Increased sensitivity of teeth (hyperesthesia) is a short-term occurrence of pain under the influence of temperature, chemical or mechanical irritating factors. Usually occurs when drinking cold water, sour, sweet, salty, or touching with a toothbrush. The intensity of pain varies from mild to unbearable.
According to WHO, every second person in the world suffers from hypersensitivity. In Russia it is about the same: 45–65% of adults aged 20–55 years. More often women make complaints.
A little anatomy
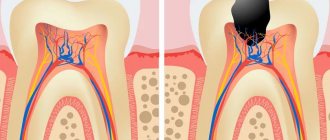
A tooth consists of a crown and root part, connected by a neck. The coronal part is covered with enamel, the root part is covered with cement. Beneath the enamel and cement there is dentin, a hard tissue. Inside there is soft tissue - the pulp; blood vessels and nerves pass through it.
Dentin is not sensitive, but consists of many tubules in which fluid circulates. The irritant causes fluid movement, which is detected by the nerve endings of the pulp. A person feels their reaction as pain.
Tooth reacts to heat after filling
Dental treatment uses a huge range of effects on tooth tissue. And a reaction to hot food after visiting a doctor is a common situation. Even a dead tooth, from which the nerve and pulp have been completely removed, can react to temperature. Normally, within a few days, maximum 2 weeks, the discomfort will completely disappear.
But in some cases, the pain in a filled tooth not only does not subside, but also becomes stronger. There may be several reasons for this:
- not all affected tissue was removed;
- the doctor did not follow the filling technology and the integrity of the filling was damaged;
- there is an air bubble under the filling;
- the pulp burn provoked inflammation of the soft tissues;
- Individual intolerance to the filling material manifested itself.
For the same reasons, hot teeth also hurt. Most likely, the canal was treated poorly. Or the doctor simply removed one canal and did not find the second. This situation is very common when treating anterior teeth. Often, even on their x-rays, 2 channels look like one. In any case, only a dentist can identify and eliminate problems in an already healed tooth.
An overreaction to hot drinks after a whitening procedure is a clear sign of low professionalism of the dentist. In clinics that value their reputation, after whitening, teeth are coated with a protective composition with a high calcium content. And at the slightest manifestation of hyperesthesia, the patient will simply be denied such aggressive intervention, and will be recommended a more gentle method of creating a Hollywood smile.
Tooth sensitivity: causes
- Demineralization of enamel. It becomes more loose due to the leaching of calcium, phosphorus, and other trace elements.
- Thinning of enamel. As a result of increased abrasion due to malocclusion and the occurrence of wedge-shaped defects.
- Untreated caries or violation of the marginal seal of the filling.
- Exposure of roots as a result of injury, metabolic-dystrophic process or inflammation of the gums.
- Changes in the pH of saliva due to the consumption of certain drinks, foods, and medications. A pH of less than 5.5 is considered dangerous.
- Some diseases accompanied by gastroesophageal reflux and endocrine disorders.
- Vitamin deficiency, exposure to radiation, work in hazardous industries, living in a region with an unfavorable environmental situation.
- Smoking.
More often than not, several reasons are discovered at once. The enamel becomes thinner, loses strength, and cannot protect dentin from irritants. The result is pain.
Causes of hyperesthesia
Dental hypersensitivity is caused by many factors and may indicate problems with the teeth and periodontal tissues. Hypersensitivity is one of the most common diseases in dental practice and, according to WHO, is increasing every year.
The mechanisms of the occurrence of pain syndrome due to irritating factors stimulate increased interest among both researchers and practicing dentists, prosthetists, and hygienists. This attention is explained by the fact that pain is a key symptom of most dental diseases. However, the increased susceptibility of hard tissues cannot be justified by the known pathways of nerve signal transmission. This fact prompted a series of studies to be carried out, which resulted in several theories of the development of hyperesthesia:
- odontoblastic;
- receptor;
- threshold;
- hydrodynamic.
Sufficient evidence has been collected in favor of the hydrodynamic theory. It is supported by most dental clinicians. The dentinal tubule, according to theory, is considered as a capillary tube containing fluid inside.
Exposure to air, high temperatures, etc. it shifts, the pressure in the dentin changes. This leads to increased activity of nerve endings. Penetration of irritants into the tubules is possible when dentin, the main hard tissue of the tooth, is exposed. It is exposed not only against the background of carious lesions and diseases of periodontal tissues, but also as a result of non-carious defects: hypoplasia (underdevelopment of teeth), enamel erosion, etc.
Provoking factors
Hyperesthesia does not appear immediately. There are several factors that you need to pay attention to in order to eliminate them in time. Don't wait for discomfort to appear. It is better to initially develop healthy habits that will help you maintain your health so that you never experience acute dental pain. Sensitivity increases when any of the factors listed below are present.
- Insufficient oral hygiene. Soft plaque is an accumulation of microbes that eat food microparticles stuck in crevices, releasing organic acids that dissolve enamel minerals. Externally, the dental unit looks intact, but the density of the enamel is significantly reduced. Its demineralization occurs. The first alarm bell is increased sensitivity, then caries develops.
- Consumption of certain foods. Juices, wine, sweet soda, fruits, candies, and other sweets contain phosphoric and other acids that negatively affect the strength of enamel.
- Constant use of aggressive whitening pastes containing abrasive and chemical components.
- Ultrasonic cleaning. Under a dense coating, the enamel becomes thinner and becomes loose. After professional cleaning, it is exposed, its sensitivity increases sharply. Usually, dentists, taking this point into account, use strengthening pastes at the end of the procedure for the preventive treatment of tooth sensitivity.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing dentin hypersensitivity, it should be borne in mind that it is often a symptom of a disease. Therefore, when a patient approaches, the dentist begins treatment with a survey, during which he receives answers to the following questions:
- duration and nature of the pain syndrome;
- number of units with dentin sensitivity;
- localization of increased susceptibility;
- characteristics of stimuli that cause pain.
After the examination, the patient is required to undergo probing of sensitive areas and other diagnostic tests (thermal, electrical, osmotic, evaporative), as well as percussion (tapping on individual areas of the tooth). At the same time, they find out whether the element is sensitive when biting, identify microcracks in the enamel, damage inside and around the filling, malocclusion, and signs of bruxism.
In addition, diagnostics are carried out using hardware methods and “hidden” carious lesions and periapical changes are identified if they are present.
Much attention is paid to determining the level of pain and the degree of tooth sensitivity:
- no pain;
- mild discomfort;
- medium intensity;
- severe pain or unbearable.
The patient's pain reaction may occur to a greater extent to thermal stimuli (cold, heat), tactile (tactile), evaporative (air), electrical or osmotic (solutions of weak acids).
Dentists note that the reaction most often occurs to cold, brushing teeth, heat and sweets.
The more dentin is exposed due to dental diseases and other factors contributing to enamel loss, the higher the degree of hyperesthesia. This is explained by the fact that in completely exposed dentin there are more dilated tubules with open holes.
Types of hypersensitivity
If sensitivity is increased on one or more teeth, it is called limited. If for everyone - generalized.
Table 1. Types of hyperesthesia
| № | View | Reaction |
| 1. | Light | for cold, hot |
| 2. | Average | as with 1st degree plus for sour, sweet, salty |
| 3. | Expressed | as in grade 2 plus mechanical irritants (when brushing teeth, eating) |
Symptoms
Symptoms of toothache during hypothermia can manifest themselves in the following types:
- sharp, dull or aching pain;
- pain occurs if you touch your teeth;
- headache may occur due to toothache;
- inflammation of the gums;
- swelling of the face and the appearance of small pimples on it.
If the trigeminal nerve is cold, its symptoms appear:
- distortion of facial expressions;
- pain in the teeth extending to the face;
- a painful sensation occurs when chewing food or touching the face.
Sensitivity of teeth. Stages of treatment
- Eliminate the cause of hyperesthesia: get rid of plaque, deposits, stones, caries, wedge-shaped defects.
- Carry out professional oral hygiene.
- Strengthen the enamel with calcium and fluoride.
- Teach the patient how to use a toothbrush and floss correctly.
- Choose suitable dental care products: toothpaste, mouthwash.
Table 2. Tooth sensitivity: causes and how to treat
| № | Cause | What to do |
| 1. | Soft coating. | Careful hygiene with home remedies. |
| 2. | Hard coating. | Professional hygiene in dentistry. |
| 3. | Caries in the white spot stage. | Deep fluoridation, remineralization. |
| 4. | Caries, pulpitis, periodontitis. | Dental treatment. |
| 5. | Exposure of the cervical part, wedge-shaped defect. | |
| 6. | Malocclusion. | Orthodontic therapy. |
Colds and viral diseases
They undermine an already weak immune system. He fights them, and all sluggish infections immediately “spread their wings.” If there was such a hidden infection in the teeth, which was previously controlled by the immune system, and the person did not even know about it, now, left without supervision, it begins to gain strength. As a result, a toothache suddenly appears and the temperature begins to rise.
By lowering the temperature, you don’t need to wait for the tooth to “somehow” go away. The infection “lived” there for a long time, and a decrease in immunity made it possible to detect it, so it is necessary to begin treatment immediately, otherwise it is unknown how all this will affect the condition of the teeth.
Elimination of tooth sensitivity
Using ultrasound, the doctor removes soft and hard deposits from the teeth. After removing plaque, teeth become more sensitive for a short time, so remineralization or deep fluoridation is immediately carried out. During remineralization, the enamel is treated with active compounds of calcium and phosphates. Deep fluoridation – coating with sodium fluoride. Both procedures significantly strengthen the enamel's resistance to irritants.
The doctor uses agents that reduce the movement of fluid in the dentinal tubules. It “seals” them using desensitizers or reduces their volume through remineralization. Protecting exposed dentin reduces the force of transmission of the irritant impulse from the enamel to the nerve.
Why does a tooth without a nerve hurt from cold and hot?
It is generally accepted that after the nerve is removed, the tooth will no longer be able to hurt. In fact, the reaction of a dead tooth to temperature is rather normal, and there is no need to worry. Over time, the pain will subside on its own, because most often the cause lies in microtraumas to the enamel of neighboring teeth that were received during treatment.
If after a few days the reaction to hot or cold does not decrease, but intensifies, you should not hesitate! It is likely that the dentist did not completely remove the nerve, and the inflammatory process was not stopped. Such mistakes are extremely rarely made by dentists with extensive experience, but among beginners it is not at all uncommon.
There is no point in blaming the aesculapians: what we are accustomed to calling a nerve is, in fact, a branched system of tiny hairs, spreading in all directions of the tooth. It is sometimes impossible to see all the “tentacles” even on an x-ray. And only with experience comes an intuitive feeling of how the “labyrinth” of nerves is located in a particular patient.
In the practice of Western dentistry, a separate specialty has long been distinguished: an endodontist, a specialist in root canal treatment. In Russia, only large, well-equipped clinics can afford specialists of such a narrow profile.
Basic points of proper hygiene
Use a synthetic, medium-hard or soft brush. Change it every three months.
The toothpaste should be suitable for very sensitive teeth. Typically, such products contain hydroxyapatite, strontium chloride, fluorides, potassium nitrate, or a combination of calcium carbonate and arginine.
Take enough paste. For children under 3 years old - the size of a grain of rice, from 3 to 14 years old - the size of a pea, for adults you need to squeeze out about one centimeter.
Brush your teeth for 2 minutes: 30 seconds on each surface, top and bottom. Monitor time using an hourglass or mobile phone timer. Electric toothbrushes emit a short beep every 30 seconds and a long beep every 2 minutes from the start of brushing.
Cleaning sequence
- Using sweeping movements, clean the outer and then the inner surfaces of the bottom row. Move from molars to incisors. Then do the same on the top row. Hold the brush at a 45-degree angle and do not use a sawing motion. This leads to damage to the enamel.
- Brush chewing surfaces with small circular movements.
- Close your jaws and walk along your gums in a circular motion.
- Brush your tongue using a leisurely four to five strokes from root to tip.
- Treat the interdental spaces with dental floss.
- Rinse your mouth.
It is more effective to clean with an electric brush or irrigator. The quality of hygiene increases 3–4 times. Hyperesthesia can be dealt with faster.
Is it possible to strengthen sensitive teeth at home?
Yes. If you can’t get to the dentist, you can try to help yourself. There are several remedies that can solve the problem of hyperesthesia at home.
Table 3. Popular products for home use
| № | Name | Mechanism of action | Age category |
| 1. | ROCS Medical Minerals, GC Tooth Mousse | Remineralizing gels | Adults and children |
| 2. | Colgate Duraphat 2800 ppm | Fluoridating paste | 10–15 years |
| 3. | Colgate Duraphat 5000 ppm | From 16 years old | |
| 4. | ELMEX junior | Fluoridating paste | 6–12 years |
| 5. | ELMEX | From 13 years old | |
| 6. | LACALUT Extra Sensitive | Paste that reduces tooth sensitivity | For adults |
| 7. | Colgate Sensitive Pro-Relief | ||
| 8. | PRESIDENT Sensitive | ||
| 9. | LACALUT Sensitive, 300 ml | Rinse for sensitive enamel | From 15 years old |
Why do my teeth hurt so much?
Not every toothache is highly intense, but with pulpitis it is truly one of the most severe in the body.
Pain is one of the five main manifestations of inflammation. Another sign of an inflammatory reaction is tissue swelling. A peculiarity of dental nerve endings is their location inside hard tissue (dentin), which cannot expand when the pulp is inflamed. Elsewhere in the body, swelling slightly reduces pain by reducing pressure on nerve endings due to the cushioning effect of the increased volume. In a closed pulp chamber, swelling leads to even greater pressure on the nerves - which is why the intensity of toothache is the highest. However, there is a large category of people who do not feel pain at all from caries - they may not notice pulpitis (or there is sensitivity, but it is weak). This is due to the body’s hypoergic reaction to inflammation and the high rate of production of replacement dentin. Due to obliteration of the tooth cavity, the blood supply deteriorates, the pulp becomes ischemic and gradually dies quietly.
Algorithm of actions for hyperesthesia
- Adjust your diet. Avoid completely or significantly reduce the consumption of foods and drinks containing acids and sugar. Especially fruit and berry juices, wine, candies. Eat more green vegetables, fiber-rich foods, and whole grains.
- Change your toothpaste. Never use bleach. Choose from those labeled "Sensitive".
- Check if you are practicing proper oral hygiene. If it's wrong, correct it.
- Make an appointment with your dentist to find out the type of tooth sensitivity, find out the cause and get treatment.
- Visit the dentist twice a year, even if nothing hurts.
How to protect teeth from hyperesthesia?
Many people believe that it is enough to brush their teeth twice or thrice a day, and they will always be fine. However, this is a common misconception! If you brush your teeth incorrectly, they will not only not become stronger, but, on the contrary, they can be seriously harmed. For example, a high abrasive content in toothpaste will cause the enamel to become thinner.
The best solution would be to buy a fluoride-containing paste that has a medium level of abrasiveness. During the research, it was possible to identify why this disease occurs less often in men. The fact is that due to stress, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is seriously deteriorated. Because of this, the acidity of the oral cavity changes. Due to frequent exposure to acid, they become highly sensitive to irritants, which results in severe pain that causes a lot of discomfort.
To avoid hyperesthesia, you need to brush your teeth every day and try as much as possible to protect yourself from stress.
Treatment of hyperesthesia in the “Family Doctor”
If hyperesthesia occurs, make an appointment with a dentist by calling the contact center in Moscow +7 (495) 775 75 66 or using the online appointment form. Our clinic has been operating for more than 26 years. Experienced doctors help patients cope with pressing problems, including hypersensitivity.
The doctor will find out the cause of tooth sensitivity and provide effective treatment. In most cases, it is enough to select suitable oral care products and carry out proper hygiene procedures. In more complex situations, full treatment is used, and if necessary, surgical treatment.
The clinic takes a gentle approach to patients. All procedures are accompanied by adequate pain relief, which eliminates the occurrence of discomfort and pain. Increased sensitivity of teeth is not just a feature of them. This is the beginning of a disease that must be cured. And it's better to do it as quickly as possible.
Professional treatment
Hyperesthesia is a reason for medical intervention.
You should not try to cope with the problem yourself, otherwise complications will not be avoided. High-quality therapy should first of all be aimed at eliminating provoking factors. What to do if your tooth hurts and reacts to cold and hot water, food, air:
- It is necessary to go through remineralization and fluoridation. The enamel layer is additionally fed with fluoride and calcium. A special composition with a high concentration of these components is applied to the surface. The procedures are carried out for preventive purposes to prevent caries.
- Iontophoresis involves the introduction of a special drug into hard tissues using galvanic current.
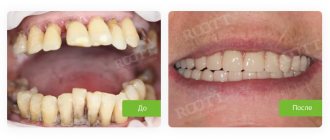
- Installation of prostheses, implantation. If the rows are very damaged, they can only be restored in this way. The doctor determines which method is optimal in a particular case: restoration with veneers, the use of composites, artificial crowns.
What to do if your teeth are afraid of cold and hot, first of all? Dentists adhere to a clear algorithm:
- initial examination and diagnosis of possible dental diseases, inflammations;
- development of a plan for further action;
- sanitation of the oral cavity and elimination of pathological foci;
- elimination of plaque and stone;
- treatment with remineralizing compounds.