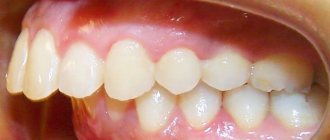
The formation of a primary occlusion is a multi-stage process, which is characterized by a number of features that can largely affect the further development of a person’s dentition. It is during this period that the fundamental basis of the dentofacial apparatus is formed.
Primary occlusion is characterized by gradual teething, and it is sequential in nature - teeth erupt one after another. The characteristics of primary teeth differ from those of permanent teeth.
There are two stages of primary occlusion:
- emerging: the period from the appearance of the first tooth, usually between the ages of 6 months and 3 children. Characterized by active eruption and growth of baby teeth. It is at this stage that it is recommended to make the first visit to the dentist and orthodontist - at the age of 2-3 years;
- formed: characterized by the presence of all teeth and active growth of the jaws.
Development of primary occlusion
The primary occlusion is one of the most important periods in the formation of the dentofacial system. The fact is that even the slightest deviation that occurs at this time can lead to the development of serious violations in the future.
To assess the correct development of the primary occlusion, the following characteristics are used:
- timing of eruption: normally, the first milk tooth erupts at 6 months, and the last at 30 months. The norm is also a deviation of 3-5 months. Violation of eruption juices is the main sign of the presence of anomalies in the development of the dentofacial apparatus;
- pairing: during the period of primary occlusion, simultaneous eruption of antagonist teeth occurs on both sides of the jaw. Growth retardation of one of them for a period of no more than 1 month is the norm. A more significant violation of pairing may signal disturbances in the development of the jaw, for example, slow growth of bone tissue.
Consequences
What are the consequences of incorrect occlusion, and why is it important to correct a child’s bite in a timely manner? Proper closure of the dentition promotes high-quality chewing of food and evenly distributes muscle load (so that the temporomandibular joint does not suffer).
Correct closure depends on:
- straight posture;
- correct articulation;
- blood circulation of the brain;
- symmetrical facial features;
- gastrointestinal health.
Also, the health of the mucous membranes and soft tissues of the oral cavity depends on proper closure. With uneven chewing load, those parts of the periodontium that are most loaded suffer.
How is a milk bite different from a permanent bite?
Signs of a milk bite are:
- the length and radius of the upper tooth are usually greater than the same parameters for the lower tooth;
- the dentitions have a semicircular, symmetrical shape;
- the interdental space of the front teeth coincides on the upper and lower jaws;
- not all teeth of the same name touch each other;
- the enamel is intact and does not wear off;
- There is no overlap of the lower row of teeth with the upper ones.
As the dentofacial system develops, these signs become less pronounced and completely disappear by the period of permanent dentition.
The main difference between a temporary bite and a permanent one is the number of teeth. With a permanent bite, there are normally 32 of them, and with a milk bite there are only 20. The shape of the teeth also differs: temporary teeth have a more convex shape with a pronounced relief, while permanent teeth are smooth and flat.
What it is?
The period of formation of temporary teeth begins at the 20th week of pregnancy, when all the rudiments are formed in the fetus. The first baby teeth appear only 5 or 6 months after birth and continue to grow until about six years of age.
Concept
Temporary type occlusion represents the initial phase of the formation of permanent dentition. During this period, the foundational basis for the proper development of the dentofacial apparatus is laid.
The primary occlusion is characterized by the gradual sequential eruption of teeth, whose characteristics differ from permanent ones.
Stages
Temporary occlusion, from the moment the first tooth appears until the last one is fully formed, goes through two stages:
- Emerging .
It is counted from the appearance of the first specimen, which occurs at the age of about 6 months and continues until 3 years. During this interval, active eruption and growth of primary teeth occurs. Despite the fact that the bite is considered to be developing, with a 2-year-old child it is already recommended to visit the dentist, since after the appearance of the incisors, deviations in the development of the dentition or jaw arch can be identified and corrective treatment can be prescribed, which will quickly correct the situation. - Formed. This stage refers to the age period from 3 to 6 years. The period of formed occlusion is characterized by the presence of all temporary teeth and active growth of the jaws.
The tissues of the alveolar ridge begin to prepare for the growth of molars, the appearance of which means the development of a removable and then permanent dentition.When the temporary dentition is fully formed, its anomalies and deviations in the development of the jaw apparatus can be determined independently.
Our next review is devoted to the topic of possible complications of malocclusion.
In a separate article we will tell you how long a child should wear braces.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/okklyuzii/pravilnyiy-prikus-u-cheloveka-raznovidnosti-i-foto.html we will talk about what constitutes a correct bite of a person’s teeth.
How to prevent the development of anomalies?
Some parents mistakenly believe that deviations in the development of the jaws at the stage of primary occlusion are only temporary and do not need to be treated. This is wrong.
To prevent possible serious consequences that arise already during permanent occlusion, parents need to visit the dentist in a timely manner - the first visit should take place at the age of 2-3 years, if indicated, it is necessary to undergo an examination by an orthodontist.
It is also necessary to prevent the development of harmful orthodontic habits in a child: prohibit gnawing and sucking objects, intentionally swallowing incorrectly, breathing through the mouth with normal nasal breathing.
Causes of pathology
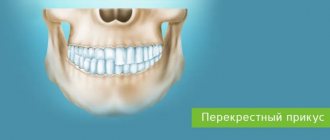
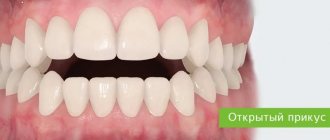
The most common occlusion defects are open or cross bite. Also common defects include a large distance between units, a sagittal gap. The reasons for the development of anomalies can be various factors. But more often, defects originate at the stage of intrauterine development of the baby. A genetic predisposition cannot be ruled out.
Pathologies in the development of the dental system can appear as a result of bad habits: prolonged pacifier sucking, thumb sucking in sleep.
Sometimes the shape of the pacifier and improper grip of the nipple by the lips of the newborn are directly related to the incorrect formation of occlusion. Timely diagnosis of the cause will allow you to find optimal methods for correcting the defect.
Possible reasons for the formation of a pathological bite:
- maxillofacial injuries;
- absence of a large number of molars;
- musculoskeletal disease;
- presence of bad habits;
- foreign objects in the baby's mouth;
- breathing through the mouth;
- infantile type of swallowing.
Malocclusion is also directly affected by untimely eruption of permanent molars.
Myths and reality
Everyone knows that milk bite is not permanent.
Sooner or later, baby teeth are replaced by those that a person uses for the rest of his life. But few people think that the quality of permanent teeth directly depends on the condition and care of milk teeth. The first most common misconception about children's teeth is that baby teeth do not need to be treated; they will fall out anyway. The misconception is as widely known as it is stupid. I would even say dangerous for the child’s health. Caries is an infectious process that affects baby teeth quite quickly and deeply. Along with the baby teeth, the child’s mouth contains unerupted permanent teeth. If we ignore caries on baby teeth, then when they erupt, we end up with permanent teeth affected by caries. Caries that has deeply affected baby teeth and transferred to permanent ones is also enamel dysplasia, pigment spots, irregularities and other anomalies of future teeth and bite. A good start to the life of permanent teeth? Don't think. Visiting the dentist from childhood, knowing and following the rules of hygiene is a necessity for a child and an obligation for parents who care about the health of their children.
Another common misconception leading to the appearance of malocclusions and improper tooth growth is the early, unjustified removal of baby teeth. A child's jaw is not developed, rapidly growing and ill-considered removals can lead to the appearance of malocclusions in the future. Nature does not tolerate emptiness, and the place of the extracted tooth will quickly be taken by neighboring ones. There simply won’t be room for a permanent tooth germ at the right time. Naturally, it will erupt anywhere, but not in its place. If removal cannot be avoided, special orthodontic structures come to the rescue, which will hold adjacent teeth and maintain the necessary space for eruption. Otherwise, braces will help you by the age of 12-14.
And just in time, another frequently asked question about braces: are braces placed on baby teeth?
Definitely no.
Until the roots have formed and the permanent teeth have completely erupted, braces cannot be installed. And installing a brace system too early does not lead to anything good. The optimal time for correcting a bite with braces is 12-18 years. But this does not mean that the first meeting with orthodontists should occur at this age. I recommend taking your child to an orthodontist once a year, starting at age five. This will save you, at a minimum, money in the future and will provide your child with a correct bite and a beautiful profile by maturity. In the doctor’s arsenal there are many devices that correct primary occlusion: silicone mouth guards, trainers, plates, non-removable functional devices…. Among them is the miracle invention of modern orthodontics: the Haas apparatus. I won’t go into details, you can read about him and his abilities here. Just think about it: 80% of children who come to me for consultation have indications for installation and bite correction with a Haas apparatus. I am convinced that competent early bite correction significantly reduces the likelihood of correcting the bite with braces in adolescence. Prevents the possibility of orthognathic surgery. And even if braces cannot be avoided, then after early correction of the bite, the complexity of the anomaly, as well as the treatment and time frame, are much simpler and shorter. Therefore, dear parents, go to a consultation with an orthodontist with your child. It is important.
Pulpitis and periodontitis are not scary for children, these are diseases for adults
Absolutely unsubstantiated, erroneous opinion. Children, just like adults, suffer from these ailments. Moreover, due to the structure of the baby tooth (large pulp chamber and neurovascular bundle compared to hard tissues), even with small advanced caries, the carious cavity may end up close to the nerve and then pulpitis rapidly develops - a harbinger of periodontitis. Remember, caries, pulpitis and periodontitis develop much faster in children than in adults. Visit the dentist's office once every six months for preventive care and for the sake of your children's health. Don't forget about your teeth)
Correct dental occlusion in children
Correct bite can be determined by the following signs:
- the upper dentition covers the lower one by one third;
- the teeth of one jaw are in contact with the antagonists of the second jaw arch;
- there are no gaps or cracks;
- The midline of the face runs exactly between the front incisors.
The above characteristics refer to the ideal relationship of the dentition - orthognathic. However, three more bite options are considered correct.
- Straight
- when closing, the teeth of both jaws touch each other with a sharp edge. - Biprognathic
- the front teeth are inclined in the direction of the lips, but are in contact with the antagonists. - Progenic
- the lower jaw arch moves forward slightly.
Pediatric doctor vs. Adult doctor
I would also like to dispel the incorrect belief that a child can also be treated by an adult doctor. So, there is a clear distinction between doctors for children and adults. These are different departments at universities. Other approaches, and as for dentistry, other materials for filling and dental treatment. These materials are simply not available in adult dentistry. And materials for adults can harm a child’s body. As I mentioned above, there is a difference in the structure of a child’s and an adult’s tooth, this must be known and taken into account. A child is physically smaller than an adult - accordingly, the tools, at least turbine tips, should be somewhat smaller than usual. A pediatrician must have not only an appropriate certificate, but also extensive experience in communicating with young patients. A child is often afraid of the strict environment of an adult medical facility, while modern dental clinics aimed not only at adults are equipped with screens with cartoons, pleasant design, and most importantly, gentle, patient doctors.
IV PERIOD - from 3 to 6 years (the period of formed temporary occlusion)
Prevention of dental anomalies:
- plastic surgery of a shortened or improperly attached frenulum of the tongue
- complexes of therapeutic exercises to normalize lip closure, position of the lower jaw and tongue at rest and during functions
- combating sluggish chewing, avoiding eating hard foods, learning to swallow correctly
- learning the correct pronunciation of individual sounds (“r”, “l”, hissing)
- planned sanitation and hygiene of the oral cavity using special-purpose products
- monitoring the depth of the incisal overlap and the shape of the dental arches
- identification of postural disorders, flat feet, teaching correct body position while standing, sitting, lying, walking
- introduction to outdoor games
Correction methods
Early identification of the problem and timely correction is the path to successful correction of occlusion. The correction technique is selected individually.
Correction methods:
- special gymnastics;
- removable plates;
- aligners, aligners;
- braces;
- trainers;
- surgical correction.
With the help of special gymnastics, minor occlusion defects can be leveled. The child also breaks the habit of bad habits that led to improper closure: thumb sucking, addiction to a pacifier.
Removable plates are installed for children under 14 years of age. These are special orthodontic devices made of polymer materials that are attached to the teeth using hooks. The purpose of the plate is to form the jaw. If a child has a naturally narrow jaw, the plate stimulates its growth. If the jaw is wide, the plate prevents it from expanding even more.
Aligners are custom orthodontic appliances made from an impression of the patient's jaw. Modern aligners can also be worn by adult patients; they are a successful alternative to braces. If mouth guards are prescribed to children, parents should constantly monitor them. Children do not realize the importance of the issue and may secretly remove the aligners.
Braces are prescribed only to children over 14 years of age, as well as adults. This is an effective way to correct occlusion, but is quite inconvenient. Caring for your mouth while wearing braces is difficult. The method also causes pain at the initial stage of addiction.
Trainers correct occlusion and also correct other defects of the dental system. First, the patient wears soft silicone trainers, then puts on a more rigid structure.
Surgical intervention is prescribed for severe anomalies when hardware methods do not produce results. This happens in rare cases.
II PERIOD - from birth to 6-9 months (before the eruption of the first milk teeth)
Prevention of dental anomalies:
- identification of congenital anomalies (cleft palate, lip) and development of a treatment plan
- rational regimen and balanced nutrition of mother and child
- breastfeeding baby
- correct artificial feeding of the child: correct positioning during feeding, preventing pressure from the neck of the bottle on the alveolar process, regulating the child’s efforts when sucking by squeezing the mother’s breast with the fingers, correct selection of the hole in the nipple, the length of the nipple and the degree of its insertion into the oral cavity, monitoring regularity swallowing
- identifying prematurely erupted teeth and deciding on their removal
VI PERIOD - from 9 to 12 years (the final period of the mixed dentition)
Prevention and treatment of dental anomalies:
- planned sanitation and training in oral hygiene using special-purpose products
- identification of dental anomalies and their orthodontic treatment
- selective grinding of unworn cusps of temporary canines and molars
- plastic surgery of the shortened frenulum of the tongue, lips (according to indications)
- removal of erupted or impacted supernumerary teeth
- identification of impaired posture, flat feet, torticollis. Therapeutic exercises and consultation with an orthopedist
- combating bad habits and incorrect postures, including during sleep
- therapeutic orthodontic gymnastics to normalize lip closure, nasal breathing, posture
- teaching proper chewing, swallowing, speech
- monitoring the sequence of eruption of premolars, canines, second molars, finger massage in this area
- rehabilitation of ENT organs
First year: attention to congenital characteristics
Immediately after birth, the baby is examined by a neonatologist. This is necessary to detect possible developmental abnormalities, for example, defects of the palate, which occur approximately once in 2,500 children. Most birth defects need to be corrected surgically at an early age to avoid problems with health, nutrition and speech development.
At one month, the child should be shown to the dentist - by this time you may notice a shortening of the frenulum of the tongue. If the tongue is pulled too far towards the lower jaw, it will negatively affect the development of the bite.
A short frenulum is also a cause of difficulties with breastfeeding
Trimming the frenulum of the tongue is a very simple and quick procedure that is performed right at the appointment and does not cause any discomfort to the child.
Ways to correct a bite
Correction of the bite of primary teeth, depending on the correction means used, is of three types:
- Preventive. It is implemented by installing artificial plastic teeth in case of premature loss of milk teeth. Thus, it is possible to maintain the functional load on the jaw bones and chewing processes. And the place of a previously fallen milk tooth is preserved for smooth growth and development of the permanent one.
- Expanding. Using removable plates to make room for existing teeth to grow, develop and straighten. Such correctors are made from special hypoallergenic plastic on an individual basis. The plates come in different colors with glitter, hearts and smiley faces. Such variety will allow the child to enthusiastically choose the design of the devices he likes.
- Activation. Installation of silicone devices in which you need to stay during sleep and for two hours during the day. The soft material of these devices provides comfort at night, and their excellent suction properties ensure a strong hold on the teeth.
Prevention
But the most important thing in the prevention and prevention of dental diseases, I never tire of repeating, is the responsibility of parents, by their own example, to teach their child to brush their teeth correctly. Daily, twice a day, at least 2-3 minutes per brushing. It would be a good idea to teach how to use dental floss or brushes to clean the spaces between teeth. The movements of the brush over the teeth should be sweeping; you should not vigorously rub or press on the brush. This is harmful to the teeth, especially if it moves in a horizontal plane.
A child needs a good children's toothpaste and there is no need to skimp on it. Firstly, there are no abrasive particles in children's toothpastes. They are not added to children's toothpastes, because a child's enamel is softer than an adult's tooth enamel; abrasive particles will simply scratch children's teeth. Secondly, good baby toothpastes are hypoallergenic and do not contain fluoride, calcium or other substances. However, adults do not feel any particular need for these supplements. They are added to the paste by the manufacturer at the insistence of marketers and advertisers. Let me remind you that children tend to swallow “tasty” paste, so high-quality children’s paste is absolutely safe if swallowed.
The same applies to brushes; children’s brushes should be an order of magnitude softer, and the brush head should be smaller compared to an adult. In addition, modern children's toothpastes and brushes are varied in their design and, with cheerful colors and shapes, stimulate children to this difficult, but so important process. You need to get used to brushing your teeth from an early age. To begin with, you can use your mother’s finger instead of a brush, gradually accustoming your baby to the taste of the paste and new sensations. Finger brushes also appeared on sale. They fit perfectly in place of the first brush.
I’ll say a few words about electric brushes. I was convinced from my own experience that electric brushes are a good thing for little, sleepy lazy people. I really liked the model with a small addition. A watch on a suction cup that controls the cleaning time and gives the child a rating in the form of crystals or emoticons from sad (cleaning for less than a minute) to happy (three or more minutes). Great morning incentive. However, do not forget to change the attachments and brushes every 1-2 months. Teach your children to wash and dry their brushes. Stubble is an ideal breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms. Do not use brushes with natural bristles. This is the last century and besides, natural bristles are hollow inside - an excellent refuge for bacteria. Change the brush after ARVI, flu and other diseases of the respiratory system. There is a high probability that the disease will return through the brush. Daily hygiene should not become a duty, duty or periodic task, but a natural everyday routine. I cannot give universal advice on how to convince a child of the need for this process, but I explained this issue based on the consequences of poor hygiene. She showed pictures of teeth affected by caries and other diseases. She talked about the unpleasant smell and the attitude of others towards it. In general, it worked.
Children and adults will also benefit from AirFlow professional hygiene, which removes plaque. As well as removing subgingival deposits and tartar using ultrasound. The procedures are safe and beneficial. They must be carried out at least once a year. I also recommend that children undergo fissure sealing. Permanent teeth must be protected from a young age. Fissure sealing is carried out on the chewing surface of permanent teeth. First, plaque is removed from the chewing surface of the tooth, and all cavities are treated with ultrasound. Then treatment with an antiseptic, application of sealant and highlighting. Polishing... and the most problematic areas in terms of caries are reliably sealed with a composite material that is stronger than enamel. In addition, the light-curing polymer composite is not subject to destruction by bacteria.
Bottom line
A correct bite is not only about a beautiful smile. Health, symmetry of facial features, and psychological comfort depend on it. The baby bite differs from the adult bite in the number of teeth (there are only 20), but the formation of the entire dental system depends on it. It is in childhood that it is easiest to correct occlusal defects, so parents should show their child to an orthodontist as early as possible.
Sources used:
- Guide to prosthetic dentistry, ed. A. I. Evdokimova, M
- Handbook of Dentistry, ed. A. I. Rybakova and G. M. Ivashchenko, M.
- Klineberg I., Jaeger R. Occlusion and clinical practice. - 2nd ed. - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2008.
- Academy Of Prosthodontics
A little about harmful things.
And in conclusion about the painful issue. About sweets. I am amazed at the quantity and availability of sweets for modern children. Dear parents, sweets may be, somewhere, somehow useful for brain activity, but they are completely useless and dangerous for the child as a whole. If you don’t care about multiple caries, which the doctor will probably cure, then take pity on the child’s pancreas and gastrointestinal tract. Excessive consumption of sweets puts an end to health and leads to a whole range of serious diseases and metabolic disorders.
As a mother, I understand that it is impossible to completely limit sweets, but we can protect our child from especially unnecessary foods. Try to exclude viscous sweets, chocolate with nuts, halva, toffee and caramel - they perfectly clog all cavities and are an ideal breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria. Difficult to clean. All this can be replaced with high-quality dried or candied fruits. Eliminate carbonated sugary drinks from your diet. Phosphoric acid and carbon dioxide, which are part of them, successfully corrode not only tooth enamel, but also the stomach, contributing to gastritis. Compotes and fruit drinks are quite easy to cook; they are without gas, sweeteners and dyes. Buns, cheesecakes, cookies and cakes form fat well and contain a large amount of vegetable = palm oil of unknown quality - replace them with fruit and grandma's pancakes.
Engage in hygiene and prevention issues with your children. Don't forget to visit your dentist and orthodontist regularly. Remember that for a child, there is nothing more convincing than your personal example and be healthy!