Content:
- Tooth enamel: general characteristics and properties:
- Possible reasons:
- What to do if your child’s baby teeth are brown.
1.1. Maturation of enamel.
2.1. Plaque. 2.2. Enamel hypoplasia. 2.3. Fluorosis. 2.4. Caries. 2.5. Other reasons.
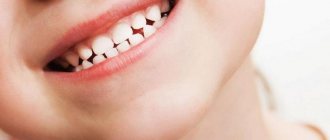
Regardless of its cause, such a problem is a mandatory indication for comprehensive diagnostics. Moreover, we are talking not only about visiting the dentist, but also about consulting a pediatrician and highly specialized specialists, since brown plaque on children’s baby teeth can be the result of either a banal lack of hygiene or any diseases.
Is it possible to remove plaque at home?
Everyone knows how reluctant children, especially young ones, are to visit the dentist's office. Therefore, parents, having discovered plaque on their children’s teeth, first of all ask themselves: is it possible to solve this problem at home? Even if brushing your teeth with an ordinary brush and toothpaste does not give the desired result, there are several methods for getting rid of plaque on your own.
Activated carbon
The simplest recipe involves the use of activated carbon. To do this, you need to grind one tablet to a powder. Then add a couple of drops of water to the resulting powder (you can add them using a pipette) to make a paste. Apply this paste to the child’s teeth using a toothbrush, and then brush the teeth with the same brush. After a few minutes, the activated carbon should be washed off completely.
It is common to use lemon to clean teeth from plaque. But it is only suitable for cases where the plaque is not very dense. You need to cut a small slice from the lemon and press it to your teeth. But you need to pay attention to the fact that not every child will like the taste of lemon, and in some cases, lemon can cause irritation of the mucous membranes.
Strawberry puree
This method of dealing with plaque will surely appeal to all children. You need to grind strawberries into puree and apply to the surface of your teeth. After a few minutes, the puree can be washed off.
However, you need to remember that the best way to remove plaque from your child’s teeth is to take him to a dentist, who will perform professional teeth cleaning.
Tooth enamel: general characteristics and properties
This is the hardest and most durable tissue in our body, its thickness on the outer surface reaches almost 2 mm. It consists of many layers formed at various stages of mineralization and has a crystalline structure. The chemical composition is represented predominantly by apatites, calcium and phosphorus predominate from inorganic compounds, and proteins, lipids and carbohydrates from organic compounds.
The main function is to protect dentin from external factors: mechanical, chemical and temperature stimuli. Thanks exclusively to this tissue, teeth can fulfill their main purpose - grinding and chewing food.
Despite its extraordinary strength, enamel is permeable to water and many organic and inorganic substances contained in saliva. It has been found that the degree of permeability for much-needed connections depends on several factors. If we talk about temporary occlusion, this is:
- condition of the oral cavity;
- nutritional features;
- long-term treatment with certain medications (in particular, tetracycline antibiotics);
- features of intrauterine development.
Enamel maturation
The composition of the protective tissue covering dentin is constantly changing, which is associated with age-related characteristics. Throughout the year after teething, there is an active accumulation of calcium and phosphorus, and during this period it is extremely important to receive all the necessary elements with food or multivitamin preparations. It has been proven that a sufficient content of microelements prevents the development of caries.
Possible reasons
The white color of the enamel layer indicates not only the absence of serious problems with the oral cavity, but also the normal state of health of the child as a whole. Brown baby teeth are an abnormal phenomenon that requires mandatory diagnosis and consultation with a pediatric dentist. Sometimes such a problem “goes away” along with a change in bite, but in many cases such a violation becomes the cause of numerous pathologies in the already permanent dentition.
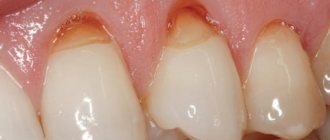
Plaque
It is a dense formation consisting of proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, and inorganic substances, which are an excellent environment for the development of bacterial flora. It is predominantly concentrated in the cervical region (in the place where the dentin comes into contact with the gum), in the fissures of the molars. Dealing with this problem is simple: all you need to do is follow the rules of daily hygiene. Otherwise, a brown coating appears, and it is not always possible to remove it yourself.
Enamel hypoplasia
It develops due to disturbances in the metabolic processes of formation and mineralization, often even before eruption and even during intrauterine development. The etiology of the disease may be associated with:
- severe infections suffered in infancy;
- rickets;
- nutritional dystrophy;
- endocrine disorders;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
The disease most often affects canines and premolars and is accompanied by the appearance of spots, depressions, and grooves of various shapes and sizes. In severe cases of the disease, the child complains of pain during hygiene procedures and reacts to the temperature of food.
Fluorosis
Fluoride is necessary for the full formation and development of both temporary and permanent teeth. But its excessive intake into the body (as a rule, this occurs due to the increased fluoride content in drinking water - up to 1.2–1.5 mg/l or more), especially with a concomitant calcium deficiency in food, leads to the opposite effect - gradual destruction of the enamel coating. This is what causes brown baby teeth to appear.
Caries
It develops against the background of gradual “dissolution” of enamel and damage to dentin by microbial flora. Recently, caries is diagnosed much more often. Experts explain this by the action of various unfavorable factors that prevent the maturation and resistance of the enamel coating. These include:
- changes in the composition of the oral microflora;
- excessive consumption of sweets;
- decreased secretory activity of the salivary glands;
- unbalanced diet;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules.
Other reasons
- hemolytic jaundice: indirect bilirubin formed during hemolysis of red blood cells and causes brown plaque on baby teeth in children;
- taking certain antibiotics (especially from the tetracycline group), drugs with a high iron content by the mother in the second half of pregnancy or by the child during the formation of the bite;
- chronic inflammatory process of the gums and oral mucosa.
Prevention methods
To prevent dental plaque from forming in a child, it is necessary to carry out prevention. There are few preventive measures - and they are easy to follow:
- do not let children drink carbonated drinks;
- do not let children, even under one year old, fall asleep with a bottle of formula or milk;
- Explain to children that brushing should be done twice a day, or even better, after every snack;
- add more vegetables and fruits to the child’s diet - in unprocessed form.
Plaque is not the most serious problem, but it can lead to tooth decay and other unpleasant dental diseases. The best way to combat it is prevention. What is arsenic read in our article.
What to do if your child's baby teeth are brown
The scope and scope of therapeutic measures is determined only by the dentist after an examination. Usually this:
- correction of nutrition, introduction of foods rich in calcium into the diet, limiting the consumption of sweets and baked goods;
- training in oral hygiene rules;
- taking multivitamins;
- the use of rinsing solutions (these can be ready-made medications or self-prepared decoctions of chamomile, calendula, etc.);
- professional plaque removal;
- filling (if the volume of work is large, this procedure is sometimes performed under general anesthesia).
Modern pediatric dentistry allows you to painlessly and without unnecessary stress cope with the problem of brown baby teeth and prevent damage to an already permanent bite.
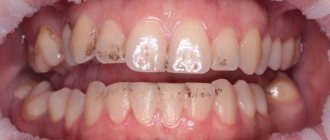
Types of plaque
Plaque on teeth is divided into two large groups:
- the occurrence of which is associated with external contamination of the tooth;
- appearing due to the deposition of pigments.
If oral hygiene is not maintained, plaque may appear on the teeth:
- soft microbial;
- mineralized;
- hard, often called tartar.
If everything is in order with hygiene, then black plaque is a consequence of:
- regular consumption of tea, coffee and nicotine;
- use of medications with high iron content;
- vital activity of chromogenic bacteria;
- use of certain types of rinses and antiseptics.