Treatment of caries of children's primary teeth
Caries of primary chewing and front teeth has long been treated without the slightest pain.
New modern techniques have reduced the use of drills and drilling to a minimum, and timely scheduled examinations make it possible to detect the disease at a very early stage. The doctors at Aza&Buka Pediatric Dentistry who work with young patients are distinguished by an amazing sense of tact and constant positivity. Knowledge of the child’s psychology allows doctors to build communication and dialogue in such a way that children sit in the dental chair without the slightest fear. If the child already has some dental phobia, then adaptation techniques can solve the problem.
Caries on baby teeth in children is treated using the following technologies:
Types of sedation in pediatric dentistry
Sedation for children has a number of features, since not all methods and drugs are suitable for the child’s body.
- Inhalation method (nitrous oxide).
Nitrous oxide sedation is a very common technique in pediatric dentistry. There are several reasons for this. First, nitrous oxide is safe and can be used even on children under 5 years of age. Secondly, dental treatment with gas for children does not require a special license for the use of psychotropic substances. Nitrogen has a minimal effect on the body's systems, and the child recovers very quickly after the procedure. On the other hand, expert reviews of this method are mixed. Many people consider nitrous oxide not the best means for sedation, and sometimes individual intolerance occurs. Dental treatment for children with nitrous oxide cannot last long: the duration of action of laughing gas is very limited. - Oral method.
The effect of sedation is achieved by oral administration of drugs from the benzodiazepine group (Valium, diazepam and similar drugs). This type of sedation is not recommended for children under 5 years of age, and the dosage must be calculated very accurately. - Intravenous method.
The most powerful type of sedation that causes significant depression of consciousness. The drugs are given through a vein, and the patient may require an oxygen mask to maintain breathing. This type of sedation is not given to children.
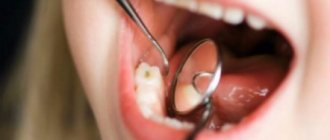
Classic filling
requires a special approach when treating young patients, since the doctor has to use dental equipment, which often causes fear in children.
Aza&Buka dentistry uses both traditional and modern methods of treating caries of primary teeth, selecting a method taking into account the age of the child and the degree of neglect of the process.
Plaksina Margarita
“Modern parents are great! They themselves are not afraid of dentists, and children are taught the same thing: to come on time for preventive appointments and examinations. In such cases, doctors can intercept the very beginning of a cavity infection and prevent tooth decay without drilling.”
Where can you get your child’s teeth treated without fear?
It is good if the child is observed by one dentist throughout the entire period from early childhood to 18 years.
Firstly, the baby will always see a familiar doctor in front of him and will not be afraid, cry or worry. And secondly, a specialist who monitors the child’s dental health from an early age knows all its features and will notice the problem at the very beginning of its development. It is important not only how teeth are treated for children 2 years of age and older, but also where it is done. All establishments in the city are divided into three large groups:
- State clinics. This option is best left for last resort. Why? There are long queues, many capricious children, nervous parents and doctors who are given a limited time for an appointment and not a minute more. At the same time, dental equipment, as a rule, remains from the last century, and no one has heard of good medicines and fillings.
- Special children's rooms in high-profile private hospitals. If you are looking for a good combination of price and quality, then this option is suitable. There is all the necessary equipment, modern medications designed specifically for baby teeth, and a specialist doctor whose competence includes only the treatment of children’s first teeth will work with a boy or girl.
- Private specialized children's dental clinics. They are intended exclusively for small patients. Here everything is done for their coziness and comfort, there are no long queues, all patients come only at the appointed time, and you can make an appointment for a convenient day for an appointment. All equipment, instruments and medications are intended exclusively for children's teeth. Well, the quality of service always remains at the highest level. The only negative is the high prices, and even a simple consultation will be paid.
Which treatment methods to choose and where exactly the baby should be treated is, of course, decided by the parents. You should not go to extremes and should choose according to your financial capabilities. After all, even in a free city clinic you can get access to competent and experienced specialists. The only thing that remains is to read the reviews and ask your friends who and how they treat the teeth of children aged 4 years. If possible, immediately contact a paid pediatric dentistry.
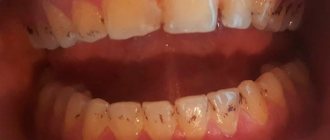
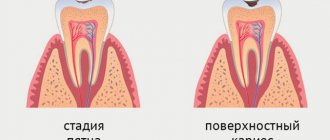
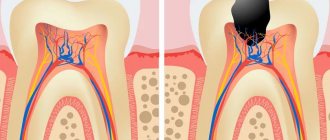
Milk caries: initial, superficial, medium, deep
Doctors distinguish 4 stages of the formation of carious areas:
- Initial caries - tooth enamel becomes covered with small spots of white or yellowish tint.
- Superficial caries - the enamel begins to deteriorate, small and light cavities are observed.
- Medium – the layer of tooth enamel is destroyed, the affected area extends deeper.
- Deep - the layers of dentin have already been affected, and the pulp is under threat.
It is necessary to treat milk caries at the very first stage, although it does not cause any discomfort in the child. The fact is that the enamel and crowns of temporary teeth are subject to rapid destruction, and the development of caries occurs very quickly. Deep caries often provokes irreversible changes, which leads to premature removal of the baby tooth.
Rodikova Tatyana
“Medium and deep caries most often occurs in schoolchildren, almost teenagers. Children brush their teeth poorly, and they talk about problems only when caries has already affected the pulp. In this case, the treatment turns out to be more unpleasant, since removal of the pulp cannot be avoided. That’s why I always ask parents to carefully monitor their teenagers’ hygiene and bring them to appointments on time.”
Reverse overlap of incisors
Reverse incisor overlap is when the lower teeth protrude forward). Reverse overlap blocks the normal growth of the upper jaw in length. The most optimal time to correct such a bite is from the age of 5-6 years. At this age, the incisors of the upper and lower jaws erupt and this is the most favorable time to begin orthodontic correction. If you notice a reverse overlap in a child at a later age, it is also important to contact an orthodontist in order to rid the upper jaw of the blockage as quickly as possible and give it the opportunity to continue to grow actively.
Reasons for the development of caries in temporary teeth
When visiting a dentist, parents are invariably interested in the reasons for the appearance of such an unpleasant disease. This is important because it helps prevent damage to new teeth. Sometimes it is enough to change eating habits and hygiene patterns so that the child forgets about fillings for a long time, and only comes to the dentist for examinations.
Causes of caries:
- Poor or insufficient oral hygiene. Food remains in the interdental space and on the enamel are an excellent environment for the development of carious bacteria.
- An unbalanced diet with a preponderance of sweets and carbohydrates - during the fermentation of simple carbohydrates, acids are formed that provoke the destruction of enamel.
- The lack of solid foods in the menu leads to a decrease in the frequency of chewing, reduces salivation and becomes a common cause of caries of primary teeth in young children.
- Long-term use of nipples, including on bottles and sippy cups, increases the risk of developing single or multiple bottle caries of the anterior milk teeth in children.
- Rickets is a pathology that provokes the destruction of dental tissues.
- Genetic predisposition of the child.
- Problems with bite – various anomalies in the formation of the dentition.
- Decreased natural immunity due to frequent acute respiratory viral infections, chronic diseases, and taking various medications.
- Damage to tooth germs in the prenatal period - due to maternal illness or neglect of health in the first trimester.
At what age can you treat
There are no strict age limits regarding the age at which children can have their teeth treated. Indications for visiting a doctor are:
- carious foci of infection in the oral cavity;
- inflammation of periodontal tissues;
- baby has bad breath;
- enamel fluorosis.
What happens if dental problems are not treated? A chronic source of infection can lead to premature tooth loss and other health problems - pharyngitis, laryngitis, disruption of the functioning of the intestines and stomach. Children with untreated caries become vulnerable to viral, fungal and bacterial pathogens due to the fact that their immunity cannot work at full strength.
Caries can spread not only to enamel and dentin, but also to the rudiments of permanent elements, provoking the development of periodontitis. One of the serious complications of dental disease is pulpitis, accompanied by acute pain.
Pulpitis has several stages of progression, and the most complex of them lead to complete destruction of the tooth and involvement of the neurovascular bundle of the unit in the pathological process. An infection through the bloodstream can spread throughout the body and cause a malfunction of the respiratory system and heart.
Untimely loss of dentition elements leads to improper chewing of food due to unevenly distributed load between different parts of the jaw. Insufficiently processed and crushed food is poorly absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, children should be shown to dentists at the moment when they show the first signs of dental disease, regardless of age.
What is rehabilitation like after treatment under anesthesia?
After waking up from anesthesia, in the vast majority of cases, children feel well. Most often, the only thing that bothers them is numbness in the areas where the local anesthetic was injected.
As for behavioral changes, there are three types:
- excitement - the baby may be capricious and cry. This is accompanied by increased activity. But it quickly gives way to fatigue;
- fatigue - the child wants to sleep, refuses to eat, sits in the arms of the parents;
- no behavioral changes after waking up.
The first two scenarios are typical for children under the age of 7-10 years, the third - for adolescents and adults.
Hyperactivity and agitation upon awakening are unpleasant for both the child and those around him. To avoid it, we try to implement the second scenario; to do this, we put the baby to sleep and wake him up gently.
The child can eat immediately after waking up, unless the anesthesiologist gives other recommendations.
Very rarely, recovery from anesthesia is accompanied by nausea or a feeling of motion sickness. This lasts no longer than 2-3 hours. This reaction is typical for children who get motion sickness in transport. In this case, you will be able to eat and drink within an hour or after the nausea has passed.
There is no need to worry about the postoperative period - the anesthesiologist will always be in touch.
Endolaryngeal infusions
Recommended for acute laryngitis, along with nebulizers, mucolytics and much more.
The cause of acute laryngitis in most cases is a viral infection. Therefore, the main treatment here is time. The use of antibiotics is not indicated even for mild bacterial infections in the larynx, which are much less common than viral ones.
With endolaryngeal infusion, the solution enters directly onto the vocal folds at the time of phonation, which means there is a very high risk of it entering the lower respiratory tract. In cases where the larynx is poorly visible and the procedure technique is not followed, the doctor pours the solution into the esophagus, the patient swallows it, and there is no positive effect after the procedure, even temporary. At the same time, such a “blind” infusion of the solution increases the risk of aspiration (entry into the respiratory tract).
Antibiotics are used for infusions into the larynx, which, when applied topically, do not have a bactericidal effect. Oil solutions can be used, the positive effect of which is easily replaced by a home humidifier and ventilation. The effect of using hormonal agents (dexamethasone or hydrocortisone) is very short-lived. Moreover, in emergency situations, for example, for singers before a concert, preference should be given to the systemic use of hormonal therapy. The use of hormones leads to the rapid disappearance of inflammation of the vocal folds and improvement of voice quality, but one has to put up with the possible side effects of this group of drugs, so in standard situations the potential risk of their use outweighs the possible benefits.
A number of studies have shown that the voice is restored in equal time - when treated with antibiotics and when taking a placebo.
Important to know : viral laryngitis usually lasts 7-10 days and goes away on its own.
Puncture of the maxillary sinus
Practically not used in modern otorhinolaryngology. For acute bacterial sinusitis, systemic broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are indicated, which successfully cope with the bacterial process without punctures and “cuckoos”.
Punctures for a bacterial process in the maxillary sinuses are mainly indicated if culture of the sinus contents is needed - usually when 1-2 courses of antibacterial therapy are ineffective.
Very rarely, such punctures are performed for diagnostic purposes, when it is not possible to perform radiography or computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses. Another indication is severe pain associated with the pressure of the contents on the walls of the sinus. The puncture is done once during the main treatment. Several punctures are indicated only in the case of a persistent bacterial process with two or more courses of antibiotics, and there is no possibility of performing endoscopic surgery on the sinuses.
It has been proven that puncture of the maxillary sinus does not speed up the healing process.
It is important to know : puncture, like any invasive method, can have complications, including trauma to the medial wall of the orbit, nasolacrimal duct, soft tissues of the cheek, and nosebleeds.
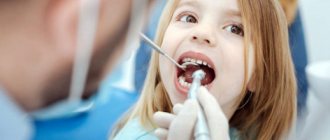
How to choose a doctor for your child
A child's first visit to the dentist is a very important event that should be taken very seriously. It is imperative to find a doctor who gets along well with children and to whom the child will go with great pleasure. This will determine whether he will have a fear of dentists in the future.
It is recommended that you spare no expense for the first time and take your child to a paid clinic . In such institutions, treatment is accompanied by a friendly attitude from the staff; children are often shown cartoons and given toys to play with.
How is dental treatment performed for children under sedation?
Specific preparation measures are selected depending on the type of sedation, but the preparatory stage cannot be avoided. This is especially true for deep sedation, when it is necessary to take blood tests and determine possible allergic reactions to drugs. Before the procedure, you need to completely give up smoking and alcohol (although this requirement is not so important for a child), and also not eat food 8-10 hours before treatment. During inhalation sedation using nitrous oxide, a light breakfast is possible. After all the necessary preparatory measures have been taken, the entire treatment process is divided into four stages:
- final examination of the oral cavity;
- introduction of a sedative into the body;
- anesthesia;
- treatment.
Treatment of baby teeth and tooth extraction usually does not take much time. The more extensive the treatment, the longer the sedation should last. In some cases, treatment is divided into two stages.
Superficial sedation does not require additional measures to emerge from drug-induced sleep. Deep sedation often involves the use of special antidotes.