31.10.2019
A trip to the dentist does not always end the way you would like. A common situation is when a tooth reacts to exposure to cold after a filling procedure. The reaction of a tooth to cold is a complication that results from the installation of a filling. This material will tell you why this situation occurs and how you can deal with it.
Causes of hypersensitivity
After treatment does the tooth react to cold?
The increased reaction of the tooth to exposure to low temperatures indicates only one thing - the dental nerve is alive, and its reaction is hypersensitive.
This occurs under certain circumstances listed below.
If you have illnesses:
- Pulpitis is an inflammation of the neurovascular bundle. Here the pain is prolonged and can last from a couple of hours to several days.
- Caries is the destruction of hard tooth tissues. In this case, the pain will occur for a short period of time and gradually fade away.
The dentist will carry out the process of installing a filling only after he has eliminated the true cause of the tooth disease.
Preventing excessive tooth sensitivity
Comprehensive prevention of dental hypersensitivity includes:
- a scheduled visit to the dentist every 6 months;
- timely treatment of caries in the “spot” stage (prevents the occurrence of pulpitis and other complications);
- proper dental care;
- proper nutrition;
- minimum stressful situations.
If the problem of tooth sensitivity already exists, daily hygiene includes the use of medicinal paste (based on extracts of medicinal herbs and oak bark).
Installing a filling after caries treatment as a problem of discomfort
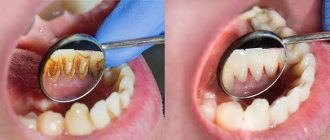
Caries has two degrees of progression: chronic and acute. There are also several forms of dental damage by this pathology: deep, medium and initial.
The dentist treats deep and medium forms of lesions by mechanical treatment of the affected area, followed by installation of a filling.
If during the treatment of the tooth part of the tissue affected by caries was left behind, this may become the root cause of pain when exposed to cold.
In some dental offices, doctors use a special liquid that stains the affected part of the dental tissue with a certain color. This is very convenient, since the dentist can clearly see which area needs to be removed. But not all doctors use this drug.
In a filled tooth, pain can also be caused by other reasons, for example, improper filling procedures for deep caries. The chronic course of caries will be expressed by dense pigmented dentin, in which case the procedure for removing the affected tissue can be stopped, followed by the installation of a filling.
If the dentin is soft, the dentist may decide to strengthen it with a lining containing calcium. In this case, it does not open the tooth cavity. The infection contained in the affected bottom of the cavity gradually penetrates into the dental cavity through the dentinal canals.
Inflammation of the neurovascular bundle, accompanied by pain, is a response to infection.
The occurrence of pulpitis can be provoked by incorrect tactics of the procedure, when in the process of removing tissues affected by caries, sufficient air-water cooling of the tooth tissues was not applied. The consequence of this is heating of the pulp tissue, which provokes the occurrence and development of pulpitis.
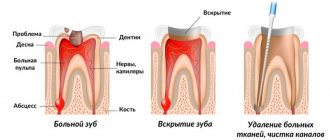
Pulpitis as a cause of pain after filling
With this pathology, inflammation of the nerves and blood vessels that are located in the dental tissue occurs.
Its occurrence can be provoked by nervous strain, infection and overheating of the pulp tissue.
Painful sensations after filling again indicate that the procedure was performed incorrectly.
Due to frequent night pain, the tooth is amputated, since the infection penetrates from the crown to the root area.
Another cause of pain is incomplete removal of the neurovascular bundle. There is a possibility that not all canals were found and passed through by the dentist.
The process of treating pulpitis most often extends over several visits to the doctor. In this case, the dentist will place a temporary filling from visit to visit until the treatment process is completed and the permanent filling is installed. If the treatment is delayed, after some time microscopic gaps appear between the temporary filling and the dental tissue, through which irritants (including cold ones) penetrate into the dental cavity, causing pain.
Why can teeth react to cold?
There are many reasons why discomfort and pain may occur when drinking cold or hot drinks or food. Most of them are directly related to diseases of the oral cavity, but there are also those that are not directly related to dental pathologies:
- Damage to tooth enamel.
Violation of the integrity of the outer covering of the tooth can be caused by a variety of reasons: frequent consumption of hard and dry food, which scratches the enamel during chewing; - mechanical chips;
- an incorrectly selected toothbrush (doctors recommend using medium-hard brushes for adults and soft-bristled brushes for children);
- eating foods that can negatively affect the condition of enamel (carbonated sweet drinks, sour fruits, food additives, etc.).
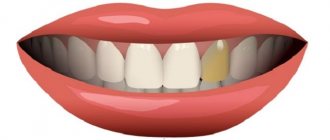
is one of the most common causes. The fact is that most people don't even think about the fact that they have tooth decay until a distinct black spot appears on the tooth. In fact, caries in the early stages can only be distinguished by an experienced dentist - a tiny gray dot (and this is what “young” caries looks like), if it is not examined in time and urgent measures are not taken to eliminate it, it first becomes the cause of increased sensitivity, and then acute pain.
. Untreated caries invariably leads to another, even more serious disease - pulpitis - destruction of the soft tissues of the tooth. Naturally, with pulpitis, the dental nerves are exposed, which causes acute pain when eating cold, hot, sweet or sour food.
. If the gums become inflamed, in most cases the subgingival part of the tooth, the dentin, is exposed. Dentin is completely devoid of a protective layer - enamel - therefore, at the slightest contact with cold water, food, or even just cold street air, patients invariably experience discomfort and pain.
If you suspect one of the above reasons, you should not delay visiting the dentist for long - an experienced specialist will quickly identify the problem and prescribe a course of treatment.
Reasons not related to oral diseases include the following:
- any hormonal disorders
and changes in the body. As a rule, such conditions occur while taking hormonal drugs, oral contraceptives, during pregnancy or breastfeeding; - suffered nervous shocks
, life in a state of constant stress, etc.; - deficiency of vitamins
, minerals and nutrients in the body. “Seasonal” sensitivity can often occur - when in spring and autumn, due to vitamin deficiency, many patients begin to complain of a certain discomfort after taking cold or hot; - damage to the immune system
, viral diseases; - endocrine diseases
(disorder of one or more endocrine glands).
If increased tooth sensitivity is caused by these particular pathological conditions, then no special dental treatment is required - the main treatment should be aimed at eliminating the root cause.
If, after a serving of ice cream or a glass of cold juice, you suddenly feel discomfort, which smoothly turns into acute pain, it is quite acceptable to take a tablet of a pain reliever that is suitable for you - this can be Nimessil (powder for dissolving in warm water), Aertal (tablets), Ketonov , Dexalgin.
When pain is normal
There are very frequent cases when the procedure for treating caries and pulpitis is carried out according to all the rules, but pain still occurs.
In this case, the cause of the pain is hyperesthesia.
Excessive sensitivity of dental tissues to various irritants is hyperesthesia.
Symptoms intensify if there are small cracks in the enamel of the teeth. Various factors contribute to the appearance of such cracks:
- Damage to the enamel from mechanical impact (hard bristles of a toothbrush, during the whitening process, due to impact or scratch with cutlery, etc.).
- Exposure of enamel tissue to aggressive nutrients (for example, citric acid).
What complications may arise?
If the disease is not treated, it will certainly cause very extensive complications. Hyperesthesia is no exception. If we take into account the fact that the reaction of teeth to cold and hot can be the result of a variety of pathologies, then this problem needs to be solved as quickly as possible, without waiting for these complications to make themselves felt.
Untreated hyperesthesia at an early stage eventually leads to severe toothaches - patients complain of the inability to eat, and feel pain when air enters the mouth. At stage 3, it is much more difficult to cope with the problem - after all, by this time the enamel is already quite badly destroyed, which is why numerous carious cavities are formed, etc., and drastic measures may be required.
Enamel is the protective layer of the tooth. When it is abraded, deformed or mechanically damaged, soft tissue becomes vulnerable to a huge number of bacteria. Therefore, you should not put off going to the dentist at the first signs of a reaction to cold or hot foods.
Diagnosis of pathology
At home, you can check the correct installation of the filling in a simple way - pour cold or hot water into your mouth.
If pain occurs immediately and passes just as quickly, the cleaning procedure for removing tissue affected by caries has not been carried out sufficiently.
Taking into account the fact that not all procedures were performed correctly in the treatment of pulpitis, the pain will gradually increase and just as slowly go away.
In some cases, pulsation appears inside the tooth - this is the result of overheating of the dental tissue during the preparation process.
If symptoms do not go away within a few days, consult a doctor.
Dentists diagnose the cause of pain by examining the oral cavity. The tightness of the seal is examined and exposure to cold air and water is applied. After removing the filling, the doctor performs probing by tapping on the tooth. When painful sensations appear in various areas, the existing pathology is determined.
Pain in the walls is a sign of medium caries, in the bottom of the tooth – its deep form, and deep in the mouth of the canal – pulpitis.
Treatment at home
Visiting the clinic is a prerequisite for quality therapy. If it is not possible to see a doctor, you can temporarily turn to folk remedies. The following show the greatest effectiveness:
- Infusions and decoctions of herbs. Rinsing allows you to cope with the manifestations of the inflammatory process, kills bacteria, relieves swelling, and promotes rapid healing.
- Propolis. The most effective are rinses with an alcohol tincture based on this substance. However, it is important to remember that such manipulations are only allowed for adult patients. They are contraindicated for children.
- Warm milk. It is worth drinking it warm as often as possible, holding it in your mouth for a short time. Dairy products contain calcium, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of enamel.
It is recommended to use special gels and rinses designed to clean sensitive incisors, canines and molars. They contain fluoride.
But you can’t rely solely on home treatments. They can only be an addition to complex drug therapy. Even if the unpleasant symptoms have disappeared, you should not neglect a visit to the doctor.
Choosing toothpaste
When deciding what to do when teeth become sensitive to cold and hot, the dentist will first of all recommend to the patient special products for daily cleaning. Bleaching compounds should be completely abandoned, even if they do not contain abrasives.
Let's look at what you need to pay attention to when purchasing:
- Stick only to specialized paste-like and gel-like preparations. Most manufacturers put a special mark on the packaging about the purpose of the product.
- At the pharmacy you can additionally purchase medications that reduce sensitivity.
- The more fluoride a product contains, the better in this situation. The substance has a positive effect on the condition of the enamel. The hard outer layer of the units is restored, they cease to hurt and respond to stimuli.
The brush should also be suitable. Medium-hard bristles are the best option for high-quality cleaning and preventing surface scratching. But before purchasing any hygiene items, it is better to consult a doctor.
Solution
If after the filling procedure pain is diagnosed, then you need to wait 2-3 days, perhaps they will pass.
During this period, it is recommended to take painkillers with anti-inflammatory properties.
The pain does not subside after 72 hours - you should contact your dentist.
At a repeated appointment, the dentist performs the following series of actions for caries:
- Produces local anesthesia.
- Removing the seal.
- Removal of the area affected by caries.
- Reinstallation of the filling.
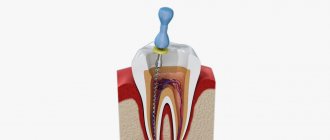
The stages of treatment of pulpitis (primary or repeated) are as follows:
- Administration of an anesthetic drug.
- Removing the filling and providing access to the tooth canals.
- Treatment of canal-containing areas using dental instruments with parallel exposure to an antiseptic.
- Installing a filling on a dental canal.
- Filling a tooth with a permanent or temporary filling (this is decided by the dentist).
If a doctor has installed a temporary filling for you, this means one thing - you will definitely have to visit him on the appointed day. If this is not done, the consequences may be negative.
Diagnostics
The occurrence of discomfort after cold or hot food is one of the signs that the filling was performed incorrectly. If in doubt, just drink a glass of cold water. With caries, pain will occur immediately, with pulpitis it will appear over time. If any painful symptoms occur, you should immediately make an appointment with your doctor for a follow-up appointment. Read more about identifying hidden caries in the article.
Don't expect the problem to go away over time. Complicated caries and pulpitis progress over time, leading to tooth destruction.
To identify damaged areas, a special drug called “Caries Control” is used. After application to the tooth cavity, the dead areas are painted in a contrasting color. After this it is easier to remove them completely.
Prevention and prevention
In order to prevent pathology from occurring, it is necessary to protect your enamel from various damages. To do this, follow a number of simple rules:
- Visit your dentist at least twice a year for a checkup.
- Balance your diet so that sour and sweet foods are found in minimal quantities.
- Avoid using toothbrushes with hard bristles. They can not only damage gum tissue, but also cause microscopic scratches on the enamel.
- Avoid eating excessively hot foods with cold foods (such as hot coffee and ice cream). Due to sudden temperature changes, tooth enamel can crack.
- Avoid teeth whitening procedures using aggressive chemicals. If you want your teeth to be snow-white, use whitening pastes. The process is longer, but safe for the enamel.
- Maintain personal hygiene: brush your teeth 2 times a day with toothpaste that does not contain aggressive elements.
A very effective prevention would be the use of mouth rinses. They can be produced by pharmaceutical companies and sold in finished form. Or you can make a special decoction at home, based on various herbs and plants.
If you experience pain while brushing your teeth or eating cold food, contact your dentist immediately. Delay will lead to destruction of the integrity of the tooth and nerve endings.
Causes of hyperesthesia
A tooth can hurt from cold or hot temperatures for various reasons. A natural factor is the thinning of the enamel, which protects the tooth from the aggressive influence of the external environment. Beneath it there is dentin, which is in direct contact with the nerve endings that penetrate the pulp, which is why teeth hurt after drinking cold water or eating hot food.
Such a non-dental cause of a negative phenomenon, such as thinning of tooth enamel, which provokes increased sensitivity of the tooth, can arise under the influence of the following factors:
- bruxism;
- toxicosis during pregnancy;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- infectious or viral lesions;
- lack of minerals, calcium or phosphorus;
- exposure of the tooth to chemicals contained in air or water.