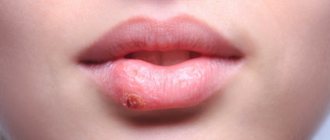
The oral cavity is covered with mucous membrane. Inflammation of this layer of epithelium is stomatitis. The disease is a response of the immune system to the occurrence of unfavorable factors. Previously, stomatitis was considered an exclusively childhood disease, but today it is increasingly affecting adult patients. Often the areas affected by the disease are the lips, cheeks, and palate.
Types and forms of lip cancer
Malignant formations of soft tissues are not uncommon; they are formed literally “out of nothing.” This is what is commonly believed, but in reality not everything is so simple.
The appearance of a tumor is associated with several factors. Previously, it was believed that smoking and addiction to alcohol were to blame. Now, the risks of cancer are increasing due to frequent infection with the human papillomavirus.
There are several types of malignant process; it is worth noting that oncological formations of the lip are rarely reactive in nature (that is, they develop rapidly).
What classification does the disease have?
- Squamous cell keratinizing cancer develops slowly, the disease involves new tissues in the process, but metastases rarely appear. Due to the long course of the pathological process.
- Squamous cell non-keratinizing cancer is characterized by rapid development, the process involves nearby tissues, and metastases affect the lymph nodes of the jaw and submandibular region.
It is worth noting that in comparison with other types of malignant process, cancerous tumors of the lips rarely metastasize, but it all depends on the stage of development of the disease:
| At the first stage: | As the disease progresses, the chances of metastases increase and are: | At stage 3: | If the pathological process reaches its final stage: |
| metastases appear only in 5-8% of cases. | no more than 20%. | metastases appear in 35% of patients. | then metastasis is observed in 70% of patients. |
If we talk about the forms of the disease, there are only 3 of them:
Prevention
The most common reason for the onset of the disease is injury to the oral mucosa. That is, damage is the first thing to watch out for. Sharp edges of teeth, broken or poorly filled, burns and other factors that can lead to minimal wounds should be excluded. In addition, it is recommended:
- Carefully observe hygiene, both in the mouth and elsewhere - wash food before eating, keep your hands and nails clean.
- Brush and floss your teeth carefully, and do not use low-quality toothpastes.
- Keep dentures, if any, clean.
- At the first alarming manifestations, immediately contact your dentist.
- Monitor the general condition of the body and digestive system.
- To refuse from bad habits.
Paying attention to your body and timely visits to dentistry in Moscow at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences will help you avoid the disease or stop it at the very beginning, avoiding complications.
Causes and risk factors
Any disease has causes; you should include a list of factors that can provoke the formation of a cancerous tumor of the lip:
- Bad habits: alcohol, nicotine.
- Infectious diseases of soft tissues.
- Metabolic disorders in the body.
- Exposure to the sun's rays.
- Mechanical injuries to the skin of the lips.
- Surgical interventions in this area.
- Poor heredity, predisposition to cancer diseases.
- Poisoning with chemical reagents, which is systematic.
- Contact with carcinogenic substances.
The risk of developing the disease increases if a person has ulcers and erosions of the skin of the lips. When damage does not heal over a long period of time, the risk of secondary infection increases. As a result, the risk of developing atypical cells in the tissues of the lips increases several times.
The seal, consisting of connective tissue, can “degenerate”. A similar thing happens with formations (papillomas, warts, creatures).
Effect of smoking
Addiction to tobacco has been linked to various forms of cancer. Including malignant formations of the lip. With systematic contact with tobacco smoke, the human body is “saturated” with carcinogens (combustion products). As a result, the risk of developing cancer diseases increases significantly.
What happens to lip tissue with systematic tobacco use:
- contact with cigarettes thins the skin;
- microcracks and erosions form on the lips, invisible to the human eye;
- tobacco smoke successfully penetrates microcracks, leading to the development of a malignant process in tissues.
If a person has a cracked lip, wound or damage to the tissue in this area, the risk of developing cancer increases.
But not only cigarettes are dangerous for humans; smoking a pipe, chewing tobacco leaves and using nasvay can also have a detrimental effect on a person’s health.
The appearance of infectious processes on the lips, cracks, the development of inflammation in the tissues - all this is regarded as a precancerous condition. Although there may not be any atypical cells in the affected area. But only diagnostic measures can refute or confirm this fact.
Causes of stomatitis
There are several reasons that provoke stomatitis:
- The addition of infection is viruses and bacteria, which very quickly colonize, revealing damaged areas of the mucous membrane.
- Poor nutrition – if the diet is too poor, the body does not have enough strength and resources to fight the pathogens attacking it.
- Wounds and other injuries in the mouth - these can be scratches from sharp edges of teeth with carious cavities, bitten cheeks, cracked lips, burns.
- Improper oral hygiene - insufficient cleaning leaves plaque on the tooth and tongue, in which bacteria multiply very quickly.
- Insufficient hygiene in general - dirty hands, unwashed fruits, which become sources of bacteria.
- Consequences of dental intervention performed in violation of norms.
- Using pastes with sodium lauryl sulfate, which reduces salivation. In such a situation, the epithelium may dry out and, as a result, not be sufficiently resistant to bacteria.
- Alcohol and smoking.
- Chronic diseases of a general nature that affect the state of the body, digestion of food, and other vital processes.
Symptoms and first signs
It is known that cancer begins to manifest itself at a time when it is too late to treat it. But if we are talking about lip cancer, then its first signs appear long before the formation of metastases.
Most often, patients complain:
- For the appearance of a lump in the area of the damaged part of the lip.
- The seal causes some discomfort as it increases in size.
- The top of the tumor is covered with a dense film, and when you try to remove it, severe pain occurs.
- Gradually, the compaction grows and increases in size, involving new tissues in the pathological process.
When the process of metastasis begins, a person exhibits other, specific signs:
- lymph nodes enlarge, they lose their mobility;
- their pain on palpation is noted.
The process of eating is gradually disrupted. A person cannot chew food and takes it in liquid form, resulting in exhaustion. The patient loses weight, his body cannot fully absorb nutrients and vitamins.
initial stage
At the first stage of disease development, scanty manifestations of cancer may be present. The person is not bothered by anything at all or the symptoms are mild.
It is worth paying attention:
- The appearance of a non-healing wound in the lip area. This could be a deep crack or ulcer that does not heal over a long period of time.
- The edges of the wound become thicker and painful. Gradually the size of the damage decreases.
- And the compaction grows, involving other tissues in the process.
Since tumor growth can be slow, it is recommended to pay attention to a wound that does not heal. It can bleed and secrete.
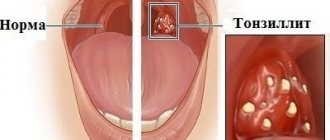
What can stomatitis tell you?
The appearance of stomatitis may indicate the appearance of some more serious pathologies in the body. Sometimes stomatitis is a concomitant symptom of conditions such as:
- Received ionizing radiation or chemotherapy.
- Oncological diseases of the nasopharynx, mouth, neck.
- Disorders of the digestive tract, intestinal parasites.
- HIV infection.
- Prolonged dehydration.
- Hormonal disorders in women.
- Diabetes.
- Anemia.
- Bronchial asthma.
Precancerous diseases of the lips
Precursors of oncology are pathological processes in tissues: inflammation, infection, bacterial damage. All this can provoke the development of oncology.
What diseases can lead to the development of lip cancer:
- Leukoplakia lips.
- Precancerous cheilitis.
- Hyperkeratosis of the red border.
Recently, there has been a tendency for papillomas to degenerate into malignant formations. If a wart appears on the surface of the lips, it should be removed. This will reduce the risk of developing cancer, but will not eliminate it completely. Since HPV is in the blood, which means it can recur when the activity of the immune system decreases.
Obligate precancer
Characterizes itself by the presence in a person of an innate predisposition to the development of malignant formation.
Such diseases include xeroderma pigmentosum, which manifests itself as increased sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet radiation.
Recommended video:
Diagnostics
To give the patient an accurate diagnosis, the doctor conducts a series of studies that will help understand the problem and determine the stage of cancer and the presence of metastases.
What examinations will you have to go through:
- Having contacted the doctor with complaints, the patient will undergo a palpation examination of the lip, oral mucosa and cheeks.
- The doctor will also examine the lymph nodes for tenderness and mobility.
- To get an accurate picture of the patient’s condition, you will need to do an ultrasound of the lip, as well as undergo a series of tests.
- A biopsy and histological examination of tissues are performed. In rare cases, a blood test for tumor markers is prescribed, but it can be uninformative.
- In addition to biopsy and histology, MRI and CT of the organ are performed, and if necessary, ultrasound examination of the cervical lymph nodes is prescribed.
Types of stomatitis
- Viral.
Infection with the Epstein-Bar virus or herpes simplex. It appears in the form of bubbles, in place of which erosion subsequently occurs. - Bacterial.
Caused by the proliferation of streptococci and staphylococci. It looks like pustules turning into wounds. - Fungal.
Decreased immunity and proliferation of Candida fungi. It looks like small foci of white plaque, after damage to which painful erosions remain. - Chemical.
Burns from acids and alkalis. Deep ulcers with the formation of scars and deformations of the mucosa. - Ray.
Arising as a result of exposure to ionizing radiation. Expressed in the form of erosions and tissue deformations. - Allergic.
Occurs as a reaction to medication or dentures.
Treatment methods
There are several ways to get rid of cancer. When choosing a tactic, pay attention to the presence of complications, as well as the stage of the disease.
At the initial stage of cancer development, tumor removal and drug treatment are combined.
Medicines
At the initial stage of development of the disease, the use of medications is permissible. But more often they resort to an integrated approach. If the cancer is at stage 1, then it is recommended to remove the tumor, along with the tissues surrounding the formation.
As a rule, drug treatment is part of combination therapy and is carried out after excision of the tumor.
Surgery
Let's consider options for surgical intervention, depending on the stage of development of the disease:
| Stage 1: | The affected tissue is excised, the structures surrounding the tumor are also removed, the excision is carried out to 1.5-3 cm. |
| Stage 2: | The focus is irradiated and the lymph nodes in the neck area are taken under control; if they continue to increase in size, then the subcervical tissue is excised. |
| Stage 3: | They practice radiation irradiation of the tumor focus, then use targeted administration of radioactive drugs, after such therapy they perform resection of the lip. |
| Stage 4: | Irradiation is carried out before and after surgery, not only the formation is removed, but also part of the cervical tissue. After surgery, irradiation is repeated. |
It is noteworthy that in this type of oncology chemotherapy is not widely used and is carried out in exceptional cases.
Folk remedies
Treatment of cancer with folk remedies is considered an extremely dubious activity. Because it doesn't bring any results. Such therapy can take time and cause serious harm to a person’s health.
Therefore, you should not cauterize the seal with iodine, vinegar, or apply a strong decoction of celandine to it - this is unlikely to stop the pathological process.
Alternative Methods
Similar methods exist and in practice they are used with varying success, they are used:
- in case of superficial lesions of organic tissue, it is permissible to administer a photosensitizing drug, after which the tumor is subjected to laser irradiation;
- The cryogenic method allows one to avoid radiation and chemotherapy; it is also used in case of tumor recurrence.
Recommended video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3sBT8g9z8qM&t=15s
Prognosis and survival
It is difficult to make a prognosis for oncology, but as for lip tumors, the prognosis is conditionally considered favorable.
| If the pathological process is at the initial stage of development (stage 1-2): | The survival rate for patients is good and ranges from 97-100%. |
| If cancer develops and metastases appear: | The survival rate decreases and is about 85% if the tumor can be surgically removed. |
| In severe condition, when the cancer reaches stage 4: | The survival rate of patients decreases and amounts to 55%. |
Much depends on the individual characteristics of the body. But lip tumors develop slowly, and the survival rate decreases when metastases appear. They destroy lymph nodes and jaw bones.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, such complications can be avoided.