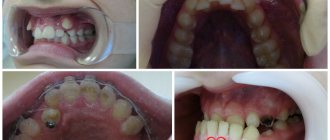
Excessive tooth mobility is a common symptom indicating the development of severe dental diseases.
Unfortunately, many patients underestimate the danger of this pathology and postpone visiting the doctor until the last minute, depriving themselves of the opportunity to receive timely dental care. Meanwhile, in the absence of treatment, tooth mobility progresses and becomes irreversible. It is for this reason that any delay in starting restorative therapy significantly reduces the chances of maintaining the integrity of the dentition.
Symptoms accompanying mobility
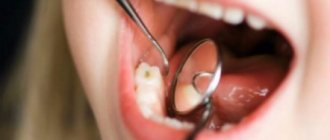
In fact, there is only one symptom - when you touch a tooth with your finger, tongue or any object, as well as during eating, its mobility is clearly felt. As a rule, horizontally, that is, a shift to the right-left or forward-backward. Other symptoms are mainly associated with the underlying disease and, as a rule, we are talking about inflammation of the gums, exposure of the roots, the formation of copious amounts of deposits under the soft mucous membranes, even rotting of the contents of periodontal pockets.
What to do if loosening occurs?
If you notice your teeth are moving, immediately make an appointment with a dentist. The specialists at Dr. Granov’s clinic are ready to help you at any time. We urge you not to ignore your symptom, since subsequently the treatment of the provoking pathology can become very complicated.
While you are at home, try to follow three basic rules:
- Never loosen the tooth with your fingers or tongue. Try not to touch it at all, so as not to aggravate the current situation;
- Rinse your mouth with warm water (or a mild saline solution), but do not brush your teeth with a brush or toothpaste;
- If a tooth falls out, see a doctor immediately. If this has just happened, you still have the option of emergency implantation. The more you delay the process, the less opportunities there will be for high-quality restoration.
When a tooth falls out, we must not forget that parts of it may still remain inside the gums. And this can also have very dangerous consequences for you if you continue to ignore the warning signs.
Causes of mobility
There are quite a few reasons that cause abnormal mobility. The main ones are the following:
- age-related changes, hormonal imbalances,
- lack of vitamins and minerals,
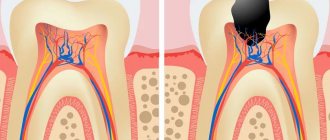
- inflammatory processes of the gums, i.e. diseases of periodontal tissues – periodontitis and periodontal disease. These are the main reasons why teeth begin to become loose. In turn, their development is caused by poor oral hygiene,
- the presence of gaps in the row, as the teeth begin to shift towards the empty space,
- injury to the jaw system or the tooth itself, its root,
- complications of chronic diseases associated with disruption of the endocrine or immune system,
- purposeful loosening of the tooth,
- incorrect bite, as well as uneven pressure on one or a group of elements of the dentition.
Timely identification of the cause of the problem will allow you to save your teeth by restoring the functionality of the ligamentous apparatus and jaw bone cells.
Causes and diagnosis
Healthy people have physiological tooth mobility, which is necessary so that during eating, chewing loads are distributed evenly throughout the entire dentition. We are talking about pathological mobility when the displacement of tooth roots in the sockets becomes noticeable visually or according to the patient’s subjective sensations. There are three degrees of abnormal mobility: in the first, the teeth can only move back and forth, in the second - also to the sides, in the third they can move around their axis and vertically (as if raised in the socket). The doctor identifies the pathology through examination and x-ray diagnostics.
The causes of this condition may be:
- Periodontal diseases (periodontitis, periodontal disease). Insufficient or improper oral hygiene plays an important role in the development of such diseases, since poor care contributes to the accumulation of plaque and the deposition of tartar, and these are predisposing factors for the development of oral diseases.
- Resorption (sparseness) of jaw bone tissue . Often occurs as a result of tooth extraction and inflammatory processes.
- Bite defects . Abnormal positions of teeth in rows can cause their pathological mobility.
- Injuries and mechanical damage.
In order for the treatment of tooth mobility to be high-quality and successful, it is important for the dentist to first establish the exact cause of this condition.
Problem classification
Russian dentists use Entin's typology to determine the degree of development of tooth mobility.
Typology of tooth mobility according to D.A. Entina
| Degree | Direction of movement | Amplitude |
| I | Buccolingual (back and forth) | Up to 1 mm |
| II | Buccolingual + distal-palatal (lateral) | More than 1 mm |
| III | Buccolingual + distal palatal + vertical | More than 1 mm |
| IV | Rotation around its own axis |
What to do if an adult’s tooth is loose and hurts when pressed?
Normally, our teeth have little mobility. Dentists call it physiological; it is necessary to absorb the loads during chewing, as well as for their more even distribution over the entire dentition. But such mobility is so insignificant that it is impossible to notice it. Therefore, if an adult suddenly discovers that a tooth in his gum has begun to loosen, this is already a symptom or an indicator of pathology that requires the participation of a dentist. In the absence of timely medical care, such violations very often lead to irreversible loss of a tooth.
How to treat tooth mobility
For this problem, the true disease that resulted in this symptom is treated. Most often, one of the following measures is used:
- surgical or conservative treatment of dental problems;
- a set of measures to correct the bite;
- professional dental cleaning of teeth;
- selection of oral care products.
To relieve teeth from mobility after complex treatment, orthodontists resort to splinting. This method involves combining the dentition with a special device - a removable or non-removable splint.
Why does this pathological mobility occur?
Several factors can lead to this violation:
- Diseases of the tissues surrounding the root and holding it in its place are periodontitis and periodontitis.
- Malocclusion with excessive chewing load on individual crowns.
- Tooth displacement under the influence of incorrectly positioned adjacent teeth.
- Poorly made or poorly installed prosthesis.
- Congenital disorders of the anatomical structure of the dentofacial apparatus.
- Mechanical injuries.
- Wrong choice of toothbrush and too strong or uneven impact on tooth surfaces during daily hygiene.
There are several degrees of tooth mobility:
- I degree - the crown moves no more than 1 mm horizontally;
- II degree - the crown shifts by more than 1 mm horizontally and moves vertically, as if pressed, “sinking” into the gum;
- III degree - the crown is strongly displaced in all directions;
- IV degree - the crown is capable of rotating around its own axis.
Manifestations of the problem
In addition to loose teeth, patients may experience the following symptoms:
- Bleeding gums;
- Increased sensitivity to temperature changes, chemical irritants;
- Redness, swelling of the gums;
- Bad breath;
- Purulent discharge;
- Pain in the gum area.
In dentistry, doctors try to quickly and with minimal risk of relapses restore reliable fixation of the dentition. Dentists are sure to check for additional symptoms in order to deal with them and identify the cause of loosening.
Who is at risk?
Some chronic diseases in the body can also affect the strength of incisors and molars, including:
- cardiovascular diseases;
- arthrosis, arthritis, psoriasis;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland.
Tooth mobility is typical in women during pregnancy, as well as in older people whose hormonal levels change and the body suffers from a lack of essential microelements.
Because of this, the gums become loose and can no longer securely hold the tooth in the socket. It is necessary to constantly monitor the condition of the soft tissues of the oral cavity and consult a dentist in a timely manner.
Solution
Mobility of teeth is not a final sentence that the patient will lose them. Comprehensive, timely therapy is the key to the fact that the situation can be corrected and the periodontal tissues will return to normal, firmly fixing the tooth. Effective ways to combat tooth mobility and exposure are:
- Cleaning dental plaque;
- Splinting of teeth;
- Injection and massage procedures.
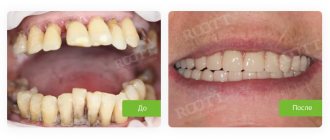
If the situation is advanced or very progressive, drug treatment may be an ineffective way to solve the problem. Then the lost teeth, as a result of dental mobility, can be “replaced”.
Option 1. Basal dental implantation, which will allow, despite bone tissue atrophy and other periodontal problems, to install implants, fixing them in the deep layers of the jawbone.
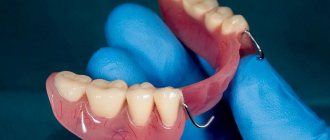
Option 2. Modern removable dentures - nylon or plate type - are suitable for large-scale edentia. To fix them, supporting teeth are not required, since the structure is securely held due to suction to the gums.
What to do if you are worried about moving teeth?
A timely visit to a trusted dental clinic significantly increases the chances of a successful recovery and maintaining your own smile. Tooth mobility is treated with conservative methods, resorting to surgical intervention only when prosthetics are necessary. Treatment methods are selected individually.
In modern conditions the following are used:
- Splinting. The technique allows you to reliably fix the dentition. It is used in the initial stages of unsteadiness and is highly effective.
- Splinting clasp prosthesis. Used in the middle stages of the disease. Attached to healthy teeth, maintaining mobile teeth in a physiological position.
- Curettage. Professional, deep cleansing of periodontal pockets.
- Application of cap. Used for bruxism. They can be prescribed only at night or for constant wear.
- The use of local and systemic drugs to combat the cause of the disease. Anti-inflammatory drugs, antiseptics, antibiotics, ointments that accelerate healing and others.
The Nurimed Clinic practices modern dental treatment without pain or discomfort. Dentistry uses only proven materials, safe and effective drugs that help quickly restore a beautiful smile. Highly qualified doctors allow us to minimize risks and deal with even the most advanced cases.
Selective grinding of teeth
- one of the most common methods in the system of complex therapy of periodontal diseases. According to some data, 95.8% of patients with periodontal pathology need it.
Objectives of selective teeth grinding:
1. Elimination of premature occlusal contacts
2. Elimination of moments that block and interfere with the movements of the lower jaw
3. Elimination of deformation of the occlusal surface of the dentition.
There are different methods of grinding teeth, the most popular are the Jenkelson and Schuller methods.
The technique proposed by Jankelson (1979) is considered a functional method, however, premature contacts are removed in central occlusion.
According to Jenkelson's classification, premature contacts are divided into 3 classes:
1st contacts on the vestibular slopes of the buccal cusps of molars and premolars and the vestibular surface of the lower incisors
2nd contacts on the oral slopes of the palatine cusps of the upper molars and premolars;
3rd contacts on the vestibular slopes of the palatal cusps of the upper molars and premolars.
Indications for selective grinding:
— Presence of premature contacts of antagonist teeth in central, anterior and lateral occlusions;
— Absence or uneven wear of hard dental tissues;
— Deformations of occlusal surfaces;
— Bite abnormalities
Method of selective grinding of teeth:
-carried out before therapeutic and surgical procedures or in parallel with them.
- Preliminary grinding of teeth involves shortening protruding teeth and is intended to eliminate significant deformations of the occlusal surfaces that occur due to defects in the dentition. If significant shortening is necessary, depulpation of the latter is indicated.
- The final sanding is carried out in a certain sequence. First, premature contacts in various types of occlusion are eliminated, then when moving the lower jaw from central to anterior and lateral occlusions.
- Before grinding, an occludogram is obtained, which is stored to monitor the results of grinding. After carrying out this manipulation, it is necessary to polish the ground surfaces and coat them with fluorine varnish.
Orthodontic preparation for orthopedic treatment for periodontal diseases
In patients with periodontal pathology, the clinical picture is often complicated by deformations of the dentition; in addition, malocclusions in some cases can themselves lead to periodontal pathology, so orthodontic preparation before orthopedic treatment is of great importance.
Structurally, orthodontic appliances have some differences from classical ones, these include:
— Application of minimal forces to move teeth.
- Longer active treatment and retention period.
Temporary splints can be used as retention devices.