Many people are familiar with the unpleasant manifestations of herpes. This is not surprising, because according to WHO, more than 78% of the world's population is infected with the most common types of the virus: 67% are infected with herpes simplex virus type 1, and another 11% with herpes simplex virus type 2.
What is herpes, what causes it, why is it dangerous, and how should it be treated? Having knowledge about the disease, you can minimize the risk of its exacerbation, and most importantly, avoid complications.
Herpes on the lips
Herpes is a virus
The source of the disease is the so-called herpes viruses. These are DNA-containing microorganisms that are causative agents of various types of infections.
The initial entry of the virus into the body usually occurs through the mucous membranes (although entry through damaged skin is not excluded). Having overcome tissue barriers, harmful microorganisms enter the blood and lymph and spread throughout the body. They are able to penetrate the cells of internal organs and nerve endings. The peculiarity and danger of herpes is that it is genetically introduced into the nucleus of nerve cells, after which it remains in the body forever.
Many people do not even realize that they are carriers of the virus, since the pathology in most cases is asymptomatic, not showing itself in any way (this is called a latent state).
The human immune system is capable of suppressing the development of the virus, but if it is weakened, the infection “awakens.”
Herpes Virus
Treatment of herpes
VACCINE “VITAGERPAVAC”
against herpes simplex virus (HSV) serotypes Ι and ΙΙ
Relapses that affect the lips or nasal mucosa respond well to local treatment with cream or ointment. In more severe cases, your doctor may recommend pills.
It must be remembered that early initiation of herpes treatment is the key to success. Before the bubbles appear, the lips become very sensitive, itching and tingling occur. And if the disease begins to be treated at the stage of these precursors, then rashes may not appear, and recovery will occur as soon as possible.
Today there are no drugs that would completely destroy the herpes virus in the human body. However, there is a group of special antiviral agents that effectively suppress the reproduction of HSV-I.
If you start using antiviral cream for existing rashes, healing occurs faster than with other treatment methods.
Taking tests to diagnose herpes and CMV infection.
INITIAL CONSULTATION
from 2,500 rub.
Symptoms of different types of herpes
A “sleeping” virus may not bother its host for years. But if for some reason the virus enters the active phase, it is easy to recognize - by its characteristic rashes. The “classic” visual sign of herpes is itchy, watery blisters that can appear in different places - on the face and on the body.
There are several types of herpes virus - they differ in their manifestations. Most often in medical practice, diagnoses such as HSV-1 and HSV-2 are encountered - this is the abbreviated name for herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2.
Cold sores and chicken pox are related diseases caused by herpes. Several types of the virus can “coexist” in one person.
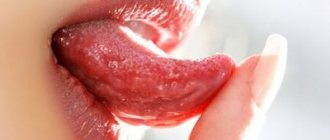
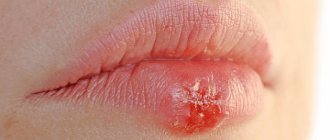
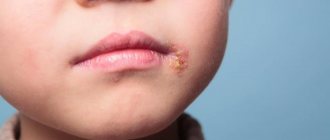
| Many people call this pathology a “cold on the lips,” although the “classic” cold and herpes are different things. We are talking about the herpes simplex virus type 1, which usually “attacks” the lips and nasolabial triangle. Externally, the disease manifests itself in the form of rashes. They represent one or a whole cluster of bubbles with liquid contents. When asked whether there can be a fever with herpes, the answer is positive: many patients complain of fever, headaches and general weakness. Among doctors, there is another name for pathology: when you see a diagnosis such as oral or labial herpes in your medical record, know that we are talking about the herpes simplex virus type 1. Herpes on the lip is usually very itchy |
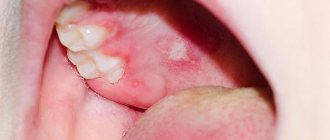
| The second type of herpes simplex is accompanied by the development of genital (genital) infections. The disease in most cases is asymptomatic or, as with labial herpes, is accompanied by the appearance of blisters (ulcers), but only in the area of the external genitalia. Other signs of HSV-2 are fever, body aches, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes in the genitals. Most often, the disease is transmitted sexually, but infection can also occur from a person with labial herpes. |
| Virus type 3, also known as the herpes zoster virus, is the culprit of chickenpox. To become infected, it is enough to enter into a conversation with a sick person (transmission occurs through airborne droplets). Having had chickenpox, a person remains a carrier of this virus for the rest of his life. In case of relapse, there is a risk of developing herpes zoster. This disease is characterized by the appearance of itchy rashes throughout the body, as well as fever. Chicken pox |
| Herpes type 4 causes such a serious infectious disease as mononucleosis. This disease is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes and fever; the patient complains of a sore throat and general weakness. The liver and spleen are also affected. |
| Herpes type 5 provokes the development of cytomegalovirus. The disease manifests itself differently, depending on which organ is affected. A runny nose, disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, inflammatory diseases of the genital organs - all this can be a sign of pathology. |
| In addition to those described above, there are also types 6, 7 and 8 herpes. Scientists are now studying these viruses. |
Classification of viruses
According to the existing international classification, primary and recurrent genital herpes . The latter, in turn, is divided into typical and atypical clinical forms and asymptomatic viral shedding.
The term “genital herpes” arose at the beginning of the 20th century. to designate the lesion on the skin and mucous membranes of the external genitalia. With the development of virological research methods, information about “atypical” forms of the disease began to appear. The diagnosis “atypical form of genital herpes” is made by gynecologists to designate a chronic inflammatory process of the internal genitalia (colpitis, vulvovaginitis, endocervicitis, etc.) in the presence of a laboratory confirmed herpetic nature of the disease, in contrast to the “typical” picture of the disease, in which on the mucous membrane These organs have lesions with vesicular-erosive elements. At the same time, herpetic lesions of the urethra, anal area and rectal ampulla fall out of this group, although these organs are anatomically and functionally closely related to the genital area.
Research conducted at the Herpetic Center has shown that diagnosing the HSV virus is now complicated due to the fact that in 65% of cases the disease is atypical.
Herpes - what causes it?
The risk of contracting an infection arises from a very early age, because there are a huge number of adults around a small child, most of whom are carriers of herpes. Infection can also occur in the womb of an infected mother.
So, what can cause herpes on the lips? Children (and adults) often become infected through kissing, as well as through sharing utensils. If you are near a person with herpes who coughs or sneezes, there is a high risk of infection through airborne droplets. In addition, the virus is transmitted sexually (primarily this concerns HSV-2). People who receive blood transfusions are also at risk.
Fortunately, most people infected with the herpes virus (about 80%) have an inactive form of the infection. However, there are factors that provoke a relapse - then the “sleeping” virus begins to actively multiply. So, some people regularly suffer from sores on their lips - the hated “cold” can appear 5-10 times a year. The cause of recurrence of the disease may be:
- diseases – endocrine, viral and bacterial;
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- exhaustion of the body;
- overwork;
- injuries;
- metabolic disorders.
In women, another provoking factor is menstruation.
Reminder in case of illness
It must be remembered that when a rash appears, a person becomes acutely contagious. Moreover, not only those around him can suffer, but also the sick person himself. For example, from a lesion on the lips with dirty hands, the herpes virus can be carried into the eyes or genitals.
Therefore, it is important to follow the following rules
- Do not touch lips affected by rashes. If you touch them, wash your hands thoroughly.
- Use your own towel and utensils.
- If your lips are affected, do not squeeze the blisters or pick off the scabs. This may cause additional skin infection.
- Refrain from kissing and oral-genital contact.
- If you wear contact lenses, do not wet them with saliva to moisten them.
- Apply antiviral cream to your lips not with your fingers, but with cosmetic sticks.
Is there any prevention against herpes?
To resist the virus, you need a strong immune system. Therefore, those who suffer from frequent colds on the lips need to pay attention to their immune system. Take care of a healthy, balanced diet, do not forget about sports, maintain a normal daily schedule (first of all, ensure that you get adequate sleep) and try to get rid of bad habits (smoking, etc.).
It is important to practice basic hygiene, including regular hand washing. It is recommended to use personal hygiene products. During infectious epidemics, it is advisable to avoid staying in crowded places if possible.
To reduce the risk of genital herpes, you should use condoms.
Causes
There are many provoking factors leading to exacerbation of the disease. In addition to the weakening of immune forces, there are a number of other reasons:
- Emotional stress, physical fatigue, stressful situations.
- Long-term insolation.
- Surgical interventions.
- Taking immunosuppressive drugs.
- Hormonal imbalances.
In addition, there may be a combination of several negative factors leading to the activation of infection in the body. During illness, it is important to isolate yourself from others.
How to find out if there is a virus?
Already during the initial examination of the patient, the doctor can determine the presence of herpes (often people who have visual manifestations of the disease seek medical help). But in order to confirm the diagnosis and determine the degree of development of the infection, laboratory tests are prescribed.
Tests are important when planning pregnancy, since the virus is dangerous to the fetus. Tests are also required for patients preparing for transplantation.
There are several diagnostic methods - which one will be optimal in a particular case, the doctor will tell you. The presence of the herpes virus and its type can be determined by blood tests (enzyme immunoassay, PCR analysis, immunofluorescence reaction) and scrapings (culture method, immunofluorescence reaction). The most accurate, but also the most time-consuming and expensive method is the cultural method, which involves “growing” a virus obtained from a patient’s biomaterial in laboratory conditions.
Diagnosis of herpes
How long does the virus live?
Fully formed and ready for subsequent reproduction, “daughter” infectious virions appear inside the infected cell after 10 hours, and their number becomes maximum after 15 hours. During its entire life, the primary (“mother”) viral particle reproduces from 10 to 100 “daughter” ones. viral particles, and 1 ml of the contents of a herpetic vesicle contains from 1000 to 10 million viral particles. Virions are extremely thermostable - they are inactivated (destroyed) at 50-52 degrees for 30 minutes, at 37.5 degrees for 20 hours, stable at 70 degrees, and remain in tissues for a long time. On metal surfaces (coins, door handles, water taps) it survives for 2 hours, on plastic and wood - up to 3 hours, in damp medical cotton wool and gauze during the entire drying time at room temperature (up to 6 hours). A unique biological property of viruses is the lifelong preservation of viruses in a modified form in the nerve cells of the regional (relative to the site of virus introduction) ganglia of sensory nerves. The most active herpes simplex viruses (labial and genital) in this regard, the least active are the Epstein-Barr virus.
All known varieties of viruses are capable of recurrence . For example, recurrence of infections caused by the herpes simplex virus is often observed against the background of stress, nonspecific endocrine disorders, changes in the geographic area of residence, increased solar radiation, etc. Asymptomatic relapses of cytomegalovirus infection are most often observed in pregnant women and patients receiving immunosuppressive and hormonal therapy . In general, herpetic infections take a recurrent course in no more than 8-20% of patients with obvious malfunctions of the immune system.
Herpes viruses can lead to infection of the fetus during pregnancy. Pregnancy is very often a physiological immunosuppressive factor (there is a natural decrease in immunity). In the cervical canal of pregnant women, the risk of intrauterine infection of the fetus, as well as infection of the child during childbirth, significantly increases. The virus is the most common sexually transmitted infection in pregnant women. Therefore, before an expected pregnancy, we recommend that expectant mothers be examined for the presence of herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus infection on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, determine the presence and level of antibodies to these viruses, and, if necessary, receive a course of preventive treatment.
Organs and systems of the body that can be affected by the herpes simplex virus and the diseases it causes:
- Optic tract (keratitis, iridocyclitis, chorioretinitis, optic neuritis, phlebothrombosis)
- ENT organs (pharyngitis, “herpetic sore throat”, laryngitis, external ear, sudden deafness, vestibular disorders)
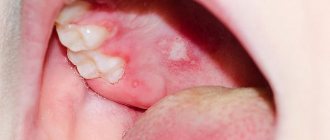
- Oral organs (stomatitis, gingivitis)
- Skin and mucous membranes (face, lips, genital herpes, etc.)
- Lungs (bronchopneumonia)
- Cardiovascular system (myocarditis, myocardiopathy, participation of HSV in the processes underlying atherosclerosis)
- Gastrointestinal tract (hepatitis, ileo-colitis, proctitis)
- Female genital organs (colpitis, intrauterine HSV infection: endometritis, amnionitis, chorionitis, metroendometritis, reproductive dysfunction)
- Male genital organs (prostatitis, urethritis, sperm damage)
- CNS (encephalitis, sympathoglioneuritis, nerve plexus damage)
- Psycho-emotional sphere (depression, aggravating influence of HSV on the course of hydrocyanic dementia and nuclear schizophrenia)
- Lymphatic system (HSV lymphadenopathy)
How does herpes simplex develop?
- It all starts with itching and/or tingling in the place where herpes develops - as we have already found out, most often this is the area of the nasolabial triangle. The skin turns red and begins to itch.
- Next, the stage of inflammation begins. Swelling appears in the affected area and a small, painful pimple appears - a blister containing clear liquid. Over time, this liquid becomes cloudy. A small pimple(s) gradually increases in size.
- The blisters burst 3–5 days after the onset of the disease. A liquid flows from them, containing an uncountable number of viral particles. During this period, contact with a sick person should be stopped, since the risk of infection is very high. At the site of the rash, ulcers with a purulent crust (scabs) form. When the scab is damaged, bleeding begins.
A natural question for every patient is, how many days does it take for herpes to go away? This usually takes about 10 days. If symptoms do not disappear during this time, you should see a doctor, since herpes can signal the presence of other diseases.
Herpes ointment
Is herpes just a rash? What other symptoms are there?
There may be no symptoms at all
A person can suffer from herpes unnoticed - without rashes on the face or genitals. However, the risk of virus transmission remains. The fewer relapses a person has and the more time has passed since infection, the safer he is for other people. Under these conditions, it produces too little virus to transmit it to someone.
Symptoms of genital herpes
The appearance of blisters on the genitals. In women - on the vagina, vulva, cervix, buttocks, inner thighs, anus. In men - on the penis, scrotum (testicles), anus, buttocks or inner thighs. The bubbles may merge into one large bubble or bypass this stage and burst. Then they turn into erosions - crusts, which then fall off and heal without a trace.
Burning, itching and pain in the genital area. Especially when you pee and the urine touches erosions on the mucous membranes.
Cold-like symptoms. This may include headache, fever, chills, weakness, and enlarged cervical and inguinal lymph nodes.
Symptoms of orolabial herpes, or “fever on the lips”
The only symptom is blisters on the lips. And before the bubbles appear, you may feel a tingling sensation on your lips. From this point on, the virus revives and you can pass it on to another person.
Possible complications
The herpes virus should not be perceived as an unpleasant but harmless “sore.” This is a rather insidious disease that poses a particular danger to pregnant women, infants and people with weakened immune systems (patients with cancer, people with HIV and AIDS).
The virus is not limited to superficial tissues - it easily penetrates into internal ones. The main targets of herpes are the mucous membranes, skin, eyes (conjunctivitis can also be a consequence of herpes), as well as the central nervous system and brain. Lymph nodes and internal organs can be affected by the virus. Due to the fault of the pathogenic microorganism, the functioning of the liver, lungs, intestines and kidneys can be disrupted.
The consequences of herpes can be stomatitis, infertility, miscarriage, congenital deformities in children, encephalitis, inflammation in the joints, prostatitis, benign and malignant tumors. Scientists, based on research, associate the development of multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease with herpes.
If a person’s immune system is weakened, other infections, both viral and bacterial, can “join” herpes, and this, in turn, puts an increased burden on the heart.
Precautionary measures
In order for the disease to pass in a mild form and its complications to appear, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Rule #1. Avoid touching your face with your hands, especially in the area of blisters. Otherwise, you risk spreading the infection to a larger area of skin.
- Rule #2. During illness, be especially careful about your personal hygiene.
- Rule #3. Isolate yourself and try to avoid close contact with people, especially the elderly and children.
Which doctor's help might be needed for herpes?
With the questions “what causes herpes to constantly appear on the lips” and “I’m tormented by herpes - what to do?” You can contact your therapist first. He will subsequently refer you to an infectious disease specialist or dermatologist (if we are talking about an oral virus). Patients with a genital infection should see a gynecologist (women) or a urologist (men). Since the pathology may be associated with diseases of the internal organs, you may need to consult a gastroenterologist, hepatologist or pulmonologist.
How to treat herpes?
It is impossible to completely destroy a virus that has entered the body. But it is quite possible to suppress its activity so much that it does not bother you. In modern medicine, an integrated approach is used for this. The best results are obtained by combination therapy, which involves the use of antiviral drugs (they are available in the form of drugs for internal use and in the form of external agents), as well as drugs that strengthen the immune system. In some cases, the patient is additionally prescribed local analgesics and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Many people are interested in whether it is possible to burn herpes with alcohol? Alas, this method does not affect the virus, but only damages the mucous membranes, so it is better to use special ointments.
What remedies are usually prescribed for herpes on the lips? The table shows a list of the most common medications used to treat the virus.
| Name, dosage form | Description |
| Acyclovir (aka Zovirax). Available in the form of tablets, cream, eye ointments, injection solutions. | An inexpensive antiviral drug that stops the replication of the virus. Addressed to adults and children over 3 years old. Not recommended for use during pregnancy. Antiviral ointment |
| Valacyclovir (aka Valtrex) Available in the form of 500 mg tablets. | One of the best drugs for herpes. It differs from Acyclovir in the method of delivery of the active ingredient. Suppresses the activity of the virus and reduces symptoms. When taking the drug, the risk of infection through contact with other people is reduced. Treatment of herpes in 3 days |
| Famciclovir (aka Famvir) Available in the form of tablets 125, 250 and 500 mg. | Just like Acyclovir and Valtrex, it blocks the replication of the virus. Helps in the treatment of simple virus and the virus that causes chickenpox. Famciclovir is effective against viruses resistant to Acyclovir. Famciclovir |
| Panavir Available in the form of a solution for intravenous injection, as well as in the form of a gel and suppositories (suppositories). | Antiviral, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory drug of plant origin. Increases the body's resistance to infections and has an antipyretic effect. |
| Docosanol (aka Erazaban) Available in the form of a cream for external use. | Has an antiviral effect. Intended for use in adults and children over 12 years of age. Pregnant women are prescribed with caution. |
| Proteflazid Available in the form of drops. | Antiviral agent for systemic use. Intended for the treatment of herpes simplex in children and adults. Used in pediatric practice (including in children under 1 year). |
| Flavoside Available in the form of syrup. | Effective in the treatment of herpes simplex, as well as in the treatment and prevention of influenza. Used in pediatric practice (including in children under 1 year). |
The presented list of drugs is far from complete - the doctor, depending on the characteristics of a particular patient, may recommend other drugs. For example, in some cases antibiotics cannot be avoided (if there is a risk of contracting other infections).
Is herpes contagious? Should I now avoid kissing and sex if I have a flare-up?
Herpes is contagious and spreads from person to person. But in general, there is nothing wrong with this - the disease is not dangerous for most healthy people.
If you are afraid of infecting your partner with herpes or becoming infected yourself, always use a condom during vaginal, oral and anal sex. And during cunnilingus, create a barrier between the mucous membranes of the mouth and genitals using a special latex napkin - a rubber dam. But remember, such protection still does not provide a 100% guarantee that you will not become infected.
If you do not want to use a condom, and your relationship with your partner is long and monogamous, then a healthy partner can take a course of antiviral drugs to prevent the disease. This is advice from the Herpes Virus Association. In this way, you can reduce the risk of transmitting herpes, but you need to consult a general practitioner about treatment. He will tell you which pills to take, for how long and in what dosage.
During the period of exacerbation of herpes, it is better to avoid sex and close contacts. As soon as you have a burning and tingling sensation on your lips, blisters around your mouth or on your genitals, the virus is in an active reproduction phase. From now on until the rash and crusts disappear, it is better to refrain from close contact.