The tongue itches - what to do if the organ literally itches
The tongue can itch not only in a figurative sense. If you experience unpleasant irritating sensations, the first thing you should do is figure out what could be the reason for the appearance of this symptom. The organ is a muscle containing a huge number of nerves and blood vessels. The occurrence of discomfort, burning, soreness, swelling and itching in the tongue always indicates some pathological condition, and the symptom itself may be associated with dental disease and disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
Why might my tongue itch?
In any case, if this symptom develops, you should immediately see a specialist. Further in this article we will find out why the tongue may itch, what preconditions contribute to this, and what to do in such a situation.
What can cause an itchy tongue?
A phenomenon such as itching of the tongue and lips can be caused by one of many different factors. Here are the most common causes of this unpleasant symptom:
- mechanical injury: the tongue of both a child and an adult may begin to itch due to banal biting or damage of another nature, for example, as a result of a burn. Very often, the culprit is rubbing the mucous membrane with the sharp edges of a crown, an incorrectly fitted prosthesis or an incorrectly adjusted brace system. Also, this symptom may well be a consequence of the use of low-quality cosmetics or oral hygiene products,
Tongue injury can cause itching
“Somehow this happened to me too. Right in the middle of the day, for no apparent reason, my tongue itched. And let me tell you, this is not a pleasant feeling! And your hands just reach out to scratch at least a little! In general, I immediately decided that it was because of the spicy food, at home I thoroughly cleaned my tongue with a brush, and in the morning the itching appeared again, and most importantly, only on one side. At lunchtime I ran to the dentist, and he immediately said that it was all about the sharp crown. It apparently became so uncomfortably worn over time, and as a result, it scratched the tongue. This is where it started to itch...”
LudaKam, 31 years old, Saratov, from correspondence on a thematic forum
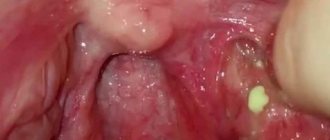
- Oral diseases: one of the most common causes of itching is a disease such as glossalgia. In this case, it is usually the tip of the organ that begins to itch, but in some cases patients experience severe itching on the sides. Associated symptoms include burning, pain, tingling in the tongue, as well as dryness of the oral mucosa. Quite often, the disease develops against the background of strong emotional experiences and stressful situations, but the disease can also be triggered by injury to an organ, taking certain medications, or malfunctions in the internal systems of the body,
The photo shows glossitis of the tongue - Gastrointestinal pathologies: problems in the gastrointestinal tract in most cases are reflected specifically in the condition of the tongue. For example, pathologies such as gastritis, ulcers or pancreatitis can provoke itching and burning in an organ,
- stress and depression: against the background of severe nervous exhaustion, some changes occur in the composition of saliva and the volume of its secretion,
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements: sometimes due to a lack of B vitamins, iron and folic acid, the tongue begins to itch very much,
- allergy: such a manifestation may well be an allergic reaction of the body to some irritant, for example, to hygiene products, the presence of an allergen in the oral cavity in the form of metal parts of braces or a prosthetic device,
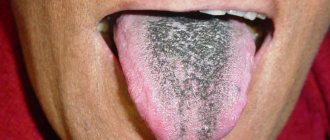
- candidiasis: the development of a fungal infection often becomes the body’s response to a sharp weakening of the immune defense. In this case, along with itching, burning and tingling occurs, and a dense cheesy coating appears. Quite often, the cause of this problem is long-term use of antibiotics. By the way, in children the disease in question develops almost twice as often as in adults.
This is what a fungal infection on the tongue looks like
Other possible provoking factors include the constant irritating effect of tobacco smoke, abuse of too spicy, salty or acidic foods - in such cases, it often begins to tingle and itch directly under the tongue. Excessive consumption of low-quality alcoholic beverages can also lead to the development of this symptom.
Burning sensation in the mouth and tongue - causes
Local factors:
- Decreased saliva secretion. The mucous membrane becomes dry, lips and tongue crack. Food and liquid irritate the damaged areas, and they sting quite severely.
- Fungal candidiasis. Popularly known as thrush. Fungi, during their rapid proliferation (which happens when the immune system is weakened), provoke a burning sensation in the oral mucosa and painful sensations.
- Hard dental deposits. The formation of tartar is accompanied by the simultaneous delamination of old layers. The separated particles affect the mucous membrane, causing an unpleasant reaction.
- Allergy. A burning sensation in the mouth is nothing new for those with intolerance to certain foods, medications, and even denture materials.
- Leukoplakia. Excessive keratinization on any part of the epithelium usually does not provoke tingling sensations, but this disease cannot be excluded from the list of possible persons involved.
- Diseases of the tongue. Desquamative glossitis, or “hairy” tongue, is a common cause of persistent burning sensation in the mouth. The papillae become very sensitive.
- Herpetic infection. The blisters, which quickly transform into erosions, cause severe itching and unbearable burning both in the normal state and when eating.
- Grinding of teeth. Unconscious movements of the teeth during sleep, called bruxism, automatically affects the tongue with the appearance of microtraumas on it, and, accordingly, a burning sensation.
- Lichen planus. Erosive damage to the mucous membrane, white ulcers haunt the patient during an exacerbation, causing severe discomfort.
General factors:
- Unbalanced diet
- Blood diseases
- Hormonal disbalance
- Stomach pathologies
- Nervous disorders
- Avitaminosis
- Insulin-dependent diabetes
- Bulimia
In these conditions, a burning taste in the mouth may appear and disappear, as it is a concomitant symptom.
Appearance in children
Children often face this problem. The appearance of similar symptoms in a child almost always indicates the development of candidiasis. Here it is necessary to conduct a careful visual examination of the oral mucosa for the presence of a dense white coating with a cheesy consistency - this is the very first sign of the pathology in question. If your baby is still very young and cannot tell you about the symptoms that are troubling him, pay attention to whether he is constantly sticking out his tongue. This is how little children usually make it clear that they feel discomfort in the organ.
Stomatitis is common in infants
A common accompanying symptom is burning, and this is a good reason for parents to worry. Here you need to monitor the child’s psycho-emotional state, make sure that he does not experience any serious worries or stress. If you suspect that the cause of the itching lies precisely in the psychological state of the baby, it makes sense to show him to a neurologist. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe a course of sedatives. A childhood disease such as scarlet fever can also provoke itching in the tongue and even in the throat. In any case, if suspicious signs of pathology appear, the child should be shown to a doctor as soon as possible.
Stomatitis: causes
A variety of factors and diseases contribute to the development of stomatitis in adults. For ease of diagnosis, doctors combined the causes of stomatitis into four groups, highlighting the main problem conditions:
- Mechanical injury. Ulcers appear as a result of some irritating factor. Damage can be caused by eating hard foods, poorly installed dentures, tartar buildup, and sharp edges of chipped crowns. Pathogenic microflora enters the damaged area, causing inflammation and active formation of ulcers.
- Chemical or thermal burn. Aggressive chemical agents can be food (citrus fruits), medications, nicotine, incorrectly selected toothpastes or mouth rinses. Thermal burn occurs when consuming excessively hot food or drinks.
- Poor oral hygiene. Failure to comply with regular hygiene procedures, tartar, and plaque provoke the active proliferation of bacterial microflora, which leads to inflammation of the oral mucosa.
- Chronic diseases. In adults, stomatitis develops as a reaction to problems of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, due to anemia, endocrine pathologies, and HIV infections.
In addition to the listed categories, the causes of stomatitis can also be internal problems:
- vitamin deficiency, micronutrient deficiency - unbalanced diet, metabolic disorders in the body;
- allergies - of any origin;
- heredity - the individual reaction of the immune system to deteriorating health;
- a general decline in immunity - as a result of serious illnesses.
Unfavorable factors become catalysts for the development of pathology, and external circumstances aggravate the course of the disease.
The variety of causes points to an important point: there is no obvious causative agent of stomatitis. In order for an ulcer to localize, several circumstances must coincide - decreased immunity for any reason, an abundance of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity, a traumatic agent.
Diagnostic measures
The only correct decision regarding the appearance of the symptoms described above is to contact a knowledgeable specialist. Only a doctor can conduct a competent examination and identify the true cause of the discomfort. Thus, the main diagnostic procedures include:
- general blood analysis,
- taking a swab from the throat.
Tests can determine the true cause of the problem.
Having the test results in hand, the doctor can significantly narrow the range of suspected diseases and even immediately make an accurate diagnosis. It is likely that at the stage of identifying the source of the problem, consultation with highly specialized specialists - a dentist, neurologist, gastroenterologist - may be required. Without knowing the exact doctor’s conclusion, you should not make any attempts to solve the problem yourself, otherwise you can only worsen the situation.
Therapeutic measures – complex treatment
In order to get rid of an annoying symptom once and for all, you first need to identify its root cause, and it is this that needs to be treated. Medications may be prescribed as symptomatic therapy. Typically, complex treatment involves taking antihistamines, antipsychotics, immunostimulants and anti-inflammatory drugs. If the patient has a deficiency of beneficial vitamins and microelements, additional multivitamin complexes may be prescribed to strengthen the body's defenses.
Only a specialist can prescribe the correct treatment
If oral candidiasis is to blame, a specialist may prescribe antifungal agents. It is also mandatory to carry out complete sanitation of the oral cavity in order to eliminate any provoking factors. Other methods of relieving acute symptoms include all kinds of baths and applications using medicinal herbs: wheat germ, rose hips, sea buckthorn oil and others. In this regard, rinsing with a soda solution has worked well - one tablespoon per glass of water. However, it should be understood here that the use of any traditional medicine must first be agreed with the attending physician.
First aid for food allergies
They independently provide first aid for allergies to food additives, if the person’s life and health are not in danger.
What symptoms indicate a direct threat:
- breathing problems;
- swelling of the neck, tongue;
- altered speech;
- confusion.
All of the above is a reason to call an ambulance . If an allergic reaction appears for the first time, even without symptoms that threaten health, it is necessary to get medical help as soon as possible, especially if we are talking about a child.
If symptoms are not expressed, it is permissible to take the first measures yourself. The following categories of drugs are used for this:
- Sorbents. They allow you to bind and remove harmful substances from the gastrointestinal tract. Such drugs accelerate the elimination (removal) of allergens, alleviate the condition and speed up recovery.
An effective product from this group is Fitomucil Sorbent Forte, which contains the shell of psyllium seeds, as well as the prebiotic inulin and a complex of live probiotic bacteria. Psyllium seed husk is a natural soluble fiber that absorbs water and allergens into a mucilaginous gel. The drug does not irritate the intestinal walls, gently stops diarrhea, promoting thickening of stool.
- Antihistamines. Today there is a wide range of new generation medications that do not have side effects such as drowsiness and are well tolerated. It is better to choose medications from those you have already taken before, or consult a doctor.
For skin manifestations, it is possible to use local agents with antihistamine and soothing, antipruritic effects. Severe allergies, manifested by severe redness and itching of the skin, will most likely require the use of local hormonal ointments and creams.
But remember that they are prescription drugs and cannot be used for longer than the time prescribed by the doctor - usually about 7-10 days for mild to moderate cases. Hormonal drugs for oral administration or injection also require a prescription from a specialist who will develop a suitable regimen for use.
Developed vomiting and diarrhea require action. Taking sorbents will help in the second case, and in case of uncontrollable vomiting, you should seek emergency help. If vomiting and diarrhea occur sporadically, several times a day, it is necessary to replenish fluid loss with the help of special rehydration solutions - pharmacy or self-prepared.
It is necessary to drink enough fluids to prevent dehydration and the occurrence of associated disorders. Kozyarin suggests using herbal tea, decoctions of plants: “chamomile, St. John’s wort, calendula, calamus, valerian” (Kozyarin N.P., 2009, p. 66).
Preventive actions
To minimize any risks of developing diseases leading to the symptoms discussed above, you should take care of high-quality and regular oral hygiene. Every day, morning and evening, you should thoroughly clean not only the surface of your teeth, but also your tongue, because a huge amount of bacteria and food debris also accumulate on it. To do this, you can use a regular toothbrush or purchase a special device, such as a scraper.
Regular tongue cleaning will help avoid the problem.
As a preventive measure, from time to time you can rinse your mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs or special antiseptic solutions, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. And do not forget about the importance of systematically visiting the dentist for preventive examinations.
- Sergeev A.O. Diagnosis and treatment of superficial candidiasis, 2001.
Treatment
The course of treatment can be divided into two parts: the use of medications when symptoms immediately appear and therapy aimed at prevention. Doctor Luss o (Luss L.V., 2005, p. 140).
Antihistamines are not a panacea, since both with true allergies and with pseudo-allergies, it is important to promptly eliminate risk factors for the development of severe manifestations.
The main ones include concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to failure of the digestion process, changes in the permeability of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract, and a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice. For this purpose, enzyme preparations, enterosorbents, and probiotics are used.
The most important point after the first measures is to accelerate the elimination of the allergen and prevent further contact with it. The main stages of treatment look like this:
- Symptomatic therapy: taking antihistamines for first aid.
- Elimination of the allergen from the body: prescribing a hypoallergenic diet, pharmacological methods, or a combination of these approaches. If the “provocateur” entered the digestive system recently (several hours ago), enterosorbents will be especially effective. They bind substances in the intestinal lumen, preventing them from further entering the bloodstream. If allergens have been in the body for a long time or a lot of time has passed after a single exposure, elimination occurs naturally, and sorbents will only help in eliminating symptoms.
- Allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT). This stage follows only after elimination, comprehensive diagnosis, and accurate identification of the provoking antigen.
ASIT is relevant when irreplaceable dishes are added to the list of those prohibited for consumption; the human body is not provided with everything necessary. This method consists of introducing certain dosages of the allergen, which are gradually increased, which allows the development of immunological tolerance.
Author Luss emphasizes that “the attitude towards ASIT in patients with IPA is not yet clear and contradictory. Basically, preference is given to prescribing elimination diets” (Luss L.V., 2005, p. 140). Perhaps this is due to the need to undergo comprehensive diagnostics and constant long-term treatment when the allergy no longer manifests itself. After all, ASIT can be recommended six months after changing the diet. However, this method is the only option to get everything you need from food when you have allergies.
Nutrition for food allergies
The complex of therapeutic measures necessarily includes a nutritional method. Eliminating the cause—the antigen—is extremely important to improve the condition and prevent exacerbations. A complete avoidance of intolerant foods is expected. For convenience, we have provided a list of permitted and prohibited items in the table:
| Allowed | Prohibited |
| Unfortunate bread | Smoked meats |
| Tea | Vinegar |
| Sugar | Fish |
| Boiled lean beef | Mushrooms |
| Butter and vegetable oils | Bird |
| Fresh cucumbers | Nuts |
| Parsley dill | Whole cow's milk |
| Watermelons | Honey |
| Baked apples | Nuts |
| One-day fermented milk products | Fruits and berries: strawberries, melon, pineapple, citrus fruits |
| Cereals: rice, buckwheat, oatmeal | Vegetables: eggplant, radish, horseradish |
Fasting is strictly prohibited for people with chronic diseases, blood diseases, malignant neoplasms, sore throat, other respiratory diseases, liver and circulatory diseases in history.
You will need to limit or eliminate ready-to-eat cereals, pasta (without eggs), ready-made pies, gingerbread cookies, colored marshmallows, and caramels due to the tartrazine they contain. It is necessary to limit the consumption of wine, beer, fruit juices, gelatin, baking mixes, marinades, and most prepared sauces, as they contain sulfites.
There are different options for therapeutic nutrition:
- Grain-free diet. Involves avoiding cereals, flour products, seasonings, and sauces. Preference is given to meat, vegetables, fruits, and dairy products.
- Egg-free diet. Excludes eggs, seasonings, mayonnaise, sauces and creams, pasta, baked goods containing eggs. The diet consists of meat, dairy products, cereals, vegetables, and fruits.
- Dairy-free diet. Milk, milk porridge, cottage cheese, confectionery, and butter are excluded from the diet. The menu is based on dishes of meat, fish, eggs, cereals, vegetables and fruits.
- Diet excluding milk, cereals, eggs.
Thus, it is not necessary to give up all possible allergens. When you consult a doctor, you will receive accurate recommendations. It is important to make your own assumptions about what exactly could have been the source of unpleasant manifestations.
Keeping a diary will help determine which food allergens could cause a response and which ones are not perceived aggressively by the body. At the same time, you should write down not only everything you eat during the day, but also the cooking methods. Note exactly what manifestations of allergies are observed: skin itching, stool disorders, redness of the skin, nausea.
The main feature of nutrition for allergies is not simply to refuse a certain food, but to find an adequate replacement. The diet must remain balanced, otherwise severe restrictions are likely to lead to vitamin and mineral deficiencies. If you are forced to completely give up milk and eggs, your diet should include a variety of meat and fish dishes. It is better to search for alternatives together with your doctor.