Causes Types of prevention Hygiene Treatment in the stain stage How to avoid?
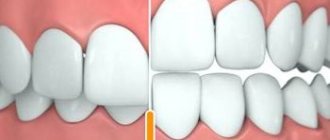
Caries is damage to hard dental tissues with the formation of cavity defects. First, the enamel is destroyed, then areas of dentin, pulp, periosteum and bone. It is the most common dental disease in the world and the leading cause of tooth loss. Comprehensive prevention of dental caries increases the resistance of the enamel layer to various cariogenic factors and prevents destruction of tooth structures.
Oral hygiene
It is necessary to regularly, at least twice a day, thoroughly (each time for at least five minutes) brush your teeth. When brushing your teeth, the brush head should make vertical (from the gums to the teeth), horizontal and circular movements. It is imperative to remove plaque from the tongue, and use dental floss to clean the interdental areas. For effective dental cleaning from the point of view of prevention, a correct, qualified selection of toothpaste is necessary, taking into account the individual characteristics and pathologies of the patient.
FLUOREPREVENTION OF CARIES Zhurbenko V.A.
Text of a scientific article
The principle approach to the prevention of dental caries is determined from the etiology and pathogenesis of this process. Many etiological factors take part in the occurrence of caries, which are divided into general and local. Local factors include: dental plaque and plaque, a violation of the composition and properties of oral fluid, which is an indicator of the condition of the body as a whole, carbohydrate sticky food residues in the oral cavity, resistance of dental tissues due to the full structure and chemical composition of hard dental tissues, deviations in the biochemical the composition of the hard tissues of the tooth and the defective structure of the dental tissues, the condition of the dental pulp, the condition of the dental system during the period of formation, development and eruption of permanent teeth. Common factors include: poor diet and drinking water, somatic diseases, changes in the functional state of organs and systems during the formation and maturation of dental tissues, extreme effects on the body, heredity that determines the usefulness of the structure and chemical composition of dental tissues, unfavorable genetic code. Knowledge of the causes and development of the disease is a necessary condition for the implementation of preventive measures. An epidemiological survey of the world's population showed that dental caries and periodontal disease are the most common diseases in the world, which manifest themselves in early childhood. The prevalence of dental caries in different regions of Russia ranges from 60 to 98%, and the intensity of dental caries according to the WHO classification ranges from very low to very high. Prevention of the occurrence of the carious process can be achieved by acting in two directions: increasing the resistance of enamel to the action of acid and/or reducing the cariogenic situation in the oral cavity. An increase in enamel resistance due to changes in its structure is achieved when fluorides enter the body. In addition, local exposure to fluoride directly on the tooth surface (solutions, toothpaste) also prevents the development of caries. The cariogenic situation in the oral cavity is undoubtedly influenced by two factors - microorganisms and carbohydrates. Based on this, strategic directions are obvious, which, in turn, determine the tactics of carrying out preventive measures. The optimal condition for successful prevention of dental caries is the introduction of a system of public and individual measures. Long-term clinical observations conducted in a number of countries have shown the effectiveness of fluoridation of drinking water (optimal concentration 1 ppm) in the prevention of caries. It is important to note that the effect is observed if the drinking water contains insufficient fluoride. Systemic methods of caries prevention also include fluoridation of salt and milk. Observations in a number of countries show that consumption of fluoridated milk from early childhood has a pronounced anti-caries effect. When choosing a systemic method of introducing fluoride into the body, it is necessary to have clear indications, the main of which are: • high incidence of dental caries among the population • low fluoride content in drinking water (less than half the optimal dose for each climatic zone) • lack of additional sources of systemic fluoride administration Despite Despite the high efficiency of systemic methods of fluoride administration, in many regions they cannot be implemented due to technological or economic reasons, so there is a need to use local methods to prevent dental caries. Fluoride-containing products for topical use include toothpastes, varnishes, rinses, solutions and gels for application, sealants and filling materials that gradually release fluoride. The use of fluoride in the form of drops or tablets can also be recommended as one of the possible ways of introducing fluoride into the body. Sodium fluoride tablets contain 2 mg of fluoride. Based on pure fluoride ion, each tablet contains 0.85 mg of fluoride. The use of sodium fluoride tablets can begin at 2 years of age and continue until 14-15 years of age. The number of tablets used will depend on the fluoride content in the water in a particular area and on the age of the child. However, the need for daily administration of the drug and dosage control significantly reduce the possibility of using this method. Contraindications to the prescription of tablets: 1) fluoride content in the environment is more than 50% optimal 2) any other methods of taking fluoride orally. Fluoride is also used in the form of drops - the drug “Vita-fluorine”. It is most effective to start taking fluoride with vitamins no later than 2 years after the birth of the child. “Vita-fluorine” is a light yellow liquid with a complex of vitamins A, C and D and sodium fluoride. 1 ml of the drug contains sodium fluoride 0.22 mg. It is used orally during or after meals for a month at intervals of 2-4 weeks every 3 months in areas where the fluoride content in drinking water is minimal. For children from 1 year to 6 years, the drug is prescribed ½ tsp. 1 per day; from 7 to 14 years - 1 tsp, 1 time per day for a month. After a 2-week break, the course is repeated. 4-6 courses of prevention are carried out per year. Fluoride-containing toothpastes are an effective means of prevention. It should be borne in mind that oral hygiene is an effective measure in itself, and its combination with the application of fluoride to the surface of the enamel has an active effect on reducing morbidity. Numerous observations indicate that to achieve a pronounced anti-caries effect, it is sufficient to apply small doses of fluoride to the tooth surface. It is important to do this systematically. Fluoride-containing pastes are also used in pediatric practice. But due to the fact that small children often swallow the toothpaste when cleaning, it is recommended to limit its use to those under 6 years of age. In this case, the amount of paste applied to the brush should not exceed the size of a pea. One of the most common means of local prevention of dental caries are varnishes, which are used to prolong the period of exposure to fluorides on the enamel. They form a film adjacent to the enamel that remains on the teeth for several hours, and in fissures, crevices and microspaces for several days and even weeks. Fluoride-containing varnishes are used 2 times a year, but in groups with an increased risk of caries - 4 times a year. Rinsing with fluoride solutions is carried out for 1-3 minutes, avoiding swallowing the liquid. After this procedure, be sure to rinse your mouth with clean water. It is not advisable to use this method for small children 2-4 years old. Rinses begin to be used when children erupt their first permanent teeth. This method of prevention does not require significant investment of time and material resources and at the same time is quite effective. In addition, fluoride-containing gels are used, which, in case of high caries susceptibility, are recommended to be used 4 times a year. The constancy of the enamel composition is ensured by the dynamic balance between the processes of demineralization and remineralization. If this balance is disturbed, either remineralization or demineralization will predominate, resulting in caries. By carrying out fluoride prophylaxis, it is possible to achieve a shift in the balance towards remineralization. Fluoride increases the acid resistance of enamel, which is very important in the presence of carious lesions. It has now been established that the effective anti-caries effect of fluoride is manifested even at low concentrations in application solutions or toothpaste. It is important to carry out these activities systematically and combine them with careful oral care.
Preventive examinations with a dentist
Like any disease, caries is better, easier and cheaper to treat at the very initial stage. The initial stages of caries cannot always be diagnosed by a non-specialist: for example, white (or chalky) spots, which indicate the beginning of the carious process, are not always clearly visible, may be in places difficult to see, and may be covered with a layer of plaque. Regular preventive examination by a dentist, which is recommended once every six months, will help you begin timely treatment and get rid of unpleasant, often painful and expensive procedures in the future, and will help you maintain healthy teeth for a long time.
Methods for preventing caries
Conventionally, methods of caries prevention can be divided into household and professional. Household methods include time-tested and proven methods that are passed down from generation to generation. They do not require any energy expenditure, but they do need regularity. Professional prevention includes various hygiene procedures and timely treatment of caries. They also distinguish endogenous prevention, which is aimed at strengthening teeth from the inside, and exogenous, when all actions are carried out locally. So how can you stop dental caries?
Cost of treatment
| Inspection, general recommendations | For free |
| Anesthesia | |
| Appliqué | 200 |
| Injection | 550 |
| X-ray diagnostics (Visiograph “Satelek” Germany) | |
| Dental image without printing on a printer | 300 |
| Panoramic shot | 1000 |
| Dental filling (1-2 surfaces) | |
| Light-curing filling “Charisma” (Germany) | 2800 |
| Light-curing filling “Filtek” (USA) | 3970 |
| Restoration and cosmetic restoration of teeth (3 or more surfaces) | |
| Light-curing filling “Charisma” (Germany) | 3160 |
| Light-curing filling “Filtek” (USA) | 4260 |
| Veneering of anterior teeth | 6550 |
Payment by installments / Tax deduction
all prices
Primary or endogenous prevention of caries
Proper nutrition is important in preventing tooth decay. This is not only about giving up chocolate and cakes, but also soda and concentrated juices. You should not eat sour apples, as they disrupt the acidity of saliva. It is better to replace them with hard, raw carrots, which clean your teeth almost better than a good specialized paste. It wouldn’t be a bad idea to nibble on Japanese horseradish – wasabi – from time to time. Japanese scientists have found that it blocks the growth of carious microbes.
Paradoxically, kissing is a great way to defeat tooth decay. When we kiss, the gums are massaged and salivation becomes more intense, and along with it, the acid-base balance is evened out.
If you have a tendency to develop caries, it makes sense to consult a specialist for recommendations on taking vitamins. Russian scientists have found that the demineralization of enamel is affected by a deficiency of vitamin C. During the experiment, it was found that those who were attacked by caries had a decrease in its content in the body several months before. In addition, vitamin D also increases the resistance of teeth to caries, since calcium is easily absorbed with it. Don't forget about such a useful element as fluorine. It has a pronounced anti-caries effect.
How to brush your teeth correctly?
It is impossible to thoroughly clean the entire surface of the teeth if the movements are directed only up and down or to the sides. You will also need to make diagonal or circular movements. It is desirable that the long bristles pick up plaque from under the gums. It is recommended to hold the brush at an angle of 45°C.
But all these rules have to be broken if brushing leads to bleeding gums. For those who have this predisposition, it is advisable to spend more time rinsing the mouth and use the brush as carefully as possible. Rinse aids must be antibacterial.
In general, it can be noted that in addition to good and constant oral care, it is important to see a dentist purely for preventive purposes, as well as for professional procedures that help maintain dental health.
Expert advice
Dentists consider it important to monitor the health of teeth and the body as a whole on an ongoing basis. Unscrupulous prevention is a sure path to tooth loss and the need for dentures.
Dentists recommend to patients.
- Eat enough raw vegetables and fruits, cottage cheese, milk, nuts, hard cheeses, sesame seeds, eggs, mineral waters. Plan your diet based on age and individual characteristics of the body.
- Reduce the amount of simple carbohydrates you consume.
- Monitor the state of the immune system and strengthen it.
- Maintain oral hygiene.
- Have regular medical examinations and have your teeth professionally cleaned to remove plaque.
- Saturate the enamel with fluoride and other elements as needed, indicated by the doctor, and in his chosen way.
- Maintain physical health.
Following the rules of both primary and secondary prevention of the disease minimizes the risk of developing caries.
Products for the prevention of dental caries
Toothpaste against caries, or anti-caries, helps strengthen mineral dental tissues and prevents the formation of plaque due to the fluorine, phosphorus and calcium compounds introduced into the composition. The anti-carious effect of toothpastes is explained by the fact that topically applied fluorides increase the resistance of enamel to adverse effects. Penetrating into the enamel structure, fluorine creates a more durable fluorapatite system, fixes phosphorus-calcium compounds in hard dental tissues, and also suppresses the growth of soft plaque microflora. Anti-caries paste is most active during the period of enamel maturation, and later its effectiveness decreases significantly. Therefore, it is most reasonable to use anti-caries toothpastes in childhood to prevent caries in children.
Unlike toothpaste, a toothbrush can significantly improve or, if chosen incorrectly, worsen your oral health. For example, regular manual brushes with stiff bristles are not suitable for people with problem gums. Such brushing will only increase the colony of harmful bacteria and increase gum bleeding. The same can be said about electric toothbrushes, which also drive plaque under the gums, which leads to a serious inflammatory process. Today, the most effective way to prevent caries is to purchase a brush with ultrasound, which not only gets rid of plaque, but also destroys harmful microorganisms.
Causes of caries
The main reason for tooth damage by cariogenic bacteria is their penetration into the tooth tissue due to demineralization of the enamel. This is caused by a decrease in pH below 4.5. There could be a variety of reasons for this:
- Lack of proper oral hygiene.
- Deficiency of minerals supplied with water and food.
- Abuse of fast carbohydrates.
- Features of the anatomical structure of teeth.
- Genetic factors.
- Chemical composition of saliva.
Methods of so-called primary prevention are aimed at preventing the occurrence of caries, which are relevant precisely during the period when there are no visible lesions on the teeth. This differs from secondary prevention, which consists of treating caries and its complications. Primary prevention can be endogenous (general) and exogenous (local).