaceous gland and surrounding tissue with the formation of a rod. A furuncle, unlike a carbuncle, develops within the boundaries of one hair follicle. The boil is opened if the abscess grows in the subcutaneous tissue and prevents the rod from being rejected.
HOW IS THE OPENING OF A BOIL PERFORMED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the boil. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, the wall of the boil is pierced with a scalpel, and the rod is removed. The wound is cleaned of pus and treated with an antiseptic.
After the procedure, an aseptic dressing is applied. Dressings are required daily until the wound is completely healed.
The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes.
Acne is a purulent pimple that occurs due to blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands. Autopsy of the acne is performed for severe acne.
HOW IS THE OPTION OF AN EAL PERFORMED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the acne. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, the wall of the acne is pierced with a scalpel. The wound is cleaned of pus and treated with an antiseptic.
After the procedure, an aseptic dressing is applied. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes.
An abscess is a purulent inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue with the formation of an abscess.
HOW IS AN ABSCESS OPENED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the abscess. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, an incision is made over the abscess with a scalpel, the surgeon inserts a finger into the cavity of the abscess and destroys the walls of the chambers. A strip of gauze soaked in a special solution is inserted into the incision to drain the pus, and an aseptic bandage is applied.
The drainage is removed after 2 days. Repeated drainage is carried out as necessary until the pus is completely removed. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 25-30 minutes.
Hidradenitis is a purulent inflammation of the sweat glands.
HOW IS HYDRADENITIS OPENED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the abscess. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, a wide incision is made with a scalpel through the abscess to healthy tissue. The surgeon cleans out the pus and removes all infected fatty tissue. The wound is treated with an antiseptic.
After the procedure, an aseptic dressing is applied. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 25-30 minutes.
Panaritium is a purulent inflammation of the soft tissues and bones of the finger around the nail.
HOW IS THE OPTION OF A PANARICIUM PERFORMED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the abscess. After 2-3 minutes. after anesthesia, the subcutaneous tissue of the finger is dissected with a scalpel. The wound is cleaned of pus and treated with an antiseptic.
The affected nail may need to be removed.
If necessary, drainage of the abscess is carried out - a strip of gauze soaked in a special solution is placed under the nail fold to drain the pus. The gauze is removed after 4-5 days.
After the procedure, an aseptic dressing is applied. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes.
Paronychia is a purulent inflammation of the skin and tissues of the finger around the nail.
HOW IS THE OPTION OF PARONYCHIA PERFORMED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the abscess. After 2-3 minutes. after anesthesia, the detached part of the nail is removed using surgical scissors - the nail fold is lifted from the nail, the scissors are inserted under the edge of the root and the detached part is removed. A strip of gauze soaked in a special solution is placed under the nail fold to drain the pus, and an aseptic bandage is applied.
The drainage is removed after 2-3 days. Repeated drainage is carried out as necessary until the pus is completely removed. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 25-30 minutes.
Cellulitis is an acute purulent inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue with the formation of an abscess that does not have clear boundaries.
HOW TO OPEN PHLEGMON WITH A SCALPEL
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the abscess. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, an incision is made over the abscess using a scalpel, the cavity with pus is emptied and washed with an antiseptic solution. If necessary, a drainage is inserted into the incision to drain pus. An aseptic bandage is applied on top. The drainage is removed after the cavity is completely cleared of pus. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 25-30 minutes.
HOW IS RADIOSURGICAL OPENING OF PHLEGMON PERFORMED?
The surgeon injects an anesthetic into the healthy tissue around the abscess. After 2-3 minutes. After anesthesia, a non-contact incision is made over the abscess of the damaged tissue and cauterization of the vessels using the Surgitron apparatus. Using a special electrode resembling a thin wire, a beam of radio waves penetrates deep into the damaged area of tissue and evaporates it. The cavity with pus is emptied and washed with an antiseptic solution. If necessary, a drainage is inserted into the incision to drain pus. An aseptic bandage is applied on top. The drainage is removed after the cavity is completely cleared of pus. Until the tissues are completely healed, dressings are required every 1-2 days.
The duration of the procedure is 25-30 minutes.
During the operation, the Surgitron radiosurgical device simultaneously cuts, eliminates bleeding and disinfects the incision site, which is almost invisible.
TREATING UPRESSURES INDEPENDENTLY IS PROHIBITED
- the use of absorbable ointments without a surgeon’s prescription can provoke the spread of inflammation to neighboring tissues, lead to damage to internal organs and even sepsis - blood poisoning
- squeezing out the abscess also leads to the spread of inflammation to neighboring tissues, causing the disease to become chronic. And squeezing out acne in the nasolabial area can lead to meningitis, encephalitis, neuritis of the cranial nerves
Therefore, when an abscess passes into the stage of abscess and necrosis, it is important to contact a surgeon in a timely manner.
Pathogenesis
In the pathogenesis of purulent inflammation, a decrease in antibacterial resistance, both general and local, is important. The integrity of the skin and the bactericidal properties of the secretion of the sweat and sebaceous glands prevent the introduction of pyogenic flora. If these conditions are violated, purulent-infectious inflammation develops. It consists of successive phases. histamine , prostaglandin , serotonin , etc.) in response In the exudative phase, under the influence of histamine, the liquid part of the plasma and proteins enter the intercellular spaces. During the infiltrative phase, tissues are saturated with lymphocytes and macrophages. As a result of exudation and infiltration, interstitial pressure increases, which significantly disrupts the condition of tissues, metabolic processes in them and reduces resistance to the effects of microorganisms. Then follows the immunological phase - the cellular and humoral response.
Inflammatory infiltrates have different outcomes, depending on the cellular composition of the infiltrate. Sometimes infiltrates resolve, but in most cases, with leukocyte infiltrates, lysosomal enzymes are released, which melt the tissue with the formation of pus - a purulent focus appears. Over time, areas of softening appear in the purulent focus and the abscess opens on its own or is opened surgically. The process ends with the reparative phase - the formation and growth of granulation tissue, which fills the resulting tissue defect as a result of purulent melting. With shallow lesions, no trace remains on the skin, but with deep lesions, a scar is formed.
Classification
According to localization, purulent infection can be:
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue of the arms, torso, legs.
- Skull skin.
- Pleura and lungs.
- Mediastinum.
- Abdominal organs.
- Pelvic organs.
- Bones and joints.
The most common purulent infection of the skin and its appendages (hair follicles, sebaceous glands, nails), as well as subcutaneous tissue (the lesion is located under the skin). The localization of purulent foci can vary - on the head in the hair, on the ear or on the lip.
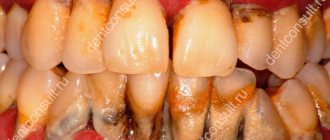
Pustular skin diseases are the most common dermatoses. Purulent sores on the body ( pyodermitis ) are caused by staphylococci and streptococci. The greatest contamination with staphylococci is in the folds of the skin and subungual spaces.
There are:
- Superficial forms of purulent skin diseases ( ostiofolliculitis , folliculitis ).
- Deep ( furuncle , carbuncle , hidradenitis ).
Staphylococcal lesions are always associated with the sebaceous gland or sweat gland, hair follicle. The lesion spreads deeper, local and general temperature rises and creamy yellow-green pus forms. Streptococcal lesions are superficial purulent lesions of smooth skin that enlarge through peripheral growth.
Ostiofolliculitis is the mildest form of staphyloderma affecting the tissue near the hair shaft. It occurs in men in the mustache and beard area and is single or multiple in nature. The process begins with the appearance of a small red papule, in its place a yellow abscess forms. After 3 days it becomes covered with a dirty yellow crust, which falls off with the formation of a residual pink spot.
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicle with the formation of pus. Unlike ostiofolliculitis, the sores in this case are surrounded by a red, inflamed cushion and are painful. Over time, a pustule forms, which opens and pus is released, forming erosion and a crust. The infiltrate resolves or a scar forms.
A furuncle is an inflammation of the hair follicle, sebaceous gland and subcutaneous tissue. The cause of the disease is a staphylococcal infection. Most often, boils form in areas that sweat, chafe, or are covered in vellus hair (legs, neck, face, and underarms). A boil often develops from folliculitis.
Furunculosis is a recurrent form of boil. There are local furunculosis (rashes in a limited area) and disseminated (elements scattered throughout the body). Chronic recurrent furunculosis has a sluggish course, periodically worsens and is difficult to treat with antibiotics.
Carbuncle is a purulent-necrotic inflammation of many hair follicles. The infiltrate is large due to the involvement of new follicles and the spread of inflammation deeper. The formation is sharply painful, and deep necrosis develops around the hair follicles in the central part.
Hidradenitis is an inflammation of the sweat glands that occurs with the formation of pus. The disease occurs at a young age, when the apocrine glands begin to function. Most often, the lesion forms in the armpit, sometimes on the nipple, around the genitals, navel or anus.
The most severe forms of purulent foci are:
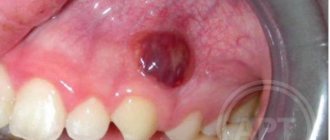
- An abscess is an accumulation of pus in tissues and organs, delimited by a pyogenic capsule (membrane). Abscesses can form due to deep infection, hematogenous introduction of microbes, as well as as a result of medical manipulations. Many people are familiar with post-injection abscess. Often, an abscess of the buttock occurs after the administration of analgin , baralgin , magnesia , oil solutions and hormonal drugs. In the development of a purulent focus, the stage of infiltration and suppuration (or abscess formation) is distinguished. In the first stage, the skin turns red, swells, and deep in the tissues a dense, painful formation is detected. With suppuration (abscessation), the skin becomes bluish and areas of softening (fluctuation) appear. The abscess code according to ICD 10 is L02.3. An abdominal abscess can develop in any part of the abdominal cavity. Most often it appears after injuries, surgical operations, peritonitis and perforation of a hollow organ and intestinal tumor. Abscesses develop when infection spreads due to appendicitis , pancreatitis , Crohn's disease , diverticulitis . Patients have a high fever and severe abdominal pain. Computed tomography is used for diagnosis. Treatment is surgical with antibiotics.
- Cellulitis is a diffuse inflammation of the tissue without demarcation (there is no pyogenic membrane), and pus spreads throughout the tissue space.
- Empyema is an accumulation of pus in hollow organs.
- Mediastinitis is an inflammation of the mediastinal tissue, often purulent in nature. This disease is life-threatening. Mediastinitis often develops after surgery on the heart, lungs, aorta, vena cava, esophagus, thoracic lymphatic duct, nerves (vagus and phrenic) and mediastinal lymph nodes. Prevention of surgical infection is preoperative and postoperative antibiotic therapy. All patients are prescribed beta-lactam antibiotics ( penicillins , cephalosporins ) or vancomycin . In addition to surgical trauma, the development of mediastinitis is caused by an infection that spreads from adjacent organs through the cellular spaces: the esophagus, lungs, descending infection of the neck, oropharyngeal and dental infections.
Types of dental abscess
- Gingival Lump with a purulent cavity is formed on the soft tissue near the gum papillae between the interdental segments. The cause of inflammation is damage to the gum tissue, accumulation of food, plaque between the teeth, or injury to the gums by a toothbrush or floss. Gingival abscess (flux) affects only the gum tissue; the tooth and ligamentous apparatus with the root are not affected.
- Periodontal Exacerbation of periodontitis. The infection affects the tissue between the alveolar process and the gum, and hypertrophy of the periodontal pocket begins. Inflammation is provoked by subgingival deposits (plaque + tartar). Purulent exudate accumulates inside the gum pocket and forms a lump. The infection will penetrate deeper into the bone tissue and tooth root.
- Periapical (root) Most often occurs in units with non-living pulp. The cause of inflammation is poor treatment of caries, chronic periodontitis of root canals. Pus accumulates to a limited extent in the periodontal tissues at the root of the tooth; a granuloma with exudate is formed at its apex. Inflammation spreads to the supporting apparatus of the tooth and periodontal tissue. As it matures, a fistulous tract forms and pus comes out to the surface of the gum in the form of a ball.
- Pericoronal (pericoronitis) The soft tissue of the gums becomes inflamed during tooth eruption. Pericoronitis often occurs in partially erupted wisdom teeth. If bacteria gets into the “hood” above the tooth or plaque accumulates, a lump with pus forms. Surgical excision of the gum or tooth extraction is recommended to avoid swelling of the face, neck and the development of angina (in the lower jaw).
- Endo-periodontal (combined) Abscess is formed in the complex of endodontic tissues (pulp, dentin, root canals). The inflammatory process in periodontal tissues is supported by infection from the root canals through the apical foramen. Bacteria spread along the dentin canals, which can cause periodontitis in adjacent teeth.
International classification ICD-10
- K-04.6 Periapical with fistula. The cavity with purulent contents communicates with the maxillary sinus, nasal or oral cavity, and facial skin.
- K-04.7 Periapical without fistula. The abscess is associated with a complicated form of periodontitis.
- Abscess in acute form of periodontitis (K-05.20 periodontal or K-05.21 periodontal). The source of infection is hidden in the periodontal tissues, periodontal pockets swell and teeth become mobile.
Classification of abscess according to severity:
- mild - a purulent sac in one anatomical area;
- moderate severity - the pathological process affected two anatomical areas (for example, an abscess on the gum and face);
- severe - abscesses of the gums, sublingual space, neck and face.
☝️ The abscess affects the surface of the gums or deep layers of the periodontium. Tooth abscesses appear in the lower jaw in 72%, and in the upper jaw in 28% of cases. Most often, the causative teeth are molars, followed by premolars; most rarely, an abscess occurs on the incisors or canines.
Stages of abscess development
- Initial. Inflammation of the gums near the tooth or implant worsens. With strong immunity, the symptoms are almost invisible, and the pathological process can go away on its own. With a lack of immunity, necrosis of soft and bone tissue, hyperemia of blood vessels, and pain syndrome begin.
- Subacute. The inflammatory process intensifies. An infiltrate (tissue compaction) forms in the area of the gingival papillae, in the periodontal pocket, and at the tooth root. A throbbing pain begins when pressing on the unit.
- Spicy. Abscess formation begins - pus accumulates in the carious cavity. Exudate, swelling of the gums, sharp constant pain. The submandibular lymph nodes become enlarged and painful.
- Chronic. Resolution of the abscess - a fistula tract is formed, through which the purulent contents of the lump come out. The pain subsides.
Causes
The nature of all purulent-inflammatory diseases is infectious. They are caused by microorganisms: gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, aerobes and anaerobes, as well as fungi.
Staphylococcus is the most common causative agent of skin and tissue diseases (causes boils , abscesses , carbuncles , cellulitis , hidradenitis ).
The most significant causes of abscesses on the body:
- Contamination of the skin with pathogenic flora and its penetration through microcracks, abrasions and cuts into the ducts of the sebaceous and sweat glands.
- Dry skin.
- Irritating effects of chemicals.
- Hypovitaminosis and unbalanced diet.
- Chronic intoxication.
- Foci of purulent infection in the body.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Endocrine diseases (pustular diseases are the most severe in diabetes mellitus ).
- Predisposing factors that contribute to the development of purulent infection are conditions after previous infections and operations, and the use of glucocorticosteroid drugs.
The main factors that determine the development of purulent inflammation are:
- Number and virulence of pathogenic microorganisms.
- State of general and local immunity.
- Anatomical and physiological features of the area of introduction of microorganisms.
- General and local blood circulation.
- Allergy of the patient.
Symptoms
Any inflammation is accompanied by redness, swelling, pain and fever. In purulent-inflammatory diseases of any localization, pus always forms. Many people are interested in the question, what does it look like and what color? Color and consistency are variable and depend on the pathogen, location and possible impurities (for example, blood). Usually fresh purulent discharge is liquid and then thickens.
Thick, creamy, white-yellow or green pus forms when infected with staphylococci. Streptococcal pus is liquid, grayish-yellow and has an unpleasant odor. Pus caused by E. coli is foul-smelling, thin, and brown in color. What does purulent discharge consist of? The cellular composition of pus is different and depends on the type of microorganism. It contains globulins and albumins from blood serum, microbial enzymes, leukocytes, tissue breakdown products, glycogen, fat droplets and microorganisms. What does pus taste like? Usually, no one specifically tries it, but if an abscess has formed in the mouth and ruptured, then the person is forced to try the purulent discharge - it has a sweetish taste.
Boils on the face
Most often on the face there is acne (blackheads), boils or abscess . With a boil, soreness and redness of the skin around the hair follicle appears. Tissue infiltration and pustule gradually increase and are accompanied by severe pain. After a few days, pus forms in the center of the boil. After opening, a purulent core is visible, separated along with pus. An ulcer forms at the site of the detached necrotic core. As the boil opens and the rod separates, the pain decreases, the inflammation subsides and the seal resolves. Gradually, the ulcer fills with granulations and scars.
Photo of boil and carbuncle
Carbuncle , which is an inflammation of several hair follicles at once (a cluster of fused boils), has larger compaction and redness and is more painful. The infiltrate has a spherical shape, and the center is bluish in color. The stage of “ripening” of the carbuncle lasts 10-12 days. The patient's condition worsens - there may be a high temperature, headache, nausea, weakness. The resulting purulent-necrotic masses acquire a dark color. When the skin breaks, green pus and necrotic masses are released from many places. Due to the combination of several rods, a large defect is formed in the skin and a deep ulcer is often formed. After tissue and pus are rejected, the condition improves. A deep defect takes a long time to heal and deep scars can form on the skin.
A purulent abscess is a more serious disease. At first, an abscess on the face is a dense, painful, well-defined formation. If the abscess is located superficially, the skin over it is red and hot. Abscess formation lasts 7-8 days. In the center, due to the formation of pus and softening of tissues, oscillation (fluctuation) is determined. In deep lesions, fluctuation is difficult to determine. The general condition of the patients is disturbed.
Many of us have had stye (medical term hordeolum ) - a purulent formation on the eyelid associated with inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash (the sebaceous gland is also involved in the process). External styes are more common. It begins with soreness, redness and swelling of the eyelids. After 2-3 days, an external stye forms at the edge of the eyelid with a yellow center of pus. The patient is bothered by lacrimation and foreign body sensation. After a few days, the abscess opens, pain and swelling gradually decrease. It must be remembered that any purulent formation on the face and head is dangerous because it is possible to develop thrombosis of the sinuses of the brain and purulent foci in the brain itself.
Ulcers on the legs
Superficial small purulent formations appear after minor injuries and cuts, and they do not affect the general condition of a person. A more serious abscess on the leg, causing discomfort, pain and accompanied by fever, is associated with a boil or carbuncle .
There may also be multiple boils (furunculosis), the treatment of which is difficult because they constantly recur. Pus under the nail is formed by subungual felon . This disease is associated with a splinter getting under the nail or with the spread of skin whitlow. After the injury, a few days later a tugging pain appears under the nail. After a few more days, pus accumulates under the nail, the pain intensifies, and the temperature rises. If pus accumulates, the doctor peels off and cuts out the nail plate either in a small area or completely.
Breast abscess
With a breast abscess, a cavity filled with pus forms in the tissues. In 90% of cases, an abscess develops in the postpartum period. Its occurrence is associated with the penetration of bacteria (streptococcus, Escherichia coli, Proteus or staphylococcus) into the mammary gland. They enter the body through cracks in the nipple that form during breastfeeding. One of the factors in the development of an abscess is stagnation of milk if a woman neglects to pump or completely refuses breastfeeding.
What does an abscess look like? Suppuration of the mammary gland is located superficially (subcutaneous abscess) or deep in the tissues (intramammary and retromammary abscesses).
Photo of subareolar abscess
The woman experiences throbbing pain that intensifies with movement (walking, running, bending). Feeding the baby becomes impossible due to severe pain.
- When examining and palpating the chest, the epicenter of pain is determined.
- Due to edema, the mammary gland increases in volume.
- over the abscess is red and hot.
- Purulent discharge often appears from the chest.
- The axillary lymph nodes on the affected side are enlarged and painful.
Abscess under the arm
It may be caused by a boil or hidradenitis. With hidradenitis, conglomerates with purulent contents form, protruding above healthy tissues (“bitch udder” is how this disease is called in everyday language). When the conglomerate is opened, several fistulous tracts are formed, but necrotic rods, as with a boil, are not formed.
An abscess on the labia may be associated with a boil of the labia majora and bartholinitis . With a boil, a painful lump initially forms that tends to enlarge. After a few days, a purulent core forms. The boil can open on its own, but sometimes prompt assistance is required.
Inflammation of the gland of the vaginal vestibule is called bartholinitis . Bartholin's glands are located at the junction of the labia majora and labia minora. Inflammation causes severe discomfort and pain. The disease begins with the appearance of a lump (painful “bump”) with redness of the mucous membrane above it. When infection penetrates into the gland, its purulent melting occurs and purulent bartholinitis , which is classified as an abscess, since the cavity of the gland is filled with pus.