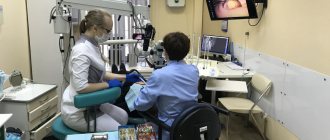
What is the difference between a dentist and a dentist? Many people are sure that synonymous words reflect the name of one profession, and there is no difference between the concepts.
In fact, there are differences, and significant ones. It is no coincidence that even in dental offices, consultations are carried out by at least 2 doctors of a narrow specialization: a general dentist and a dental surgeon. In large clinics you will find specialists in five areas. But why does a dentist in a small village independently carry out many types of manipulations? Is it correct? Let's figure it out.
How is a dentist different from a dentist?
The difference is in the level of education and credentials. According to the job description, a dentist cannot perform certain types of treatment.
In practice, patients often encounter specialists without higher education, “jacks of all trades.” This situation is common in small settlements, where a medical institution has only one staff member for the treatment of oral diseases.
Take note:
- many specialists with secondary medical education claim that they perform dental treatment no worse than dentists, supporting their arguments with reviews from satisfied patients;
- but without the necessary level of knowledge it is impossible to correctly deal with a complex case and prevent side effects;
- without constant professional development, the introduction of new technologies, and modern materials, it is impossible to offer the patient the most gentle method of treatment;
- It is no coincidence that private dental clinics regularly spend considerable sums on advanced training courses and symposiums for practicing doctors.
conclusions
There are a lot of specialists in dentistry, and the activities of each of them are different. It is important to remember that you can avoid serious oral health problems and trips to dental clinics if you follow the basic rules:
- brush your teeth twice a day;
- visit the dentist once a year, even if there is no reason for this;
- Do not delay your visit if your gums become sensitive or inflamed.
By following these conditions, you will protect yourself from problems in the future. Do not be afraid of doctors; many diseases begin completely asymptomatically, and only a specialist will be able to identify the threat in time.
Dentist
The specialist studies at a medical college for 3 years, studies the structure and features of the dental system, and learns simple dental procedures. But a doctor with a secondary medical education should not perform complex prosthetics, correct bites, or treat pulpitis.
What antibiotics can be taken for stomatitis? Watch the review with instructions for use.
Methods for treating trigeminal neuralgia at home are described on this page.
What does a dentist do:
- examines the oral cavity;
- finds out the cause of pain;
- identifies and treats gum diseases;
- fills a tooth with a small degree of tissue destruction;
- explains the rules of oral hygiene;
- gives advice on choosing toothpaste, mouthwash, dental floss, and oral irrigator;
- if periodontal disease, periodontitis, deep caries, pulpitis, curvature of tooth units destroyed by 50% or more, or other complex pathologies are detected, he is referred for consultation to a specialist.
Dentist
The specialist spent 5 years gaining knowledge at a medical institute, after 2 years he studied in residency or worked as an intern for a year. In addition to the structure of the dental system, the dentist studied physiology, anatomy, and the interaction of various organs. Biochemistry, psychology, therapy, histology, bacteriology and a dozen other subjects were on the class schedule.
After graduating from medical university, a general dentist chooses one (or several) specializations. Pediatric dentistry differs significantly from orthopedic and orthodontic treatment. A dental therapist has broader powers than a dentist, and a dental surgeon can not only administer anesthesia and remove teeth, but also perform operations on the gums and jaw bones.
Do you know who a dentist is? This is what a dentist is called in other countries. In Europe, the USA, and other Western countries, a specialist with a secondary medical education performs the same functions as a dentist in Russia.
What qualities should the best dentists in Orenburg have?
- The specialist must have the necessary education, diploma, and license to carry out his activities in Russia;
- Before starting treatment, the doctor must conduct a comprehensive consultation, explain to the patient what procedures he will perform and why - this allows for a comfortable, trusting atmosphere for the patient;
- All manipulations must be carried out in accordance with septic/antiseptic requirements: the doctor must wear a gown, mask, gloves and safety glasses.
Before starting treatment, it is difficult for the patient to assess the real qualifications of a specialist, therefore, the Internet can help in choosing, it is worth asking the search engine the query “orthopedic dentists orthopedists in Orenburg reviews” - popular sites of the city will open in front of you, where people leave their reviews about the quality of treatment from this or that dentist By carefully studying them, you can determine the strengths and weaknesses of a particular specialist in a particular clinic.
Another good way to choose a doctor is the personal experience of your loved ones, friends or colleagues. As a rule, they provide an objective picture of the quality of their own treatment from a particular specialist, and can also tell about unscrupulous representatives of the profession.
Therapist
The specialist performs the same manipulations as a dentist. In addition, a dental therapist deals with more complex problems with teeth and gums.
The doctor has a wide range of responsibilities:
- treats dental diseases: deep caries, pulpitis;
- selects and places fillings for severe tooth decay;
- carries out endodontic treatment;
- treats severe inflammation of the gums, mucous membranes, tongue;
- whitens teeth;
- carries out sanitation of the oral cavity;
- performs professional teeth cleaning with ultrasound or using Air Flow technology;
- conducts preventive examinations and gives recommendations on oral care;
- when identifying malocclusions or diseased teeth that cannot be restored, he refers the patient to specialized dentists: an orthodontist and a surgeon;
- in the absence of one or more units of the dentition, the dentist-therapist recommends a consultation with an orthopedic dentist, or “in popular parlance” – a prosthetist.
What is the difference?
Dentist and stomatologist - it seems that they are absolutely the same names.
And after all, they do one thing - treat teeth. Yes, but there is still a difference. So what is the difference between a dentist and a dentist? Firstly, the level of education. Secondly, in the range of activities. So, who is a dentist? To become a dentist, it is enough to graduate from a secondary specialized medical institution. Previously, such institutions were called medical schools; now in most cases they are called colleges.
They study there for three years. Graduates receive a diploma of secondary vocational education, which gives the right to carry out a certain range of activities. Basically, these may not be very complex manifestations of dental diseases, in particular stomatitis, carious lesions and others.
Graduates of secondary medical level have the right to carry out physical procedures that do not require high qualifications, and provide care for patients who have simple maxillofacial injuries. They also have the right to establish a diagnosis of the disease and, if the situation requires, to ensure that the patient is referred to a doctor of higher qualifications.
A dentist is a specialist of a higher level. Students study to become a dentist at a higher educational institution - a medical institute, university or academy. To receive a diploma and the right to practice one of the dental specialties, a medical school student needs to study science for 5 years.
The education he received allows him to tackle almost any disease of the oral cavity and teeth. In addition, you need to add practice to the education you receive. After all, studying at a university does not end the process of obtaining a profession. He still has practice - a one-year internship, or a two-year clinical residency.
And this is no coincidence, because modern medicine does not stand still. It places new demands on future specialists and deeper knowledge. The latest developments and technologies are appearing, treatment methods are being improved, new directions and specializations are opening up.
Therefore, while dentists are becoming more highly specialized doctors, they must nevertheless be doctors with broad knowledge of general medicine. Such knowledge cannot be acquired in a shorter period of study.
But often dentists are called dentists by habit, just like dentists are called dentists. As we found out, this is not entirely true. A dentist may have a specialization, and the list is quite extensive: if we talk about such a specialization as therapeutic dentistry, it may also include caries, aesthetic dentistry, periodontics, endodontics;
- one of the specializations is orthodontics;
- there is a specialization in orthopedic dentistry;
- Surgical dentistry may also have ramifications, for example, a doctor may be a highly qualified specialist in the field of implantology;
- the dentist may be a specialist in oral and maxillofacial surgery;
- Pediatric dentistry is divided into therapeutic surgical dentistry.
Time does not stand still; it is a thing of the past, when the profession of a doctor who dealt with dental diseases was the only one, and it was impossible to get confused in the names. Nowadays, it is sometimes difficult to understand which specialist to go to if suddenly problems arise, for example, about caries. Let's try together to understand the specialization of doctors who treat diseased teeth.
Surgeon
The specialist deals with the following issues:
- removes diseased teeth if the therapist has given a conclusion that restoration is impossible;
- carries out extraction (removal) of healthy teeth that interfere with the normal growth of neighboring units;
- performs correction of dental anomalies, removal of impacted (unerupted) wisdom teeth, supernumerary units;
- the help of a dental surgeon will be needed if certain units grow incorrectly, for example, in 2 rows;
- The specialist's competence includes implantation and various types of prosthetics.
Orthopedist
Patients who have lost one or more units of dentition turn to this specialist. The doctor will help people who have ugly stumps sticking out instead of teeth, causing injuries to the mucous membrane.
What does an orthopedic dentist do:
- performs full or partial prosthetics;
- restores the beauty of a smile;
- selects the optimal method for normalizing chewing function.
Important! Before consultation with a prosthetist, it is mandatory to sanitize the oral cavity and eliminate inflammatory processes of various etiologies. A visit to the dentist or dental therapist is the first stage of orthopedic treatment.
Related materials:
dentist | Givenchy | SEPHORA COLLECTION | Dior | Givenchy | Sephora | Dior | teeth | white teeth | smile | beautiful smile | prosthesis | surgery
Articles
- In the know: fall makeup trends August 29, 2015, 00:00
- Virtual Stylist: The Most Stylish Apps December 17, 2022, 00:00
- Pastel makeup: making accents January 25, 2022, 00:00
Video
- New birth of four-color shadows from Givenchy September 15, 2010, 00:00
- Little tricks for a dazzling smile from Givenchy October 20, 2010, 00:00
- Beauty in Korean October 24, 2016, 12:00
Orthodontist
Most people encounter a specialist in this category during their lifetime. Bite anomalies, according to statistics, are observed in 80% of residents of different countries. Some studies suggest a higher percentage of patients who are candidates for orthodontic treatment.
The main task of an orthodontist is to restore the beauty of a smile. According to scientists, bite defects not only worsen aesthetics, but also provoke serious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, cause headaches, and severe diseases of the gum and bone tissue.
What does an orthodontist do:
- aligns the dentition;
- eliminates wide interdental spaces, removes diastema - the gap between the “units” in the center of the dentition;;
- corrects the growth of milk and permanent units;
- gives recommendations for the prevention of malocclusions;
- controls the formation of the jaw in childhood.
Take note:
- the specialist draws up a treatment plan, takes impressions, sends the jaws for x-rays, sends the collected materials to the dental laboratory;
- after receiving the finished product, the doctor installs the design, gives recommendations for care and correct correction;
- During the entire period of treatment, the patient is observed by a doctor who installed braces, retainers or other special devices;
- The duration of correction is calculated in months, often years (especially in adults).
Removable and non-removable orthodontic structures help correct bite defects:
- stretching plates;
- bracket systems;
- veneers;
- lumineers;
- orthodontic devices;
- lip bumpers;
- retainers;
- trainers;
- aligners;
- orthodontic aligners;
- clasp devices.
Otolaryngologist
Cases where there is a direct connection between problems with the respiratory system and bite are not frequent, but sometimes a consultation with an ENT doctor is necessary. This is especially true for those who, before contacting an orthodontist, suffered from chronic ENT diseases with frequent exacerbations and impaired nasal breathing.
At the first appointment, the orthodontist collects information about the patient and asks about other diseases. A complete picture of your health condition will help you prescribe comprehensive treatment to achieve the best result and minimize the risk of regression.