Teething in infants and older children is no different: the gums swell, a white spot appears, a tooth emerges, followed by a second one (they appear in pairs).
The only difference is that older children can tell where it hurts and what is wrong, but infants need to be constantly monitored in order to quickly detect approaching teeth and help them grow calmly.
In this article we will talk about the procedure for teething in infants, the main symptoms and ways to make this process more relaxed.
What happens if childhood caries is not treated?
Treatment of caries of primary teeth, as well as prevention of dental diseases are very important.
And waiting for your teeth to change is wrong and unreasonable. Arguments in favor of monitoring children's health and timely treatment will be:
- High probability of infection of permanent units. Under the milk teeth are the rudiments of the molars. Untreated caries can easily spread to permanent teeth and cause more serious problems.
- Early removal of milk units. In children, caries spreads quickly, and if the crown is severely damaged, doctors remove the tooth. But if the molar is not yet ready to grow, the incisors, canines and molars in the mouth begin to shift. The child’s bite deteriorates, which then has to be corrected with braces, aligners or other orthodontic systems.
- Serious problems with diction. Extracted and damaged teeth make it difficult to clearly pronounce sounds, which complicates communication with peers and often negatively affects school performance.
- Vulnerability to infections. A bad tooth threatens not only the dental health of neighboring units, but can also cause frequent throat diseases and provoke problems with the gastrointestinal tract and heart.
- The appearance of complexes. Decayed teeth look unsightly, which is why the child smiles less and grows aloof and uncommunicative.
- Delayed bite change. After suffering from pulpitis or periodontitis, the resorption of the roots of temporary teeth often stops. This means that baby teeth stop falling out on their own, and they have to be removed by a surgeon.
It is also worth remembering that the process of updating the bite is extended over time and can take up to 6-8 years. Does a child really have to suffer with bad teeth all this time?
Rodikova Tatyana
Unfortunately, parents still have to be convinced to treat caries of baby teeth in children. Many people do not see the danger in this disease and believe that the problem will disappear in the process of changing teeth. After explaining the harm of a carious infection in the oral cavity, many, however, agree with the doctor’s opinion. And every such case makes me very happy!
When can I expect my first tooth?
Caring for your first teeth
Even though baby teeth will still fall out, they need to be thoroughly cleaned and treated if necessary. Edith Kuzmina, head of the Department of Prevention of Dental Diseases at Moscow State Medical University, talks about the rules of caring for the first teeth.
Many parents are waiting for the first teeth when the baby begins to drool and put his fingers in his mouth.
This occurs at the age of three to four months. However, this behavior is a normal stage in the development of a child who has begun to become familiar with his own hands, but has not yet learned to swallow saliva normally. Experts say that the first tooth can appear at any time from the third to the 15th month of a baby’s life. Most children begin teething between four and seven months
.
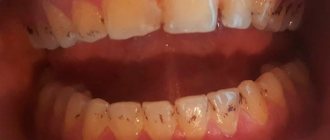
Signs of caries in children
After solving the question “does caries of baby teeth need to be treated,” a new one appears. Namely: how to understand that a child has caries?
The symptoms of dental diseases are simple:
- Complaints of pain - at night, during meals or during the day.
- The appearance of yellow or brown spots on the enamel of the teeth.
- Bad breath.
- Excessively careful chewing of food - with teeth on only one side.
Unfortunately, caries can occur without visible signs. For this reason, dentists advise periodically examining the child’s oral cavity and monitoring the quality of teeth cleaning.
Teething symptoms
- Sharp increase in drooling
- Decreased appetite for solid foods
- The child bites, pulls all available objects into his mouth and tries to chew them
- Baby tries to rub his ear
- The baby is irritable and whiny
- The child has trouble sleeping
These symptoms usually occur three to four days before the tooth appears and disappear within a day or two after its eruption. As a rule, after one or two teeth appear, the baby’s body “takes a break” and teeth do not cut for several weeks or months.
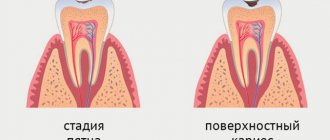
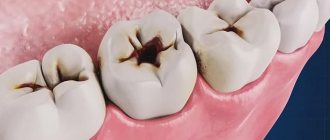
Types of caries
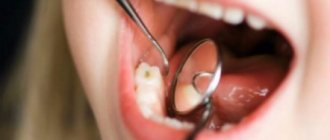
You can learn to distinguish caries on baby teeth by stages from a photo, or by knowing a description of external signs:
- Initial caries of baby teeth is noticeable on the enamel as a matte white spot. It is treated by strengthening the enamel with fluoride compounds, which can be quickly eliminated if detected in a timely manner.
- Surface. The spots are still light, but pain is already possible when eating.
- Average. Carious cavities become deeper - the tooth enamel is already destroyed, pain appears when cold or hot.
- Deep caries. Requires an urgent appointment with a dentist and treatment, since the infection has already reached the dentin and can spread to the pulp. If you ignore caries of baby teeth at this stage, the risk of root infection and the appearance of a baby tooth cyst increases significantly.
Dolotova Marina
Little patients of Aza&Buka rarely encounter deep caries. After all, we, doctors, do everything necessary for this - we make appointments on time, teach how to brush teeth and eat right. And if caries occurs in baby teeth, we treat it as early as possible!
Signs of teething in infants
The only primary sign of the appearance of the first teeth is the appearance of a white spot on the gum (transparent through the thin skin of the enamel).
The remaining signs can be considered secondary - they are not always symptoms of teething:
- Poor sleep, appetite, mood.
- Red hot cheeks.
- Pain in the nose and ears, runny nose, sore throat.
- Increased salivation (sometimes this causes vomiting - the child constantly swallows his saliva).
- Fluid blisters and redness on the gums.
In some cases, a soft ball of liquid (pink or slightly bluish) may appear on the gum where the first teeth appear. This is a common occurrence, but if the lump has become very large and is bothering the child, you should consult a dentist.
Important:
fever, vomiting, and diarrhea are not consequences of teething in infants. They may be the result of certain symptoms (for example, vomiting due to excessive swallowing of saliva). But in most cases, the cause is other diseases that require treatment. If your child is teething and this is accompanied by fever, nausea, or abdominal pain, you should consult a doctor.
Methods for treating caries in children - without pain and fear
There are many methods available for the treatment of caries in primary teeth. All of them are adapted for children and do not cause pain, discomfort or anxiety to the child. Depending on the complexity of the situation, dentists offer the following solutions:
- Remineralization of tooth enamel – restoration of a balanced structure of the tooth surface using special pastes. Formulas with a high content of calcium and sodium should be applied to baby teeth for some time, which will stop the spread of bacteria and the deepening of carious cavities.
- The ICON method is an ideal treatment option for superficial caries. The doctor applies a composition to the carious spot to remove the affected area of enamel, and then closes the cavity with a safe, quick-hardening polymer. The treatment takes place without a drill - quickly and painlessly.
- Ozone therapy is an effective method of combating caries. The damaged area is subjected to targeted exposure to ozone to disinfect the enamel and eliminate carious bacteria. Children tolerate the procedure very well, as it does not cause any discomfort.
- Filling. Cleaning carious cavities is done using a drill or manually without drilling. Next, the doctor treats the tooth with antiseptics and places a filling - white or colored. Treatment of caries of a baby tooth is carried out with anesthesia with local anesthetics or under sedation.
- Laser dental treatment. Advanced technology in which laser beams remove carious lesions quickly and accurately. A filling is placed on the cleaned and disinfected cavity.
A method for treating caries is suggested by the doctor after assessing the degree of damage to the baby tooth.
How long does teething take?
The process of teething in boys begins a little later than in girls. The entire cycle of complete appearance of both primary and permanent teeth takes from 5 months to 14-16 years. In very rare cases, a baby is already born with one or more lower incisors and this is not considered a pathology or complication. As a rule, the eruption of the first teeth occurs on the lower jaw in a period of 5 to 9 months. A similar eruption of the upper teeth—deciduous incisors—occurs with a time lag of several months. A one-year-old baby normally has 4 upper and 4 lower incisors. At two years of age, canines and first molars appear, and by two and a half to three years, second molars appear. The period for the eruption of permanent teeth in children begins at 5 years and ends at 14-16 years.
Delayed teething in a child can be caused by several reasons:
- general developmental and growth retardation;
- significant lack of mineral elements and vitamins;
- absence of tooth germs.
If nothing has erupted in the mouth of a one-year-old baby, you need to contact a pediatric dentist and take a panoramic x-ray.
Teething of upper teeth, photo
Teething symptoms
Over the past few decades, the term “teething syndrome in infants” has appeared in pediatric dentistry. An Internet forum and thematic groups of mothers on social networks and portals actively discuss various symptoms: runny nose, fever, inflammation, blood and pain during the eruption of both milk and permanent molars in children on the upper and lower jaw.
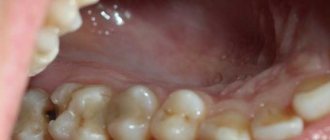
Photo of gums during teething
The most common signs indicating the rapid eruption of children's baby teeth are redness and swelling of the gums in the places where they will appear. Visually, this can appear either as a whitish dense strip or as a red-brown sac (hematoma) that bleeds when touched. Most children do not go through this stage of their life before teething very calmly. The children's oral cavity is already inhabited by various microbes, streptococci, staphylococci, veillonella and others. With swelling on the gums and mucous membrane, both independent pain and infectious processes are possible, accompanied by an increase in temperature to 37-38 degrees. The baby becomes restless and irritable, and his saliva becomes more viscous and viscous. The amount of saliva increases and, when it gets on the skin of the face, it can lead to diaper rash and dermatitis. During this period, sleep and appetite are disturbed, the baby is capricious and puts everything in his mouth to scratch his gums. A rash or painful blush may appear on the cheek. Sometimes, infectious processes not related to the dental system and inflammation in the oral cavity can overlap each other, mutually complicating the baby’s condition. Accordingly, a joint consultation with a pediatrician and pediatric dentist may be required to clarify treatment.
Closer to 4-5 years, gaps (threes) appear between the baby teeth. This is a sign of normal jaw growth and preparation for the planned replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones. But the absence of such gaps by the specified age is a reason to contact a pediatric dentist.
How to make teething easier: tips for parents
Responsible parents, knowing what awaits their baby, ask in advance how to help their child before teething? So what to do before teething?
- using soft cloth wipes, clean the skin around the mouth from excess saliva to prevent dermatitis;
- To facilitate teething, the child can be offered chilled rubber rings - “teething stimulants”; gum massage is also possible (the mother must wear latex gloves on her fingers).
Teething stimulants, photo
- In a child under 2 years of age, it is necessary to brush emerging teeth with a fingertip (a small brush placed on the mother’s finger), be sure to do so every day before bed, and ideally after every meal.
Children's fingertip, photo
- after 2 years, you need to teach your child to rinse his mouth after every meal and start using a children's toothbrush with soft bristles
- The diet must be balanced, with the obligatory presence of cheese, fish, cottage cheese, raisins or dried apricots; carbonated sweet drinks and sweets such as candies and lollipops containing sugar are strictly prohibited
- in the absence of any visible pathologies, the first scheduled visit to a pediatric dentist should be at 2-2.5 years of age
- You are strictly forbidden to lick the baby's pacifier and the spoon with which you will feed the baby to avoid germs from your mouth getting into the baby's mouth.
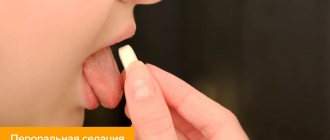
Painkillers for teething
Situations in which children are teething without fever, pain, runny nose, bad breath and other complications are quite rare. Therefore, during this period, the most frequently asked questions from parents are: “What should I put on my teeth when teething? Can you recommend the best remedy or best gel for teething?”
Modern and effective medications (gels, ointments, drops) for pain relief during the eruption of primary and permanent teeth in children contain three components:
- directly anesthetic substance, most often lidocaine;
- antiseptic substances, extracts and extracts of medicinal plants, chlorhexidine;
- antimicrobial elements, such as cetylperidinium chloride.
The combined therapeutic effect of all components ensures disinfection, pain relief and prevention of infection in the child’s oral cavity.
Below is a list of the most effective and used painkillers for teething in children in Russia:
- gel for gums for children “Kalgel”, contains lidocaine and cetylperidinium chloride, recommended for use from 5 months, average price 250-300 rubles
- children's gel for gums "Kamistad baby" contains extracts of medicinal herbs and lidocaine, reduces pain and itching in the gums of a child, the average price is 200-250 rubles per tube
- drops for gums during teething “Dentinox”, contain polydecanol and chamomile extract, reduce pain, swelling and inflammation during the eruption of baby teeth in a child, average price 250-300 rubles
Before using any oral medications on a child, consult a pediatric dentist!
Deputy Chief physician Sergey Evgenievich Brodsky
Sign up for a free consultation
+7
Just CALL US!
+7
We will answer any of your questions and will definitely help you!
Prevention of caries
Many pediatric dentists offer painless and fun treatment. But it is easier to prevent than to treat. Simple preventive measures will help preserve the integrity of baby teeth for as long as possible:
- Daily oral hygiene. As soon as the first tooth appears, you need to purchase children's toothpaste and a brush. Grooming should be done twice a day - morning and evening, and gradually become a healthy habit for the child.
- Proper nutrition. It is necessary to include foods high in calcium (kefir, cottage cheese, cheese, etc.), as well as vegetables and fruits, in the child’s diet. Harmful sweets and fast carbohydrates, on the contrary, should be excluded or reduced as much as possible in the daily menu.
- Preventative examinations with a doctor. A pediatric dentist should be visited 2-4 times a year. This will allow you to monitor dental health and reduce the risk of caries in your child.
It is recommended that a child’s first meeting with a dentist take place after the incisors appear – at 1-1.5 years. This will be a preventive examination, during which parents will be told the principles of caring for children’s teeth and advised on the optimal scheme for monitoring the growth of temporary units.
Watch an informational video on this topic
How to help your baby?
Pediatricians say that most children experience teething relatively painlessly, and the condition does not require intervention. However, you can help your baby and his teeth a little:
- Buy rubber and silicone teethers
. Some of them can be cooled in the refrigerator - cool material reduces discomfort. - Some children prefer to chew and suck on tissue
. Give your baby a few pieces to chew on. Don't forget to wash them daily. - Massage your baby's gums with a clean finger or silicone toothbrush
. - If your baby constantly cries and cannot fall asleep, consult your pediatrician and ask him to find a remedy to relieve pain. Remember that such medications intended for infants can only be given from six months.
- The pediatrician may also recommend special gels that relieve pain and swelling
in the baby's mouth. Don't overuse these remedies: Many parents confuse teething symptoms with other problems, such as viral infections, ear diseases or sleep disturbances.
Healthy habits - from childhood
By the age of three, a child can learn basic self-care skills. Find out how to teach your child good personal hygiene.