Dental diseases include not only inflammatory processes occurring directly in the tooth, but also damage to the tissues surrounding the tooth - bone, periosteum or ligamentous apparatus. And basically all damage to surrounding tissues leads to tooth loss.
Inflammation of the periosteum
Periosteum is the lining or connective tissue between the bone tissue and the tooth. Periostitis is an inflammation of the periosteum; this disease is also commonly called “flux”. Periostitis is very easy to detect - a lump appears on the gum, usually filled with pus. Flux is a very serious disease that requires surgical intervention, but in no case self-medication.
The reasons for the appearance of flux can be various injuries that caused hematoma of internal tissues, as well as advanced caries or incomplete dental treatment. For example, the cause of gumboil can be pulpitis, the treatment of which the patient abandoned halfway through. If the doctor did not remove the nerve, but applied, for example, arsenic or a drug, you should definitely visit the dentist again to remove the temporary filling and install a permanent one, otherwise the nerve may begin to become inflamed and even rot, which will invariably lead to inflammation of the periosteum or bone tissue.
Don't suffer toothache! Come visit us today!
Complex treatment of caries - 6500 rub. for all! Flux treatment, full complex - 6500 RUR!
Periostitis: symptoms
- pain in the gum area
- the appearance of a lump on the gum
- increase in body temperature
- cheek tumor
Periostitis: treatment
- mandatory removal of carious cavity
- treatment or removal of an inflamed tooth nerve
- root canal treatment
- removal of a purulent source of inflammation (usually by a surgical method, which involves cutting the gums and releasing pus out)
- filling and prosthetics of damaged teeth
- drug therapy is used simultaneously with dental treatment
In case of flux, you should never treat yourself! The formation of pus indicates a serious inflammatory process. With self-medication, the purulent focus can increase and spread throughout the body. Traditional methods are used only to relieve pain and facilitate the treatment process, but nothing more.
Inflammation of bone tissue
Following the periosteum is bone tissue, in which the tooth root is securely fixed. Inflammation of bone tissue is always a very serious disease that leads to the destruction of hard bone and, accordingly, tooth loss. Periodontitis is an inflammation of the bone tissue surrounding the tooth. With periodontitis, the tooth is not alive, since the bacteria first attack the root and nerve of the tooth, and only then spread to the bone tissue.
The main causes of periodontitis include dental trauma, as well as acute caries or pulpitis, in which the nerve of the tooth dies.
Periodontitis: symptoms
- sharp pain
- the presence of carious cavities on the tooth
- bad breath
- tooth mobility
- fistulas on the gums (in the most severe stages)
What is osteitis of the jaw?
Osteitis of the jaw is an inflammatory process that occurs in the jaw bone tissue and spreads beyond the periodontium of one of the teeth to the spongy substance of the bones. This is a dental disease that develops along the neurovascular bundle, as well as through contact. It is often accompanied by periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum), less often osteomyelitis (inflammation of the bone marrow with the formation of fistulas, abscesses, and phlegmon).
Osteitis can be acute or chronic. Acute is characterized by destruction of dental bone tissue, and chronic develops in the presence of a chronic focus of infection in the periodontium of the tooth, followed by proliferation, when cells cannot perform a protective function, and the infection spreads deeply.
Why does bone atrophy occur?
Let us list the main causes of the atrophic process of bone:
- Diseases of teeth and gums. These include periostitis, periodontitis, osteomyelitis, periodontal disease, cysts in the maxillary sinuses, as well as roots, etc. Any inflammatory phenomena in the jaw bone provoke its gradual atrophy;
- No implantation or prosthetics. For example, a patient has had a tooth removed or it has fallen out on its own, and the person is in no hurry to restore the lost dental unit. All this time, the bone tissue atrophies, and other changes also occur: the chewing load is incorrectly distributed due to lack of support and incorrect pressure, the dentition is deformed, etc.
- Advanced age. Unfortunately, in people aged 50+, bone tissue becomes looser, and osteoporosis often occurs. The structure of the bone is disrupted, its density decreases, and its mass decreases. The problem of osteoporosis becomes aggravated if a person is diagnosed with diseases of the heart and blood vessels, central nervous system, thyroid gland, stomach and intestines, etc.
- Congenital abnormalities of the jaw and teeth. It often happens that a person is already prone to bone atrophy from birth. The pathology is accompanied by a reduced jaw size, its underdevelopment and other visible defects that form complexes in people over the years. All these points can be corrected by orthodontic treatment or plastic surgery;
- Congenital abnormalities of the jaw and teeth. It often happens that a person is already prone to bone atrophy from birth. The pathology is accompanied by a reduced jaw size, its underdevelopment and other visible defects that form complexes in people over the years. All these points can be corrected by orthodontic treatment or plastic surgery;
Main symptoms of jaw inflammation
There are symptoms of osteitis that occur at the beginning of inflammation in bone tissue. This:
- sudden pain that occurs in the affected area of the jaw;
- swelling (hyperemia) of the sore spot;
- difficulty chewing food;
- spread of pain throughout the entire oral cavity.
If the source of infection is a sore tooth, then difficulty occurs when opening the mouth. If the disease develops rapidly, an increase in body temperature is possible.
With further development of osteitis, the inflammatory process is accompanied by suppuration in the affected area. The general condition of the patient depends on the associated secondary damage surrounding the bone tissue (periostitis, abscess, phlegmon).
Osteomyelitis of the jaw - symptoms and treatment
Treatment is carried out only in a hospital under the supervision of a physician and can be medicinal and surgical [9]. Individually, these methods are ineffective and can even harm the patient. Treatment regimens depend on the stage of the disease.
Treatment of acute and subacute osteomyelitis
At the first visit, the neglected damaged tooth is urgently removed. Then the oral cavity is thoroughly washed with antibiotics. This must be done to remove germs and pus from the wound.
In the following days, the wound is treated with disinfectants and injections of antimicrobial drugs are administered. With their help, it is possible to act directly on the source of infection and prevent it from spreading. In addition to the main treatment, nutritional compositions with vitamins C and B are used.
At the subacute stage of the disease, it is important to contain the spread of infection and prevent inflammation from spreading to surrounding tissues.
For this use:
- IVs with antibiotics;
- drugs that reduce or suppress inflammation;
- rubber drainage for exudate drainage.
Vitamin complexes and preparations are also introduced into the bloodstream to cleanse the body of microbes and their waste products. Specific medications and dosages are selected by the attending physician.
Physiotherapy methods can be additional therapy after the main treatment: UHF therapy or treatment with non-constant currents. They are believed to speed up the healing process [7][16].
Treatment of chronic osteomyelitis
If necrotic cavities appear with decay of the bone and surrounding tissue, surgery will be required. To do this, the damaged area is dissected, the affected areas are removed and a splint is applied. Subsequently, using x-ray methods, the doctor monitors how the bone tissue is restored [11].
To help the body fight infection, additional antibiotics are taken in tablets. Metronidazole is most often prescribed and its effect is enhanced by drugs from the group of 3-4th generation cephalosporins.
If the patient's condition does not improve, then fluoroquinolones or Rifampicin are added. The main task of antibiotics is to prevent bacteria from multiplying [7]. Medicines help reduce inflammation and keep the pathological process within the affected area.
Also, the oral cavity is treated daily with bactericidal agents, droppers with vitamins and plasma-substituting fluids are used, which cleanse the body of toxins.
Additionally, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with infusions of chamomile, St. John's wort, mint and comfrey. Herbal remedies reduce inflammation, speed up recovery and have virtually no side effects.
Treatment methods for osteitis of the jaw
Patients who suffer from inflammation of the jaw require complex treatment for osteitis. It includes surgery, as well as taking antibacterial drugs and special immunostimulating agents. If the teeth located in the area of tissue inflammation are severely destroyed and are a constant source of infection and inflammatory processes, then they must be removed.
If there is a general infectious disease that has caused inflammation of the bone tissue (tuberculosis, syphilis), treatment begins with its elimination. In other cases, the doctor drains the inflammation of the jaw through the root canal of the teeth. Physiotherapeutic treatment of the oral cavity is also carried out. Sometimes they resort to laser irradiation on the area affected by osteitis.
If you have the slightest suspicion of inflammation of the bone tissue in the oral cavity, you should immediately contact your dentist. If you start treating osteitis at the initial stage, it will not lead to serious complications and will not cause severe pain. After successful treatment, you should strictly adhere to the doctor’s prescriptions, carefully care for your mouth and teeth in order to prevent relapses of the disease and the transition of osteitis to a chronic form.
What are the possible consequences of atrophy?
Losing a tooth is not only fraught with cosmetic consequences, i.e. aesthetic defects. Functional impairments also occur. After all, healthy teeth have to take on excess load while chewing food. This means they break down much faster. In addition, all the teeth in the row shift and become mobile - after all, some of them lack lateral support. In general, the bite and facial expressions are disturbed, and wrinkles appear. The lips sink inside the mouth, problems arise with the pronunciation of various sounds, because the tongue loses support in the form of teeth, a decrease in the lower part of the face is observed, and flabbiness of the masticatory and facial muscles develops2. In addition, the digestive organs suffer, since a person most often switches to softer foods, since it is too difficult to chew excessively hard foods.
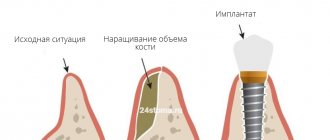
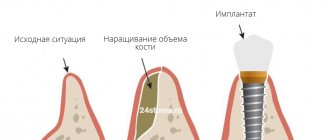
Options for solving the problem of bone loss
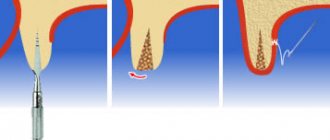
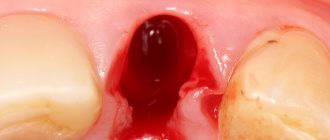
The main solution to the problem of bone loss is, of course, to prevent it, i.e. prevention. This means that after tooth extraction, you need to consider the option of surgical restoration or protecting the bone tissue from shrinkage. The first option will be discussed below, but the second involves the installation of protective barrier membranes. They are installed in the socket of the extracted tooth, and if necessary, a little artificial bone is added inside. In this way, it is possible to replenish the missing bone volume, making it possible to implant a tooth without using an extension procedure (but this is provided that it was not possible to install the implant immediately, i.e. at the time of tooth root removal).
So, when a patient is faced with a problem such as atrophy, bone tissue restoration can be performed using the following methods:
- sinus lift: performed exclusively on the upper jaw and allows you to lift or shift the maxillary sinus in order to make room for new bone. This operation is only applicable to change the height of the jaw bone,
- bone grafting with artificial materials: in this case, the jaw bone tissue is split and the freed space is filled with synthetic bone,
- bone block grafting method: for this procedure, the patient’s own bone material is used, usually extracted from the lower jaw (from the wisdom teeth area). The gum is cut, a bone block of the required size is cut out - it is transplanted to a new place and fixed with screws. Bone granules are placed around, and a membrane is attached to protect the tissue from being washed out.
Bone augmentation is a procedure that, although not complicated for an experienced surgeon, is very specific (and for the patient as well). When transplanting a bone block, at least 2 incisions are made, which means the patient will have to monitor the condition of several wounds at once. Plus additional material expenses: building up a large area of bone tissue is especially expensive.
“The cost of bone grafting is from 19-20 thousand rubles. And this does not take into account the implantation itself. In addition, the operation significantly lengthens the treatment process - at least 3-4 months must pass before the grafted bone can be used to install implants. Therefore, in our practice we use implantation methods that eliminate bone grafting. For the patient, this saves both time and money.”
Zhilenko Evgeniy Aleksandrovich, Implant surgeon, periodontist, orthopedist Work experience over 18 years make an appointment
Prevention
To reduce the risk of developing the disease, you should follow simple recommendations:
- Brush your teeth at least 2 times a day. It is advisable not to use hard brushes to avoid injury to the gums.
- After eating, rinse your mouth with warm, clean water or a special mouthwash.
- Use toothpicks less often.
- Visit your dentist regularly.
- Remove tartar twice a year and undergo professional cleaning.
- Get rid of bad habits. Alcohol and smoking greatly impair dental health.
Periodontitis is one of the most common dental diseases. If you take good care of your teeth and maintain oral hygiene, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of its occurrence.
Back
What is dental periodontitis?
Periodontal inflammation is the stage of infection spreading from a carious tooth. It follows pulpitis. The source of infection is located at the apex of the root. This is a small cavity that, in advanced cases, can be filled with pus.
As the disease develops, a cavity appears around the roots. It will open sooner or later. If the disease becomes chronic, it is accompanied by constant suppuration and outflow of pus through a fistula - ducts in which the walls do not fuse.
Content:
- What is periosteum
- Signs of the disease
- Diagnostic measures
- Classification
- Treatment of the disease
- Prevention
Some dental diseases lead to severe inflammation due to untimely treatment.
As a result, periosteal tissue is included in the pathological process. If qualified dental care is not received at this stage of the disease, osteomyelitis or other dangerous pathologies may develop. Inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth should not be allowed. It is difficult to treat and may require surgery.
Types of dental periodontitis
Based on localization, the disease is divided into the following types:
- Regional periodontitis. In this case, tissue damage occurs near the edge of the gums. Often occurs due to injury.
- Apical periodontitis. The tissues are affected near the apical part of the root or at the base. In some cases, it is misdiagnosed as pulpitis.
According to stage, the disease is divided into:
- acute form;
- chronic form.
Acute periodontitis
May be purulent or serous. The first type is especially dangerous, as it can lead to the destruction of periodontal tissue. As a result, the teeth become mobile.
Chronic periodontitis
The chronic form is divided into granulomatous, granulating and fibrous periodontitis. The first two types are the most dangerous, as they are accompanied by pronounced bone resorption.