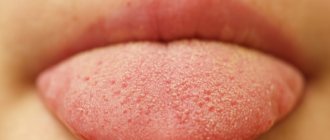
White coating on the tongue is usually perceived as a symptom of the disease. A person, as a rule, does not consider his language. In order for us to stand in front of the mirror, stick out our tongue and begin to look at it, there must be some reason that prompted us to do so - discomfort in the throat or oral cavity or some other dissatisfaction with our health. And then we discover a white coating on the tongue (or, as they sometimes say, that our tongue is coated ). However, don't be scared right away. Even a healthy person can have a white coating on the tongue. On the other hand, plaque on the tongue can indeed be a manifestation of the disease. Therefore, it is useful to know how pathological plaque on the tongue differs from plaque, which is considered a variant of the physiological norm.
Physiological white coating on the tongue
White coating on the tongue is most often found in the morning. At night, less saliva is produced, which contributes to the activation of bacterial activity. As a result, by morning, almost all people develop a white coating on their tongue. Sometimes it is accompanied by bad breath.
As a rule, such plaque is easily removed during morning oral hygiene. When we brush our teeth, it is advisable to also brush our tongue, especially its root. Modern toothbrushes have a surface specially modified for this purpose (the other side in relation to the bristles).
However, the white coating disappears on its own as the day begins. It is erased when eating, and the greater amount of saliva released prevents it from forming again.
Reasons for appearance
Why does white plaque appear? The main reason lies in food debris that gets stuck between the lingual papillae. As a result, a favorable environment is created for the proliferation of bacteria. Most of these microorganisms die, but do not disappear without a trace. When in contact with saliva and epithelial particles, they stick to the tongue, forming a plaque. In this case, this plaque is partially removed by salivation. The film usually remains in hard-to-reach places, for example, at the root of the tongue. If it is not cleaned in time, it begins to spread to other areas, gradually covering the entire tongue. Considering that these are the remains of bacteria, the likelihood of developing dental diseases increases sharply.
Pathological plaque on the tongue
If the white coating on the tongue is caused by an illness, it persists throughout the day. A thin white coating occurs with any ARVI. It disappears as soon as the patient recovers.
Particular attention should be paid to the compaction of plaque. The body of the tongue is not visible through the thick coating. Such plaque is difficult to remove. Thick plaque is considered a sign indicating the severity of the disease.
The color of the coating on the tongue is also important. The more intense the color, the more serious the pathology that caused the plaque. The color of plaque is not only white. A yellowish tint to the plaque may be associated with a malfunction of the gallbladder or pancreas. Gray plaque is possible in case of stomach disease - gastritis, peptic ulcer. In some severe infectious diseases, plaque may acquire a black, bluish or greenish tint.
However, it should be taken into account that the color of plaque can be affected by smoking, drinking and eating.
Other means
When cleaning your tongue at home, other means can be used. One of the most popular ways is to use vegetable oil. A tablespoon of oil is carefully rubbed throughout the entire oral cavity. After cleansing, the oil should turn white. It must be spat out and your mouth rinsed with warm water.
The duration of the procedure is at least 15-20 minutes. It is more effective if done in the morning before eating.
Another way is to use baking soda. Dilute 2-3 teaspoons in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth with the resulting solution. A small amount of baking soda can be applied directly to the brush to clean the tongue.
You can buy tongue cleaning gel at the pharmacy. It eliminates pathogenic bacteria, produces a softening effect, moisturizes the soft tissues of the oral cavity and provides fresh breath.
A small amount of gel is applied to the surface of the organ to be cleaned, carefully distributed, left for a few seconds and removed with a brush. The procedure can be recommended for both adults and children. Children under 12 years of age should only brush their tongue with the gel under adult supervision.
If there are injuries and various injuries, blood may bleed while cleaning the tongue. To stop bleeding, you need to press a sterile napkin to the wound surface and hold it for about 10 minutes. Hands should be washed well and disinfected with alcohol. Then rinse your mouth with cold water. Do not cauterize wounds with alcohol or treat them with iodine.
Diseases that cause plaque on the tongue:
- stomatitis;
- thrush (candidiasis). Caused by fungi of the genus Candida. The disease can be caused by long-term use of antibiotics or decreased immunity. With oral candidiasis, a typical manifestation is a dense milky-white coating that covers the tongue in spots. Similar spots may also appear on the roof of the mouth or gums. In severe cases, plaque covers the entire tongue as well as the walls of the throat, making swallowing and breathing difficult.
- scarlet fever. In the first days of the disease, the tongue is covered with a white-gray coating. Then the coating disappears, and the tongue acquires a crimson color;
- whooping cough. A pale yellowish coating on the tongue may be accompanied by bad breath;
- dysentery. A thick white coating is typical;
- cholera. Characterized by a dark coating (even black);
- diphtheria;
- gastritis;
- stomach ulcer;
- enterocolitis;
- pancreatitis;
- stomach cancer;
- kidney diseases;
- some other diseases.
Professional cleaning at the dentist
Even such thorough self-cleaning of the oral cavity is not enough to be sure that you will be free from periodontal disease or caries. From time to time it is necessary to contact a dentist so that he can carry out professional sanitation. Typically it includes:
- preventive examination and assessment of the condition of gums and teeth;
- removal of tartar mechanically or using ultrasonic devices;
- treatment with a special powder mixture to get rid of food pigmentation of teeth, typical for smokers, lovers of strong coffee and tea;
- final flossing to remove tartar fragments from the most difficult to reach places;
- polishing using a special paste to create the most even surface relief of the teeth.
It is recommended to carry out such cleaning every six months, in case of predisposition to caries and periodontal disease - once every 3 months.
When and which doctor to contact about a coating on the tongue
As a rule, tongue coating is not the main symptom.
And it is other symptoms that tell you which doctor you should see. If plaque on the tongue is accompanied by symptoms of ARVI, you should consult a physician. If you have symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases, contact a gastroenterologist. If there are no such symptoms, and the cause of your concern is plaque, in case of white plaque you can consult a dentist, in case of yellowish or gray plaque, you can consult a gastroenterologist. And in any case, you can consult a general practitioner - family doctor or therapist. A child with a persistent coating on the tongue should be shown to a pediatrician.
Diagnostics
To establish a complete picture of the state of the body, the doctor determines the color of the tongue, its structure, position, motor functions, and possible other pathologies in the oral cavity. Among the laboratory and instrumental research methods aimed at clarifying the characteristics of plaque and the reasons for its appearance, the following may be prescribed:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- sowing on flora from the surface of the tongue;
- determination of antibodies to the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- scatological research.
If you are concerned about the condition of your tongue, plaque on it, pain, unpleasant odor, contact the ENT doctors of our clinic. High-precision equipment and the experience of our specialists allow us to quickly make correct diagnoses and prescribe treatment.
Treatment
For your information! In certain cases, treatment may differ radically (based on the root cause of the appearance of white plaque).
So, depending on the underlying pathology, the patient is prescribed the following treatment:
- In case of problems with the gastrointestinal tract the diet is , excluding all harmful foods from the diet. First of all, fatty meat, fried foods, fast food. This also includes sour cream, butter, alcohol and sweet carbonated drinks. Prescribe medications appropriate to the current disease. The treatment is carried out by a gastroenterologist.
- For influenza and ARVI, antipyretics (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, etc.) and drugs for topical use are prescribed Among them, nasal drops - Naphthyzin, Xylometazoline, Otrivin, etc.; tablets and lozenges for resorption with anti-inflammatory action - Doctor Mom, Strepsils, etc.
- In case of fungal infection of the oral cavity , the patient is prescribed antifungal drugs. Among them: Rumicosis, Fungicidin, Diflucan, Nystatin, etc.
- If you have a sore throat and other throat diseases , drugs such as Faringosept, Ingalipt, Neo-angin, Septolete , etc. are recommended. Antiseptics (Miramistin and Chlorhexidine), Furacilin solution (1 tablet per glass of warm water) are prescribed as rinses. You can use a soda-salt solution (1 teaspoon of each per glass of warm water). Decoctions of chamomile, sage, and calendula are also suitable (1 tablespoon of raw material per glass of boiling water).
- For bacterial infections , oral antibiotics are indicated (Sumamed, Amoxiclav, Cephalexin, Azitrox, etc.). In this case, it is necessary to complete the full course of treatment. Even if the symptoms go away a few days after starting therapy.
- For glossitis , first of all, it is necessary to exclude hot and spicy foods from the diet. Remove from the diet too salty, with the addition of red or black pepper, garlic, onion, mustard, various sauces, etc. And it is important to rinse your mouth with Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, a weak solution of potassium permanganate, Furacilin, herbal infusions, etc. .
- In case of hormonal disorders , treatment is carried out by an endocrinologist. The course of treatment and dosage of certain medications is prescribed by the doctor. Self-medication is unacceptable, because without knowing the true cause of plaque, therapy will be meaningless and can only worsen the situation.
HIV
- HIV is the virus that causes AIDS.
Dehydration of the body. In this case, additional symptoms will be observed, such as: dryness of the mucous surface of the tongue, skin, tendency to constipation, fatigue.
- Taking hormonal medications or undergoing antibacterial therapy, which can cause dysbacteriosis to develop.
- Poor nutrition. May be triggered by excessive consumption of salty, spicy or fried foods.
Why are tonsils needed?
The tonsils are an integral part of our immune system. And their main purpose is to protect the body from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. In total, a person has six of them: palatine and tubal (paired), pharyngeal and lingual. By their names you can roughly understand in which part of the pharynx they are located. Their general arrangement resembles a ring. This ring acts as a kind of barrier for bacteria. When we talk about inflammation of the tonsils, we mean only the palatine tonsils (aka tonsils). Let's look at them in more detail.
If you open your mouth wide, then in the mirror you can easily see two formations that look like almonds - tonsils, these are tonsils. Each tonsil consists of small openings (lacunae) and winding canals (crypts).
Bacteria that enter the air, in contact with the tonsils, are rebuffed and are immediately disposed of, without having time to cause an outbreak of a particular disease. Normally, a healthy person does not even suspect that real fighting is taking place inside him. Now you understand the importance of the mission of the palatine tonsils. Therefore, a good otolaryngologist will never rush to recommend their removal. Although to hear from a doctor, speaking about tonsils: “They need to be removed!” - a common phenomenon in our time. Unfortunately, today not all clinics can offer high-quality treatment for tonsillitis, and sometimes the turnaround rate is off the charts. That is why it is sometimes easier for a doctor to brush it off and refer the patient for surgery.
Types of tonsillitis.
The disease occurs in two forms - acute and chronic. Acute tonsillitis is an illness of an infectious nature and manifests itself in acute inflammation of the tonsil. The cause of exacerbation is staphylococci and streptococci. Acute sore throat in children and adults is also divided into catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, ulcerative-membranous and necrotic.
Chronic tonsillitis is a long-term, persistent inflammatory process in the tonsils. It manifests itself as a consequence of past inflammation, acute respiratory viral infections, dental diseases, and reduced immunity. Chronic exacerbation of the disease in adults and children occurs in three forms: compensated, subcompensated and decompensated. In the compensated form, the disease “dormants”; exacerbation of tonsillitis symptoms occurs infrequently. In the case of a subcompensated form of the disease, exacerbations occur frequently, the disease is severe, and complications are common. The decompensated form is characterized by a long, sluggish course.