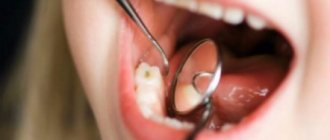
Inflammation of the oral mucosa is observed in 70% of pregnant women. This disease is diagnosed as gingivitis and occurs for several reasons, one of which is hormonal changes in the body. During pregnancy, there is an active production of hormones such as gonadotropin, progesterone, and somatomammotropin. These hormones cause significant changes in the systems of the female body, in particular in the gums.
During the period of fetal formation, the expectant mother experiences a disturbance in the blood supply to the tissues. For the skin, this is fraught with the appearance of acne and stretch marks in certain areas of the skin, and the mucous tissue of the gums can be subject to chronic inflammatory processes to varying degrees during pregnancy. At the same time, the gum tissue becomes vulnerable and is easily subject to mechanical and chemical irritation.
The second factor that provokes gingivitis is considered to be insufficiently thorough hygiene of the gum tissue. Bacteria living in dental plaque begin to actively multiply. They settle in periodontal pockets and cause pathological processes in soft tissues. It must be taken into account that pregnant women tend not to deny themselves nutrition and all kinds of delicacies. A large amount of sweet and carbohydrate foods is also a factor in the growth of pathogenic microflora and the occurrence of gum gingivitis. An imbalance in the acid balance in the tissues of the oral cavity promotes the active growth of pathogenic bacteria: they form more and more plaque in the gums.
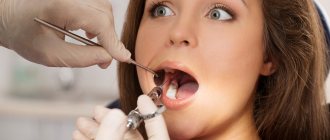
When carrying a child, the expectant mother should pay special attention to the condition of the gum tissue. And if there is a need to visit a doctor, if there is a suspicion of gingivitis, then we hasten to inform you that the safest and most favorable period for visiting a dentist is 13-24 weeks of pregnancy.
It is important for women in an interesting position to remember that their body and the body of the unborn baby are a single whole, and therefore, with gingivitis, bacteria from the mother’s mouth can easily penetrate into the child’s body, and therefore the work of the baby’s immune system may receive additional stress.
The first symptoms of incipient gingivitis may be:
- painful sensations in the gums when chewing rough food;
- reaction of soft tissues to cold and hot;
- bleeding in the area of the gingival papillae;
- swelling of tissues in the area of periodontal pockets;
- increased plaque with an intense yellowish tint;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor in the mouth.
How is catarrhal gingivitis treated in pregnant women?
Treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women begins with professional teeth cleaning: plaque and tartar are carefully removed, and the teeth are polished using special brushes and pastes. The next stage is anti-inflammatory therapy. For this purpose, the dentist prescribes the use of anti-inflammatory rinses, applications and toothpastes. The correct diet is very important - you need to reduce the consumption of carbohydrate foods and avoid frequent snacking. And of course, you need to take good care of your oral hygiene.
Why does gingivitis occur during pregnancy?
Tens of millions of microorganisms live in the oral cavity. Slight swelling of the gums leads to an increase in periodontal pockets, which become an excellent reservoir for the life and reproduction of bacterial microflora. In addition, microorganisms do not lack nutrition, since pregnant women like to pamper themselves with sweets, and carbohydrate foods are the best substrate for the development of bacteria.
Swelling of the gums, leading to an increase in periodontal pockets, excessive salivation, an acidic environment in the mouth, an increased feeling of hunger - these features that accompany pregnancy are the main factors contributing to the rapid growth of oral microflora. And this, in turn, provokes inflammation of the gum tissue - gingivitis.
How are treatment methods chosen depending on the stage of pregnancy?
The first trimester of pregnancy is associated with the risk of spontaneous abortion, so during this period interventions should be as necessary, and the indications for them are acute pain or severe swelling of the gums. Tartar can also be removed, but it is still better to postpone this manipulation for a while. In the second trimester, you can carry out complex treatment, including professional cleaning and taking antiseptics. And in the third trimester, a visit to the dentist should be as short as possible, so you should limit yourself to only hygiene procedures.
Causes and symptoms of gingivitis in pregnant women -
The development of the disease is usually associated with a restructuring of the hormonal balance during pregnancy - primarily with a high concentration of estrogens, progesterone, and prostaglandins. A number of authors also consider the phenomenon of toxicosis as an additional reason for the development of gingivitis in pregnant women. However, as we said above, there are additional reasons that are not related to hormones or any other changes in the body of a pregnant woman.
These changes relate, firstly, to changes in eating behavior. For example, women usually begin to consume significantly more carbohydrates (foods containing sugar, flour, starch). Moreover, a large amount of them is consumed between main meals, i.e. These are so-called snacks between meals. Naturally, after every cookie or bun in the middle of the day, women do not run to brush their teeth, but at most rinse their mouths with water or mouthwash.
Stuck food debris is an excellent breeding ground for soft microbial plaque, which also leads to its rapid growth. Pathogenic plaque bacteria produce toxins that trigger an inflammatory reaction in the gums. Thus, the development of gum inflammation in pregnant women is caused by both changes in eating behavior and the observed insufficient level of oral hygiene.
1) Symptoms of the first half of pregnancy -
The first symptoms usually appear at 3-4 months of pregnancy, i.e. just when the most intense hormonal changes in the body occur. The symptoms of this period are more characteristic of the form of gingivitis, which is commonly called “catarrhal gingivitis” -
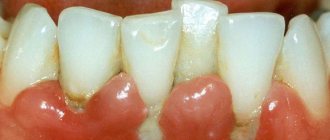
- bleeding gums,
- swelling of the gingival papillae and the marginal part of the gums,
- pain when brushing teeth,
- change in gum color from pale pink to red, and then to bluish.
At the same time, women’s complaints that their gums hurt during pregnancy can be associated not only with pain during brushing their teeth, i.e. when mechanical irritation of the gums occurs. If severe inflammation develops, pain can be observed even at rest.
Moreover, when soreness and bleeding gums appear, many women begin to “spare” their gums, starting to brush their teeth less often or less intensely (leaning more on mouth rinses). As a result, there is an even greater accumulation of soft microbial plaque in the area of the necks of the teeth, which only increases bleeding, as well as other symptoms of gum inflammation.
2) Symptoms of the second half of pregnancy -
Mild inflammation, which is manifested by swelling and bleeding of the gums, worsens in the second half of pregnancy (24stoma.ru). In many women, at this time, the growth of the marginal gums begins (polypous growth of gingival papillae). This type of gingivitis is called “hypertrophic”. It is especially pronounced in the area of the front teeth, as well as where there are overhanging edges of fillings and crowns that injure the gums.
There are 2 forms of hypertrophic gingivitis -
- Edema form - in which the gingival papillae are enlarged, bluish, soft to the touch, have a loose consistency or polypous growths.
- Fibrous form - when the gingival papillae are still enlarged, but become dense to the touch (due to the proliferation of fibrous tissue).
How can oral health affect a child?
Recent research shows that severe gum disease, accompanied by red, swollen or bleeding gums, can harm the health of an unborn baby.
Scientists have found that women with severe gum disease are 7 times more likely to have preterm birth before 32 weeks than women with healthy gums. Another study looked at women with gingivitis and more severe gum disease and found a threefold increase in the risk of giving birth before 37 weeks.
Current research into gum disease during pregnancy shows a risk of prematurity comparable to that of alcohol consumption and slightly higher than that of smoking. Premature babies may have a wider range of health problems immediately after birth than full-term babies.
Women with gingivitis may also have low birth weight babies during pregnancy. Studies have shown that if you have gingivitis during pregnancy, you are 3 times more likely to have a low birth weight baby. This estimate is comparable to the risk associated with smoking during this period.
When should you see a doctor?
Preventative examination of the oral cavity in the early stages of pregnancy is mandatory even in the absence of unpleasant symptoms. If you suspect tooth decay or inflammation, make an appointment with the clinic as soon as possible.
The changes that occur in the body due to pregnancy can also trigger the development of dental diseases.
Most often pregnant women experience:
- Pain – even if it is mild and one-time, you need to visit a dentist. Usually this symptom indicates the presence of caries, which is easier and faster to cure at the initial stage. Then the doctor will be able to do without potent drugs that are contraindicated for pregnant women.
- An unpleasant reaction to too hot or cold food - increased tooth sensitivity signals damage to the enamel. If you consult a dentist in a timely manner, he will restore the tooth’s coating and protect it from destruction.
- The appearance of inflammation on the oral mucosa is an alarming symptom of the onset of an infectious disease, which can be dangerous for the woman and the fetus. Urgent diagnosis and treatment is required.
- Bleeding gums - this sign may indicate various diseases (periodontal disease, gingivitis, exacerbation of chronic problems) and requires urgent diagnosis.
If you suspect any dental problems, contact your dental clinic. It is imperative to inform your doctor about your pregnancy so that he can draw up a treatment plan and select safe medications.
Make an appointment
Possible complications
Have you noticed that your gums have become loose? Make an appointment with your doctor. A prolonged inflammatory process provokes exposure of the neck of the tooth. This often entails the development of cervical or subgingival caries.
Lack of proper treatment increases the risk of inflammation of periodontal tissue. If left untreated, periodontitis may develop. As a result of this disease, not only the gums, but also the alveolar process, which holds the tooth root, decreases. Teeth become mobile, lose their functionality and may fall out.
How does inflammation manifest?
How to recognize the presence of an inflammatory process? It’s simple, the following factors begin to cause discomfort to a woman:
- The gums become swollen and acquire a bright red tint.
- Pain occurs on palpation or when eating.
- Acute reaction to cold and hot.
- Possible increase in body temperature.
- If left untreated, pus may appear in the space between the tooth and gum.
In order not to trigger the pathology and provoke more serious complications, we strongly recommend solving the problem in a timely manner.
Clinical researches
Multiple clinical studies have proven the effectiveness of Asept products. For example, as part of the tests, it was found that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it is 41% more effective in reducing inflammation and reducing bleeding gums by 43%.
Clinical studies have also proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% after just 4 weeks.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
Teeth cleaning
| Service | price, rub. |
| Initial consultation with a doctor | For free |
| Comprehensive professional hygiene (including ultrasonic removal of dental plaque, Air-flow, polishing, varnish coating) Promotion | 4000 3600 |
| Ultrasound removal of tartar – 1 tooth | 400 |
| Removal of pigment plaque with the “Air-flow” system – 1 tooth | 400 |
| Plaque removal using the Air-flow method – 2 jaws | 3300 |
| Ultrasonic dental plaque removal – 2 jaws | 3300 |
| Teeth whitening Opalescence Boost | 12000 |
| Skyce installation (including the cost of decoration) | 2000 |
All initial consultations are free.
How and with what to treat gums for pregnant women
Inflammation of the gums during pregnancy is one of the most common reasons for visiting the dentist during the difficult but joyful period of waiting for a baby. According to statistics, complaints about bleeding gums and other manifestations of periodontal disease during pregnancy can be heard from 75% of women.
If your gums are swollen during pregnancy, this is a good reason to visit the dental clinic. After all, the reason why gums hurt during pregnancy can be either relatively harmless gingivitis or much more serious stomatitis or periodontitis. In fact, these are consequences of the same pathological processes, but at different stages, so you should go to the clinic after the first alarming symptoms appear (for example, bleeding, ulceration, swelling and soreness of the gums).
The main task of a dentist when treating gums for pregnant women is to stop inflammation and prevent further spread of infection, using the most gentle methods possible. And the earlier treatment is started, the lower the risks of developing serious periodontal diseases, tooth loss and the impact of negative processes on the fetus.
Diseases in which the gums become loose
Looseness is a characteristic symptom of gum tissue diseases. They can be recognized by the presence of other signs.
| Disease | Features of the flow | Characteristic signs |
| Gingivitis | Only the gums become inflamed. Teeth and periodontal tissues are not affected. The disease is often diagnosed in children, pregnant women and adolescents | • soreness in the gums; • bleeding; • swelling and change in color of the mucous membrane; • appearance of ulcers (with ulcerative form). |
| Periodontitis | The supporting apparatus of the tooth, the ligament between its root and bone, is destroyed. The disease is more often diagnosed in adults | • exposure of the cervical area of the teeth; • inflammation of the lymph nodes; • the appearance of periodontal pockets and pus in them; • change in position and loosening of teeth. |
The service is provided
Zohiri Khoja Zakirovich Therapy, orthopedics
Branch: Pavshinsky, 17
Make an appointment with a specialist
Osipova Irina Gennadievna Therapy, general dentistry
Branch: Pavshinsky, 17
Make an appointment with a specialist
Gum diseases
Periodontium is a whole complex of tissues surrounding the tooth. The gums, which everyone can see, are covered with mucous on top, underneath there is a muscular-ligamentous apparatus that holds the tooth; between the teeth you can see the gingival papilla. Beneath the soft tissue is bone, which contains the roots of the teeth.
Let's consider the most common diseases of the soft tissues of the oral cavity:
- Gingivitis
. Perhaps the most well-known cause of gum inflammation, both during pregnancy and outside of it, is gingivitis. In essence, this is an acute inflammation of the gum edge, affecting the gingival papillae located in the interdental spaces. The most common symptoms of gingivitis are bleeding and soreness of the gums (especially during brushing), redness and swelling of the tissues (sometimes with noticeable hypertrophy of the gum margin), sometimes accompanied by bad breath. - Periodontitis
. This disease usually occurs in the absence or untimely treatment of gingivitis. If the gums are very swollen during pregnancy, it is quite possible that the pathological process has reached the stage of periodontitis, that is, the ligamentous apparatus (periodontal) surrounding the teeth gradually began to deteriorate. In addition to redness and bleeding of the gums, looseness of the tissues appears; when you press on them, sometimes a discharge with a putrid unpleasant odor appears; a space is formed between the tooth and the gum - a periodontal pocket. In advanced cases, tooth mobility appears. - Periodontal disease
. Unlike gingivitis and periodontitis, the cause of periodontal disease is not inflammatory, but degenerative processes. With periodontal disease, the gums practically do not change color, except in cases where periodontal disease is also accompanied by gingivitis or periodontitis. The gums may be absolutely “quiet”, but the edge of the gum is significantly lower than normal. Due to this, the necks of the teeth are exposed (normally this part of the tooth is not visible, since it is covered by the gum), teeth become sensitive to cold (since there is no enamel in the neck area), the teeth become mobile, and eventually begin to fall out. Periodontal disease is a disease that is associated with age-related changes in tissues. Previously, only older people suffered from it, but now periodontal disease has become much younger. More and more often we meet young people and middle-aged patients who already have all the signs of periodontal disease. People often call the above-mentioned gingivitis and periodontitis periodontal disease, which is wrong: these are fundamentally different diseases that require different approaches to treatment. - Stomatitis
. Unlike the above-mentioned diseases, stomatitis can develop not only on the gums, but also in any area of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. This is an infectious and inflammatory disease, manifested by redness of the mucous membrane, the appearance of ulcers or aphthae, severe pain, sometimes bleeding of the affected areas, and profuse salivation. There are several reasons for the appearance of stomatitis: exposure to irritating factors, allergic reactions, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, fungal, bacterial and viral infections. In all cases, the appearance of stomatitis indicates a decrease in immunity, both local (in the oral cavity) and general. - Periodontomas
. This group includes all kinds of benign periodontal tumors: fibromas, cysts, and so on. As a rule, they require surgical treatment, which in pregnant women is always postponed until delivery and is carried out as planned.
In addition to the above-mentioned common ailments, there are also idiopathic periodontal diseases, which we will not consider due to their rarity.
During pregnancy, gingivitis and stomatitis are most often diagnosed. They are completely curable and go away completely without a trace if you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow all recommendations.