Polyps in the throat have many manifestations; the most commonly diagnosed are benign neoplasms located on the tonsils and vocal cords. The period of polyp growth can last up to several years, so when they appear, you should contact a specialist to undergo diagnostics and determine treatment tactics.
When patients come to the Yusupov Hospital with any symptoms of this disease, the oncologist conducts an examination and prescribes diagnostic procedures to identify the shape, size and location of polyps. After examination, polyps in the throat are quickly and painlessly removed by surgeons.
Laryngeal papilloma. Symptoms
Symptomatically, laryngeal papillomatosis can be represented by hoarseness, chronic cough, difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing, recurring respiratory infections, and growth retardation in children. The presence of certain symptoms depends on the location of the papillomas. In children, the symptoms are more pronounced, since they have a significantly faster growth of papillomas, unlike adults. This can lead to situations in which emergency intervention is required for life-saving reasons, despite the histologically benign course of the disease. The prognosis is more favorable in terms of remission if the disease manifests itself in adulthood. The exception is the presence of HPV type 11 and the duration of the disease for more than 10 years.
Cyst or papilloma?
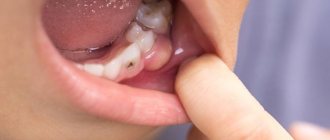
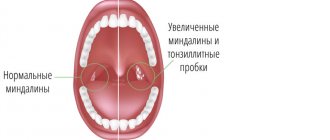
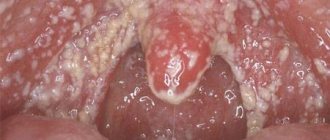
Cysts are different. The most common is a formation in the palatine tonsil. “For example, a person has developed chronic tonsillitis, the tissues of the tonsils are affected, plugs form in the thickness of the palatine tonsils - you can quite see them yourself by opening your mouth wider and looking into it with a flashlight. They look like an accumulation of pus,” says Vladimir Zaitsev.
At the same time, people do not know what to do with such formations. Either you need to ignore them - they will go away on their own, or go to the doctor, or try to squeeze them out on your own. There are situations when they are removed incorrectly. “And this content, which has been in the thickness of the tonsil for a long time, begins to encapsulate. This capsule is transparent, against which no one can see it, and no one can understand why the contents do not come out. It is clear that it will not come out, and a cyst will form. It may be small, but after a while it will begin to increase in size. And the more tonsillitis continues to rage, the larger it will become,” says the ENT specialist. The specialist notes that cysts can form in both one and two tonsils, which means you should not lead to polycystic disease - it is better to contact specialists as early as possible.
Article on the topic
Don't get cancer. How bad habits affect the appearance of cancer It is also worth understanding such a thing as the presence of another type of formation in the throat. We are talking about papillomas. These papillomas can occur on the soft palate, palatine tongue, and on the back wall of the pharynx. “In fact, this is not a cyst, but quite often people regard it as such - they see that the formation is whitish, and there may even be some kind of liquid in it. In fact, for a person there is not much difference. But the doctor, on the contrary, should show more attention,” notes the otorhinolaryngologist.
For the patient, the recommendation here is simple - do not try to eliminate it yourself. It is no secret that many people try to gnaw off their own papilloma, bite it off, tear it off, etc. “This is fundamentally wrong, since papilloma requires morphological examination. A cyst, in principle, too, but to a lesser extent. And the doctor must evaluate the papilloma, determine whether there is a tendency towards malignancy, whether it is cancer initially,” says Vladimir Zaitsev.
Causes of laryngeal papilloma. Who is at risk?
The etiological factor is human papillomavirus (HPV), in most cases types 6 and 11. The latter leads to a more severe course of the disease. Less commonly, laryngeal papillomatosis can be caused by HPV types 16 and 18, which are viruses with a high risk of developing malignant neoplasms. However, the presence of HPV in the human respiratory tract does not always lead to papillomatosis. Determining factors can be immunodeficiency states and chronic infections. Concomitant infection with the herpes simplex virus and the Epstein-Barr virus contribute to a more aggressive course of the disease.
Laser removal of papilloma in the throat. Progress in medicine helps.
The main thing is to keep up with it and take advantage of all the new opportunities. In the treatment of papillomatosis, these include the use of CO2 laser, narrow-spectrum endoscopy and certain antiviral drugs. But there is one prerequisite to achieve the best result - everything must be performed by a highly qualified surgeon with extensive experience in treating laryngeal papillomatosis. This is extremely important to understand.
Papillomatosis is characterized by the formation of exophytic growths that affect the mucous membrane of various parts of the larynx and underlying parts of the respiratory tract.
Diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal cancer
How to diagnose throat cancer in the early stages? If there are symptoms of throat cancer, diagnosis should be comprehensive. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital diagnose cancer of the throat and larynx using the following methods:
- Direct and indirect laryngoscopy,
- Hypopharyngoscopy;
- Computed tomography;
- Histological examination;
- Trial laryngofissure;
- Cytological examination of prints from the larynx and lymph nodes;
- Determination of tumor marker levels.
How to recognize throat cancer? Otolaryngologists first perform indirect laryngoscopy. When examining the true vocal cords, attention is paid to their mobility during phonation and the asymmetry of the lesion inherent in the tumor process, and the size of the tumor lesion and its location are specified. To examine the posterior parts of the larynx, they are examined with a laryngeal mirror from bottom to top, when the doctor sits in front of a standing patient.
How to diagnose throat cancer in an elderly person if the picture is not clear enough or if the tumor is masked by secondary inflammatory phenomena with decay, infiltration and edema? In this case, otolaryngologists resort to local anesthesia, elevating the epiglottis, palpating with a probe, using a magnifying mirror, and also tilting the patient’s head accordingly. If a lesion of the subglottic region or lower parts of the pharynx is suspected, direct laryngoscopy and hypopharyngoscopy are used.
How to check your throat for cancer using computed tomography. This research method expands diagnostic capabilities for tumors that are localized in the area of the ventricular and true vocal cords and laryngeal ventricles, as well as when the tumor has spread to the subglottic region. At the Yusupov Hospital, patients are examined using the latest generation computer tomographs with high resolution capabilities.
How to check the throat and larynx for cancer using laboratory methods? Histological examination determines the nature of the tumor, its structure, the degree of differentiation of cellular elements and the degree of malignancy of the tumor - all these details influence the course of the disease and are taken into account when choosing a treatment method
To avoid stimulation of increased growth and spread of the tumor process due to damage to the lymphatic and blood vessels during biopsy, oncologists perform several sessions of radiation therapy before surgery.
How to diagnose laryngeal cancer using other methods? In cases where the biopsy data are not convincing enough or it is impossible, a trial laryngofisure is used. Since during the procedure, contamination of surrounding tissues with atypical cells may occur, in such cases, a histological examination is urgently performed at the operating table, having previously obtained the patient’s consent for radical intervention. Cytological examination of prints from the larynx and lymph nodes is carried out in cases where the patient categorically refuses surgery and a biopsy is not indicated.
How to detect throat cancer at an early stage? For early diagnosis of throat and larynx cancer, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital examine the level of tumor markers SCC and CYFRA 21-1. Highly qualified doctors, equipping operating rooms with modern diagnostic equipment and instruments allows oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital to improve five-year survival rates for throat cancer.
How to treat laryngeal cancer? Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital have extensive experience in treating laryngeal cancer. The treatment method is selected depending on the stage of the disease, type and spread of the tumor. The following methods are used:
- Surgical interventions (chordectomy, laryngectomy);
- Organ-preserving laser surgery for laryngeal tumors;
- Operations to remove tumors using a shaver;
- Radiation treatment (external gamma therapy);
- Neoadjuvant, adjuvant and curative chemotherapy;
- Palliative treatment.
Expert opinion
Author: Alexey Andreevich Moiseev
Head of the Oncology Department, oncologist, chemotherapist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Throat cancer accounts for 3% of all cancers. At the same time, the tumor is the most common among neoplasms of the upper respiratory tract. It is diagnosed in 50–70% of cases. As throat cancer progresses, permanent disability occurs. As a result, the tumor remains a problem for clinical medicine.
Recently, in Russia there has been an increase in the number of newly diagnosed throat cancers. This is due to the influence of external and internal factors. Around the world, the statistics are no less comforting. Every year 15,000 new cases of pathology are diagnosed. The ratio of sick men to women is 1000:8.
The Yusupov Hospital provides a full course of diagnostics necessary to identify pathology even at the formation stages. The earlier the examination is performed, the more favorable the prognosis. The quality of treatment meets international standards. An individual therapy and rehabilitation program is developed for each patient, aimed at improving the quality of life and preventing relapse.
The main treatment method for laryngeal cancer is surgery. Radical surgical intervention for a malignant tumor is removal of the larynx. The consequences may vary. After surgery, some patients lose their voice and tumor growth resumes.
A laryngofissure is applied when the exophytic tumor is localized on the free edge of the anterior two-thirds of the true vocal cord, without the tumor spreading to the anterior commissure and the arytenoid region.
If a significant area of the larynx is affected by the cancer process, and mobility in the affected area is very limited or even completely absent, the process is macroscopically one-sided, surgeons perform throat surgery for oncology - resection of half of the larynx. Hemilaryngectomy is indicated not only for internal cancer that does not grow through the cartilage of the larynx, but also when the tumor process has spread to the anterior commissure and the area of the arytenoid cartilage.
If the tumor is localized in the anterior two-thirds of one true vocal cord with transition to the anterior commissure or even to the anterior part of the other true vocal cord, a half resection of the larynx according to Otan is performed. During this operation, the anterior parts of the larynx are removed, leaving its posterior wall. After the intervention, swallowing and voice function are preserved. Partial surgical interventions for laryngeal cancer include frontal resection of the larynx. It is used for damage to the anterior commissure.
Currently, the most common organ-preserving operations for localized laryngeal cancer remain chordectomy and diagonal resection of the larynx. After surgery, patients' voice function is impaired; they note hoarseness, fatigue during conversation, and a significant deterioration in sound when overloaded. An undesirable consequence of sagittal resection of the larynx is a disorder in swallowing after surgery.
How to cure throat cancer at an early stage? Laryngeal surgery (tumor removal) is performed using a shaver. During the operation, healthy tissue is not injured. The operation is performed endoscopically. A tracheostomy for laryngeal cancer is performed after total removal of the organ. The Yusupov Hospital provides nutrition after removal of the larynx for throat cancer.
Throat cancer is treated with anticancer drugs. Oncologists practice two treatment options: monotherapy and polychemotherapy. In monotherapy, one drug is used, to which cancer cells are especially sensitive. The drug is prescribed in large doses. For polychemotherapy, several cytostatic drugs are used sequentially or simultaneously.
Chemotherapists at the Yusupov Hospital use combinations of cytostatics recommended by the International Association of Oncologists to achieve the greatest effectiveness of treatment. They use drugs that are highly effective and have minimal side effects. Patients at the Oncology Clinic have the opportunity to receive the latest anticancer drugs thanks to a research program in which the Yusupov Hospital participates. The effectiveness of radiation therapy for throat cancer is assessed by professors and doctors of the highest category.
A combined approach to the treatment of laryngeal cancer can improve treatment results. Radiation therapy for throat cancer is used both as primary treatment and as part of combination therapy. Is there a cure for throat cancer? Most patients with early stages of laryngeal cancer are cured with radiotherapy. How suitable radiation therapy for laryngeal cancer is for a particular patient depends on the volume and location of the tumor, and is determined by the depth of its growth in the throat tissue.
In the early stages of the disease, treatment in most cases is carried out with radiation sessions 5 times a week for 3-7 weeks. The radiotherapist calculates the total radiation dose to laryngeal cancer for the entire course, and then divides it into fractions. This separation allows you to reduce the undesirable consequences of treatment. Can throat cancer be cured? If complex treatment is started on time, the prognosis for recovery improves many times over.
More than 10 years without recurrence of papillomatosis.
All patients treated by Professor Roberto Pujedo have not experienced a relapse of the disease for more than ten years .
“A comprehensive approach is a key success factor. Starting with detailed diagnostics using cutting-edge technologies, ending with careful monitoring in the postoperative period.”
Along with the expertly performed complete removal of papillomas, Professor Roberto Pujedo carries out targeted administration of antiviral drugs into the mucous membrane of the affected areas of the larynx.
Reliable source:
Enhanced contact endoscopy (ECE) in head and neck surgery
Many patients talk about dozens of surgeries in their history and endless relapses. It seems that it is impossible to cope with this disease. Each time the voice becomes worse, numerous scars form in the larynx.
Now this is history!
Possible methods of treating laryngeal papillomas.
Careful removal of papillomatous growths under a microscope and using a CO2 laser is fundamental. However, removal must be carried out exclusively within the mucous membrane, where the formations are located. Moreover, the normal mucosa must be preserved. The surgeon must be experienced and thoroughly understand the mechanism of papillomas formation. Otherwise, gross surgical intervention leads to loss of voice, severe scarring, and stenosis.
Studies have shown that intraepithelial administration of antiviral drugs can reduce the number of operations to remove papillomas, leading to partial regression of the growth of formations. Also, local administration of an antiviral drug avoids systemic toxicity.
The mechanism of action of interferons in laryngeal papillomatosis is unknown, however, they are often used as an additional treatment. Interferons are naturally produced by white blood cells in response to various stimuli, including viral infection. They bind to specific cell membrane receptors and change metabolism, providing antiviral, antiproliferative and immunomodulatory effects. The clinical effectiveness of interferons in the treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis is ambiguous and controversial. The main limitation for their use are side effects when administered intravenously: increased levels of transaminases in the blood, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. Patients may experience weakness, nausea, fever, arthralgia, and headache.
Indol-3-carbinol can be extracted from cruciferous plants (broccoli, cabbage). In vitro studies have shown promising results on the growth of papillomas by influencing estrogen metabolism. When administered orally to a small number of pediatric patients, no adverse effects were observed. However, the clinical effectiveness of this drug remains in doubt.
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccine . A prospective randomized controlled trial showed that intraepithelial administration of MMR vaccine could prolong the period of remission after surgical treatment.
HspE7. A new vaccine targeting oncogenic HPV types has also been used to successfully control relapses of laryngeal papillomatosis.
The presence of GERD was associated with an increased likelihood of complications. The irritating effect on the mucous membrane can act as a trigger for the proliferation and spread of papillomatous growths. Studies have shown that the use of drugs to treat GERD promotes better control of laryngeal papillomatosis and prolongs remission.
According to a Cochrane review, photodynamic therapy has not been shown to be effective in the treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis.
Watch the video BEFORE/AFTER surgery to remove laryngeal papillomatosis
Relapse-free postoperative follow-up for a year. Endoscopy in NBI mode. Credit: Professor Roberto Pujedo.
Look at the photos BEFORE/AFTER the operation by Prof. Roberto Pugedu
Photos “before” and “after” surgery to remove laryngeal papillomatosis. Credit: Professor Roberto Pujedo.
Move the slider to see the difference.
Treatment of tonsil plugs
When contacting an ENT doctor, the patient is offered conservative treatment, which includes washing the tonsils, physiotherapeutic procedures and drug therapy.
There are two methods of rinsing: removing pus with a syringe and hardware rinsing. The method using a syringe is used much less frequently if the patient has a strong gag reflex. The most effective method is to wash the tonsils using a vacuum method using the Tonsillor apparatus. In our ENT clinic, we use a special vacuum attachment for this, which has no analogues today! With the help of this attachment, it is possible to effectively and painlessly wash the entire contents of the lacunae of the tonsils, and improve the patient’s condition after the first session.