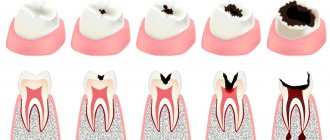
Symptoms of caries
Diagnosis of the disease should only be carried out in the dentist's office. But the person himself can determine the presence of this pathology by very characteristic symptoms:
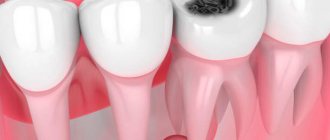
- the appearance of dark spots on the teeth: most often they appear on the chewing surface, but often inflammation develops between the teeth (but it is usually not possible for the patient to see this - special equipment will be required),
- there is a roughness of the surface of the teeth,
- When eating food, aching pain appears, teeth react to sweet and sour, as well as cold and hot. But the unpleasant sensations subside immediately as soon as contact with the irritant ceases - this is how caries, even deep ones, differs from pulpitis - inflammation of the dental nerve,
- Breath odor may become unpleasant,
- a carious cavity can even be felt with the tongue; food debris often gets clogged into it, which causes discomfort or even swelling of the tooth - for example, if a small gap appears under a filling.
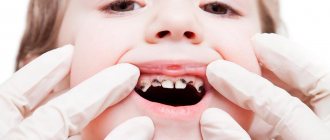
Possible complications due to improper treatment of caries and pulpitis in children
When performing a number of manipulations, some dentists with a low level of qualification may perform them insufficiently carefully or completely incorrectly. This can cause serious complications after treatment of caries of primary teeth, as well as its next stage, pulpitis.
The presence of such complications in a baby can be determined by the following signs:
- lack of positive dynamics;
- the presence of symptoms that do not correspond to the diagnosis;
- the occurrence of severe pain after treatment;
- deterioration of indicators of objective methods of examining the condition of the child’s oral cavity.
To avoid these unpleasant consequences, you should initially seek help from competent specialists who not only have a high level of professionalism, but also know the specifics of working with young children. These are the professionals who work in our dental clinic “Prodental”, located in Dolgoprudny (Moscow region).
Reasons for the development of the carious process
The development of caries largely depends on the individual characteristics of the body. For example, in women with hormonal imbalances, plaque accumulates on the teeth more often, which leads to an increased attack from bacteria. In general, caries is caused by pathological microorganisms, which become much more numerous in the oral cavity than good bacteria. And their appearance is caused by the following reasons:
- lack of proper hygiene: brushing your teeth for 20-30 seconds in the morning and evening is very little. Dentists' recommendations are at least 2 minutes twice a day, as well as removing food debris that accumulates in narrow spaces after eating. Gradually they transform into plaque, which is a provocateur of many dental diseases, including caries,
- poor nutrition: excessive consumption of sweet foods and changes in the PH composition of saliva - all this again contributes to the formation of plaque and an increased attack of bacteria,
- age: it has been established that the destructive processes of primary teeth actively develop in the first years of children’s lives. As you get older, the likelihood of developing dental diseases decreases. This is influenced by the fact that adults pay more attention to oral hygiene. In old age, the risk of caries increases again - this is the result of various diseases of the body and insufficient oral hygiene,
- pregnancy and lactation, that is, during those periods when a woman loses many vitamins and minerals, in particular calcium and fluoride,
- lack of vitamins and, as a result, increased fragility of tooth enamel,
- genetics: a predisposition to many diseases of the gums and teeth is passed on from parents.
Our advantages
Our pediatric dentists always have innovative equipment at their disposal, which allows them to treat caries in children using the most modern methods - painless and effective.
At the same time, the prices for treatment of caries in young children in our clinic are quite affordable, as you can see by reading the price list for services.
And most importantly, we know how to approach children, and therefore it is almost impossible to see a crying child in our offices and corridors. All manipulations are carried out very carefully, the baby does not experience pain and does not begin to be afraid of dentists, and goes to the preventive examination recommended twice a year with pleasure!
Make an appointment any day of the week - we work 7 days a week, without lunch breaks.
Treatment methods
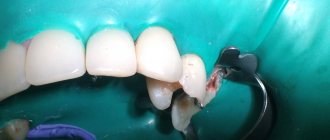
Cure caries, especially at the initial stage, is not difficult - this involves removing the inflamed tissue and then filling it. In the presence of deep lesions, binoculars and a microscope can be used, which allow you to increase the working space and remove even the smallest inflamed cells, while preserving healthy tissue. Depending on the situation, it may also be necessary to restore the coronal part if it has been severely damaged.
Fissure sealing A method that allows you to stop the carious process. Essentially, this is the prevention of inflammation. Fissures or depressions (grooves) on the surface of the enamel are filled with a special sealant, which evens them out and thereby prevents the accumulation of bacteria and plaque.
Price:
from 2500 rubles more details about the solution
Treatment of caries If the doctor notes caries at the spot stage, then the main procedure is remineralization (restoration of the required mineral content) using a special solution. If the caries is superficial, medium or deep, then the resulting cavity will need to be treated, followed by filling using composite materials. When the carious process penetrates into the deep layers, it is advisable to use medicated pads containing calcium hydroxide - this way additional protection is created to preserve the dental nerve.
Price:
2500 rubles more details about the solution
Installing an inlay In a number of situations, when the tooth is quite badly damaged and a large filling will not hold, you can develop an individual inlay made of ceramic or zirconium dioxide. It will accurately follow all the curves of the tooth and be securely fixed inside the cavity. At the same time, it will last many times longer than a large filling.
Price:
from 20,000 rubles more about the solution
Periodontitis
If the carious process is complicated by pulpitis, which is not treated, inflammation of the tissues surrounding the causative dental unit develops. Symptoms of periodontitis are bleeding of the gingival margins during hygienic sanitation of teeth and an unpleasant odor emanating from the oral cavity. Possible pain from thermal irritants.
Periodontitis is classified into acute and chronic. In an acute process, severe pain occurs, which intensifies with load on the causative tooth. Pain symptoms can also arise from the action of thermal irritants. The gums around the causative tooth become swollen, hyperemic, an abscess often appears, which spontaneously opens and purulent contents come out through it, after which the patient’s condition improves. Patients note that the causative tooth becomes higher than other dental units in the jaw.
Treatment of acute periodontitis consists of opening the pulp chamber, through the resulting defect the tooth is cleansed of purulent contents or pulp decay. To make this process go faster, dentists at Dr. Granov’s clinic recommend rinsing the mouth with a soda-saline solution. After 2–3 days, the inflammatory process stops and the tooth can be filled. If the patient’s condition does not improve, then an incision is made into the mucous membrane and periosteum in the area of the periodontitis tooth, and a rubber drainage is placed into the resulting incision. If this does not give a positive result, then the tooth is removed.
If the acute form of periodontitis is not treated, then after 7–14 days the process becomes chronic. Symptoms of chronic periodontitis:
- Excessive tooth mobility.
- Gaps appear between the teeth.
Errors in creating access to root canal orifices
The reasons for this situation are insufficient preparation of the carious cavity, incomplete excision of the roof of the pulp chamber, and lack of control over the insertion of the endodontic instrument (Fig. 2). The consequence is the following complications. Overhanging edges of the cavity do not allow completely removing the remaining pulp from the tooth cavity, which inevitably leads to the appearance of pigmentation and worsens the aesthetic parameters of the tooth.
Rice. 2. Incomplete opening of the tooth cavity.
Due to poor visibility, it is not always possible to identify all existing root canal orifices, which precludes treatment and filling of undetected canals (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Poor quality treatment of the cavity walls.
The apparent “saving” of hard tooth tissues in the process of cavity formation can lead to poor-quality endodontic treatment.
At the same time, excessive, excessive tissue removal causes a decrease in the tooth’s resistance to mechanical stress.
A measure to prevent such an error is the formation of correct access, which is characterized by the absence of overhanging edges and the straightness of the cavity walls, which should be smooth, without roughness or notches.
Perforation of the bottom and walls of the tooth cavity
May occur during the search for root canal orifices and their expansion; with poor visibility of the bottom of the tooth cavity as a result of inadequate formation of access to the root canals.
The presence of softened pigmented dentin, intense staining of hard tooth tissues after previous treatment (resorcinol-formalin method, silvering) also greatly complicate the search for root canal orifices (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Dentin pigmentation and paste residues at the bottom of the cavity.
In some cases, the causes of perforation are the following factors: insufficient or, on the contrary, excessive expansion of the tooth cavity; carrying out endodontic treatment through an artificial crown. Insufficient knowledge of anatomical features, such as displacement of the tooth axis and a decrease in the height of the crown due to its significant abrasion, contributes to the commission of errors.
Preventive measures for perforation of the walls of the tooth cavity are rational excision of hard tissues, adequate pressure on the bur during the preparation process, its correct direction and precise control of the depth of insertion of the rotating instrument.
Incomplete removal of the root pulp is allowed in cases where adequate access to the canal mouths is not provided or the latter are inaccessible due to the location of denticles in them. The reason may be insufficient expansion of the canal mouths or incorrect determination of the working length. The anatomical features of the structure of the roots can also become a factor in the poor patency of the canal for instruments. Violation of the work technique, for example, removal of tissue with a pulp extractor with rupture of the neurovascular bundle, incomplete removal of the root pulp, leads to bleeding from the canal, which prevents further endodontic interventions.
Obstruction of the canal lumen by dentine filings is manifested by the impossibility of reintroducing a small endodontic instrument to the entire working length. The reason is the accumulation of dentinal filings in the lumen of the canal and their compaction. An attempt to re-pass the canal with force may entail pushing the products of mechanical treatment of the root canal (endolubricants, dentinal filings, pulp residues, etc.) beyond the apical foramen, which can cause pain after endodontic treatment.
This complication is prevented by carefully passing the canal to the apical narrowing with small instruments after every second step, as well as washing the canal lumen with solutions.
The formation of apical enlargement (Zipping effect) most often occurs in curved canals. During canal treatment, slipping of the instrument tip during rotation leads to the so-called “Zipping” effect. The reason is the use of large, inflexible files, which cannot follow the shape of the canal. The canal lumen may be blocked by dentine filings. The risk of creating an apical expansion significantly increases when working with files that have an aggressive apex.
Excessive longitudinal expansion of the canal in the middle third along the internal curvature (Stripping) occurs during mechanical treatment of curved root canals. The reasons may be the following: the use of rigid, inflexible files; mechanical treatment without taking into account the thickness of the canal walls, as well as underestimation of the degree of root curvature.
Due to excessive removal of dentin in the area of the internal curvature of the root, not only does the tooth’s resistance to mechanical stress decrease, but there is also a real risk of longitudinal perforation of the root canal wall.
Destruction of the anatomical (physiological) narrowing occurs when the working length is incorrectly determined. Another reason is a slight decrease in the working length of the channel during straightening. If further processing of the canal is carried out to the previous working length, destruction of the physiological narrowing is inevitable.
Prevention of this complication consists in accurately determining the working length and its correction during mechanical treatment of a curved root canal.
Perforations of the root canal walls occur most often during instrumental treatment of curved roots.
Perforations of the mouth and middle thirds are formed mainly when the filling material is removed from the canal in the process of creating a bed for the anchor pin, as well as when the latter is screwed into the canal.
Apical perforations can occur when using insufficiently flexible rotating instruments in difficult, curved canals. A similar complication is possible from the application of excessive pressure during machining with hand tools, when trying to forcefully pass the canal. The cause of lateral perforation is the passage of a curved canal with an endodontic instrument with an aggressive tip without prior bending.
Measures to prevent various types of perforations are good access to the mouths of the root canals, analysis of the configuration of the root canals according to radiographs (Fig. 7). During mechanical treatment, obstruction of the canal lumen with dentinal filings should be avoided; pre-bend the tool; use an anticurvature technique for passing the canal.
Rice. 7. Excessive preparation and perforation of the wall of the first molar.