What is stomatitis and what types exist?
The name of the disease indicates its exact location; translated from Latin “stoma” means mouth. Stomatitis is an inflammatory lesion of the oral mucosa (most often ulcerative). Both adults and children can get sick. But the disease affects children more often. This is due to the fact that the mucous membrane at this age is easily infected by pathogenic microflora, because the child’s body is not yet perfect, local and general protective reactions are not sufficiently developed. Statistics show that almost 80% of young children have suffered from this disease at least once.
Stomatitis is the general name for a whole group of diseases of the oral mucosa. Therefore, each of them has its own symptoms and its own treatment methods. Depending on the etiology, stomatitis is divided into several types:
- viral, including herpes - has a viral nature, infection occurs by airborne droplets. The virus can exist on objects (clothing, toys, etc.) for some time. The initial symptoms are similar to those of ARVI: lethargy, fever, runny nose, cough (not always). On the second or third day, light ulcers with a red border appear on the tongue, mucous membranes of the cheeks and lips;
- traumatic - inflammation is provoked by mechanical damage to the inner surface of the mouth, for example, a burn from a hot drink or food, a scratch from a toy stuck in the mouth, biting if the child has an incorrect bite;
- allergic – the inflammatory process is provoked by the entry into the body of a substance that causes an allergic reaction. Most often caused by drugs;
- candidiasis (fungal) - begins when the mucous membrane is infected with the fungus Candida (“thrush”). A striking symptom is a dense white coating on the tongue.
What is a disease
Stomatitis is considered a lesion of the oral mucosa.
The reasons for the development of this pathology are:
- infection by infections (viruses, bacteria, fungi);
- medicines;
- autoimmune processes.
Children develop painful ulcers in their mouths. They are quite deep, but heal without scarring. If the baby has immune disorders, then the ulcerative process is continuous. Previously formed ulcers simply do not have time to heal before new ones appear. The acute process becomes chronic. That is why it is important that nutrition for stomatitis is gentle, at the same time complete and varied.
Symptoms
Signs indicating that a baby is suffering from stomatitis are divided into two types: local and general. It is not difficult to recognize them, especially if the baby already knows how to speak and can tell where he feels discomfort. If a baby is sick, the main symptom is general restlessness and crying. Parents should carefully examine his mouth and make sure that there is (or is not) an inflammatory process on the mucous membrane.
Local symptoms:
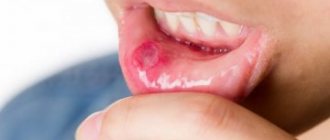
- blisters, sores or plaque on the inner surface of the lips, cheeks and/or tongue, pharynx;
- marks from biting, burns or scratches;
- swelling and redness of the mucous membrane next to the lesions;
- bad breath.
Are common:
- increase in body temperature (from slight to critical);
- increased size of lymph nodes;
- refusal to eat;
- lethargy;
- moodiness;
- nervousness.
Note to parents: symptoms can manifest themselves both complexly and individually. But the presence of even one of the listed manifestations of the disease is a reason to visit a doctor.
Features of the disease
In most cases, children suffer from candidal stomatitis, which develops against the background of the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Due to weak immunity, the body is unable to restrain the growth of bacteria; their number rapidly increases. Localized in the oral cavity - on the gums, tongue, cheeks.
External signs:
- white coating;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- purulent formations;
- sores.
A small child refuses to eat. In the absence of proper treatment, body temperature rises, chills, fever, and weakness appear.
In the viral, herpetic form, pathogenic cells enter the blood, spread throughout the body, and are localized in the mouth. The external signs of the disease are identical. Additionally, body temperature rises, weakness and malaise are present. The gums bleed, swell, become covered with plaque and ulcers. The herpes virus remains in the body for life. A strong immune system inhibits the manifestation of the disease. When it weakens, symptoms may appear again, but not so pronounced.
Allergic stomatitis manifests itself against the background of weak immunity, but the provocateurs are products containing allergens and personal hygiene products. Food, toothpaste, and mouthwash can cause the disease.
What happens if stomatitis is not treated?
Some parents do not take their child’s stomatitis seriously, they say, “it will go away on its own.” Such an attitude towards the baby’s health can lead to serious consequences. Without treatment, the infection can spread to the skin of the face. There is also a high risk of secondary infection. And this already threatens general intoxication of the body, damage to the nervous system, etc., even death. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend that if symptoms of the disease are detected, show the child to a specialist in order to avoid negative health consequences.
Treatment methods
Due to the fact that the etiology of each type of stomatitis is different, the approaches to treatment are also different. For example, a fungus needs to be fought with an antifungal drug, herpes with an antiherpes drug, allergies with an antihistamine, etc. Therefore, the main task of a doctor is to diagnose stomatitis, identify the cause of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. Therapy is carried out in two directions: relief of general symptoms and local effects on mucosal lesions. As a rule, the doctor prescribes medications and antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity in the form of applications and rinses.
What do doctors advise for home care?
The specialist makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment, and the implementation of all instructions falls entirely on the shoulders of the parents. Caring for a small child with stomatitis contains many nuances. For example, during this period you should feed your baby only warm food with a mushy consistency, excluding citrus, sour and spicy foods. After eating, be sure to rinse your mouth. If the baby is still very small, then after eating you should give him a little boiled water to drink. Treatment of the oral cavity and application of gels prescribed by a doctor should be done with a special fabric fingertip or a finger wrapped in a bandage (the bandage should then be thrown away).
Important: self-medication is dangerous. Only a doctor can correctly diagnose and give the correct therapeutic recommendations.
Inhalations for stomatitis in children
Some “experts” recommend using a nebulizer to administer antiseptic and immunostimulating agents. In this case, antiseptics act faster if they are applied directly to the affected areas. You need to rinse your mouth, lubricate the mucous membranes, and make lotions. Inhalations for stomatitis do not give the desired effect.
The effect of immunostimulants is questionable. It is impossible to say for sure whether the prescribed drug helped, or whether the immune system independently coped with the disease. Moreover, in childhood you should not interfere with the functioning of the immune system again. The body must independently develop resistance. Moreover, children are prescribed drugs that are safe for inhalation. The active ingredients are plant extracts. That is, there is no harm from the product, but there is no particular effect.
To speed up your child’s recovery, you need to maintain hygiene and adhere to a healthy diet. Additionally, they give vitamins to maintain the body. External treatments are used, inhalations are not performed.
Methods for preventing stomatitis
- Preventative visits to the dentist (twice a year), if necessary, dental treatment
- Strengthening the immune system (regime, good nutrition, hardening)
- Maintaining oral hygiene
- Getting rid of bad habits (finger sucking, toys, pencils, etc.)
- Maintaining household hygiene (thorough cleaning of premises, washing toys)
- Timely treatment of gastrointestinal diseases
The dental network offers services for the treatment of stomatitis in children. Our specialists are highly qualified and regularly improve their skills in leading clinics in Russia and Europe. The pediatric dentist will diagnose and prescribe effective treatment. We have a system of family and cumulative discounts.
You can contact any of the branches of our center in Moscow within walking distance from metro stations:
- Art. Alekseevskaya (VDNKh district, etc. Mira), address: st. 3rd Mytishchiskaya house 3, building 2;
- Art. Shelepikha, address: Shelepikhinskaya embankment, address: building 34, building 1.
Stomatitis is a serious disease; do not expect that it will go away on its own without consequences. Remember that your child's health depends only on you. If you notice the symptoms described in the article, sign up for “Smile” dentistry and get qualified help. We are waiting for you every day without breaks and weekends.
Authorized Products
The diet for stomatitis in children includes certain foods that do not irritate the oral mucosa.
Proper nutrition includes:
- Vegetables (boiled, baked, steamed) - dishes made from them do not injure, do not irritate, and at the same time provide the body with vitamins and minerals. It is recommended to take vegetables with a delicate structure (broccoli, zucchini, potatoes, pumpkin).
- Fermented milk drinks and products should definitely be included in the child’s diet, but they should not contain a lot of acid. It is worth giving preference to soft neutral cottage cheese, Varenets, and fermented baked milk.
- Cereals - they are used to prepare porridges. They have an enveloping effect. They provide the body with B vitamins. The cereal must be well boiled.
- Fruits – usually choose moderately sweet, neutral, non-acidic fruits. It is better to take bananas, watermelons, melons, crumbly sweet varieties of apples and pears.
- Fish dishes - for their preparation, it is advisable to use fatty varieties of sea fish. To prepare either minced fish or steam it, remove all the bones so that the baby cannot injure the oral mucosa. Fish is a source of easily digestible protein, vitamins, microelements and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
- Meat dishes - only soft, lean types (veal, rabbit, chicken, turkey) are used to prepare them. When cooking, it is better to prepare minced meat products. Steam them or bake them in the oven. You can cook: soufflé, cutlets, meatballs.
- Liver - it can sometimes replace meat dishes; it is also better for preparing cutlets, soufflés, pates and similar dishes.
- Casseroles - can be prepared from vegetables, cereals, pasta, cottage cheese.
- Soups and broths – puree soups and low-fat broths are widely used in dietary nutrition.
- Soft cheeses are a good source of calcium. It is high in calories, easily digestible, and nutritious.
- Dried fruit compotes and jelly are a source of vitamins and microelements. It is better to replace tea with these drinks.
- Juices must be natural, freshly squeezed. To do this, it is better to take non-acidic fruits and vegetables (pears, apples, carrots).
The use of these products in a diet for stomatitis will make the diet high in calories and nutritious, at the same time gentle.