The Frenkel appliance is one of the types of orthodontic appliances created to eliminate the problems of malocclusion, uneven teeth, and developmental deformities of the jaws in children.
This device allows parents from an early age to begin correcting congenital pathological disorders of the dentition (its use is allowed for children from 3-4 years old).
Features of the device design
The basis of the removable two-jaw apparatus is:
- complex metal frame;
- side (cheek) shields;
- lip pelota;
- loops for securing incisors and canines.
The frame is made of thin elastic wire, up to 1 mm in diameter, with three arcs:
- lingual;
- palatal;
- vestibular.
The arches are connected to plates made of plastic (less often metal); if necessary, screws and springs are additionally used to speed up the movement of certain teeth.
Device Features
The system is a removable model placed on both jaws, the structure of which consists of a metal frame, lip pads and protective elements for the inner cheek area. To make the base, medical wire with a cross-section of 0.8-1 mm is used, which is given an arched shape.
In total, the system may contain three or four arcs, each of which is connected to a functional plate. The basic principle on which the Frenkel orthodontic appliance is based is the need for constant pressure to inhibit jaw development. For this purpose, retaining loops are formed at the ends of the metal arches, which are attached to the fangs and incisors.
For the manufacture of protective plates, either plastic or metal material can be used as a basis, subjected to molding and subsequent casting. Polymer is considered a more convenient option because it allows you to smooth out the area of contact with the inner surface. The maximum width is determined depending on the characteristics of the anomaly, but cannot exceed 2.5 mm.
Operating principle of the Frenkel apparatus
Most orthodontic structures have a mechanical effect on the dentition.
Frenkel developed an absolutely unique technique based on a functional effect on the regulation of muscle tone, with its help you can achieve the following results:
- reducing pressure on the cheeks and lips on the jaw in problem areas;
- positive effect on the activation of functions and natural functioning of the muscular tissues of the oral cavity;
- normalization of nasal breathing;
- the device promotes the desired position of the tongue, closing of the lips and thereby ensures the harmonious development and growth of the jaws of young patients.
Indications for use of the Frenkel apparatus
The effective period for the treatment of children's dental pathologies is considered to be the time of their active growth (4 - 12 years).
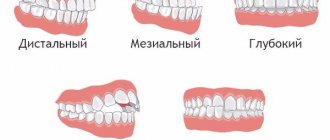
An orthodontic appliance is used for the following pathologies:
- distal bite (strong development of the upper jaw);
- mesial bite (pushing forward of the lower teeth);
- open bite (the lower and upper dentitions do not meet, a gap is formed);
- neutral bite (insufficient development of alveolar processes);
- narrowing of the dentition;
- twisted teeth.
The device in action
Every orthodontist will say that occlusion (bite) defects are most easily eliminated “on takeoff,” in childhood, when the jaw is just forming. Huge problems in the future can be avoided by correcting the child’s mixed bite in preschool age.
The Frenkel apparatus is a special device that helps eliminate complex malocclusions in children from the age of four. This is a removable structure that is put on both jaws of the child at once and fixes them in the desired position. It consists of a wire frame in the form of arches, cheek shields, and labial pads. The device is worn at night and worn for 2-3 hours during the day; the child cannot eat or talk with this device in the mouth.
All parts of the design are smoothly polished, which prevents injury to the child’s teeth and mucous membranes.
Malocclusions for which the Frenkel apparatus is used:
- mesial occlusion: lower teeth protrude forward;
- open bite: a pathology in which a vertical gap is formed between the closed front teeth of the lower and upper jaws;
- distal overbite: overdevelopment of the upper jaw;
- crowded dentition;
- narrowed dentition.
Operation of the device:
- relieves excess pressure from the cheeks and lips on the jaw;
- regulates the strength of the jaw muscles;
- strengthens the tone of the mouth muscles;
- normalizes nasal breathing;
- forms the desired position of the tongue.
The device is designed in such a way that it tones some muscles and at the same time relaxes others in problem areas that interfere with normal jaw growth. The design works for results, and the little patient does not experience pain. Everyone is happy: children, parents and dentists.
Examination before physiotherapy
The appearance of the slightest signs of abnormal development of teeth in a child obliges parents to seek advice from an orthodontist.
After a visual examination, the doctor will suggest:
- take an x-ray or orthopantomogram of the upper and lower jaw;
- cure carious teeth and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, if any.
Based on the images, the doctor will determine the type of pathology and prescribe treatment with the appropriate type of device design to eliminate the defect.
Kinds
There are 4 types of Frenkel apparatus. They have different effects on the jaw. The choice in favor of a specific device is determined by the characteristics of the anomaly.
Regulator type 1
It is used in the presence of an abnormal arrangement of the anterior teeth or distal occlusion. The functional regulator includes 2 arches (lingual and palatal) and the same number of pelotes that are adjacent to the upper and lower lips. To connect the elements, a bracket and cheek shields are used. Type 1 devices may differ from each other in design features.
Regulator type 2
It is used when a distal bite is detected, complicated by retrusion of the maxillary incisors. Unlike the previous system, the Type 2 regulator includes a palatal arch. The loops that are fixed on the fangs have a different shape. In the lip area there are double pads that stimulate jaw growth. The shields fit tightly to the teeth and alveolar margin.
Regulator 3 types
Indicated when progeny is detected. This anomaly is characterized by active proliferation of soft tissues. Type 3 regulator pilots are located near the upper lip.
The occlusal pads provided in the design of the device are adjacent to the lateral teeth, and the vestibular arch is fixed to the front teeth. The regulator helps to separate the bite and stops the development of the lower jaw.
Regulator 4 types
It is used in cases where there is an open bite with abnormally developing teeth. The regulator restrains soft tissues that prevent the formation of the mandibular row. In this design, the vestibular arch runs along the upper teeth.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
The pelotes are located in the area of the lower lip. The palatal arch returns teeth growing inside the mouth to their correct position. There are also occlusive linings made of metal attached to the sides. They enhance the effect created by the device and contribute to the separation of the open bite, normalizing breathing and speech.
All designs, regardless of their type, are used for complex pathological deviations in the shape of the jaws. More often, the Frenkel apparatus precedes other orthodontic procedures necessary to restore the bite.
Types of Frenkel apparatus
Different pathologies require different effects on the patient’s dental apparatus. There are four types of this design:
- FR - I is used to eliminate signs of distal occlusion with protrusion of the frontal teeth of the upper jaw, and with narrowing of the dentition. They consist of palatal and lingual arches, attached with upper and lower pelota. The cheek shields are connected to the lower pads using brackets. It is located in the oral cavity so that the shields do not come into contact with the alveolar ridge.
- FR-II is used to correct excessive inclination of the upper incisors (retrusion). It differs from the first type in the type of loop capes on the fangs and the presence of double pelotes. The shields are in close contact with the dentition and the crest of the alveoli. Made from transparent material.
- FR - III eliminates progeny (excessive development of the lower jaw). The design feature is the absence of lower pelotes and the presence of a vestibular arch.
- FR - IV corrects open bite, eliminates the reasons that hinder the development of the lower jaw. There are pads for the lower lip, a vestibular arch for the upper row, and metal pads. The device also helps to separate the bite.
Types
Depending on the design features, there are several types of Frenkel apparatus . Each of them has its own purpose and impact.
Read more about the stages of manufacturing the Engle apparatus in a separate publication.
In this article, we will discuss whether crooked teeth can be corrected without braces.
At the link https://orto-info.ru/sistemyi-vyiravnivaniya-zubov/lechebno-profilakticheskie-apparatyi/basharovoy.html you will find a photo of Basharova’s apparatus and the results of its use.
FR-I
The first type of Frenkel regulator is designed to form a constructive bite of a narrowed dentition . It is used to eliminate incorrect position of incisors and canines, distal occlusion with protrusion of the upper teeth.
Type 1 construction is based on the palatal and lingual arches, secured with pelotas for the upper and lower lips. Side shields and a bracket connecting the lower panels are required. The structure is installed so that the side plates do not touch the alveolar ridge.
This type of device has some distinctive characteristics, according to which varieties are distinguished :
- FR-Ia . Designed to correct neutral type bites with pronounced deep overlap of rows. Also, it is prescribed for retrusion of the arch of the movable jaw, for protrusion of the anterior part of the upper jaw and displacement of the closure by no more than ½ the width of the molars.
- FR-Ib. The device is indicated for pronounced protrusion of the distal bite of the anterior section, if the sagittal gap reaches 7 mm, but no more. The main effect here is achieved through the lingual shield, which is placed under the tongue.
The shield occupies the area between the premolars, where it is fixed with wire elements to the cheek shields so that it does not touch the surface of the teeth.In case of vestibular deviation, special springs are attached to the shield, which exert additional pressure on the dentition.
- FR-Ic. It is used to correct pronounced protrusion, distal type occlusion, in which the ratio of molars and premolars exceeds half the width of the tooth.
In terms of its design, this type of device completely copies the FR-Ib model, but with the addition of special screws fixed in the cheek shields.In addition, all segments of the device are made sectorally, which allows them to be moved using screws in a given position.
FR-II
This type of device allows you to correct the distal bite, combined with limited retrusion of the upper incisors .
It differs from the first type by the presence of a palatal arch and a different shape of loops covering the fangs. This allows the ends of the arch to be carried out simultaneously between the premolars and canines.
In addition, type 2 apparatus is equipped with double pilots. One is fixed in the lower lip area, and the second in the upper lip area, which stimulates sagittal growth of the jaw.
The device is installed so that the side shields fit tightly to the alveolar ridge and dentition.
FR-III
The main purpose of the Frenkel type 3 orthodontic apparatus is the correction of progeny .
Unlike other types of regulators, it has a significantly different design. Here, lip pelots are fixed only in the area of the upper lip. The vestibular arch puts pressure on the incisors of the lower jaw, and the palatal arch on the dentition of the upper.
Also, occlusion-type overlays are fixed on the arches in the lateral areas. When installing, it is necessary to ensure that the pelots exert pressure on the alveolar ridge, and the plates are at a short distance from it.
FR-IV
The indication for use of type 4 is any dental anomaly combined with an open bite .
The design differs from other devices in that the pelota are installed for the lower lip, and the vestibular arch is installed for the upper dentition. The palatal arch is formed in such a way that it influences the retrusion of the upper teeth in the anterior region.
In the lateral areas, linings made of metal are installed and allow for dento-alveolar shortening. During installation, the side pads should fit snugly against the dentition, and the palatal arch should apply maximum pressure.
For what indications is the Mershon device prescribed, we will tell you in the next review.
This article discusses the features of teeth straightening without braces in adults.
We will talk about the manufacturing technology of the Luri apparatus here https://orto-info.ru/sistemyi-vyiravnivaniya-zubov/lechebno-profilakticheskie-apparatyi/luri.html. In what cases is it used in orthodontics?
Rules and terms for using the Frenkel apparatus
In order for the treatment to be effective, the following rules and deadlines must be observed:
- The Frenkel apparatus is used at night and for a short time during the day (2-3 hours). During daytime treatment, it is forbidden to talk or eat food.
- It is imperative to carry out daily hygiene procedures for the oral cavity and orthodontic structure to avoid the development of caries.
- The duration of the treatment period is from 8 months to 1.5 years.
- Due to the intensive development of the child’s dental apparatus, the device changes 3-4 times during treatment.
Duration of treatment
The duration of treatment for dental anomalies will directly depend on the complexity of the pathology. It is also worth considering the patient's age.
The main age category for which this device will be most effective is 4–11 years . The younger the child’s age, the faster the correction will take place.
from 4 to 8 months to correct mild anomalies .
For more complex pathologies, this period can stretch up to 1.5 years . In addition, it is necessary to take into account the individual developmental characteristics of each child and the degree of compliance with the daily wearing regime.
The peculiarity of the device is that it must be worn only at night, putting it on while sleeping. The therapeutic effect can be enhanced by using the device for an additional few hours during the day. While wearing the structure, you should not talk or chew.
As a rule, a positive result from treatment is visible within 2–4 months, depending on the complexity of the case.
Since the correction takes a very long period, during which the growth of the jaw does not stop, regular replacement of the apparatus is required during the treatment process . Typically, during 1.5 years of treatment, replacements are made no more than 3 times.
As a result of the correctly selected type of device, not only the aesthetics of a smile improves, but also breathing and speech are normalized, and bad myofunctional habits are eliminated.
How the process of installing and adjusting the device takes place, watch the video:
Results after therapy with the Frenkel apparatus
The use of the Frenkel apparatus in eliminating deviations in the development of the dentition gives a good effect:
- eliminates the need for a surgical solution to the problem in later stages of the disease;
- Speech defects caused by dental pathologies are corrected.
- children get rid of bad habits (holding a finger, a pencil in the mouth).
- the effectiveness of treatment has a positive effect not only on the physical condition of the child, but also improves his appearance and psychological mood.
The Frenkel apparatus is actively used by orthodontists, is popular among patients and is considered a worthy alternative to the braces system.
Pros and cons of using removable orthodontic appliances
Correction of the bite in a child under the age of 13 is possible only with the use of appropriate corrective plates - braces can be installed only after the formation of a permanent dentition (more often this occurs before the appearance of the outer chewing teeth - wisdom teeth (the end of apexogenesis and mineralization of the enamel, this occurs after tooth eruption, after 3 years).
Wearing removable orthodontic devices to correct your malocclusion has many benefits, including:
- It is possible to make the base of the plates in different colors - this is especially true for young children, who will be more willing to wear a beautiful, bright design.
- High production speed - the maximum production time for a removable orthodontic appliance is one week.
- Reasonable price – the price for the simplest braces will be several times higher.
- Easy to maintain - the plate/device only needs to be cleaned twice a day with a brush and gel (morning and evening).
The disadvantages include a long period of use - to achieve a visible result, you need to be with the plate at least 12 hours a day (the more we wear by the hour, the less by month). On average, you need to wear the plate for at least one year. Adaptation to orthodontic removable appliances occurs more slowly than to braces. The child experiences discomfort while caring for the plate (at this time the plate/device must be removed).
Encourage your children to have a beautiful smile!